线性表学习1
本博文属于数据结构期末复习用,主要用来存放代码,不讲解详细知识点。
线性结构
若结构是非空有限集,则有且仅有一个开始结点和一个终端结点,并且除了首尾节点外所有结点都最多只有一个直接前趋和一个直接后继。 可表示为:(a1,a2,a3,...)
特点:只有一个首结点和尾结点
本质特征:除首尾结点外,其他结点只有一个直接前驱和一个直
接后继。
简言之,线性结构反映结点间的逻辑关系是二对一(1:1)的
线性结构包括:线性表、 堆栈、 队列、 字符串、 数组
等,其中最典型、 最常用的是线性表
线性表
由n个(n>=0)数据特性相同的元素构成的有限序列称为线性表,n=0时称为空表。
线性表逻辑结构
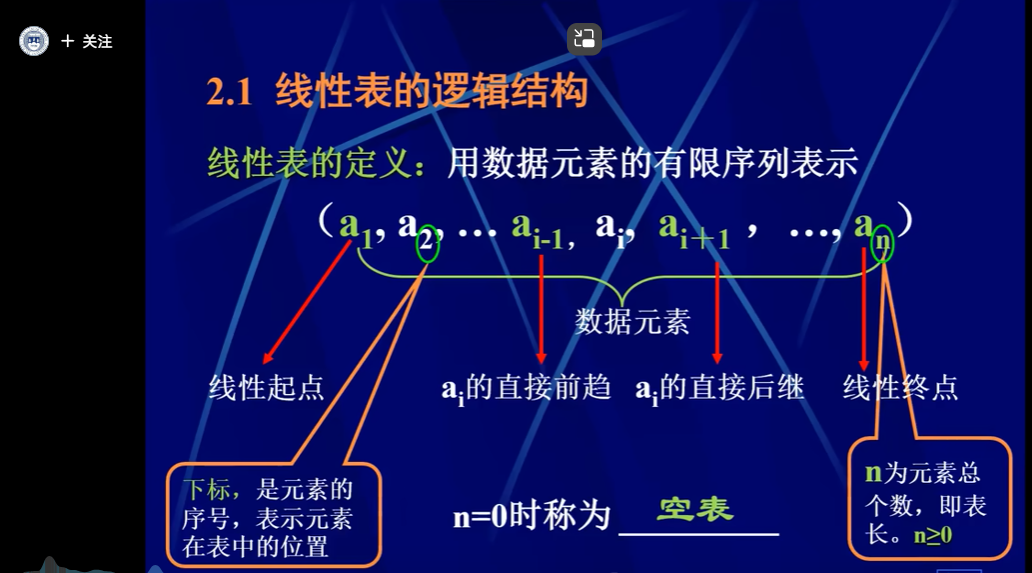
PS:空表分配了内存空间但是没有元素,不是不存在这个表
线性表的顺序存储和逻辑实现
顺序表的表示
线性表的顺序表的表示又叫顺序存储结构顺序映像

线性表顺序存储的特点
- 逻辑上相邻的数据元素,其物理存储上也相邻;
- 若已知表中首元素在存储器中的位置则其他元素存放位置亦可求出
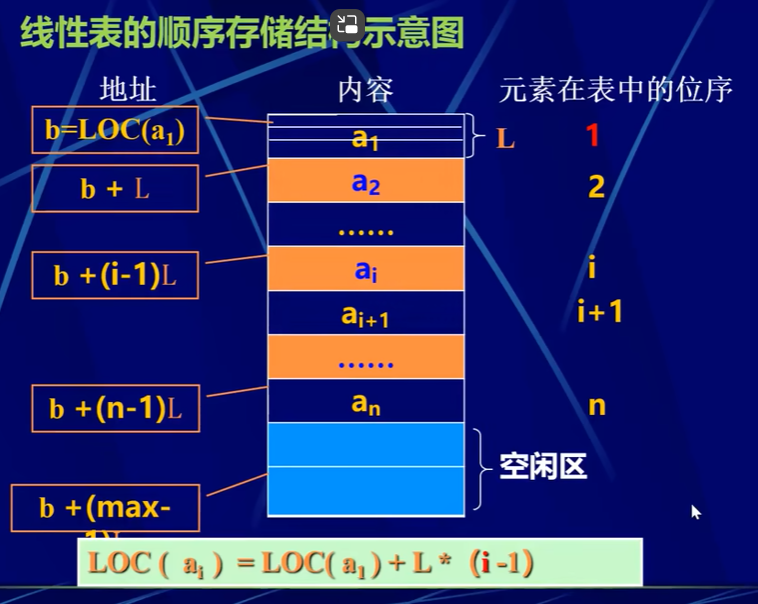
LOC(ai)=LOC(a0)+L*(i)
顺序表(基本操作)的实现
(增删改查)
- 修改

O(1)指的是对同一个元素只进行一次操作
-
增加
遍历是从第i个到第L.length个元素
在表的第i个元素前面插入一个元素

-
删除
删除线性表的第个位置上的元素

-
清空和删除表
-
排序
-
查找
下标查找即可
顺序表的运算效率分析


同理可证: 顺序表删除一元素的时间效率(时间复杂度)为
T (n)=(n-1)/2约等于o(n)
空间复杂度:0=o(1),因为没有使用辅助数据
深入讨论
顺序表各种操作的通式如何写??
写了一个晚上,思路不难,就是一些语法细节要注意(C语言基础不够牢导致的)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct{
int *numlist;
int length;
}chatDemo;
void bubble(int *arr,int length){
int temp=0;
for(int i=0;i<length-1;i++){
for(int j=0;j<length-i-1;j++){
if(arr[j]>arr[j+1]){
temp=arr[j+1];
arr[j+1]=arr[j];
arr[j]=temp;
}
}
}
}
void search(chatDemo list,int tofind){
int start=0;
int end=list.length-1;
int mid;
while(start<=end){
mid=(start+end)/2;
if(tofind>list.numlist[mid]){
start=mid;
}else if(tofind<list.numlist[mid]){
end=mid;
}
else if(tofind==list.numlist[mid]){
printf("the index is %d\n",mid);
return;
}
}
printf("404 not found");
}
void del(chatDemo *list,int position){
if(position<0||position>=list->length){
printf("OutoffpositionError");
return;
}
for(int i=position;i<list->length;i++){
list->numlist[i-1]=list->numlist[i];
}
list->numlist[list->length-1]=0;
list->length-=1;
list->numlist=(int*)realloc(list->numlist,list->length*sizeof(int));
printf("after del length:%d\n",list->length);
}
void add(chatDemo *list,int position,int addnum){
if(position<1||position>list->length){
printf("OutoffpositionError");
return;
}
list->length+=1;
list->numlist=(int*)realloc(list->numlist,list->length*(sizeof(int)));
list->numlist[list->length-1]=0;
for(int i=list->length-1;i>position-1;i--){
list->numlist[i]=list->numlist[i-1];
}
list->numlist[position-1]=addnum;
printf("after add length:%d\n",list->length);
}
int main(){
chatDemo demo;
demo.length=10;
demo.numlist=(int*)calloc(demo.length,sizeof(int));
int initial_values[] = {9, 2, 8, 3, 1, 4, 5, 6, 10, 7};
for (int i = 0; i < demo.length; i++) {
demo.numlist[i] = initial_values[i];
}
bubble(demo.numlist,demo.length);
printf("排序后数组\n");
for (int i = 0; i < demo.length; i++) {
printf("%d\n",demo.numlist[i]);
}
del(&demo,4);
printf("数组长度是%d\n",demo.length);
for(int i=0;i<demo.length;i++){
printf("%d\n",demo.numlist[i]);
}
add(&demo,4,4);
printf("数组长度是%d\n",demo.length);
for(int i=0;i<demo.length;i++){
printf("%d\n",demo.numlist[i]);
}
search(demo,8);
free(demo.numlist);
return 0;
}
线性表的链式存储和逻辑实现
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef struct Node//抽象数据类型
{
int data; //数据域
struct Node *next; //指针域,构建递归结构
}Node;
typedef struct {
Node *head; // 头指针
Node *tail;
size_t length;
// 尾指针
} List;
void InitList(List *list);//初始化
void push_tail(List *list,int x);//尾插
void push_head(List *list,int x);//头插
void show_list(List *list);//打印链表
void delAimval(List *list,int x,int ifone);//删除指定元素
void add(List *list,int x,int position,int fa);//指定位置前或后插入
void reverse(List*list);//逆序
Node *find(List *list,int x);//查找元素第一次出现位置,修改//
int main(){
int numlist[]={0,1,2,5,5,6,7,8,9,8,5,2,1,1};
int len=(int)(sizeof(numlist)/sizeof(int));
int i=0;
List demo,demox;
InitList(&demo);
InitList(&demox);
while(i<len){
push_tail(&demo,numlist[i++]);
}
printf("尾插法创建\n");
show_list(&demo);
i--;
while(i>=0){
push_head(&demox,numlist[i--]);
}
printf("头插法创建\n");
show_list(&demox);
reverse(&demox);
printf("逆序后\n");
show_list(&demox);
delAimval(&demox,5,1);
printf("删除一次指定元素5后\n");
show_list(&demox);
delAimval(&demox,5,0);
printf("删除全部指定元素5后\n");
show_list(&demox);
printf("后插元素\n");
add(&demox,99,6,1);
show_list(&demox);
printf("前插元素\n");
add(&demox,99,6,0);
show_list(&demox);
find(&demox,2);
return 0;
}
//初始化
void InitList(List *list)
{
Node* headNode=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));//此时头指针指向头节点
list->head=headNode;
assert(list->head!=NULL);
list->head->next=NULL;
list->tail = list->head; //尾指针也一起指向头节点。
list->length=0;
}
void push_head(List *list,int x){
Node *new_node=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
assert(new_node!=NULL);
new_node->data=x;
new_node->next=NULL;
//第一个节点的插入需要改尾指针的指向
if(list->length==0){
list->tail=new_node;
}
new_node->next=list->head->next;
list->head->next=new_node;
list->length++;
}
void push_tail(List *list,int x){
Node *new_node=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
assert(new_node!=NULL);
new_node->data=x;
new_node->next=NULL;
// 将当前尾节点的next指向新节点
list->tail->next = new_node;
// 更新尾指针
list->tail = new_node;
list->length++;
}
void show_list(List *list)
{
Node *p = list->head->next;
while(p!=NULL){
printf("%d-->",p->data);
p=p->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
Node *find(List *list,int x){
int j=1;
Node *p=list->head->next;
while(p){
if(p->data==x){
//可以同时修改元素,这里就不实现了
break;
}else{
j++;
p=p->next;
}
}
printf("%d是第%d个元素",x,j);
return p;
}
void delAimval(List*list,int x,int ifone){
Node *p=list->head;
while(p!=NULL&&p->next!=NULL){
if(p->next->data==x){
Node *p2=p->next->next;
Node *p1=p->next;
p->next=p2;
free(p1);
list->length--;
if(ifone==1){break;}else if(ifone==0){
p=list->head;
continue;
}else{printf("ffsr");}
}else{
p=p->next;
}
}
}
void add(List *list,int x,int position,int fa){
int j=1;
Node *new_node=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
new_node->data=x;
if(position<1||position>(int)list->length){
printf("DIANLAO");
return;
}
if(fa==0){
//前插
Node *p=list->head;
while(p&&p->next){
if(j==position){
new_node->next=p->next;
p->next=new_node;
list->length++;
break;
}else{p=p->next;j++;}
}
}else if(fa==1){
//后插
Node *p=list->head->next;
while(p){
if(j==position){
new_node->next=p->next;
p->next=new_node;
list->length++;
break;
}else{
p=p->next;
j++;
}
}
}
}
void reverse(List*list){
Node* previous=NULL;
Node* current=list->head->next;
Node*next=NULL;
while(current!=NULL){
next=current->next;// 保存下一个节点
current->next=previous;// 当前节点指向前一个节点
previous=current;// 前一个节点移动到当前节点
current=next;// 当前节点移动到下一个节点
}
list->head->next=previous;
}
运行结果
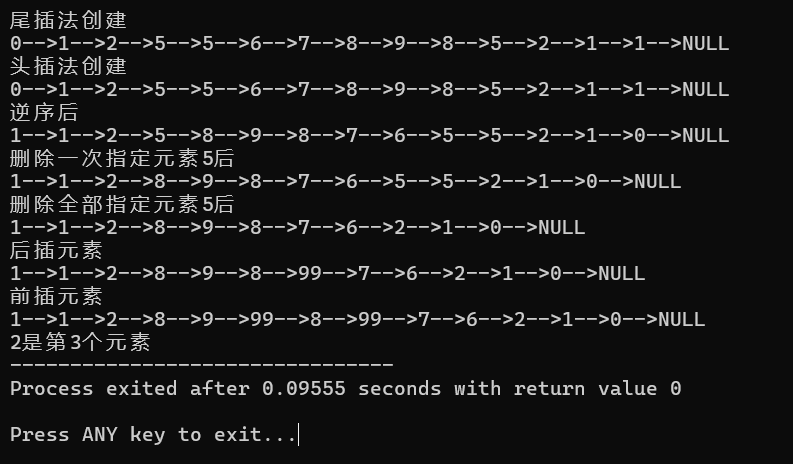
常见算法题目
线性表合并
时间复杂度n*m(两个表长的积)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//顺序表实现
typedef struct {
int *numlist;
int length;
}chatDemo;
// 合并函数
void merge(chatDemo *A, chatDemo *B) {
// 遍历表B的每个元素
for (int i = 0; i < B->length; i++) {
int found = 0; // 标记是否在表A中找到元素
// 检查表A中是否存在表B的当前元素
for (int j = 0; j < A->length; j++) {
if (B->numlist[i] == A->numlist[j]) {
found = 1; // 找到元素,此处可用其他查找算法
break;
}
}
// 如果没有找到,则将元素添加到表A的末尾
if (!found) {
// 扩展表A的容量
A->numlist = realloc(A->numlist, (A->length + 1) * sizeof(int));
if (A->numlist == NULL) {
perror("Failed to reallocate memory");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
A->numlist[A->length] = B->numlist[i]; // 添加新元素
A->length++; // 更新表A的长度
}
}
}
// 测试合并函数
int main() {
// 初始化表A
chatDemo A;
A.length = 3;
A.numlist = malloc(A.length * sizeof(int));
A.numlist[0] = 1;
A.numlist[1] = 2;
A.numlist[2] = 3;
// 初始化表B
chatDemo B;
B.length = 4;
B.numlist = malloc(B.length * sizeof(int));
B.numlist[0] = 3;
B.numlist[1] = 4;
B.numlist[2] = 5;
B.numlist[3] = 6;
// 合并表A和表B
merge(&A, &B);
// 打印合并后的表A
printf("合并后的表A: ");
for (int i = 0; i < A.length; i++) {
printf("%d ", A.numlist[i]);
}
printf("\n");
// 释放内存
free(A.numlist);
free(B.numlist);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
//链表实现
typedef struct Node {
int data; // 数据域
struct Node *next; // 指针域, 构建递归结构
} Node;
typedef struct {
Node *head; // 头指针
Node *tail; // 尾指针
size_t length; // 链表长度
} List;
// 创建新节点
Node* createNode(int data) {
Node *newNode = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
assert(newNode != NULL); // 确保内存分配成功
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
// 初始化链表
void initList(List *list) {
list->head = NULL;
list->tail = NULL;
list->length = 0;
}
// 向链表添加元素
void append(List *list, int data) {
Node *newNode = createNode(data);
if (list->head == NULL) {
list->head = newNode;
list->tail = newNode;
} else {
list->tail->next = newNode;
list->tail = newNode;
}
list->length++;
}
// 检查元素是否在链表中
int contains(List *list, int data) {
Node *current = list->head;
while (current != NULL) {
if (current->data == data) {
return 1; // 找到元素
}
current = current->next;
}
return 0; // 未找到元素
}
// 合并两个链表
void merge(List *A, List *B) {
Node *current = B->head;
while (current != NULL) {//遍历B
if (!contains(A, current->data)) {
append(A, current->data); // 添加到链表A
}
current = current->next;
}
}
// 打印链表
void printList(List *list) {
Node *current = list->head;
while (current != NULL) {
printf("%d -> ", current->data);
current = current->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
// 释放链表内存
void freeList(List *list) {
Node *current = list->head;
Node *nextNode;
while (current != NULL) {
nextNode = current->next;
free(current);
current = nextNode;
}
list->head = NULL;
list->tail = NULL;
list->length = 0;
}
// 测试合并函数
int main() {
List A, B;
initList(&A);
initList(&B);
// 初始化链表A
append(&A, 1);
append(&A, 2);
append(&A, 3);
// 初始化链表B
append(&B, 3);
append(&B, 4);
append(&B, 5);
append(&B, 6);
// 合并链表A和链表B
merge(&A, &B);
// 打印合并后的链表A
printf("合并后的链表A: ");
printList(&A);
// 释放内存
freeList(&A);
freeList(&B);
return 0;
}
- 有序表合并
顺序表时间复杂度O(m+n),空间复杂度较高
链表时间复杂度O(m+n),空间复杂度O(1)
void Mergelist_Sq(Sqlist *LA,Sqlist *LB,Sqlist *LC){
LC.length=LA.length+LB.length;
LC.elem=(Elemtype *)malloc(LC.length*sizeof(Elemtype));
Elemtype *pa=LA.elem,*pb=LB.elem,*pc=LC.elem;
while(pa<LA.elem+LA.length&&pb<LB.elem+LB.length){//LA.elem+LA.length是A表最后一个元素地址
if(*pa<*pb){
*pc=*pa;
pa++;
}else{
*pc=*pb;
pb++;
}
pc++;
}
while(pa<LA.elem+LA.length){//B表到达结尾,依次将A表剩余元素加入LC
*pc=*pa;
pa++;
pc++;
}
while(pb<LB.elem+LB.length){//A表到达结尾,依次将A表剩余元素加入LC
*pc=*pb;
pb++;
pc++;
}
}
void Mergelist_Lk(List *LA, List *LB, List *LC) {
Node *pa = LA->head->next;
Node *pb = LB->head->next;
Node *pc = LC->head;
while (pa!= NULL && pb!= NULL) {
if (pa->data <= pb->data) {
// 将LA中的节点接入LC
pc->next = pa;
pc = pa;
pa = pa->next;
} else {
// 将LB中的节点接入LC
pc->next = pb;
pc = pb;
pb = pb->next;
}
LC->length++;
}
// 处理LA链表剩余的节点(如果有)
if (pa!= NULL) {
pc->next = pa;
while (pa!= NULL) {
pc = pa;
pa = pa->next;
}
LC->length += (LA->length - (LA->head->next == pa? 0 : 1));
}
// 处理LB链表剩余的节点(如果有)
if (pb!= NULL) {
pc->next = pb;
while (pb!= NULL) {
pc = pb;
pb = pb->next;
}
LC->length += (LB->length - (LB->head->next == pb? 0 : 1));
}
// 更新LC的尾指针
LC->tail = pc;
free(LA->head);
free(LB->head);
}
链表和顺序表对比
书本有,就不写了
本文来自博客园,作者:积分别忘C,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/hackzz/p/18429846


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号