1143 Lowest Common Ancestor
The lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two nodes U and V in a tree is the deepest node that has both U and V as descendants.
A binary search tree (BST) is recursively defined as a binary tree which has the following properties:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than or equal to the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Given any two nodes in a BST, you are supposed to find their LCA.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives two positive integers: M (≤ 1,000), the number of pairs of nodes to be tested; and N (≤ 10,000), the number of keys in the BST, respectively. In the second line, N distinct integers are given as the preorder traversal sequence of the BST. Then M lines follow, each contains a pair of integer keys U and V. All the keys are in the range of int.
Output Specification:
For each given pair of U and V, print in a line LCA of U and V is A. if the LCA is found and A is the key. But if A is one of U and V, print X is an ancestor of Y. where X is A and Y is the other node. If U or V is not found in the BST, print in a line ERROR: U is not found. or ERROR: V is not found. or ERROR: U and V are not found..
Sample Input:
6 8
6 3 1 2 5 4 8 7
2 5
8 7
1 9
12 -3
0 8
99 99
Sample Output:
LCA of 2 and 5 is 3.
8 is an ancestor of 7.
ERROR: 9 is not found.
ERROR: 12 and -3 are not found.
ERROR: 0 is not found.
ERROR: 99 and 99 are not found.
题意:
给出一棵二叉查找树,判断所给出两个结点是不是在二叉树中,如果在则找出这两个结点的最近公共祖先节点.
思路:
构造二叉树的时候采用递归的方法,因为是先序遍历所以在先序遍历的序列中第一个大于父节点的结点的左侧为左子树,右侧为右子树.
寻找LCA的时候也是使用递归的方法,虽然上次做过一个相似的题目了,但是这次做的时候思路还是不太清楚,于是又看了一下之前的代码.总体的思路就是向子节点查找,如果结点的值和查找的值相等则返回这个节点,或者查找到最底层则返回NULL,否则就向下查找.返回的时候
return !left ? right : !right ? left : root;
意思就是,如果左子树为空,则返回右子树(不管其是不是空的),如果左子树非空的话,在查看右子树,如果右子树也非空的话则返回root,否则的话返回非空的左子树.
Code:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 typedef struct Node* node; 7 struct Node { 8 int val; 9 node left; 10 node right; 11 Node(int v) { 12 val = v; 13 left = NULL; 14 right = NULL; 15 } 16 }; 17 18 node buildTree(vector<int>& v, int start, int end) { 19 if (start > end) return NULL; 20 node root = new Node(v[start]); 21 int pos = start + 1; 22 while (pos <= end && v[pos] < v[start]) ++pos; 23 if (pos == start + 1) { 24 root->right = buildTree(v, start + 1, end); 25 } else if (pos == end + 1) { 26 root->left = buildTree(v, start + 1, end); 27 } else { 28 root->left = buildTree(v, start + 1, pos - 1); 29 root->right = buildTree(v, pos, end); 30 } 31 return root; 32 } 33 34 bool foundNode(node root, int x) { 35 if (root == NULL) return false; 36 if (root->val == x) return true; 37 return foundNode(root->left, x) || foundNode(root->right, x); 38 } 39 40 node LCA(node root, int x, int y) { 41 if (root == NULL) return NULL; 42 if (root->val == x || root->val == y) return root; 43 node left = LCA(root->left, x, y); 44 node right = LCA(root->right, x, y); 45 return !left ? right : !right ? left : root; 46 } 47 48 int main() { 49 int M, N; 50 cin >> M >> N; 51 52 vector<int> num(N); 53 for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) cin >> num[i]; 54 node root = buildTree(num, 0, N - 1); 55 // perOrder(root); 56 for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) { 57 int x, y; 58 cin >> x >> y; 59 bool foundX = foundNode(root, x); 60 bool foundY = foundNode(root, y); 61 if (foundX && foundY) { 62 node lca = LCA(root, x, y); 63 if (lca->val == x) 64 cout << x << " is an ancestor of " << y << "." << endl; 65 else if (lca->val == y) 66 cout << y << " is an ancestor of " << x << "." << endl; 67 else 68 cout << "LCA of " << x << " and " << y << " is " << lca->val 69 << "." << endl; 70 } else if (foundX) { 71 cout << "ERROR: " << y << " is not found." << endl; 72 } else if (foundY) { 73 cout << "ERROR: " << x << " is not found." << endl; 74 } else { 75 cout << "ERROR: " << x << " and " << y << " are not found." << endl; 76 } 77 } 78 return 0; 79 }
看了一下大佬的代码,发现自己还是真的很菜。其实这道题完全可以不构建BST来进行解答。
题目中说明了这棵树是一棵BST,也即左子树中的结点都小于根结点,右子树中的结点都大于根结点。当寻找两个数的LCA的时候,我们可以与BST中的每一个结点进行比较,如果该结点的value满足(value >= u && value <= v) || (value >= v && value <= u)则说明该结点为u和v的LCA或者u和v中的一个是另外一个的祖先结点,然后按要求输出就好了。能想到这种方法真的很厉害!!(吾不能及)
下面是大佬的代码:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <map> 4 using namespace std; 5 map<int, bool> mp; 6 int main() { 7 int m, n, u, v, a; 8 scanf("%d %d", &m, &n); 9 vector<int> pre(n); 10 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 11 scanf("%d", &pre[i]); 12 mp[pre[i]] = true; 13 } 14 for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { 15 scanf("%d %d", &u, &v); 16 for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) { 17 a = pre[j]; 18 if ((a >= u && a <= v) || (a >= v && a <= u)) break; 19 } 20 if (mp[u] == false && mp[v] == false) 21 printf("ERROR: %d and %d are not found.\n", u, v); 22 else if (mp[u] == false || mp[v] == false) 23 printf("ERROR: %d is not found.\n", mp[u] == false ? u : v); 24 else if (a == u || a == v) 25 printf("%d is an ancestor of %d.\n", a, a == u ? v : u); 26 else 27 printf("LCA of %d and %d is %d.\n", u, v, a); 28 } 29 return 0; 30 }
2022-06-12
今天刷题又碰到了这道题目,对算法实现的原理再做一次详细的分析:
LCA的核心代码
node LCA(node root, int x, int y) {
if (root == NULL) return NULL;
if (root->val == x || root->val == y) return root;
node left = LCA(root->left, x, y);
node right = LCA(root->right, x, y);
return !left ? right : !right ? left : root;
}
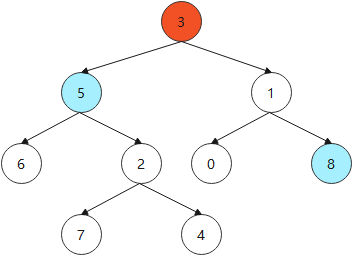
上图展示的是,5 和 8 的最近公共祖先结点是 3,按照之前的代码所示,在递归寻找的过程中,当root为3时,left和right都不会为空,所以最后返回的时候会将3作为结果返回。
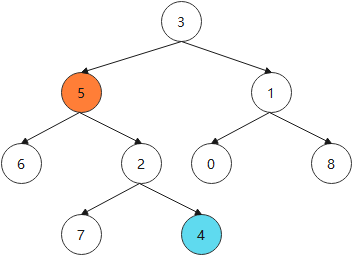
root为3,right 为 null,返回 left = LCA(root->right, x, y)
此时,以 5 作为 root 进行递归查找,5 正好是要找的元素直接返回。
其余情况都类似……


