【二叉树构造】654. Maximum Binary Tree; 105. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal; 106. Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
654. Maximum Binary Tree
问题:
用给定的数组,构成最大二叉树。
从数组中找到最大值,作为root,其index以左,作为左子树。index以右,作为右子树。
Example 1:
Input: [3,2,1,6,0,5]
Output: return the tree root node representing the following tree:
6
/ \
3 5
\ /
2 0
\
1
Note:
The size of the given array will be in the range [1,1000].
解法:Binary Tree(二叉树)
递归:help函数
- base:数组为空:end>=start
- 返回 nullptr
- 对于每个节点root :在nums[start, end)范围内
- 找到最大值maxval,及其index:idx
- root->val = maxval
- root->left = 递归求解:nums[start, idx]
- root->right = 递归求解:nums[idx+1, end]
- 找到最大值maxval,及其index:idx
代码参考:
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 8 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 9 * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} 10 * }; 11 */ 12 class Solution { 13 public: 14 TreeNode* help(vector<int>& nums, int start, int end) { 15 if(end<=start) return nullptr; 16 int maxval = INT_MIN; 17 int idx = 0; 18 for(int i=start; i<end; i++) { 19 if(nums[i]>maxval) { 20 maxval = nums[i]; 21 idx = i; 22 } 23 } 24 TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(maxval); 25 //child: 26 root->left = help(nums, start, idx); 27 root->right = help(nums, idx+1, end); 28 return root; 29 } 30 TreeNode* constructMaximumBinaryTree(vector<int>& nums) { 31 return help(nums, 0, nums.size()); 32 } 33 };
105. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
问题:
由【前序遍历】和【中序遍历】数组,构造二叉树。
For example, given
preorder = [3,9,20,15,7]
inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
Return the following binary tree:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
解法:Binary Tree(二叉树)
递归:help函数
- base:数组为空:preE>=preS or inE>=inS
- 返回 nullptr
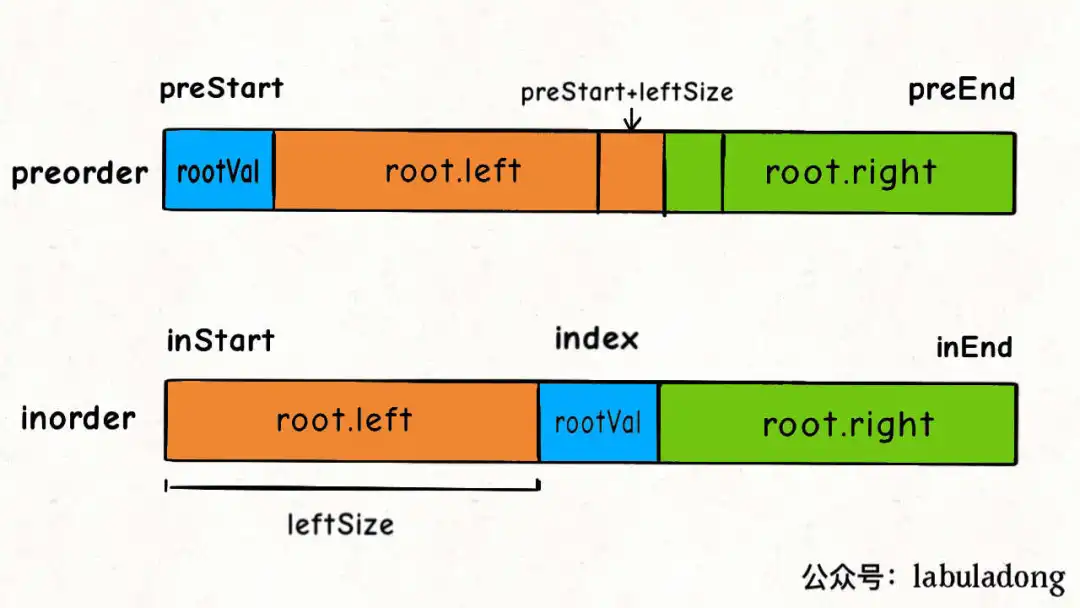
- 对于每个节点root :在preorder[preS, preE)和inorder[inS, inE)范围内
- 在中序中,找到前序遍历的第一个值val:preorder[preS],的index:idx。求出左树的长度:leftSize = idx-inS+1;
- root->val = preorder[preS]
- root->left = 递归求解:preorder[preS+1, preS+leftSize) 和 inorder[inS, idx)
- root->right = 递归求解:preorder[preS+leftSize, preE) 和 inorder[idx+1, inE)
- 在中序中,找到前序遍历的第一个值val:preorder[preS],的index:idx。求出左树的长度:leftSize = idx-inS+1;
代码参考:
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 8 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 9 * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} 10 * }; 11 */ 12 class Solution { 13 public: 14 //preorder[preS, preE) 15 //inorder[inS, inE) 16 TreeNode* help(vector<int>& preorder, int preS, int preE, 17 vector<int>& inorder, int inS, int inE) { 18 if(preS >= preE || inS >= inE) return nullptr; 19 int val=preorder[preS], idx=0; 20 for(int i=inS; i<inE; i++) { 21 if(inorder[i] == val) { 22 idx = i; 23 break; 24 } 25 } 26 //root 27 TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(val); 28 //child 29 int leftSize = idx-inS+1; 30 root->left = help(preorder, preS+1, preS+leftSize, 31 inorder, inS, idx); 32 root->right = help(preorder, preS+leftSize, preE, 33 inorder, idx+1, inE); 34 return root; 35 } 36 TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) { 37 return help(preorder, 0, preorder.size(), 38 inorder, 0, inorder.size()); 39 } 40 };
106. Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
问题:
由【后序遍历】和【中序遍历】数组,构造二叉树。
For example, given
inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
postorder = [9,15,7,20,3]
Return the following binary tree:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
解法:Binary Tree(二叉树)
递归:help函数
- base:数组为空:postE>=postS or inE>=inS
- 返回 nullptr
- 对于每个节点root :在postorder[postS, postE)和inorder[inS, inE)范围内
- 在中序中,找到后序遍历的最后一个值val:postorder[postE-1],的index:idx。求出左树的长度:leftSize = idx-inS;
- root->val = postorder[postE-1]
- root->left = 递归求解:postorder[postS, postS+leftSize) 和 inorder[inS, idx)
- root->right = 递归求解:postorder[postS+leftSize, postE-1) 和 inorder[idx+1, inE)
- 在中序中,找到后序遍历的最后一个值val:postorder[postE-1],的index:idx。求出左树的长度:leftSize = idx-inS;

代码参考:
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 8 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 9 * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} 10 * }; 11 */ 12 class Solution { 13 public: 14 TreeNode* help(vector<int>& inorder, int inS, int inE, 15 vector<int>& postorder, int postS, int postE) { 16 if(inE<=inS || postE<=postS) return nullptr; 17 int val = postorder[postE-1], idx=0; 18 for(int i=inS; i<inE; i++) { 19 if(inorder[i] == val) { 20 idx = i; 21 break; 22 } 23 } 24 //root 25 TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(val); 26 int leftSize = idx-inS; 27 //child 28 root->left = help(inorder, inS, idx, 29 postorder, postS, postS+leftSize); 30 root->right = help(inorder, idx+1, inE, 31 postorder, postS+leftSize, postE-1); 32 return root; 33 } 34 TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) { 35 return help(inorder, 0, inorder.size(), 36 postorder, 0, postorder.size()); 37 } 38 };




