882. Reachable Nodes In Subdivided Graph
问题:
给定一个无向图,n个节点
每条边可分为0个or多个node,
求从节点0开始,走maxMoves步,总共能经过多少个node。
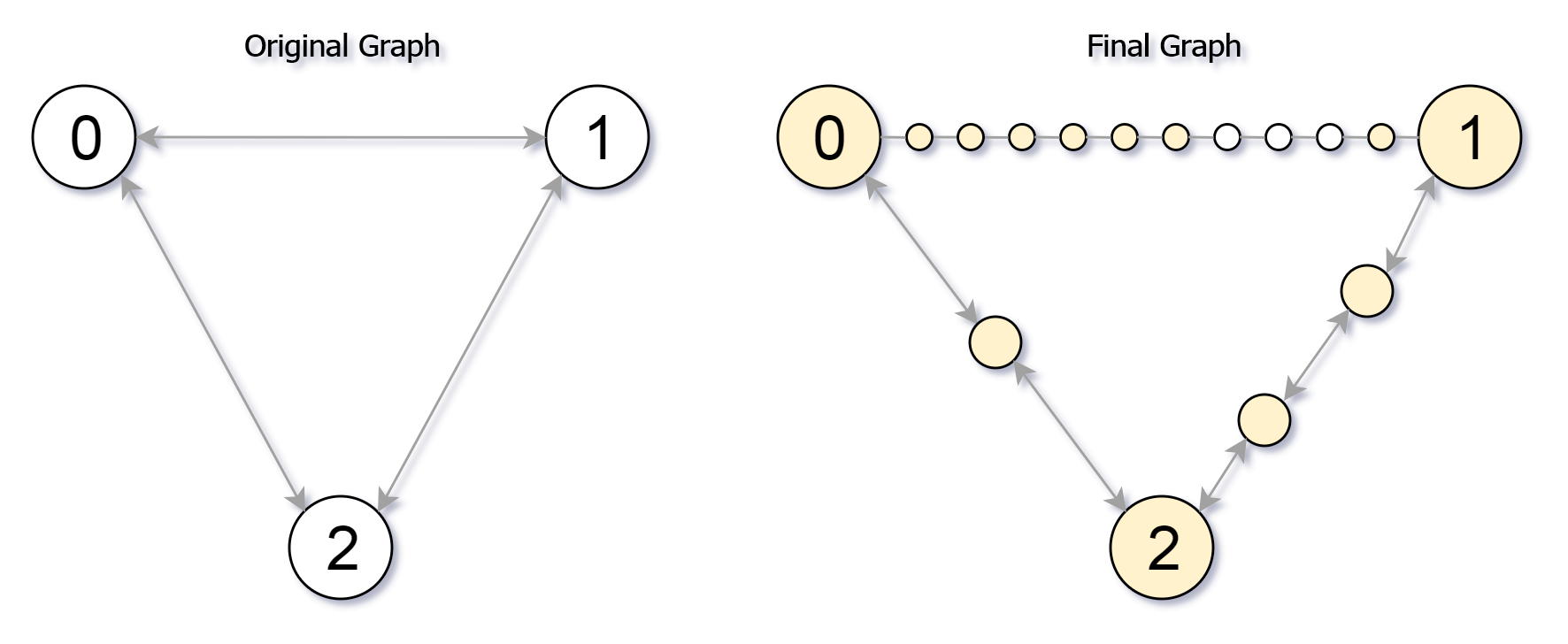
Example 1: Input: edges = [[0,1,10],[0,2,1],[1,2,2]], maxMoves = 6, n = 3 Output: 13 Explanation: The edge subdivisions are shown in the image above. The nodes that are reachable are highlighted in yellow. Example 2: Input: edges = [[0,1,4],[1,2,6],[0,2,8],[1,3,1]], maxMoves = 10, n = 4 Output: 23 Example 3: Input: edges = [[1,2,4],[1,4,5],[1,3,1],[2,3,4],[3,4,5]], maxMoves = 17, n = 5 Output: 1 Explanation: Node 0 is disconnected from the rest of the graph, so only node 0 is reachable. Constraints: 0 <= edges.length <= min(n * (n - 1) / 2, 104) edges[i].length == 3 0 <= ui < vi < n There are no multiple edges in the graph. 0 <= cnti <= 104 0 <= maxMoves <= 109 1 <= n <= 3000
example 1:
解法:Dijkstra 最小路径
思路:
- 对于本题,题意:要求最多能经过多少点。
- 可转化为:
- 求0节点到各个节点的最短距离 + 到达每个节点后剩余的步数。
- 因为:求到各个节点到【最短】距离,那么可以尽可能多的走到节点 + 且使得其剩余的步数更多。
- 使用dis数组记录,到达每个节点剩余的步数。
- 那么,遍历所有的边,对每条边:剩余步数★:
- 所求为:min{ 两个节点剩余步数之和, 两节点间的距离 }
- (去除重复计算的中间节点)
- 最终结果res
- 能到达的各个节点数:dis.size
- + 各条边的 剩余步数★。
要求dis[](0到各个节点的剩余步数):Dijkstra
- 使用优先队列,优先pop剩余步数更大的(也就是到达节点cost最小的)
- 大->小:less
- 每次pop一个节点,对该节点进行处理:
- 如果该节点已经记录过dis,那么跳过
- 否则,记录该节点dis
- 然后再展开该节点,看下一个节点next:
- 若dis[next]记录过,那么跳过。
- 下一个节点:leftmoves= cur.leftmoves-cur_next_cost - 1(节点自己)
- 若leftmoves<0那么无法到达next,跳过。
- 其他记录next到queue。
- 然后再展开该节点,看下一个节点next:
⚠️ 注意:Dijkstra算法中,每pop处理一个节点再进行dis记录。
防止在同层入队排序前,就阻止了更小的节点记录。
代码参考:
1 class Solution { 2 public://Dijkstra:shortest route to every node 3 //->to get more [left moves] after arrived node. 4 5 //conclusion: for every edge, which one of two node has left moves. 6 //res = add{all these left moves} + Count(every reachable node(leftmoves>0)). 7 8 //if both two nodes have left moves and these 2 moves duplicated in the middle. 9 // we just need the all moves between this two nodes. cnti[node1][node2] 10 // namely: min(leftmoves[node1]+leftmoves[node2], cnti[node1][node2]) 11 typedef pair<int,int> pii; 12 int reachableNodes(vector<vector<int>>& edges, int maxMoves, int n) { 13 int res = 0; 14 priority_queue<pii,vector<pii>,less<pii>> q;//leftmoves, nodeid 15 //less: first to pop the max value. 16 //greater: first to pop the min value. 17 //we need to pop max left, as to say the cost is min. 18 unordered_map<int, int> dis;//nodeid, leftmoves; 19 //undirected map->save both two node. 20 vector<unordered_map<int, int>> graph(n); 21 //graph[i]:{{node j1, moves1}{node j2, move2}...} 22 for(auto e:edges) { 23 graph[e[0]][e[1]]=e[2]; 24 graph[e[1]][e[0]]=e[2]; 25 } 26 //base: 27 q.push({maxMoves, 0}); 28 //dis[0] = maxMoves; 29 pii cur; 30 while(!q.empty()) { 31 cur = q.top(); 32 q.pop(); 33 if(dis.count(cur.second)) continue; 34 dis[cur.second] = cur.first; 35 cout<<"node:"<<cur.second<<" leftmove:"<<dis[cur.second]<<endl; 36 for(auto nextn:graph[cur.second]) { 37 int leftmoves = cur.first-nextn.second-1; 38 if(dis.count(nextn.first) || leftmoves<0) continue; 39 q.push({leftmoves, nextn.first}); 40 //dis[nextn.first] = leftmoves; 41 } 42 } 43 44 res = dis.size(); 45 for(auto e:edges) { 46 int node1 = dis.count(e[0])?dis[e[0]]:0; 47 int node2 = dis.count(e[1])?dis[e[1]]:0; 48 res += min(node1+node2, e[2]); 49 } 50 return res; 51 } 52 };


