103. Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
问题:
求二叉树的正反交替层序遍历。
第一层从左向右,第二次从右向左...
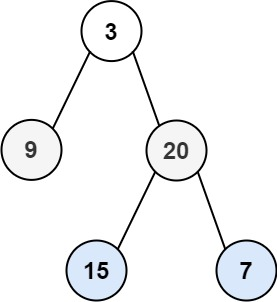
Example 1: Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: [[3],[20,9],[15,7]] Example 2: Input: root = [1] Output: [[1]] Example 3: Input: root = [] Output: [] Constraints: The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 2000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Example 1:
解法:BFS
queue:保存每一层遍历节点。
for为一层。
flg记录奇偶层,奇数层再使用reverse,将一层顺序反转。
代码参考:
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 8 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 9 * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} 10 * }; 11 */ 12 class Solution { 13 public: 14 vector<vector<int>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode* root) { 15 queue<TreeNode*> q; 16 vector<vector<int>> res; 17 int flg = 0; 18 if(root) q.push(root); 19 while(!q.empty()) { 20 int sz = q.size(); 21 vector<int> curlevel; 22 for(int i=0; i<sz; i++) { 23 TreeNode* cur = q.front(); 24 q.pop(); 25 curlevel.push_back(cur->val); 26 if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left); 27 if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right); 28 } 29 if(!curlevel.empty() && flg%2) { 30 reverse(curlevel.begin(), curlevel.end()); 31 } 32 if(!curlevel.empty()) res.push_back(curlevel); 33 flg++; 34 } 35 return res; 36 } 37 };




