查询性能优化
一、单体项目测压
1、云服务器准备一台,阿里云服务器(对于学习用,可以选择按量付费模式)
可有效降低学习成本,不使用的时候停止服务器即可,不收取费用,需要使用的时候开启即可
我的配置

2、在服务器安装相关环境(JDK、MYSQL)
模式为传统单体项目。所有都放在一个服务器中。
3、秒杀项目准备(项目资源可留言)
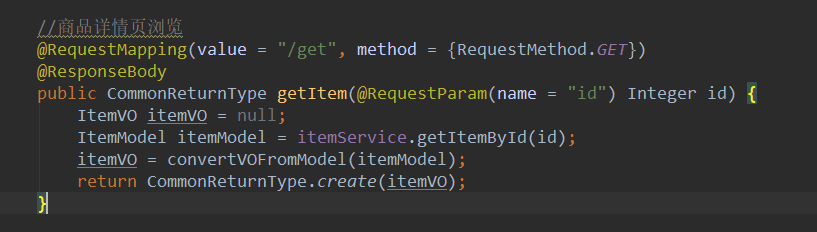
商品详情页接口展示,之后将主要使用该接口测压、优化。
4、所有环境都准备好后,打包部署(阿里云服务器需配置具体的安全组规则,开放端口,不然无法对外访问)
5、接口访问成功。
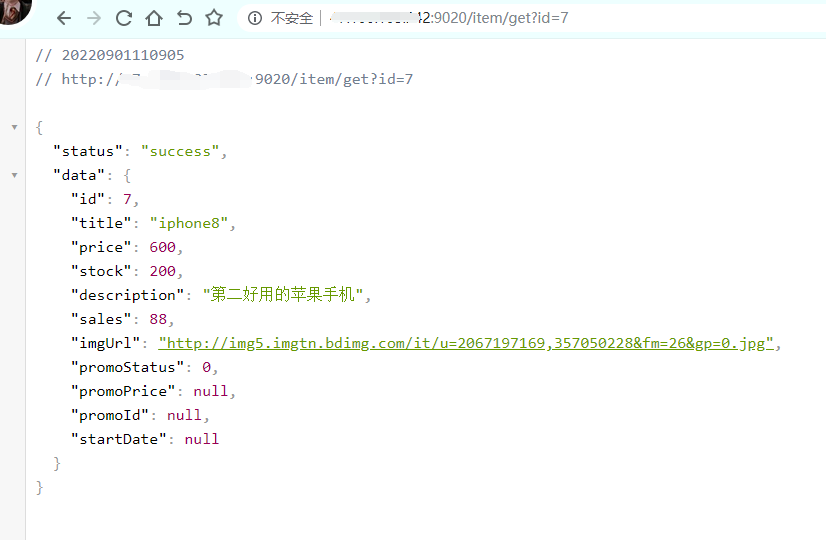
6、使用 JMeter 测压
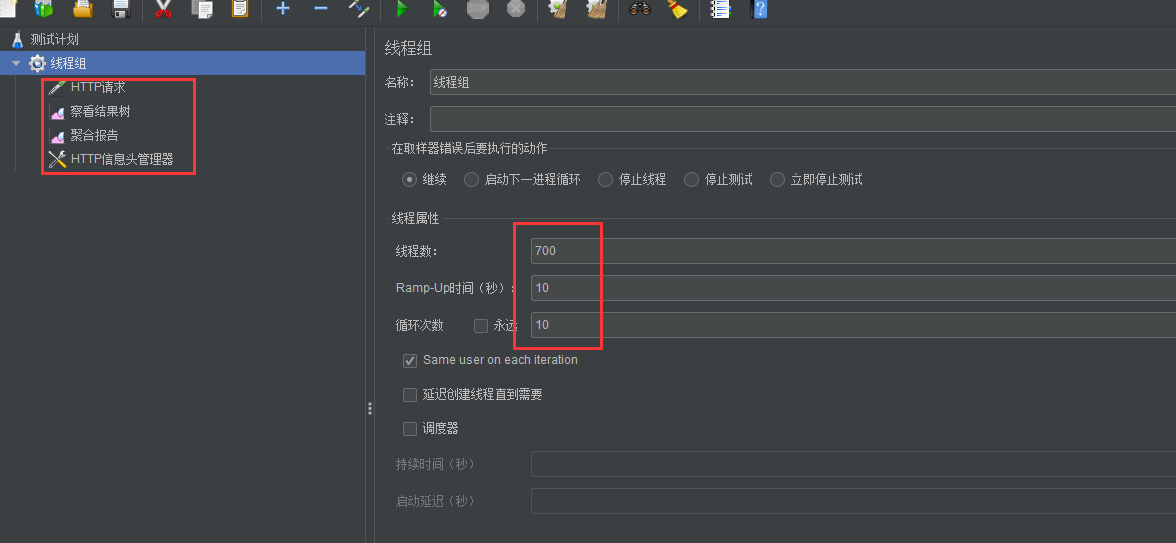
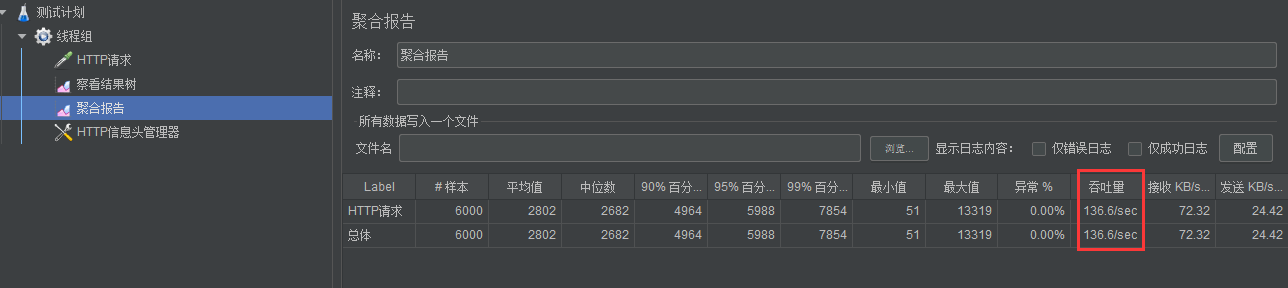
1、线程数量:700,循环次数:10。数据可进行相关调整。通过多次测压吞吐量平均值在 130/s 左右。
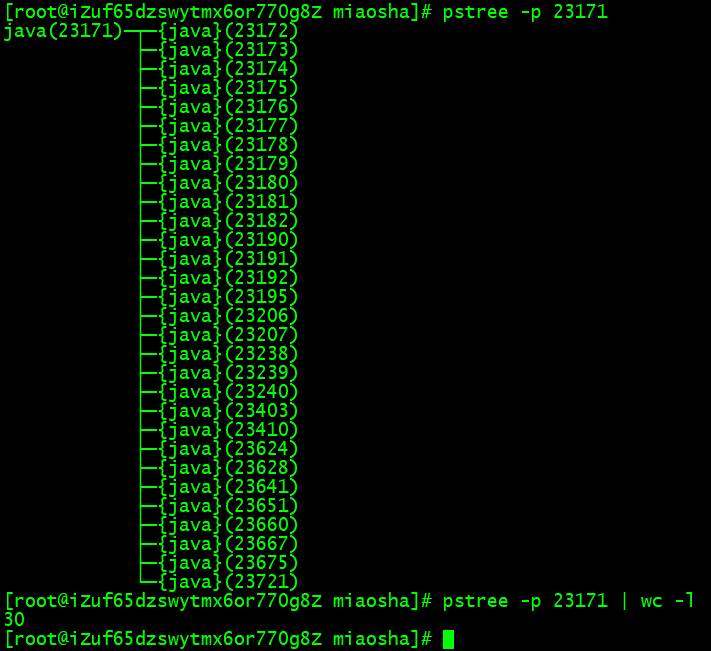
2、使用 pstree -p 端口号,查看线程数量
在没有测压情况下的数量:30(tomcat最小核心线程 10 + 其他线程)
3、使用 top -H 查看
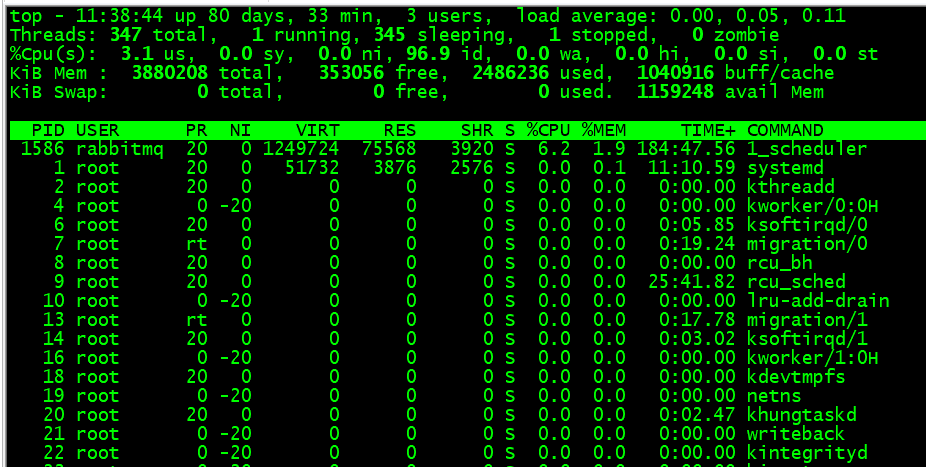
cpu us:用户空间的cpu使用情况(用户层代码)
cpu sy:内核空间的cpu使用情况(系统调用)
load average:1,5,15分钟load平均值,跟着核数系数,0代表通常,1代表打满,1+代表等待阻塞i)
memory:free空闲内存,used使用内存
7、配置 springboot tomcat 配置
· 1、查看 springboot 相关 tomcat 配置
搜索 service.tomcat
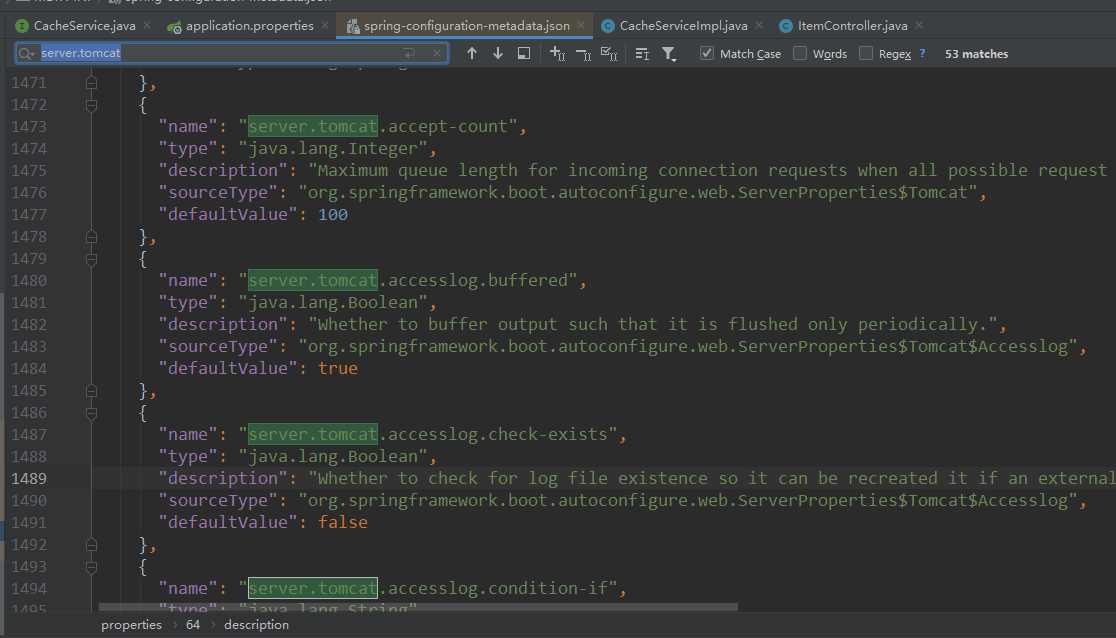
springboot内置 tomcat 所有相关 默认配置都在这里。
accept-count:默认队列数量 100,
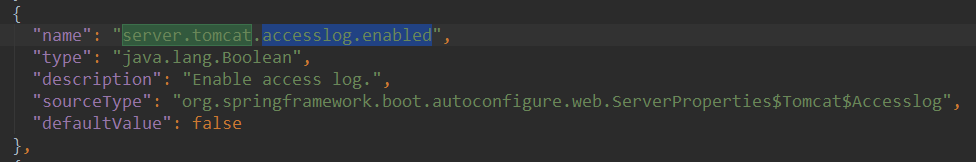
accesslog.enabled:是否开启 tomcat 日志
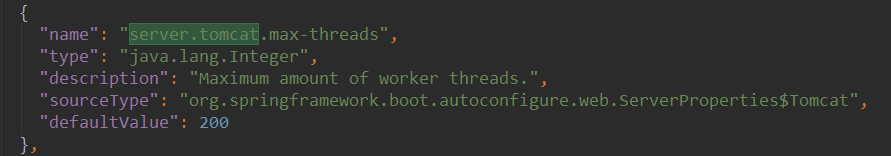
max-threads:最大线程数量
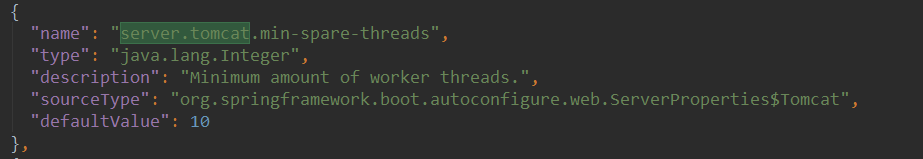
min-spare-threads:最小核心线程
2、springboot 中添加相关 tomcat 配置:
# 默认队列 server.tomcat.accept-count=1000 # (几核 * 2) *100 最大线程 server.tomcat.max-threads=400 # 最小核心线程 server.tomcat.min-spare-threads=100 # 开启 tomcat 日志 server.tomcat.accesslog.enabled=true # 日志路径 server.tomcat.accesslog.directory=/home/miaosha/tomcat # 日志格式 %h ip地址,%l ,%u ,%t 处理时长, "%r" 请求url, %s 返回状态码, %b 请求 response大小, %D 处理请求时长 server.tomcat.accesslog.pattern=%h %l %u %t "%r" %s %b %D
3、配置 tomcat Keepalived 相关配置
/** * @description 当 Spring 容器内没有 TomcatEnbeddedServerFactory 这个 Bean 时,会把此 bean 加载进 Spring 中 * @author: hq * @create: 2022-08-30 23:16 **/ @Component public class WebServerConfig implements WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableWebServerFactory> { @Override public void customize(ConfigurableWebServerFactory factory) { // 使用对应工厂类提供的接口,定制化 Tomcat connector ((TomcatServletWebServerFactory)factory).addConnectorCustomizers(new TomcatConnectorCustomizer() { @Override public void customize(Connector connector) { Http11NioProtocol protocol = (Http11NioProtocol) connector.getProtocolHandler(); // 定制化 KeepalivedTimeOut,设置 30s 内没有请求则服务端自动断开 Keepalived 连接 protocol.setKeepAliveTimeout(30000); // 当客户端发送超过 1w 个请求则自动断开 Keepalived 连接 protocol.setMaxKeepAliveRequests(10000); // protocol.setMaxConnections(); 最大 soket 连接数 } }); } }
4、重新打包部署测压

启动过后会在设置 Tomcat 日志的目录生成文件夹
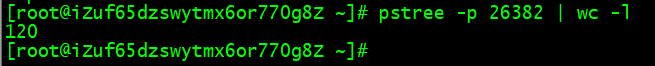
在未测压情况下,默认线程数量:120
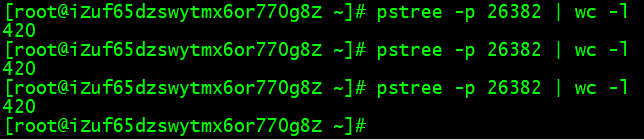
压力测试时,最大线程数量为420。与未设置 tomcat.max-threads 提升了不少。
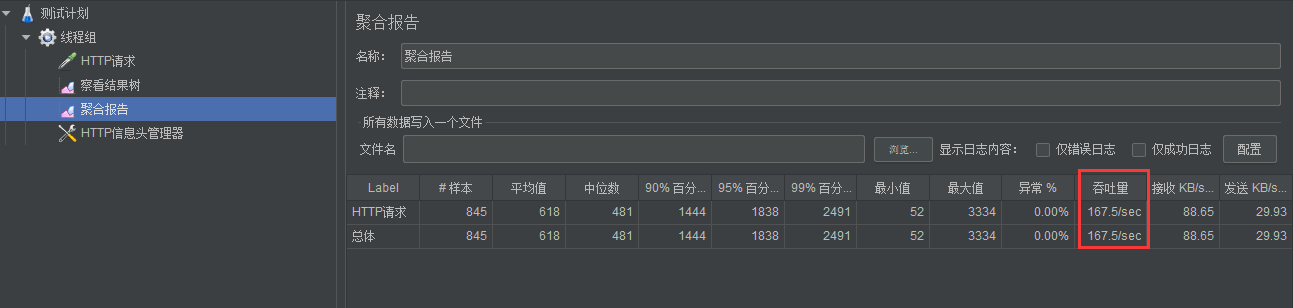
吞吐量也提升至 160/s。
查看 tomcat 日志
二、负载均衡、分布式会话
1、准备 3 台服务器(新增)
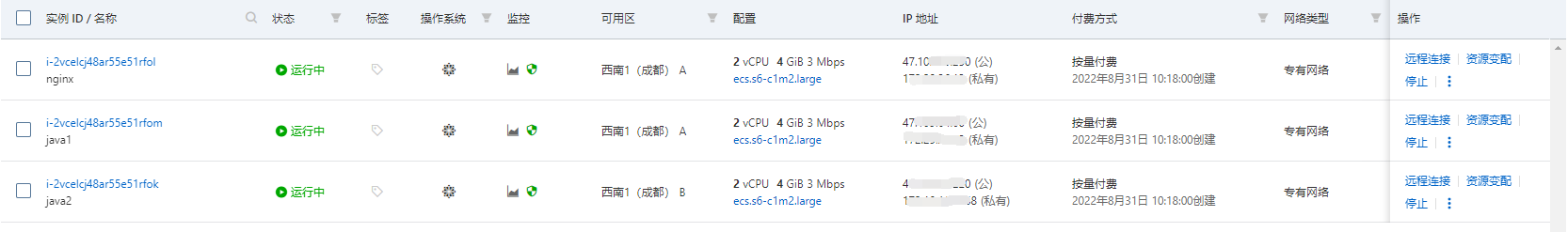
一台作为 Nginx、两台 Java。环境分别安装好。地区为成都。
开始那台机器地区为上海,之后将作为 Redis、Mysql 服务使用。
2、向两台Java1、Java2 部署程序(两台数据访问Mysql均连接上海区域服务器)
3、配置Nginx
#user nobody; CPU数量 * 2 worker_processes 4; #error_log logs/error.log; #error_log logs/error.log notice; #error_log logs/error.log info; pid /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; #log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' # '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' # '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; #access_log logs/access.log main; sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65; #gzip on; upstream tomcatServerPool{ server 172.29.26.12:9020 weight=10; server 172.18.160.168:9020 weight=10; } server { listen 80; server_name localhost; location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; proxy_pass http://tomcatServerPool; #用户IP proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } } }
4、首先测试单机
修改IP地址
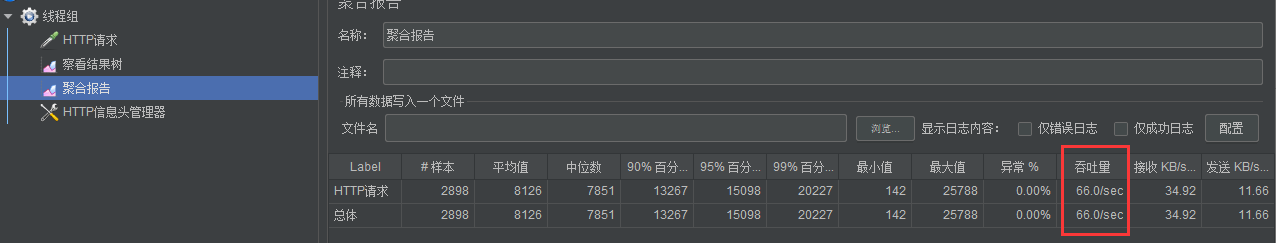
在测压的过程中,吞吐量 66/s 左右,与我们使用上海区域服务器慢了将近一般,这是因为受地区影响,后面新建的3台服务器都是成都区域,java程序数据访问上海区域,受传输距离影响所以速度就变慢了。所以看得出,跨区域太远会影响响应速度。
5、双机,nginx负载均衡测试压力
JMeter 修改IP地址为 nginx 服务器IP,端口还改为 80,线程组不变

可以看到 通过 负载均衡,已将吞吐量提升了一倍多。由 66/s 提升至 143/s 。
三、缓存
1、Redis 缓存
spring.redis.database=1 spring.redis.port=6379 spring.redis.host=******** spring.redis.password=******** spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=1000 spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait=-1ms spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle=16 spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle=8
1、修改代码
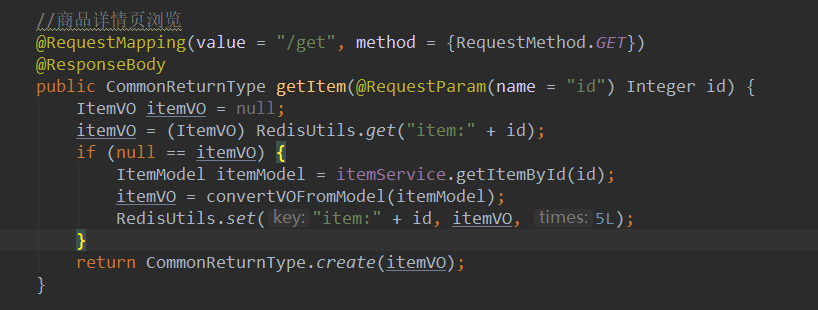
2、部署压力测试(后面都是双机测试)
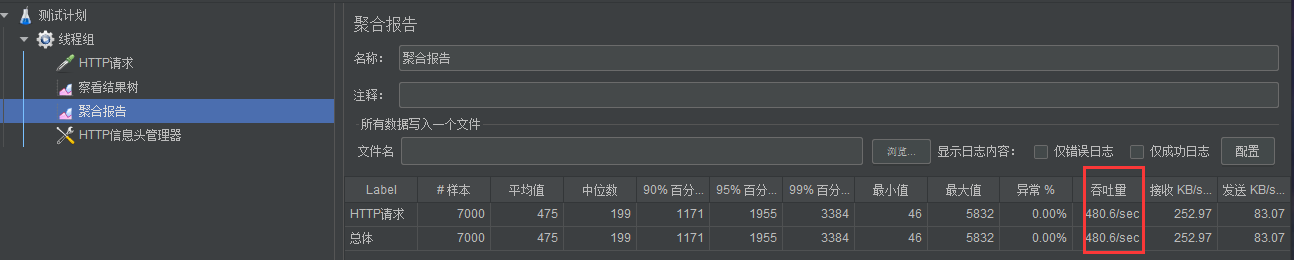
通过 Redis 缓存介入,吞吐量翻了几倍。
2、Guava 本地缓存
1、这个时候考虑加入本地缓存,在每台服务器上缓存热点数据,像直接使用 HashMap、ConcurrentHashMap格式的类型还不满足自动失效清除功能,我们可以使用 guava 提供的数据类型 Cache<String, Object>;
但是在修改方面,可以使用 MQ 消息广播,通知每台服务器进行操作,代码复杂度提高了。
2、编写代码
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>18.0</version>
</dependency>
/** * @description * @author: hq * @create: 2022-08-31 16:21 **/ @Service public class CacheServiceImpl implements CacheService { private Cache<String, Object> cache = null; @PostConstruct public void init() { cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder() // 设置缓存容器初始容量 .initialCapacity(16) // 设置缓存中最大可以存储 100 个 key,超过100个后按照 LRU 策略移除缓存项 .maximumSize(100) // 设置写缓存多少秒过期 .expireAfterWrite(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS) .build(); } @Override public void setCache(String key, Object obj) { cache.put(key, obj); } @Override public Object getCache(String key) { return cache.getIfPresent(key); } }
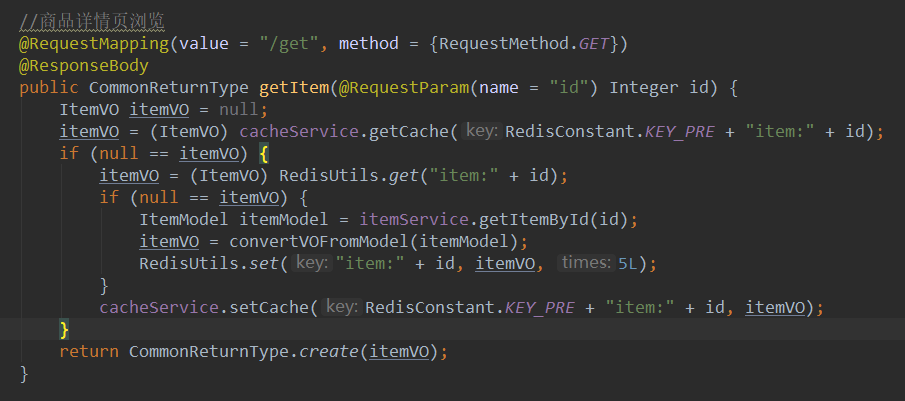
3、部署服务
4、压力测试
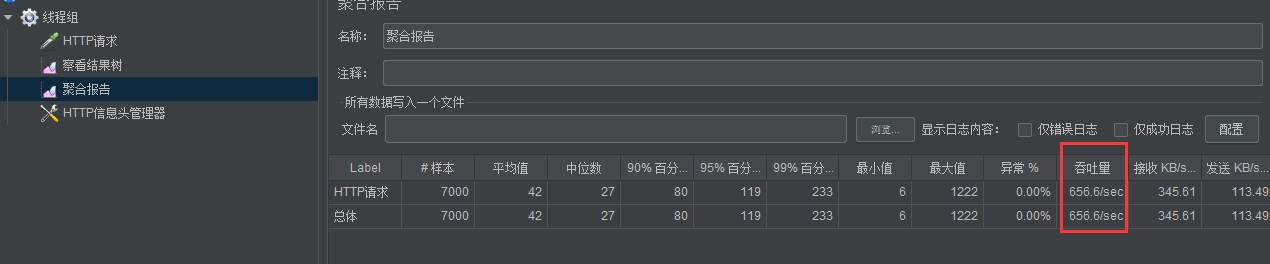
吞吐量已经提升至 650/s。
3、Nginx 缓存(反向代理废弃版)
1、在整个服务调用运行过程中,nginx 是用户第一道关卡。那么可以在用户调用的时候,先查找 nginx 缓存。
2、配置反向代理缓存
#user nobody; worker_processes 4; #error_log logs/error.log; #error_log logs/error.log notice; #error_log logs/error.log info; pid /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; #log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' # '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' # '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; #access_log logs/access.log main; sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65; #gzip on; upstream tomcatServerPool{ server 172.29.26.12:9020 weight=10; server 172.18.160.168:9020 weight=10; keepalive 30; } # proxy_cache_path 设置缓存目录 # levels 表示是两级目录,1和2表示用1位和2位16进制来命名目录名称。在此例中,第一级目录用1位16进制命名,如b;第二级目录用2位16进制命名 # keys_zone 设置共享内存以及占用空间大小 # max_size 最大缓存容量 # inactive 缓存最长时间 proxy_cache_path /usr/local/nginx/upstream_cache levels=1:2 keys_zone=mycache:50m max_size=1g inactive=5m; server { listen 80; server_name localhost; #charset koi8-r; #access_log logs/host.access.log main; location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; proxy_pass http://tomcatServerPool; #用户IP proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_cache mycache; # 缓存状态为 200 304 的数据 proxy_cache_valid 200 304 5m; } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } } }
3、重启 nginx
4、JMeter 压测
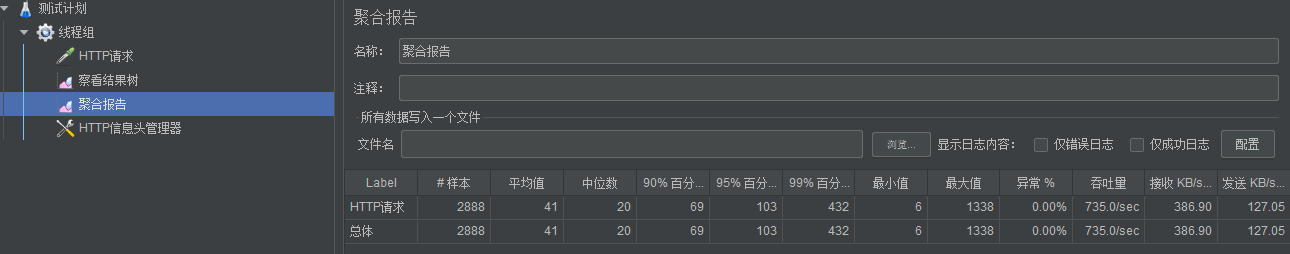
性能提升不是很大,原因是因为 nginx 是将缓存存储在磁盘上的,读取没有内存速度快。
但是它介于用户第一层关卡就返回数据,如果没有这缓存,那么也会有网络上的消耗,毕竟是上海区服务器。
4、Nginx Lua
1、lua携程机制
ngxin有对应的携程机制
携程就是线程空间在内的执行单元,叫做携程。
类似于线程一样,有自己独立的一个运行空间,它这个运行是基于用户态模拟出来的独立运行空间。本身依托于线程,并且也要像线程一样被 CPU 执行。
切换开销小
2、nginx lua 插载点
init_by_lua:系统启动时调用
init_worker_by_lua:worker 进程启动时调用
set_by_lua:nginx 变量用复杂 lua return
rewrite_by_lua:重写 url 规则
access_by_lua:权限验证阶段
content_by_lua:内容输出节点
3、安装 OpenResty (nginx 服务器)
下载地址:https://openresty.org/cn/download.html
安装为默认安装路径:https://www.runoob.com/w3cnote/openresty-intro.html
1、进入 openresty 目录
2、编写测试lua脚本(需将之间运行的 nginx 关闭)
1、创建 lua 文件夹,并进入 lua 文件夹
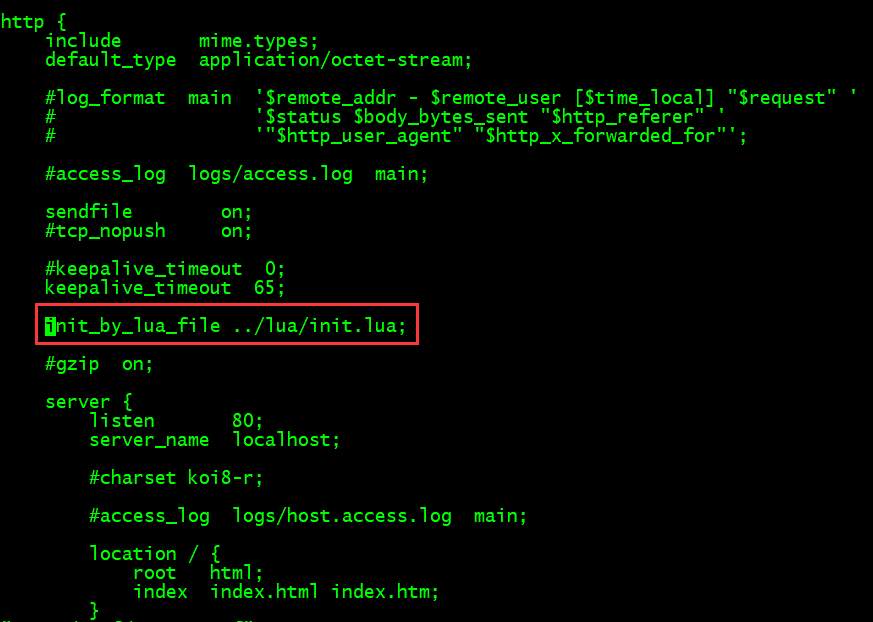
2、vim init.lua
ngx.log(ngx.ERR,"init lua success");
#调用 nginx 日志方法,打印错误日志
3、返回上一级
4、进入nginx目录 修改配置 vim nginx/conf/nginx.conf
5、启动 nginx
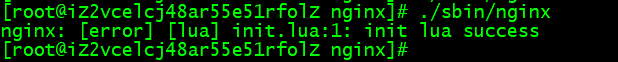
打印出了刚才的那句话
6、将刚才配置干掉,只是测试使用
3、编写 Hello World html文本输出案列
1、vim lua/helloworld.lua
ngx.exec("/item/get?id=7");
2、编辑 nginx 配置

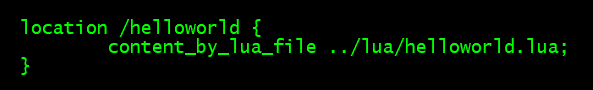
3、启动 nginx
4、测试
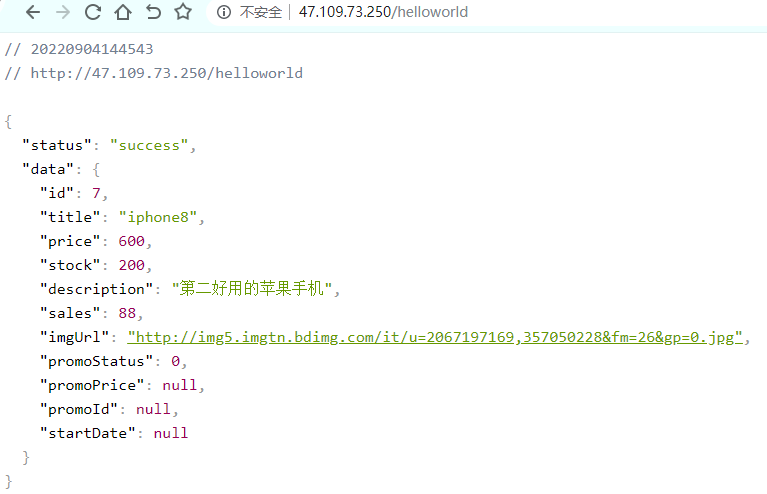
像一个代理转发,现在通过 nginx 和 lua 完成了指定某一个固定 URL 的方式。
4、Openresty 实践
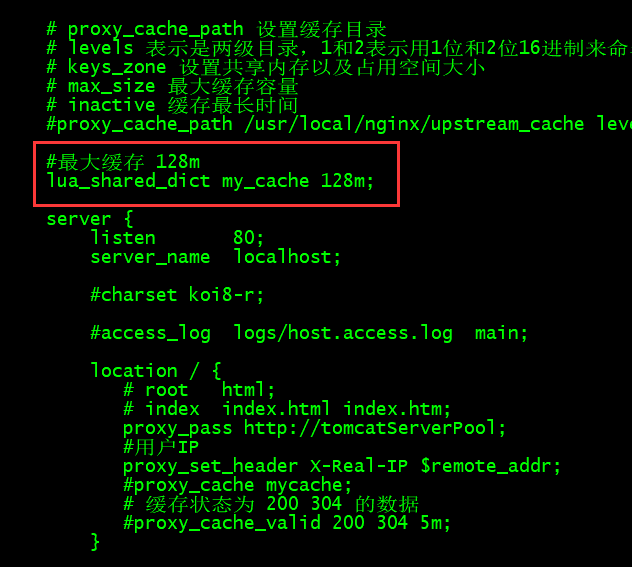
shared dic:共享内存字典,所有 worker 进程可见,lru 淘汰
1、配置 shared dic
vim nginx/conf/nginx.conf
2、编写 lua 脚本
vim lua/itemshareddict.lua
function get_from_cache(key) -- 声明一个变量:这个变量就是刚才 ngxin.conf 配置的 my_cache local cache_ngx = ngx.shared.my_cache local value = cache_ngx:get(key) return value end -- 参数 key,value exptime(过期时间) function set_to_cache(key,value,exptime) if not exptime then exptime = 0 end local cache_ngx = ngx.shared.my_cache local succ,err,forcible = cache_ngx:set(key,value,exptime) return succ end -- /item/get?id=7 local args = ngx.req.get_uri_args() -- 取到 id 参数 local id = args["id"] -- "item_"..id 两个..类似于 java 中 string 字符串拼接 + local item_model = get_from_cache("item_"..id) -- 如果缓存取不到 if item_model == nil then -- 发送 http 请求拿到 resp local resp = ngx.location.capture("/item/get?id="..id) -- 获取 body 内容 item_model = resp.body -- 将结果添加至缓存中 1分钟 set_to_cache("item_"..id,item_model,1*60) end -- 不等于 null 直接返回 ngx.say(item_model)
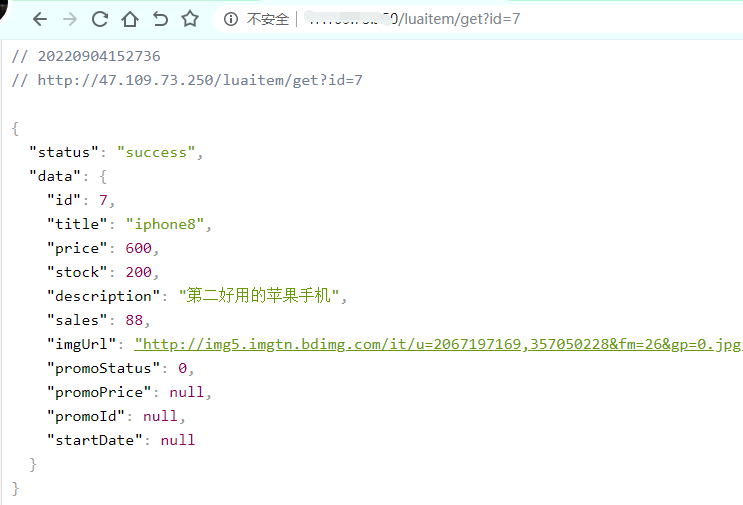
3、配置 nginx URL
location /luaitem/get { default_type "application/json"; content_by_lua_file ../lua/itemshareddict.lua; }
4、浏览器调用测试,访问成功
5、测压
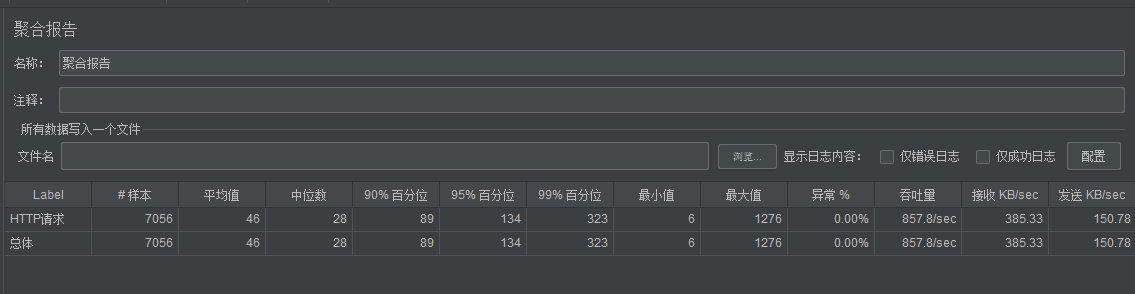
5、Openresty Redis 支持
1、安装 openresty 对 redis 的支持
进入 lualib 目录
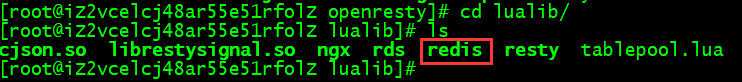
cd resty
这里面封装了常用的 redis 的操作
2、编写 itemredis.lua
-- 获取请求参数 local args = ngx.req.get_uri_args() local id = args["id"] -- 引入二次封装 redis local redis = require "resty.my_redis" local self = { ip = "172.29.26.13", port = "6379", db_index = 1, pool_max_idle_time = 30000, pool_size = 100 } local cache = redis.new(self) local item_model = cache:get("miaosha:item:"..id) if item_model == ngx.null or item_model == nil then local resp = ngx.location.capture("/item/get?id="..id) -- 正常操作是获取到数据后,是要存入 redis 中的,但是我们在程序中已经完成了这步操作了 -- 这里就不对 redis 操作了 item_model = resp.body end ngx.say(item_model)
在这里,我找了一个第三方封装好的组件
local redis_c = require "resty.redis" local ok, new_tab = pcall(require, "table.new") if not ok or type(new_tab) ~= "function" then new_tab = function (narr, nrec) return {} end end local _M = new_tab(0, 155) _M._VERSION = '0.01' local commands = { "append", "auth", "bgrewriteaof", "bgsave", "bitcount", "bitop", "blpop", "brpop", "brpoplpush", "client", "config", "dbsize", "debug", "decr", "decrby", "del", "discard", "dump", "echo", "eval", "exec", "exists", "expire", "expireat", "flushall", "flushdb", "get", "getbit", "getrange", "getset", "hdel", "hexists", "hget", "hgetall", "hincrby", "hincrbyfloat", "hkeys", "hlen", "hmget", "hmset", "hscan", "hset", "hsetnx", "hvals", "incr", "incrby", "incrbyfloat", "info", "keys", "lastsave", "lindex", "linsert", "llen", "lpop", "lpush", "lpushx", "lrange", "lrem", "lset", "ltrim", "mget", "migrate", "monitor", "move", "mset", "msetnx", "multi", "object", "persist", "pexpire", "pexpireat", "ping", "psetex", "psubscribe", "pttl", "publish", --[[ "punsubscribe", ]] "pubsub", "quit", "randomkey", "rename", "renamenx", "restore", "rpop", "rpoplpush", "rpush", "rpushx", "sadd", "save", "scan", "scard", "script", "sdiff", "sdiffstore", "select", "set", "setbit", "setex", "setnx", "setrange", "shutdown", "sinter", "sinterstore", "sismember", "slaveof", "slowlog", "smembers", "smove", "sort", "spop", "srandmember", "srem", "sscan", "strlen", --[[ "subscribe", ]] "sunion", "sunionstore", "sync", "time", "ttl", "type", --[[ "unsubscribe", ]] "unwatch", "watch", "zadd", "zcard", "zcount", "zincrby", "zinterstore", "zrange", "zrangebyscore", "zrank", "zrem", "zremrangebyrank", "zremrangebyscore", "zrevrange", "zrevrangebyscore", "zrevrank", "zscan", "zscore", "zunionstore", "evalsha" } local mt = { __index = _M } local function is_redis_null( res ) if type(res) == "table" then for k,v in pairs(res) do if v ~= ngx.null then return false end end return true elseif res == ngx.null then return true elseif res == nil then return true end return false end function _M.close_redis(self, redis) if not redis then return end --释放连接(连接池实现) local pool_max_idle_time = self.pool_max_idle_time --最大空闲时间 毫秒 local pool_size = self.pool_size --连接池大小 local ok, err = redis:set_keepalive(pool_max_idle_time, pool_size) if not ok then ngx.say("set keepalive error : ", err) end end -- change connect address as you need function _M.connect_mod( self, redis ) redis:set_timeout(self.timeout) local ok, err = redis:connect(self.ip, self.port) if not ok then ngx.say("connect to redis error : ", err) return self:close_redis(redis) end if self.password then ----密码认证 local count, err = redis:get_reused_times() if 0 == count then ----新建连接,需要认证密码 ok, err = redis:auth(self.password) if not ok then ngx.say("failed to auth: ", err) return end elseif err then ----从连接池中获取连接,无需再次认证密码 ngx.say("failed to get reused times: ", err) return end end return ok,err; end function _M.init_pipeline( self ) self._reqs = {} end function _M.commit_pipeline( self ) local reqs = self._reqs if nil == reqs or 0 == #reqs then return {}, "no pipeline" else self._reqs = nil end local redis, err = redis_c:new() if not redis then return nil, err end local ok, err = self:connect_mod(redis) if not ok then return {}, err end redis:init_pipeline() for _, vals in ipairs(reqs) do local fun = redis[vals[1]] table.remove(vals , 1) fun(redis, unpack(vals)) end local results, err = redis:commit_pipeline() if not results or err then return {}, err end if is_redis_null(results) then results = {} ngx.log(ngx.WARN, "is null") end -- table.remove (results , 1) --self.set_keepalive_mod(redis) self:close_redis(redis) for i,value in ipairs(results) do if is_redis_null(value) then results[i] = nil end end return results, err end local function do_command(self, cmd, ... ) if self._reqs then table.insert(self._reqs, {cmd, ...}) return end local redis, err = redis_c:new() if not redis then return nil, err end local ok, err = self:connect_mod(redis) if not ok or err then return nil, err end redis:select(self.db_index) local fun = redis[cmd] local result, err = fun(redis, ...) if not result or err then -- ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "pipeline result:", result, " err:", err) return nil, err end if is_redis_null(result) then result = nil end --self.set_keepalive_mod(redis) self:close_redis(redis) return result, err end for i = 1, #commands do local cmd = commands[i] _M[cmd] = function (self, ...) return do_command(self, cmd, ...) end end function _M.new(self, opts) opts = opts or {} local timeout = (opts.timeout and opts.timeout * 1000) or 1000 local db_index= opts.db_index or 0 local ip = opts.ip or '127.0.0.1' local port = opts.port or 6379 local password = opts.password local pool_max_idle_time = opts.pool_max_idle_time or 60000 local pool_size = opts.pool_size or 100 return setmetatable({ timeout = timeout, db_index = db_index, ip = ip, port = port, password = password, pool_max_idle_time = pool_max_idle_time, pool_size = pool_size, _reqs = nil }, mt) end return _M
3、修改 nginx 配置
4、压力测试
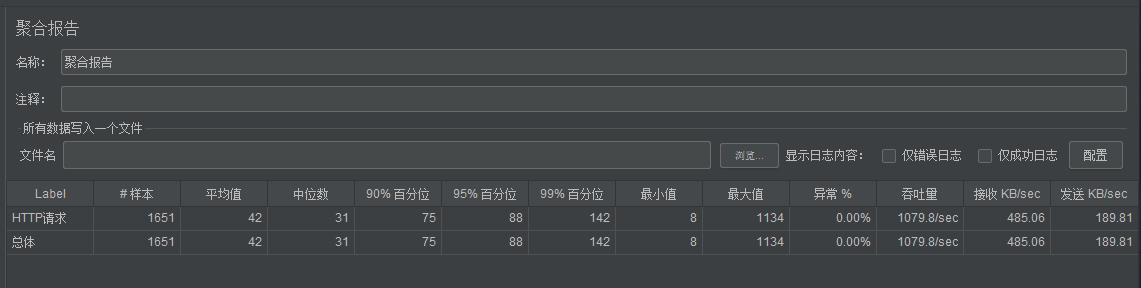
这就很给力了,峰值吞吐量 1000/s 。(从单体的 70/s 到现在的 1000/s。)
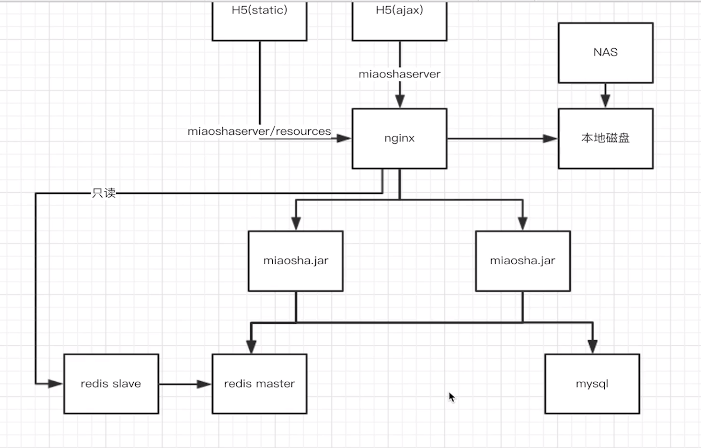
5、最后整体架构图
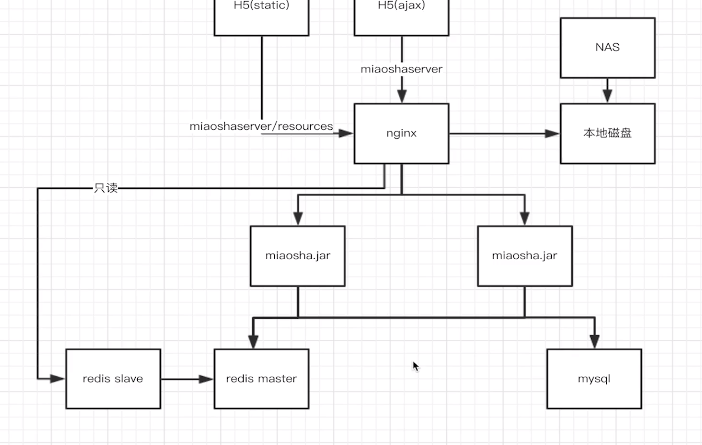
openresty 使用 redis 从节点作为缓存,减少主节点加压力,也可使用 多主多从模式。可扩展。




