133. Clone Graph
问题:
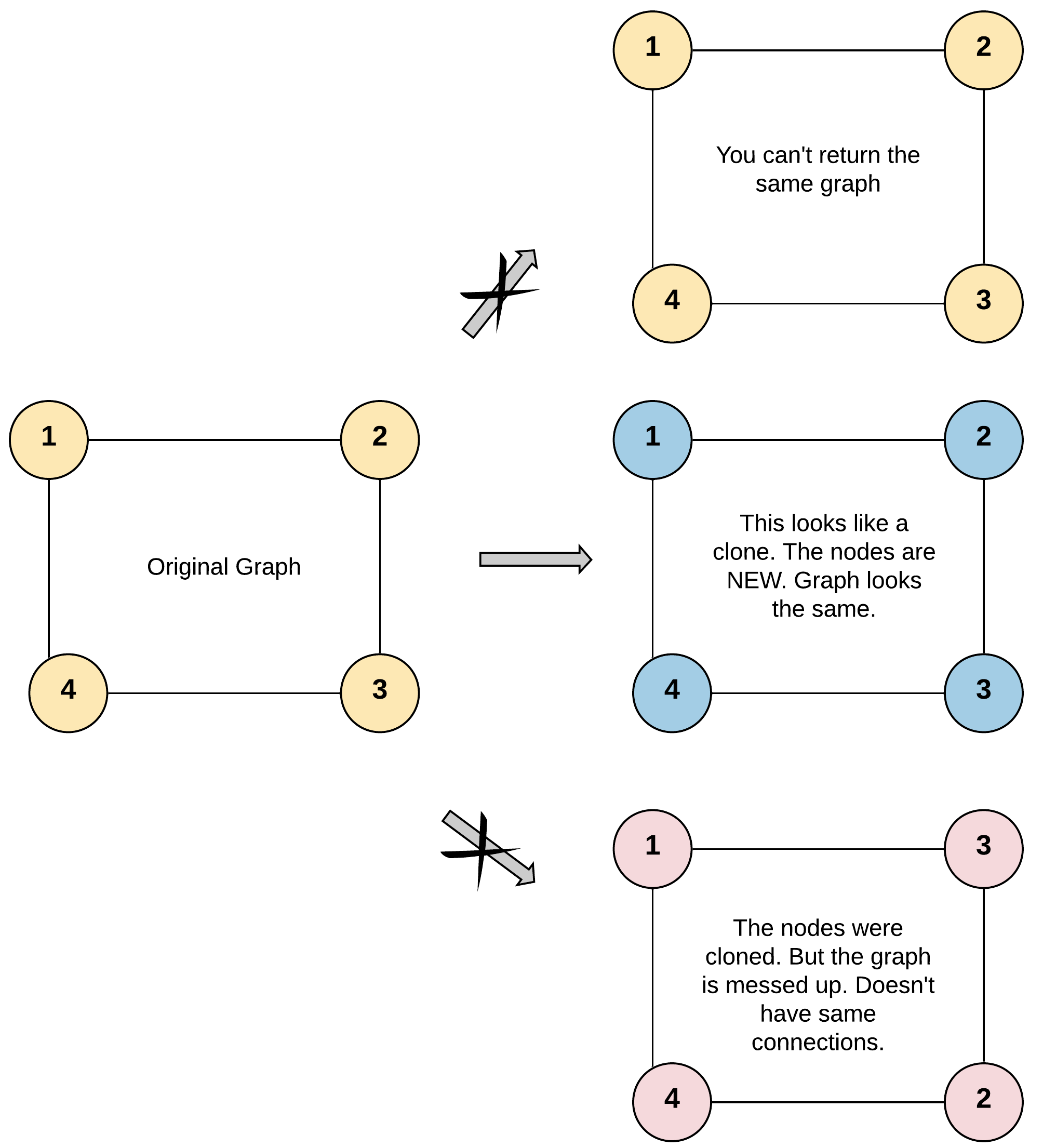
给定一个图,对该图进行深拷贝,返回拷贝出来的图。
adj[i]:代表节点 i 所相邻的节点。
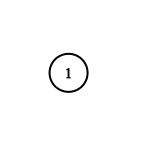
Example 1: Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Explanation: There are 4 nodes in the graph. 1st node (val = 1)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 2nd node (val = 2)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3). 3rd node (val = 3)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 4th node (val = 4)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3). Example 2: Input: adjList = [[]] Output: [[]] Explanation: Note that the input contains one empty list. The graph consists of only one node with val = 1 and it does not have any neighbors. Example 3: Input: adjList = [] Output: [] Explanation: This an empty graph, it does not have any nodes. Example 4: Input: adjList = [[2],[1]] Output: [[2],[1]] Constraints: 1 <= Node.val <= 100 Node.val is unique for each node. Number of Nodes will not exceed 100. There is no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph. The Graph is connected and all nodes can be visited starting from the given node.
example1:
example2:
解法:BFS
queue:<拷贝先res,拷贝元node>
visited:处理过的节点map: key: node->val value: Node*地址
每次对处理对象节点->neighbors节点进行new
(只有这些节点不存在在visited中的时候,若已存在,直接将visited里的地址赋值给neighbors)
new完之后的neighbor节点,加入visited中。标记为已访问。
代码参考:
1 /* 2 // Definition for a Node. 3 class Node { 4 public: 5 int val; 6 vector<Node*> neighbors; 7 Node() { 8 val = 0; 9 neighbors = vector<Node*>(); 10 } 11 Node(int _val) { 12 val = _val; 13 neighbors = vector<Node*>(); 14 } 15 Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _neighbors) { 16 val = _val; 17 neighbors = _neighbors; 18 } 19 }; 20 */ 21 22 class Solution { 23 public: 24 Node* cloneGraph(Node* node) { 25 Node* res; 26 queue<vector<Node*>> q; 27 if(node==nullptr) return nullptr; 28 unordered_map<int, Node*> visited; 29 if(node) { 30 res = new Node(node->val); 31 q.push({res,node}); 32 visited[node->val] = res; 33 } 34 while(!q.empty()) { 35 int sz = q.size(); 36 for(int i=0; i<sz; i++) { 37 vector<Node*> cur = q.front(); 38 q.pop(); 39 for(Node* n:cur[1]->neighbors) { 40 if(visited.count(n->val)==0) { 41 Node* newnode = new Node(n->val); 42 visited[n->val] = newnode; 43 q.push({visited[n->val],n}); 44 } 45 cur[0]->neighbors.push_back(visited[n->val]); 46 } 47 } 48 } 49 return res; 50 } 51 };




