139. Word Break
Given a non-empty string s and a dictionary wordDict containing a list of non-empty words, determine if s can be segmented into a space-separated sequence of one or more dictionary words.
Note:
- The same word in the dictionary may be reused multiple times in the segmentation.
- You may assume the dictionary does not contain duplicate words.
Example 1:
Input: s = "leetcode", wordDict = ["leet", "code"] Output: true Explanation: Return true because "leetcode" can be segmented as "leet code".
Example 2:
Input: s = "applepenapple", wordDict = ["apple", "pen"] Output: true Explanation: Return true because "applepenapple" can be segmented as "apple pen apple". Note that you are allowed to reuse a dictionary word.
Example 3:
Input: s = "catsandog", wordDict = ["cats", "dog", "sand", "and", "cat"] Output: false
Approach #1:
class Solution {
public:
bool wordBreak(string s, vector<string>& wordDict) {
unordered_set<string> _wordDict(wordDict.begin(), wordDict.end());
return wordBreak(s, _wordDict);
}
bool wordBreak(const string& s, const unordered_set<string>& wordDict) {
if (memo_.count(s)) return memo_[s];
if (wordDict.count(s)) return memo_[s] = true;
for (int j = 1; j < s.length(); ++j) {
string left = s.substr(0, j);
string right = s.substr(j);
if (wordDict.count(right) && wordBreak(left, wordDict))
return memo_[s] = true;
}
return memo_[s] = false;
}
private:
unordered_map<string, bool> memo_;
};
2021-04-17
给定一个非空字符串 s 和一个包含非空单词的列表 wordDict,判定 s 是否可以被空格拆分为一个或多个在字典中出现的单词。
说明:
拆分时可以重复使用字典中的单词。
你可以假设字典中没有重复的单词。
示例 1:
输入: s = "leetcode", wordDict = ["leet", "code"]
输出: true
解释: 返回 true 因为 "leetcode" 可以被拆分成 "leet code"。
示例 2:
输入: s = "applepenapple", wordDict = ["apple", "pen"]
输出: true
解释: 返回 true 因为 "applepenapple" 可以被拆分成 "apple pen apple"。
注意你可以重复使用字典中的单词。
示例 3:
输入: s = "catsandog", wordDict = ["cats", "dog", "sand", "and", "cat"]
输出: false
思路:
运用dp的思想,先判断子问题是否满足条件,然后再将当前问题拆分成若干子问题,如果拆分成的子问题都满足条件,那么当前问题也是满足条件的。
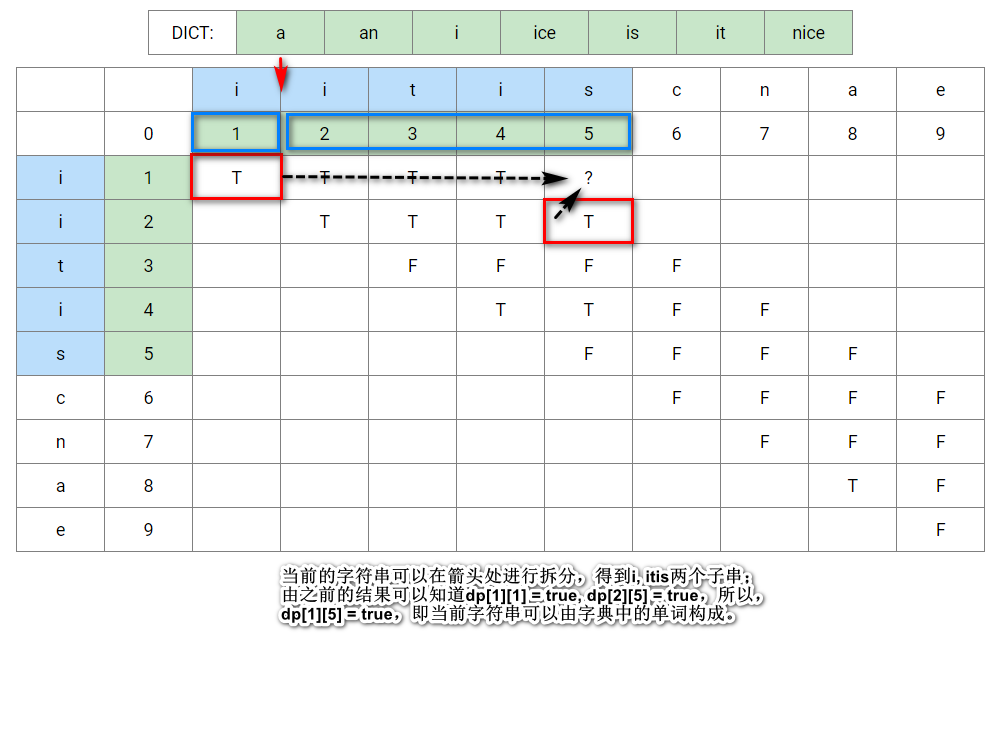
代码:
#include <iostream> #include <set> #include <string> #include <vector> using namespace std; int main() { string input; set<string> s; cin >> input; int n; string t; cin >> n; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { cin >> t; s.insert(t); } int len = input.length(); vector<vector<bool> > dp(len + 1, vector<bool>(len + 1, false)); for (int l = 1; l <= len; ++l) { for (int i = 0, j = i + l - 1; j < len; ++i, ++j) { string sub = input.substr(i, l); if (s.find(sub) != s.end()) dp[i][j] = true; else { for (int k = 1; k < l; ++k) { int t = i + k; if (dp[i][i + k - 1] && dp[t][j]) { dp[i][j] = true; break; } } } } } cout << dp[0][len - 1] << endl; return 0; }
2021-08-03
今天刷题的时候又遇到了这道题目,因为如果之前写过的话会留下之前的代码,所以就看着之前的代码重新复习了一下。
动态规划的定义:把原问题分解为相对简单的子问题的方式求解复杂问题的方法。
动态规划的思想:把原问题拆分为具有相同结构和性质的子问题,根据子问题的解来求解当前的问题。动态规划是一种自底向上(down-top)的解法,与之相对应的是递归解法(top-down)。
动态规划的应用场景:
- 最优子结构性质:
- 无后效性:
- 子问题重叠性质:
按照我自己的理解,动态规划一般都要维护一个二维的dp数组,判断子问题是否满足条件。当求一个大的问题的时候,当子问题满足条件,当新增加一个元素后,判断新加入的元素是否满足条件。这样就可以不必理会子问题,只需要判断新加入的元素是否满足条件。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号