Weekly Contest 117
965. Univalued Binary Tree
A binary tree is univalued if every node in the tree has the same value.
Return true if and only if the given tree is univalued.
Example 1:
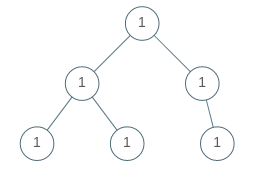
Input: [1,1,1,1,1,null,1]
Output: true
Example 2:
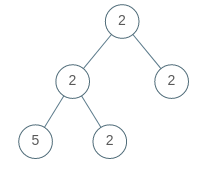
Input: [2,2,2,5,2]
Output: false
Note:
- The number of nodes in the given tree will be in the range
[1, 100]. - Each node's value will be an integer in the range
[0, 99].
Code:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isUnivalTree(TreeNode* root) {
solve(root, root->val);
return ans;
}
void solve(TreeNode* root, int num) {
if (root->val != num) ans = false;
if (root->left != NULL) solve(root->left, num);
if (root->right != NULL) solve(root->right, num);
}
private:
bool ans = true;
};
967. Numbers With Same Consecutive Differences
Return all non-negative integers of length N such that the absolute difference between every two consecutive digits is K.
Note that every number in the answer must not have leading zeros except for the number 0 itself. For example, 01 has one leading zero and is invalid, but 0 is valid.
You may return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
Input: N = 3, K = 7
Output: [181,292,707,818,929]
Explanation: Note that 070 is not a valid number, because it has leading zeroes.
Example 2:
Input: N = 2, K = 1
Output: [10,12,21,23,32,34,43,45,54,56,65,67,76,78,87,89,98]
Code:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> numsSameConsecDiff(int N, int K) {
vector<int> ans;
if (N == 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
ans.push_back(i);
return ans;
}
for (int i = 1; i < 10; ++i) {
string s = to_string(i);
dfs(s, N, K, ans);
}
return ans;
}
void dfs(string s, const int N, const int K, vector<int>& ans) {
if (s.length() == N) {
ans.push_back(stoi(s));
return ;
}
int lastNum = s[s.length()-1] - '0';
int temp = lastNum + K;
string dummy = s;
if (temp >= 0 && temp < 10) {
dummy += to_string(temp);
dfs(dummy, N, K, ans);
}
if (K != 0) {
int temp = lastNum - K;
if (temp >= 0 && temp < 10) {
s += to_string(temp);
dfs(s, N, K, ans);
}
}
}
};
966. Vowel Spellchecker
Given a wordlist, we want to implement a spellchecker that converts a query word into a correct word.
For a given query word, the spell checker handles two categories of spelling mistakes:
- Capitalization: If the query matches a word in the wordlist (case-insensitive), then the query word is returned with the same case as the case in the wordlist.
- Example:
wordlist = ["yellow"],query = "YellOw":correct = "yellow" - Example:
wordlist = ["Yellow"],query = "yellow":correct = "Yellow" - Example:
wordlist = ["yellow"],query = "yellow":correct = "yellow"
- Example:
- Vowel Errors: If after replacing the vowels ('a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u') of the query word with any vowel individually, it matches a word in the wordlist (case-insensitive), then the query word is returned with the same case as the match in the wordlist.
- Example:
wordlist = ["YellOw"],query = "yollow":correct = "YellOw" - Example:
wordlist = ["YellOw"],query = "yeellow":correct = ""(no match) - Example:
wordlist = ["YellOw"],query = "yllw":correct = ""(no match)
- Example:
In addition, the spell checker operates under the following precedence rules:
- When the query exactly matches a word in the wordlist (case-sensitive), you should return the same word back.
- When the query matches a word up to capitlization, you should return the first such match in the wordlist.
- When the query matches a word up to vowel errors, you should return the first such match in the wordlist.
- If the query has no matches in the wordlist, you should return the empty string.
Given some queries, return a list of words answer, where answer[i] is the correct word for query = queries[i].
Example 1:
Input: wordlist = ["KiTe","kite","hare","Hare"], queries = ["kite","Kite","KiTe","Hare","HARE","Hear","hear","keti","keet","keto"]
Output: ["kite","KiTe","KiTe","Hare","hare","","","KiTe","","KiTe"]
Note:
1 <= wordlist.length <= 50001 <= queries.length <= 50001 <= wordlist[i].length <= 71 <= queries[i].length <= 7- All strings in
wordlistandqueriesconsist only of english letters.
Code:
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> spellchecker(vector<string>& wordlist, vector<string>& queries) {
unordered_map<string, vector<string>> seen, tran;
unordered_set<string> matches;
for (int i = 0; i < wordlist.size(); ++i) {
string temp_tolower = _tolower(wordlist[i]);
string temp_todev = _todev(wordlist[i]);
seen[temp_tolower].push_back(wordlist[i]);
tran[temp_todev].push_back(wordlist[i]);
matches.insert(wordlist[i]);
}
vector<string> ans;
for (int i = 0; i < queries.size(); ++i) {
// match
if (matches.count(queries[i])) {
ans.push_back(queries[i]);
continue;
}
string temp = _tolower(queries[i]);
// capitalization
if (seen.count(temp)) {
ans.push_back(seen[temp][0]);
continue;
}
// vowel errors
string ant = _todev(queries[i]);
if (tran.count(ant)) {
ans.push_back(tran[ant][0]);
} else {
ans.push_back("");
}
}
return ans;
}
string _tolower(string s) {
for (auto& c : s)
c = tolower(c);
return s;
}
string _todev(string s) {
s = _tolower(s);
for (auto& c : s)
if (c == 'a' || c == 'e' || c == 'i' || c == 'o' || c == 'u')
c = '#';
return s;
}
};
In this question I reference the function of _todev with @lee215.
968. Binary Tree Cameras
Given a binary tree, we install cameras on the nodes of the tree.
Each camera at a node can monitor its parent, itself, and its immediate children.
Calculate the minimum number of cameras needed to monitor all nodes of the tree.
Example 1:

Input: [0,0,null,0,0]
Output: 1
Explanation: One camera is enough to monitor all nodes if placed as shown.
Example 2:

Input: [0,0,null,0,null,0,null,null,0]
Output: 2
Explanation: At least two cameras are needed to monitor all nodes of the tree. The above image shows one of the valid configurations of camera placement.
Note:
- The number of nodes in the given tree will be in the range
[1, 1000]. - Every node has value 0.
Code:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int minCameraCover(TreeNode* root) {
int state = dfs(root);
return res + (state < 1 ? 1 : 0);
}
int dfs(TreeNode* root) {
int needCamera = 0;
int covered = 0;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return 0;
if (root->left != NULL) {
int state = dfs(root->left);
if (state == 0) {
needCamera = 1;
covered = 1;
} else if (state == 1) {
covered = 1;
}
}
if (root->right != NULL) {
int state = dfs(root->right);
if (state == 0) {
needCamera = 1;
covered = 1;
} else if (state == 1) {
covered = 1;
}
}
if (needCamera > 0) {
res++;
return 1;
}
if (covered > 0) {
return 2;
}
return 0;
}
private:
int res = 0;
};
Analysis:
https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-cameras/discuss/211180/JavaC%2B%2BPython-Greedy-DFS


