Verification(验证)
Faults and failures
Mistake vs. Fault vs. Failure
Mistake:A human action that produces an incorrect result
Fault: An incorrect step, process or data definition in a computer program
Failure: An incorrect result. The result of the fault
![]()
Some common types of program fault
Logic errors - the program does not match the specification (e.g. the requirements, or design)
Divide by zero
Infinite loops
Exceeding array bounds
Using an uninitialised variable …
Software availability
Availability is an important quality attribute of software systems
It concerned with system failure and its associated consequences
Repair time: recovery time from a failure
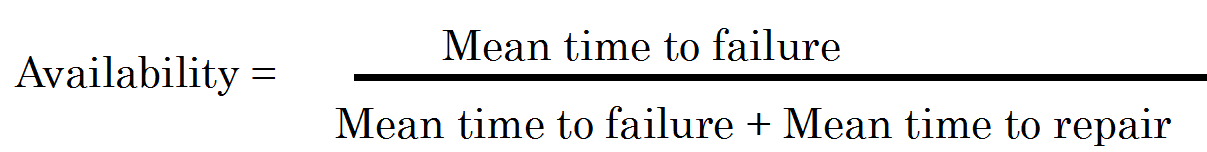
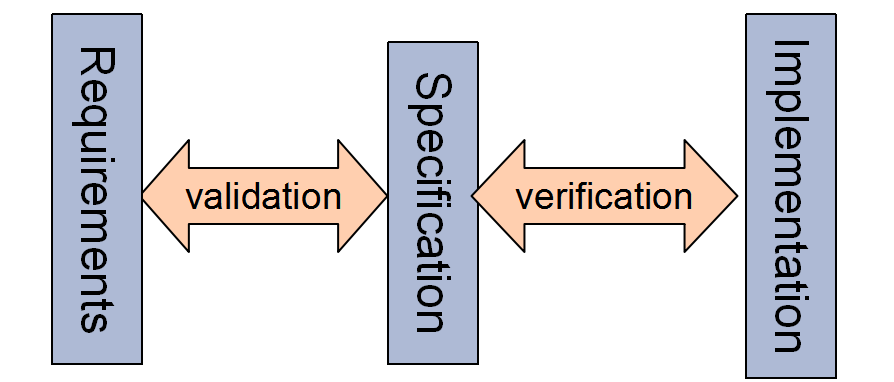
Verification and validation
Verification is any activity intended to detect faults in software and/or generate confidence that software conforms to its requirements
"Are we building the product right”.
The software should conform to its specification.
Validation: is the process of evaluating software to determine whether it satisfies specified requirements
"Are we building the right product”.
The software should do what the user really requires.
There are two main approaches to verification:
Testing - where we attempt to demonstrate some behaviour by running the code
Formal verification- formal verification is the act of proving or disproving the correctness of intended algorithms underlying a system with respect to a certain formal specification or property, using formal methods of mathematics
Testing vs. formal verification:
Testing is more commonly used
Formal verification is more difficult, hence more costly
What is testing?
Testing is running the program to see what it does
Detecting deviations from the specifications
Detecting behaviour in violation of common sense
Learning about the behaviour of a system (help you to understand the system better)
You may not understand the methods, classes, packages you adopted
You may not know the system’s behaviour in an operation system or hardware system
Kinds of testing
Low-level testing (performed by developers)
Unit (module) testing
Integration testing
High-level testing (preferably performed by independent test group)
System function testing
Acceptance testing
Usability testing
Stress testing
Performance testing
…
High level testing
System function testing
-Test program as a whole
-Detect discrepancies between program's functional specifications and its actual behaviour
Usability testing:
Evaluate a product by testing it on users
Measures the usability, or ease of use
Performance testing:
Testing performed to determine how a system performs in terms of responsiveness and stability under a particular workload
Stress testing:
A form of deliberately intense or thorough testing used to determine the stability of a given system or entity Involves testing beyond normal operational capacity, often to a breaking point, in order to observe the results
Low level testing
Unit (module) testing
Components must be tested in isolation
A functional test can tell you that a bug exists in the implementation
A unit test tells you where the bug is located
Integration testing
Combining and testing multiple components
Discover errors in the interfaces between component

Black-box
Specification oriented: does the software implement the specification?
Pros: we are testing what we need to test (what will be delivered)
Cons: are we sure we know what we need to test? We won’t test all possible behaviours
White-box
Code oriented: if we exercise the code in all possible ways (or the most probably ways) do we get good behaviour?
Pros: finds all (or many) interesting behaviours
Cons: quickly gets difficult as code gets larger - to the point of impracticality
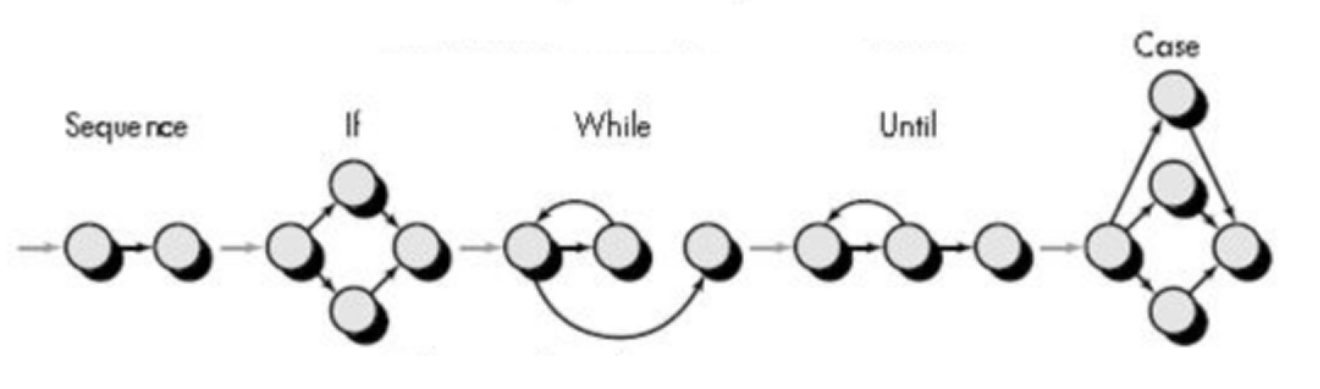
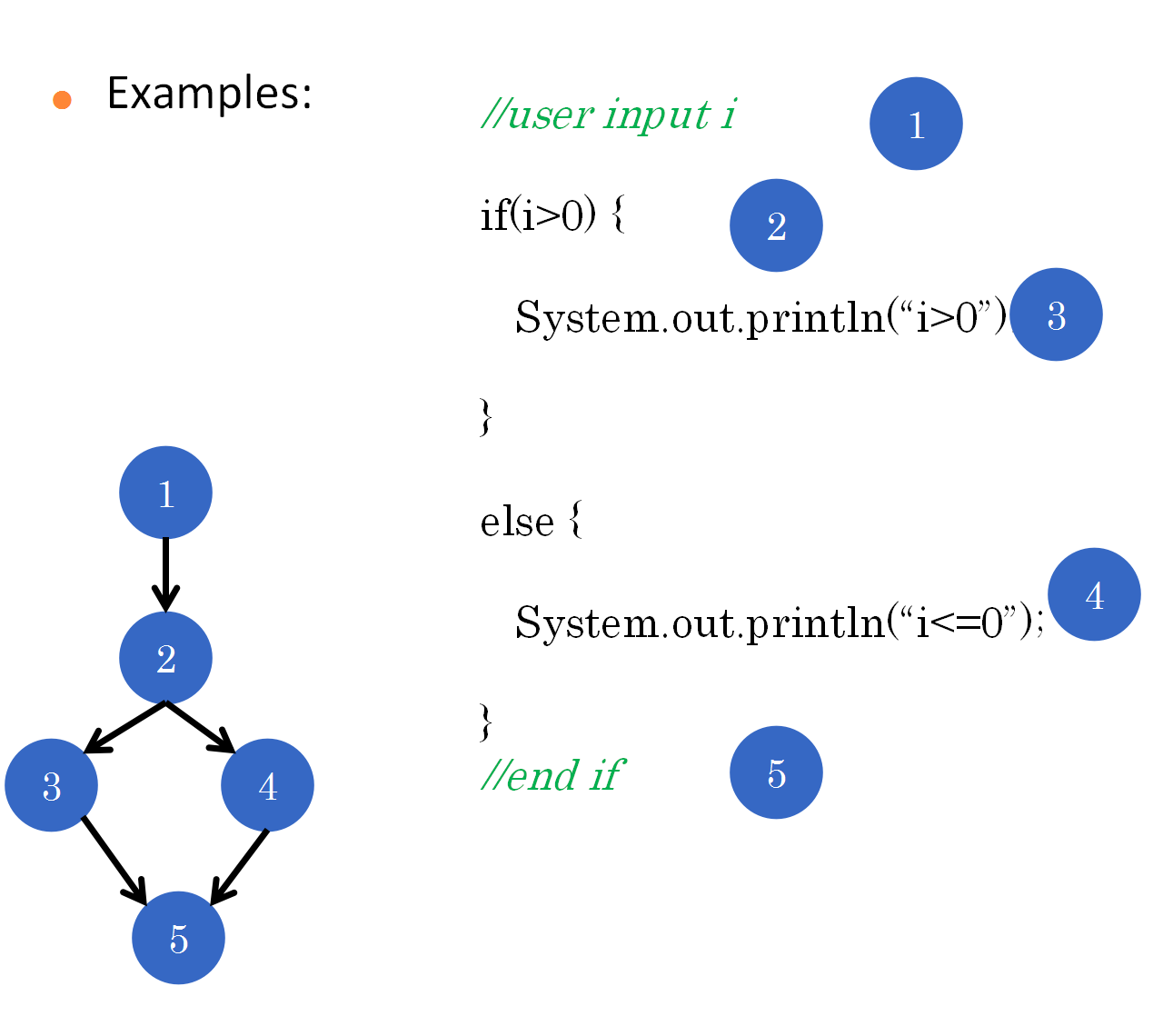
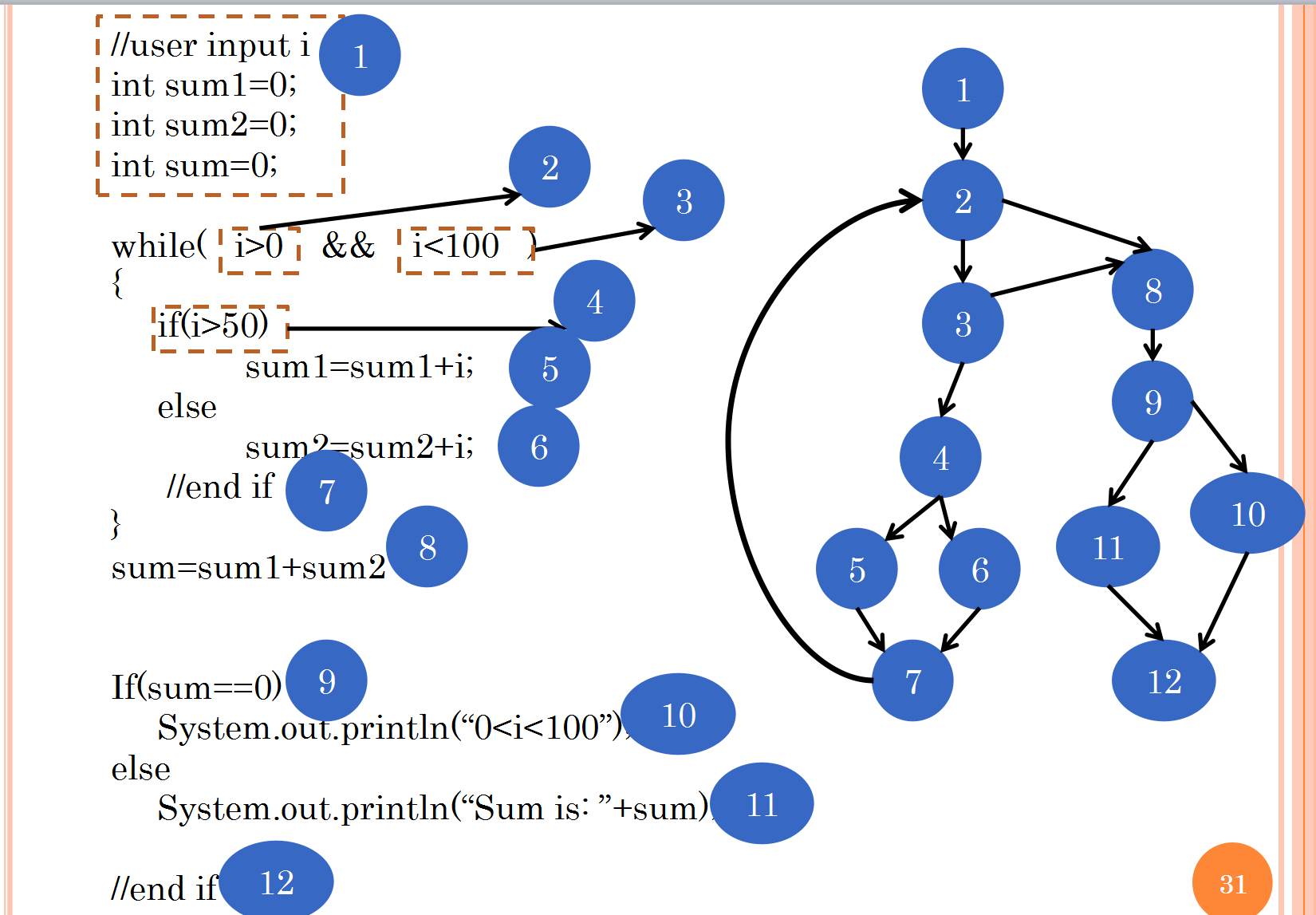
Flow graph:
Each circle represents one or more procedural statements, a decision condition, or the end of a decision (end if)
The arrows on the flow graph, called edges or links, represent flow of control and are analogous to flowchart arrows.
An edge must terminate at a node
Summary
Fault is an incorrect step, process or data definition in a computer program
Failure is an incorrect result caused by one or more than one fault(s)
Availability is an important quality attribute of software products, which is concerned with system failure and its associated consequences
Difference between verification and validation
Two test design strategies: black box and white box
Black box testing:
Exhaustive testing Equivalence partitioning
White box testing:
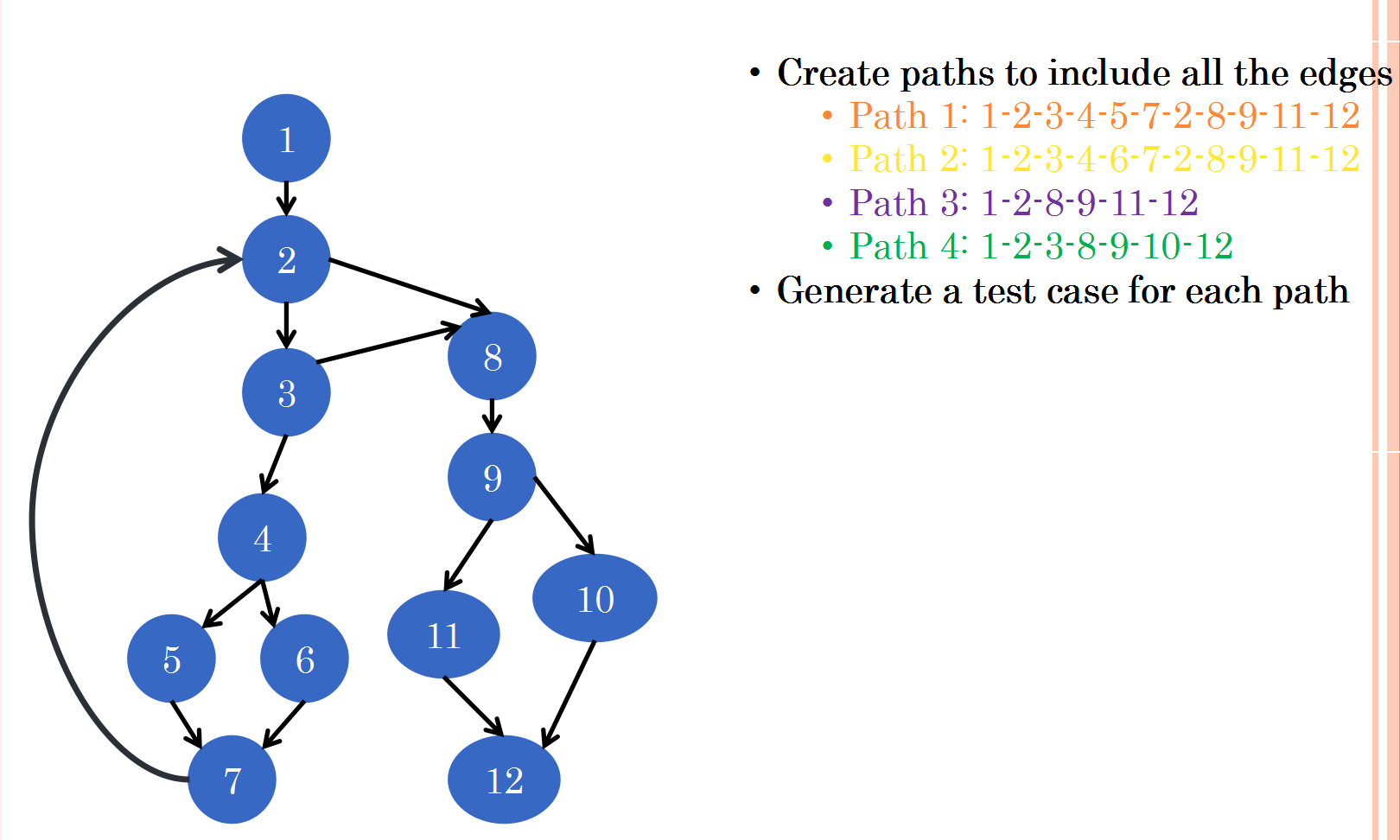
Using flow-graph to generate test cases (you need to be able to generate a flow graph for a program and design test cases)



