1007. Minimum Domino Rotations For Equal Row
In a row of dominoes,
A[i]andB[i]represent the top and bottom halves of thei-th domino. (A domino is a tile with two numbers from 1 to 6 - one on each half of the tile.)We may rotate the
i-th domino, so thatA[i]andB[i]swap values.Return the minimum number of rotations so that all the values in
Aare the same, or all the values inBare the same.If it cannot be done, return
-1.
Example 1:
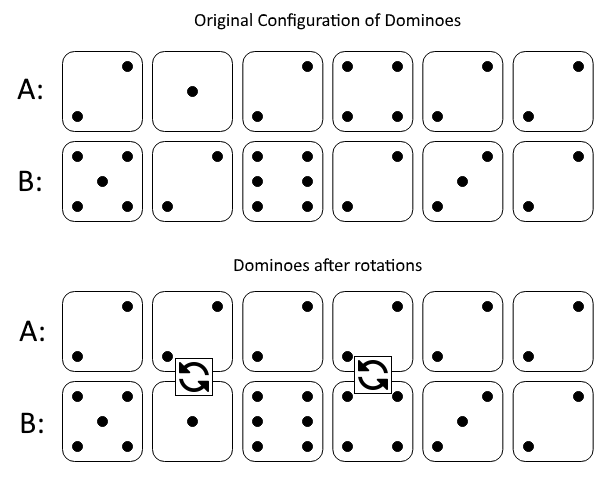
Input: A = [2,1,2,4,2,2], B = [5,2,6,2,3,2] Output: 2 Explanation: The first figure represents the dominoes as given by A and B: before we do any rotations. If we rotate the second and fourth dominoes, we can make every value in the top row equal to 2, as indicated by the second figure.Example 2:
Input: A = [3,5,1,2,3], B = [3,6,3,3,4] Output: -1 Explanation: In this case, it is not possible to rotate the dominoes to make one row of values equal.
Note:
1 <= A[i], B[i] <= 62 <= A.length == B.length <= 20000
Approach #1: [Java]
class Solution {
public int minDominoRotations(int[] A, int[] B) {
int n = A.length;
for (int i = 0, a = 0, b = 0; i < n && (A[i] == A[0] || B[i] == A[0]); ++i) {
if (A[i] != A[0]) a++;
if (B[i] != A[0]) b++;
if (i == n-1) return Math.min(a, b);
}
for (int i = 0, a = 0, b = 0; i < n && (A[i] == B[0] || B[i] == B[0]); ++i) {
if (A[i] != B[0]) a++;
if (B[i] != B[0]) b++;
if (i == n-1) return Math.min(a, b);
}
return -1;
}
}
Analysis:
1. try A[0]
2. try B[0]
3. return -1;
one observation is that if A[0] and B[0] are all work, the result will be the same.
Approach #2. HashSet. [Java]
class Solution {
public int minDominoRotations(int[] A, int[] B) {
int n = A.length;
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6));
int[] countA = new int[7], countB = new int[7];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
set.retainAll(new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(A[i], B[i])));
countA[A[i]]++;
countB[B[i]]++;
}
for (int s : set) return Math.min(n - countA[s], n - countB[s]);
return -1;
}
}
Analysis:
Find intersection s of {A[i], B[i]}.
s.size() == 0: no possible reslut.
s.size() == 1: one and only one reslut.
s.size() == 2: it means all dominoes are [a, b] or [b, a], try either one.
s.size() > 2: impossible.
Reference:
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/arrays-aslist-method-in-java-with-examples/
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/set-retainall-method-in-java-with-example/