1146 Topological Order
This is a problem given in the Graduate Entrance Exam in 2018: Which of the following is NOT a topological order obtained from the given directed graph? Now you are supposed to write a program to test each of the options.
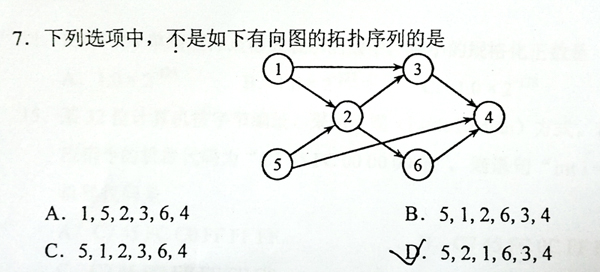
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives two positive integers N (≤ 1,000), the number of vertices in the graph, and M (≤ 10,000), the number of directed edges. Then M lines follow, each gives the start and the end vertices of an edge. The vertices are numbered from 1 to N. After the graph, there is another positive integer K (≤ 100). Then K lines of query follow, each gives a permutation of all the vertices. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
Print in a line all the indices of queries which correspond to "NOT a topological order". The indices start from zero. All the numbers are separated by a space, and there must no extra space at the beginning or the end of the line. It is graranteed that there is at least one answer.
Sample Input:
6 8
1 2
1 3
5 2
5 4
2 3
2 6
3 4
6 4
5
1 5 2 3 6 4
5 1 2 6 3 4
5 1 2 3 6 4
5 2 1 6 3 4
1 2 3 4 5 6
Sample Output:
3 4
题意:
给出一个拓扑图判断,所给的序列是不是拓扑排序。
思路:
用连接矩阵来存储拓扑图,判断是不是拓扑序列的时候,只需要检查还有没有指向这个节点的边。如果没有指向这个节点的边,就将所有以这个结点为起点的边删除。
Code:
#include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <vector> using namespace std; int main() { int n, m; cin >> n >> m; int s, e; vector<vector<int> > grap(n + 1, vector<int>(n + 1, 0)); for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { cin >> s >> e; grap[s][e] = 1; } int k, t; cin >> k; bool isTopo = true; vector<int> ans; vector<vector<int> > dummy; for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) { isTopo = true; dummy = grap; for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { cin >> t; for (int k = 1; k <= n; ++k) { if (dummy[k][t] != 0) isTopo = false; else { dummy[t][k] = 0; } } } if (!isTopo) ans.push_back(i); } cout << ans[0]; for (int i = 1; i < ans.size(); ++i) { cout << " " << ans[i]; } cout << endl; return 0; }
上面的代码最后一组数据超时,又优化了一下代码,通过了全部的测试点。
#include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <vector> using namespace std; int main() { int n, m; cin >> n >> m; int s, e; vector<vector<int> > grap(n + 1, vector<int>(n + 1, 0)); for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { cin >> s >> e; grap[s][e] = 1; } int k, t; cin >> k; vector<int> ans, temp; vector<vector<int> > dummy; for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) { dummy = grap; temp.clear(); for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { cin >> t; temp.push_back(t); } bool flag = false; for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { for (int k = 1; k <= n; ++k) { if (dummy[k][temp[j]] == 1) { flag = true; ans.push_back(i); break; } else dummy[temp[j]][k] = 0; } if (flag) break; } } cout << ans[0]; for (int i = 1; i < ans.size(); ++i) { cout << " " << ans[i]; } cout << endl; return 0; }
参考了一下别人的代码,变更了一种解体的思路,代码也更加的简洁。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <queue> 3 #include <vector> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 int main() { 8 int n, m; 9 cin >> n >> m; 10 11 int s, e; 12 vector<int> v[n+1], in(n+1, 0); 13 for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { 14 cin >> s >> e; 15 v[s].push_back(e); 16 in[e]++; 17 } 18 int k, t; 19 cin >> k; 20 vector<int> ans; 21 for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) { 22 bool flag = true; 23 vector<int> temp = in; 24 for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { 25 cin >> t; 26 if (temp[t] != 0) flag = false; 27 for (int it : v[t]) 28 temp[it]--; 29 } 30 if (!flag) ans.push_back(i); 31 } 32 33 int isFirst = true; 34 for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); ++i) { 35 if (isFirst) { 36 cout << ans[i]; 37 isFirst = false; 38 } else { 39 cout << " " << ans[i]; 40 } 41 } 42 43 return 0; 44 }
这种方法是通过记录每个节点的入度,根据遍历的过程中是否有入度不为0的结点来判断所给序列是不是拓扑排序。

