一、概述
本章使用的是JDK8。
二话不说,一上来就点开源码,发现里面有一段介绍如下:
Hash table based implementation of the Map interface. This implementation provides all of the optional map operations, and permits null values and the null key. (The HashMap class is roughly equivalent to Hashtable, except that it is unsynchronized and permits nulls.) This class makes no guarantees as to the order of the map; in particular, it does not guarantee that the order will remain constant over time.
翻译一下大概就是在说,这个哈希表是基于 Map 接口的实现的,它允许 null 值和 null 键,它不是线程同步的,同时也不保证有序。
This implementation provides constant-time performance for the basic operations (get and put), assuming the hash function disperses the elements properly among the buckets. Iteration over collection views requires time proportional to the “capacity” of the HashMap instance (the number of buckets) plus its size (the number of key-value mappings). Thus, it’s very important not to set the initial capacity too high (or the load factor too low) if iteration performance is important.
An instance of HashMap has two parameters that affect its performance: initial capacity and load factor. The capacity is the number of buckets in the hash table, and the initial capacity is simply the capacity at the time the hash table is created. The load factor is a measure of how full the hash table is allowed to get before its capacity is automatically increased. When the number of entries in the hash table exceeds the product of the load factor and the current capacity, the hash table is rehashed (that is, internal data structures are rebuilt) so that the hash table has approximately twice the number of buckets.
不要急,我真的不是来翻译的。再来看看这一段,讲的是 Map 的这种实现方式为 get (取)和 put(存)带来了比较好的性能。但是如果涉及到大量的遍历操作的话,就 尽量不要把 capacity 设置得太高(或 load factor 设置得太低),否则会严重降低遍 历的效率。
影响 HashMap 性能的两个重要参数:“initial capacity”(初始化容量)和”load factor“(负载因子)。简单来说,容量就是哈希表桶的个数,负载因子就是键值对个数与哈希表长度的一个比值,当比值超过负载因子之后,HashMap 就会进行 rehash 操作来进行扩容 HashMap 的大致结构如下图所示,其中哈希表是一个数组,我们经常把数组中的每 一个节点称为一个桶,哈希表中的每个节点都用来存储一个键值对。在插入元素时, 如果发生冲突(即多个键值对映射到同一个桶上)的话,就会通过链表的形式来解 决冲突。因为一个桶上可能存在多个键值对,所以在查找的时候,会先通过 key 的 哈希值先定位到桶,再遍历桶上的所有键值对,找出 key 相等的键值对,从而来获 取 value
二、结构图
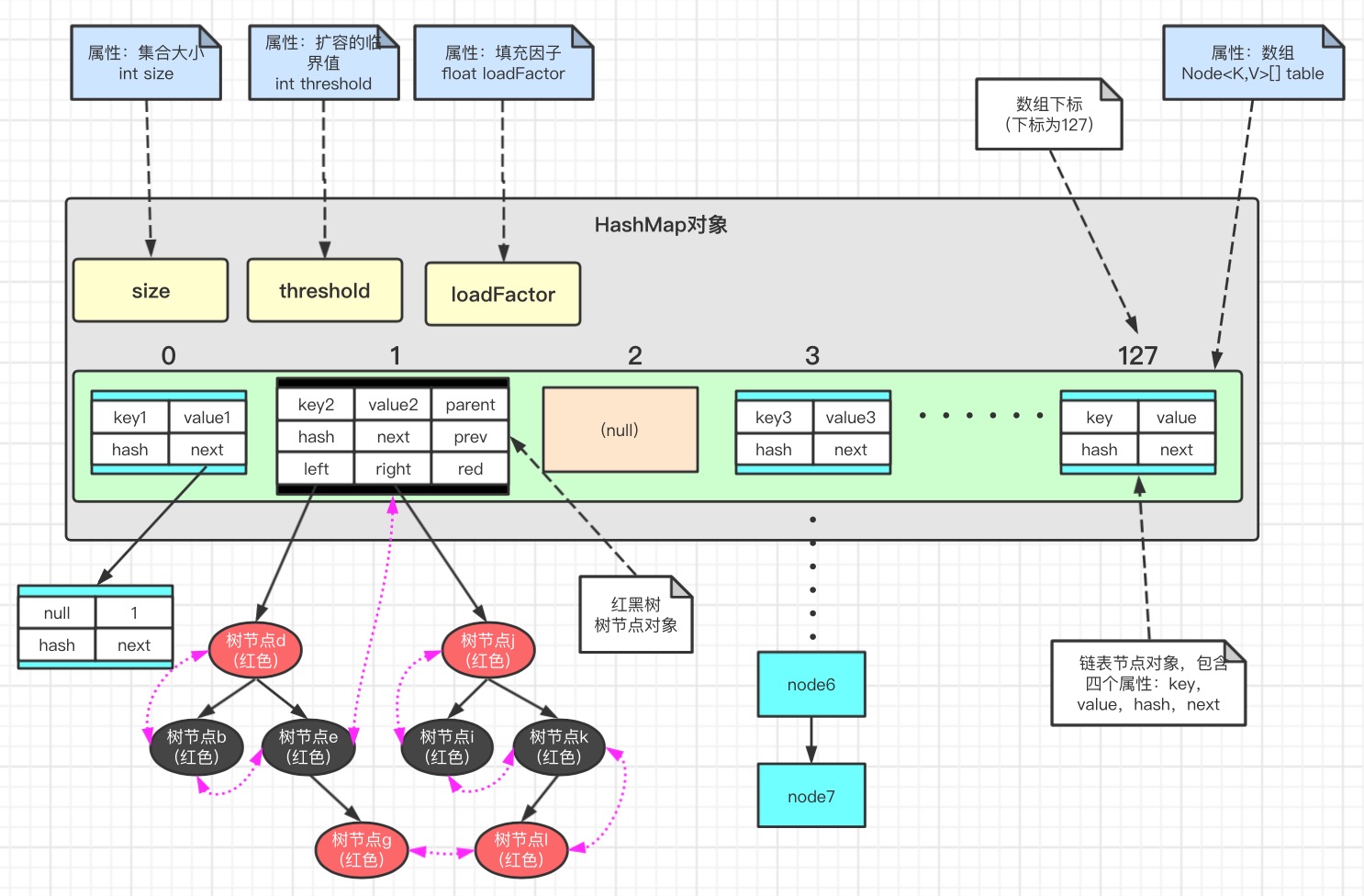
由上图,可知HashMap的结构是:数组 + 链表 + 红黑树
三、属性
看看 HashMap 类中包含了哪些重要的属性,这对下面介绍 HashMap 方法的实 现有一定的参考意义。
1 //默认的初始容量为 16 2 static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; 3 //最大的容量上限为 2^30 4 static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; 5 //默认的加载因子为 0.75 6 static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; 7 //变成树型结构的临界值为 8 8 static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; 9 //恢复链式结构的临界值为 6 10 static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6; 11 //哈希表 12 transient Node<K,V>[] table; 13 //哈希表中键值对的个数 transient int size; 14 //哈希表被修改的次数 transient int modCount; 15 //它是通过 capacity*load factor 计算出来的,当 size 到达这个值时, 就会进行扩容操作 16 int threshold; 17 //负载因子 18 final float loadFactor; 19 //当哈希表的大小超过这个阈值,才会把链式结构转化成树型结构,否则仅采 取扩容来尝试减少冲突 20 static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
下面是 Node 类的定义,它是 HashMap 中的一个静态内部类,哈希表中的每一个 节点都是 Node 类型。我们可以看到,Node 类中有 4 个属性,其中除了 key 和 value 之外,还有 hash 和 next 两个属性。hash 是用来存储 key 的哈希值的,next 是在构建链表时用来指向后继节点的
1 static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { 2 final int hash; //存储指向下一个Entry的引用,单链表结构 3 final K key; 4 V value; 5 Node<K,V> next; //对key的hashcode值进行hash运算后得到的值,存储在Entry,避免重复计算 6 7 Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { 8 this.hash = hash; 9 this.key = key; 10 this.value = value; 11 this.next = next; 12 } 13 14 ...... 15 }
四、方法
1、构造方法
HashMap 提供了三种方式的构造器,可以构造一个大小为 0 的空数组的空哈希表、一个指定初始容量的空哈希表以及构造一个指定初始容量以及加载因子的哈希表。
1 // 创建一个空的哈希表,且 loadFactor = 0.75 2 public HashMap() { 3 this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted 4 } 5 6 // 构造 一个指定初始容量的空哈希表, 且 loadFactor = 0.75 7 public HashMap(int initialCapacity) { 8 this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR); 9 } 10 11 // 构造 一个指定初始容量以及加载因子的空哈希表 12 public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { 13 if (initialCapacity < 0) 14 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + 15 initialCapacity); 16 if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) 17 initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; 18 if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) 19 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + 20 loadFactor); 21 this.loadFactor = loadFactor; 22 this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity); 23 }
2、put 方法
1 //put 方法的具体实现也是在 putVal 方法中,所以我们重点看下面的 putVal 方法 2 public V put(K key, V value) { 3 return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); 4 } 5 6 7 final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, 8 boolean evict) { 9 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; 10 // 如果哈希表为空,则先创建一个哈希表 11 if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) 12 n = (tab = resize()).length; 13 // 如果当前桶没有碰撞冲突,则直接把键值对插入,完事 14 if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) 15 tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); 16 else { 17 Node<K,V> e; K k; 18 // 如果桶上节点的 key 与当前 key 重复,那你就是我要找的节点 19 if (p.hash == hash && 20 ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 21 e = p; 22 // 如果是采用红黑树的方式处理冲突(节点是树节点),则通过红黑树的 putTree Val 方法去插入这个键值对 23 else if (p instanceof TreeNode) 24 e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); 25 else { // 否则就是传统的链式结构 26 // 采用循环遍历的方式,判断链中是否有重复的 key 27 for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { 28 if ((e = p.next) == null) { 29 // 创建一个新节点插入到尾部 30 p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); 31 if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st 32 //如果链的长度大于 TREEIFY_THRESHOLD 这个临界值,则把链变为红黑树 33 treeifyBin(tab, hash); 34 break; 35 } 36 // 找到了重复的 key 37 if (e.hash == hash && 38 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 39 break; 40 p = e; 41 } 42 } 43 // 这里表示在上面的操作中找到了重复的键,所以这里把该键的 值替换为新值 44 if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key 45 V oldValue = e.value; 46 if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) 47 e.value = value; 48 afterNodeAccess(e); 49 return oldValue; 50 } 51 } 52 ++modCount; 53 // 判断是否需要进行扩容 54 if (++size > threshold) 55 resize(); 56 afterNodeInsertion(evict); 57 return null; 58 }
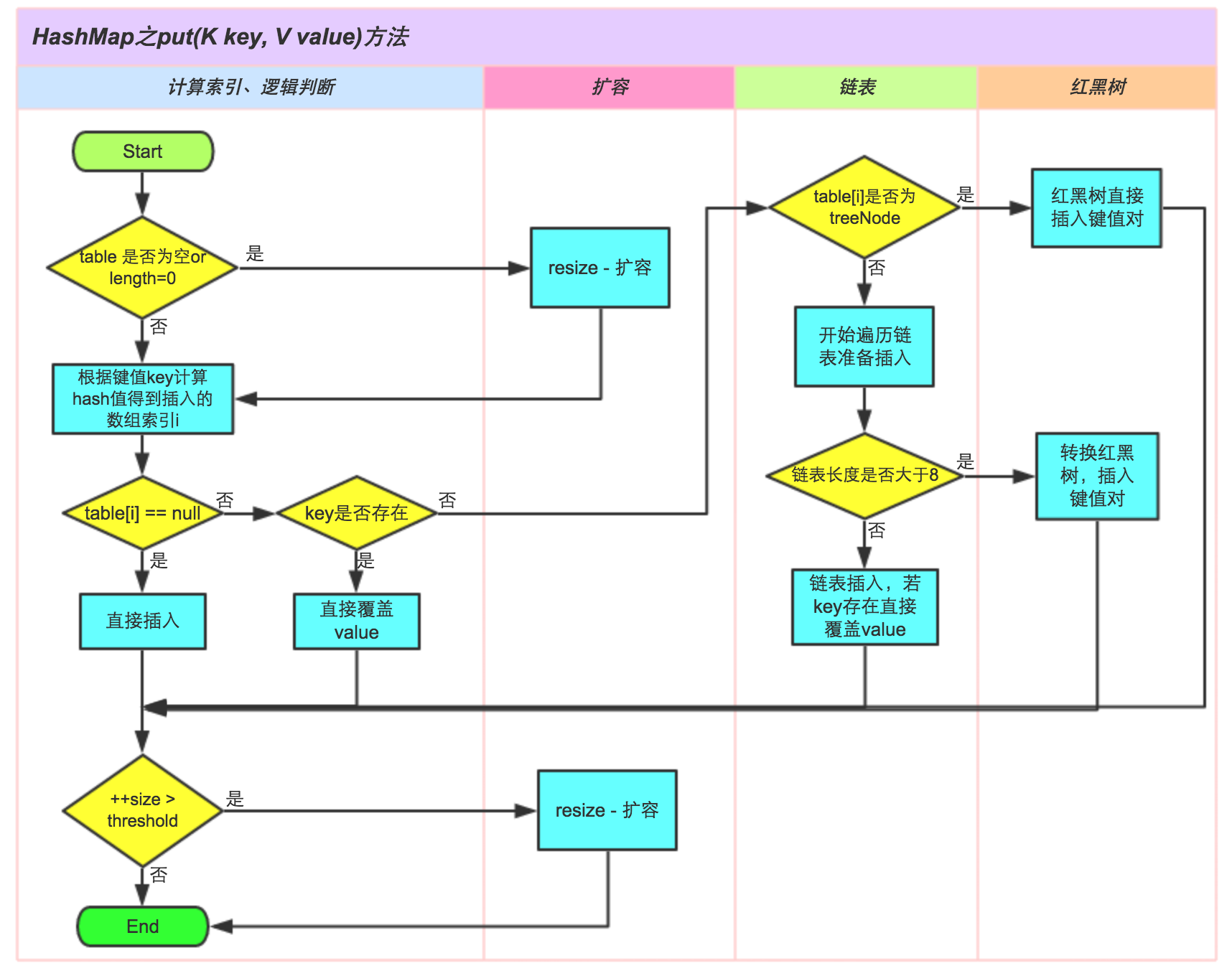
put 方法比较复杂,实现步骤大致如下:
1、先通过 hash 值计算出 key 映射到哪个桶。
2、如果桶上没有碰撞冲突,则直接插入。
3、如果出现碰撞冲突了,则需要处理冲突:
(1) 如果该桶使用红黑树处理冲突,则调用红黑树的方法插入。
(2) 否则采用传统的链式方法插入。如果链的长度到达临界值,则把链转变为红黑树。
4、如果桶中存在重复的键,则为该键替换新值。
5、如果 size 大于阈值,则进行扩容。
3、get 方法
1 // get 方法主要调用的是 getNode 方法,所以重点要看 getNode 方法的 实现 2 public V get(Object key) { 3 Node<K,V> e; 4 return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value; 5 } 6 7 8 9 final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) { 10 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k; 11 // 如果哈希表不为空 && key 对应的桶上不为空 12 if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && 13 (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) { 14 // 是否直接命中 15 if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node 16 ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 17 return first; 18 // 判断是否有后续节点 19 if ((e = first.next) != null) { 20 // 如果当前的桶是采用红黑树处理冲突,则调用红黑树的 get 方法去获取节点 21 if (first instanceof TreeNode) 22 return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); 23 // 不是红黑树的话,那就是传统的链式结构了,通过循环的 方法判断链中是否存在该 key 24 do { 25 if (e.hash == hash && 26 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 27 return e; 28 } while ((e = e.next) != null); 29 } 30 } 31 return null; 32 }
get实现步骤大致如下:
1、通过 hash 值获取该 key 映射到的桶。
2、桶上的 key 就是要查找的 key,则直接命中。
3、桶上的 key 不是要查找的 key,则查看后续节点:
(1)如果后续节点是树节点,通过调用树的方法查找该 key。
(2)如果后续节点是链式节点,则通过循环遍历链查找该 key。
4、remove 方法
1 // remove 方法的具体实现在 removeNode 方法中,所以我们重点看下面的 r emoveNode 方法 2 public V remove(Object key) { 3 Node<K,V> e; 4 return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ? 5 null : e.value; 6 } 7 8 9 final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value, 10 boolean matchValue, boolean movable) { 11 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index; 12 // 如果当前 key 映射到的桶不为空 13 if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && 14 (p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) { 15 Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v; 16 // 如果桶上的节点就是要找的 key,则直接命中 17 if (p.hash == hash && 18 ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 19 node = p; 20 else if ((e = p.next) != null) { 21 // 如果是以红黑树处理冲突,则构建一个树节点 22 if (p instanceof TreeNode) 23 node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key); 24 // 如果是以链式的方式处理冲突,则通过遍历链表来寻找节点 25 else { 26 do { 27 if (e.hash == hash && 28 ((k = e.key) == key || 29 (key != null && key.equals(k)))) { 30 node = e; 31 break; 32 } 33 p = e; 34 } while ((e = e.next) != null); 35 } 36 } 37 // 比对找到的 key 的 value 跟要删除的是否匹配 38 if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value || 39 (value != null && value.equals(v)))) { 40 // 通过调用红黑树的方法来删除节点 41 if (node instanceof TreeNode) 42 ((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable); 43 // 使用链表的操作来删除节点 44 else if (node == p) 45 tab[index] = node.next; 46 else 47 p.next = node.next; 48 ++modCount; 49 --size; 50 afterNodeRemoval(node); 51 return node; 52 } 53 } 54 return null; 55 }
5、hash 方法
在 get 方法和 put 方法中都需要先计算 key 映射到哪个桶上,然后才进行之后的操作,
计算的主要代码如下:
1 (n - 1) & hash
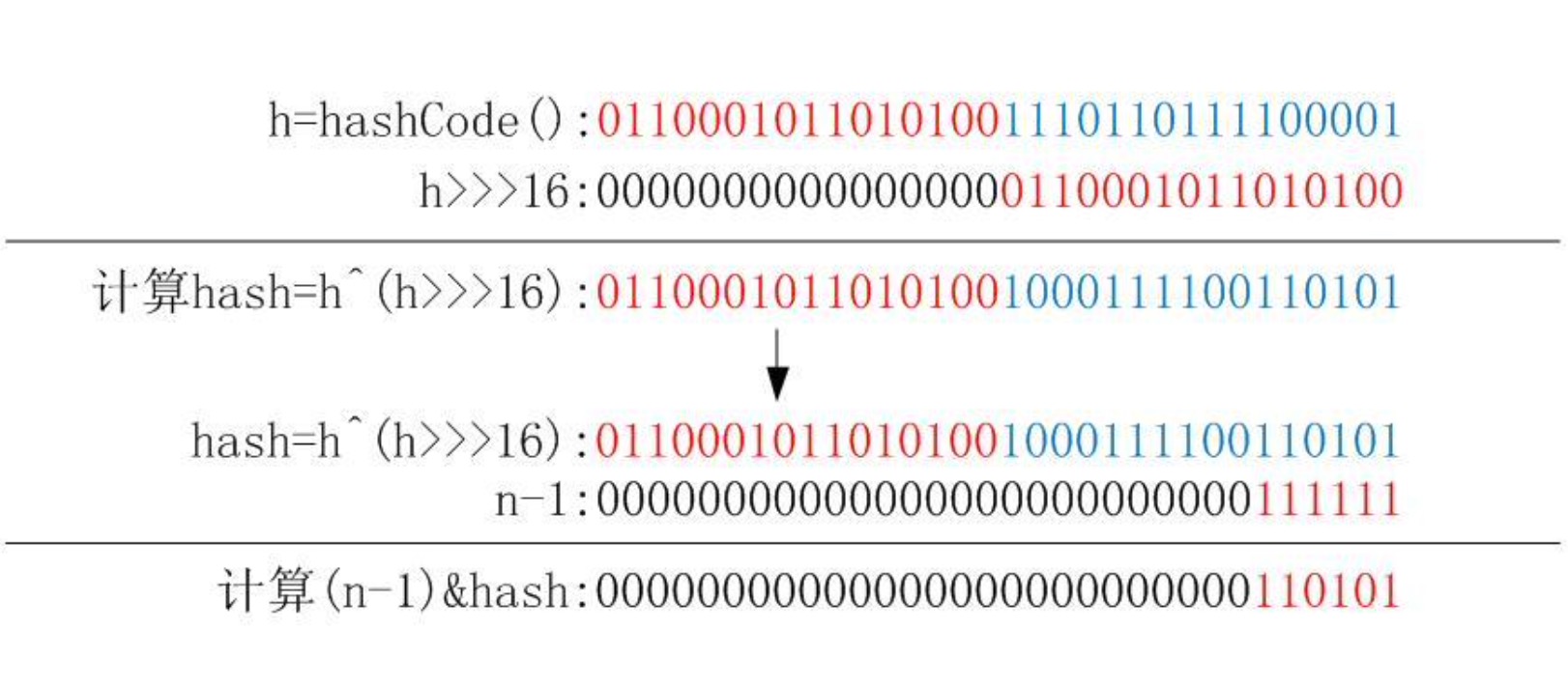
上面代码中的 n 指的是哈希表的大小,hash 指的是 key 的哈希值,hash 是通过下面 这个方法计算出来的,采用了二次哈希的方式,其中 key 的 hashCode 方法是一个 native 方法
1 static final int hash(Object key) { 2 int h; 3 return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); 4 }
这个 hash 方法先通过 key 的 hashCode 方法获取一个哈希值,再拿这个哈希值与它 的高 16 位的哈希值做一个异或操作来得到最后的哈希值,计算过程可以参考下图。 为啥要这样做呢?注释中是这样解释的:如果当 n 很小,假设为 64 的话,那么 n-1 即为 63(0x111111),这样的值跟 hashCode()直接做与操作,实际上只使用了哈希 值的后 6 位。如果当哈希值的高位变化很大,低位变化很小,这样就很容易造成冲 突了,所以这里把高低位都利用起来,从而解决了这个问题
正是因为与的这个操作,决定了 HashMap 的大小只能是 2 的幂次方,想一想,如果 不是 2 的幂次方,会发生什么事情?即使你在创建 HashMap 的时候指定了初始大小, HashMap 在构建的时候也会调用下面这个方法来调整大小
1 static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) { 2 int n = cap - 1; 3 n |= n >>> 1; 4 n |= n >>> 2; 5 n |= n >>> 4; 6 n |= n >>> 8; 7 n |= n >>> 16; 8 return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1; 9 }
这个方法的作用看起来可能不是很直观,它的实际作用就是把 cap 变成第一个大于 等于 2 的幂次方的数。例如,16 还是 16,13 就会调整为 16,17 就会调整为 32
6、resize 方法
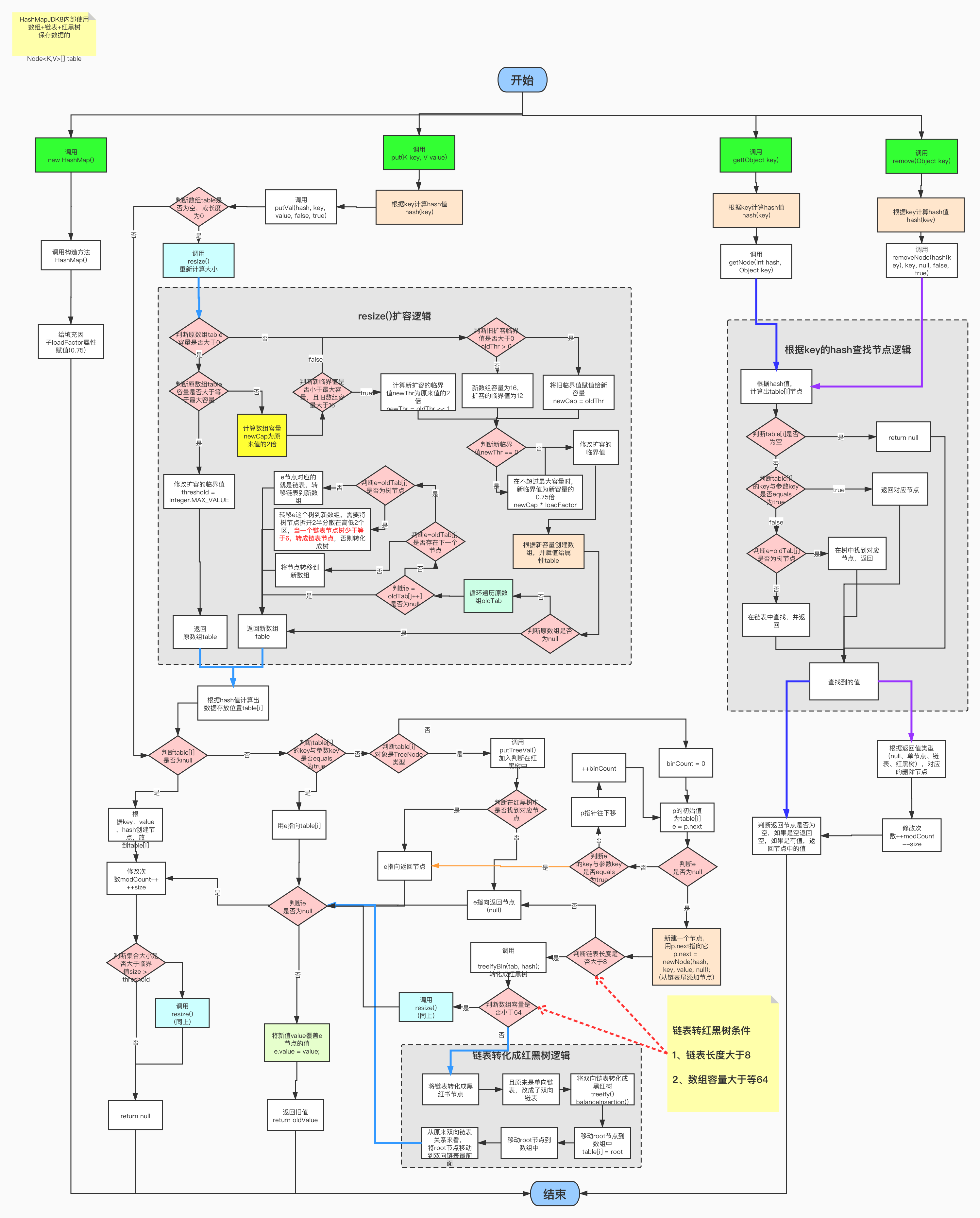
HashMap 在进行扩容时,使用的 rehash 方式非常巧妙,因为每次扩容都是翻倍,与 原来计算(n-1)&hash 的结果相比,只是多了一个 bit 位,所以节点要么就在原来 的位置,要么就被分配到“原位置+旧容量”这个位置。
例如,原来的容量为 32,那么应该拿 hash 跟 31(0x11111)做与操作;在扩容扩到 了 64 的容量之后,应该拿 hash 跟 63(0x111111)做与操作。新容量跟原来相比只 是多了一个 bit 位,假设原来的位置在 23,那么当新增的那个 bit 位的计算结果为 0 时,那么该节点还是在 23;相反,计算结果为 1 时,则该节点会被分配到 23+31 的 桶上。
正是因为这样巧妙的 rehash 方式,保证了 rehash 之后每个桶上的节点数必定小于等 于原来桶上的节点数,即保证了 rehash 之后不会出现更严重的冲突。
1 final Node<K,V>[] resize() { 2 Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table; 3 int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length; 4 int oldThr = threshold; 5 int newCap, newThr = 0; 6 // 计算扩容后的大小 7 if (oldCap > 0) { 8 // 如果当前容量超过最大容量,则无法进行扩容 9 if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { 10 threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; 11 return oldTab; 12 } 13 // 没超过最大值则扩为原来的两倍 14 else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && 15 oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) 16 newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold 17 } 18 else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold 19 newCap = oldThr; 20 else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults 21 newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; 22 newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); 23 } 24 if (newThr == 0) { 25 float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor; 26 newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? 27 (int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE); 28 } 29 // 新的 resize 阈值 30 threshold = newThr; 31 // 创建新的哈希表 32 @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) 33 Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap]; 34 table = newTab; 35 if (oldTab != null) { 36 // 遍历旧哈希表的每个桶,重新计算桶里元素的新位置 37 for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) { 38 Node<K,V> e; 39 if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) { 40 oldTab[j] = null; 41 // 如果桶上只有一个键值对,则直接插入 42 if (e.next == null) 43 newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e; 44 // 如果是通过红黑树来处理冲突的,则调用相关方法把树分离开 45 else if (e instanceof TreeNode) 46 ((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap); 47 // 如果采用链式处理冲突 48 else { // preserve order 49 Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null; 50 Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null; 51 Node<K,V> next; 52 // 通过上面讲的方法来计算节点的新位置 53 do { 54 next = e.next; 55 if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) { 56 if (loTail == null) 57 loHead = e; 58 else 59 loTail.next = e; 60 loTail = e; 61 } 62 else { 63 if (hiTail == null) 64 hiHead = e; 65 else 66 hiTail.next = e; 67 hiTail = e; 68 } 69 } while ((e = next) != null); 70 if (loTail != null) { 71 loTail.next = null; 72 newTab[j] = loHead; 73 } 74 if (hiTail != null) { 75 hiTail.next = null; 76 newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead; 77 } 78 } 79 } 80 } 81 } 82 return newTab; 83 }
在这里有一个需要注意的地方,有些文章指出当哈希表的桶占用超过阈值时就进行 扩容,这是不对的;实际上是当哈希表中的键值对个数超过阈值时,才进行扩容的。
五、HashMap源码分析
简单流程图
详细图
六、HashMap 原理jdk7和jdk8的区别
1、实现方式:
jdk7中使用数组+链表来实现,jdk8使用的数组+链表+红黑树
2、新节点插入到链表是的插入顺序不同
jdk7插入在头部,jdk8插入在尾部
3、jdk8的hash算法有所简化
jdk8的右移比较简单,没有jdk7那么复杂,jdk8提高查询效率的地方由红黑树去实现,没必要像jdk那样右移那么复杂。
4、扩容机制有所优化
jdk8减少了移动所有数据带来的消耗,jdk为了优化
JDK1.7 VS JDK1.8 的性能
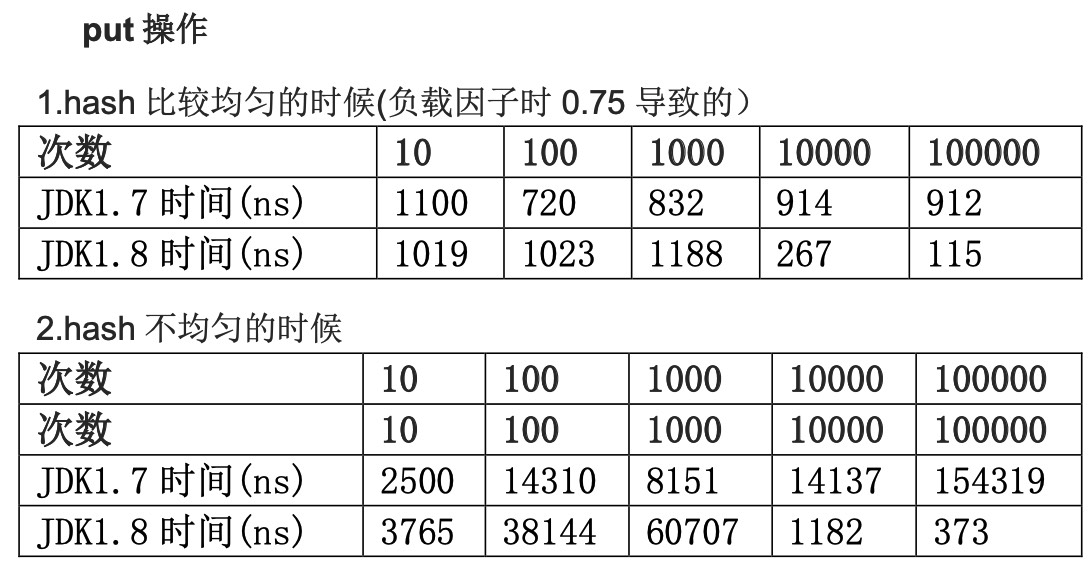

七、总结
通过红黑树的方式来处理哈希冲突是我第一次看见!学过哈希,学过红黑树,就是从来没想到两个可以结合到一起这么用!
按照原来的拉链法来解决冲突,如果一个桶上的冲突很严重的话,是会导致哈希表 的效率降低至 O(n),而通过红黑树的方式,可以把效率改进至 O(logn)。相比 链式结构的节点,树型结构的节点会占用比较多的空间,所以这是一种以空间换时 间的改进方式。
2、HashMap 每次扩容都以当前数组大小的 2 倍去扩容。
3、HashMap 的 链表长度大于8,且数组容量大于等于64,链表转化成红黑树。
4、HashMap 是非线程安全的(可以使用 Collections.synchronizedMap(map) 方法解决List线程安全问题)。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号