本章介绍SpringBoot监控管理
Actuator 简介
Actuator 是 Spring Boot 提供的对应用系统的自省和监控功能。通过 Actuator,可以使用数据化的指标去度量应用的运行情况,比如查看服务器的磁盘、内存、CPU等信息,系统的线程、gc、运行状态等等。
Actuator 通常通过使用 HTTP 和 JMX 来管理和监控应用,大多数情况使用 HTTP 的方式。
Actuator 端点说明
| 端点 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| auditevents | 获取当前应用暴露的审计事件信息 |
| beans | 获取应用中所有的 Spring Beans 的完整关系列表 |
| caches | 获取公开可以用的缓存 |
| conditions | 获取自动配置条件信息,记录哪些自动配置条件通过和没通过的原因 |
| configprops | 获取所有配置属性,包括默认配置,显示一个所有 @ConfigurationProperties 的整理列版本 |
| env | 获取所有环境变量 |
| flyway | 获取已应用的所有Flyway数据库迁移信息,需要一个或多个 Flyway Bean |
| liquibase | 获取已应用的所有Liquibase数据库迁移。需要一个或多个 Liquibase Bean |
| health | 获取应用程序健康指标(运行状况信息) |
| httptrace | 获取HTTP跟踪信息(默认情况下,最近100个HTTP请求-响应交换)。需要 HttpTraceRepository Bean |
| info | 获取应用程序信息 |
| integrationgraph | 显示 Spring Integration 图。需要依赖 spring-integration-core |
| loggers | 显示和修改应用程序中日志的配置 |
| logfile | 返回日志文件的内容(如果已设置logging.file.name或logging.file.path属性) |
| metrics | 获取系统度量指标信息 |
| mappings | 显示所有@RequestMapping路径的整理列表 |
| scheduledtasks | 显示应用程序中的计划任务 |
| sessions | 允许从Spring Session支持的会话存储中检索和删除用户会话。需要使用Spring Session的基于Servlet的Web应用程序 |
| shutdown | 关闭应用,要求endpoints.shutdown.enabled设置为true,默认为 false |
| threaddump | 获取系统线程转储信息 |
| heapdump | 返回hprof堆转储文件 |
| jolokia | 通过HTTP公开JMX bean(当Jolokia在类路径上时,不适用于WebFlux)。需要依赖 jolokia-core |
| prometheus | 以Prometheus服务器可以抓取的格式公开指标。需要依赖 micrometer-registry-prometheus |
Actuator 使用及配置
1、新建一个SpringBoot Web项,引入spring-boot-starter-actuator依赖
1 <dependency> 2 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 3 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> 4 <optional>true</optional> 5 </dependency>
完整pom如下:

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> 5 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> 6 7 <groupId>com.test</groupId> 8 <artifactId>test-springboot-actuator</artifactId> 9 <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> 10 11 12 <parent> 13 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 14 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> 15 <version>2.1.8.RELEASE</version> 16 </parent> 17 18 <properties> 19 <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> 20 <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> 21 <java.version>1.8</java.version> 22 </properties> 23 24 <dependencies> 25 <dependency> 26 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 27 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> 28 </dependency> 29 30 <dependency> 31 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 32 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> 33 <optional>true</optional> 34 </dependency> 35 36 37 <dependency> 38 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 39 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> 40 <scope>test</scope> 41 </dependency> 42 43 </dependencies> 44 45 46 <!-- SpringBoot打包插件,可以将代码打包成一个可执行的jar包 --> 47 <build> 48 <plugins> 49 <plugin> 50 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 51 <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> 52 </plugin> 53 </plugins> 54 </build> 55 </project>
2、启动项目,访问地址 http://localhost:8080/actuator,获取内容如下:
{
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator",
"templated": false
},
"health": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/health",
"templated": false
},
"health-component": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/health/{component}",
"templated": true
},
"health-component-instance": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/health/{component}/{instance}",
"templated": true
},
"info": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/info",
"templated": false
}
}
}
可以看到,只有health和info是因为actuator默认只暴露了health和info端点
2、编辑application.properties配置文件,打开其他端点,以及配置管理端点的访问路径
1 # 默认端点可用 2 management.endpoints.enabled-by-default=true 3 # 通过HTTP公开所有的端点 4 management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=* 5 # 自定义管理端点路径 默认是:/actuator 6 management.endpoints.web.base-path=/actuator
常用端点详解
1、health
默认情况下 health 端点是开放的,访问 http://127.0.0.1:8080/actuator/health 即可看到应用运行状态。
{"status":"UP"}
如果需要看到详细信息,则需要做添加配置:
management.endpoint.health.show-details=always
显示内容如下:
{"status":"UP","details":{"diskSpace":{"status":"UP","details":{"total":250790436864,"free":150934597632,"threshold":10485760}}}}
2、info
查看应用信息是否在 application.properties 中配置。如我们在项目中配置是:
info.app.name=Spring Boot Actuator Demo info.app.version=v1.0.0 info.app.description=Spring Boot Actuator Demo
访问 http://127.0.0.1:8080/actuator/info 返回信息如下:
{"app":{"name":"Spring Boot Actuator Demo","version":"v1.0.0","description":"Spring Boot Actuator Demo"}}
3、env
通过 env 可以获取到所有关于当前 Spring Boot 应用程序的运行环境信息,如:操作系统信息(systemProperties)、环境变量信息、JDK 版本及 ClassPath 信息、当前启用的配置文件(activeProfiles)、propertySources、应用程序配置信息(applicationConfig)等。
可以通过 http://127.0.0.1:8080/actuator/env/{name} ,name表示想要查看的信息,可以独立显示。
4、beans
访问 http://127.0.0.1:8080/actuator/beans 返回部分信息如下:
{
"contexts": {
"application": {
"beans": {
"endpointCachingOperationInvokerAdvisor": {
"aliases": [],
"scope": "singleton",
"type": "org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint.invoker.cache.CachingOperationInvokerAdvisor",
"resource": "class path resource [org/springframework/boot/actuate/autoconfigure/endpoint/EndpointAutoConfiguration.class]",
"dependencies": [
"environment"
]
},
"defaultServletHandlerMapping": {
"aliases": [],
"scope": "singleton",
"type": "org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping",
"resource": "class path resource [org/springframework/boot/autoconfigure/web/servlet/WebMvcAutoConfiguration$EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class]",
"dependencies": []
},
...
},
"parentId": null
}
}
}
5、conditions
通过 conditions 可以在应用运行时查看代码了某个配置在什么条件下生效,或者某个自动配置为什么没有生效。
{
"contexts": {
"application": {
"positiveMatches": {...},
"negativeMatches": {...},
"unconditionalClasses": [...]
}
}
}
6、loggers
获取系统的日志信息。
访问 http://127.0.0.1:8080/actuator/loggers 返回部分信息如下:
{
"levels": [
"OFF",
"ERROR",
"WARN",
"INFO",
"DEBUG",
"TRACE"
],
"loggers": {
"ROOT": {
"configuredLevel": "INFO",
"effectiveLevel": "INFO"
},
"com": {
"configuredLevel": null,
"effectiveLevel": "INFO"
},
...
}
}
7、mappings
查看所有 URL 映射,即所有 @RequestMapping 路径的整理列表。
访问 http://127.0.0.1:8080/actuator/mappings 返回部分信息如下:
8、heapdump
访问:http://127.0.0.1:8080/actuator/heapdump会自动生成一个 GZip 压缩的 Jvm 的堆文件 heapdump,我们可以使用 JDK 自带的 Jvm 监控工具 VisualVM 打开此文件查看。
9、threaddump
获取系统线程的转储信息,主要展示了线程名、线程ID、线程的状态、是否等待锁资源等信息。在工作中,我们可以通过查看线程的情况来排查相关问题。
访问 http://127.0.0.1:8080/actuator/threaddump
10、metrics
访问 http://127.0.0.1:8080/actuator/metrics 可以获取系统度量指标信息项如下:
{
"names": [
"jvm.memory.max",
"jvm.threads.states",
"jvm.gc.pause",
"http.server.requests",
"process.files.max",
"jvm.gc.memory.promoted",
"system.load.average.1m",
"jvm.memory.used",
"jvm.gc.max.data.size",
"jvm.memory.committed",
"system.cpu.count",
"logback.events",
"tomcat.global.sent",
"jvm.buffer.memory.used",
"tomcat.sessions.created",
"jvm.threads.daemon",
"system.cpu.usage",
"jvm.gc.memory.allocated",
"tomcat.global.request.max",
"tomcat.global.request",
"tomcat.sessions.expired",
"jvm.threads.live",
"jvm.threads.peak",
"tomcat.global.received",
"process.uptime",
"tomcat.sessions.rejected",
"process.cpu.usage",
"tomcat.threads.config.max",
"jvm.classes.loaded",
"jvm.classes.unloaded",
"tomcat.global.error",
"tomcat.sessions.active.current",
"tomcat.sessions.alive.max",
"jvm.gc.live.data.size",
"tomcat.threads.current",
"process.files.open",
"jvm.buffer.count",
"jvm.buffer.total.capacity",
"tomcat.sessions.active.max",
"tomcat.threads.busy",
"process.start.time"
]
}
11、shutdown
开启可以接口关闭 Spring Boot 应用,要使用这个功能需要做如下配置:
1 # 开启应用关闭端口 2 management.endpoint.shutdown.enabled=true 3 # 暴露shutdown的web端口 4 management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=shutdown
可以通过 post(仅支持 post) 请求访问 http://127.0.0.1:8080/actuator/shutdown 关闭应用。

自定义HealthIndicator
1、自定义组件,实现HealthIndicator接口,并注入容器中,代码如下:
1 // 注入Spring容器中 2 @Component 3 public class MyAppHealthIndicator implements HealthIndicator { 4 @Override 5 public Health health() { 6 // 自定义的检查方法 7 Health build = Health.up().build(); 8 return build; 9 } 10 }
2、启动项目,访问 http://localhost:8080/actuator/health,效果如下:

3、修改组件代码,如下:
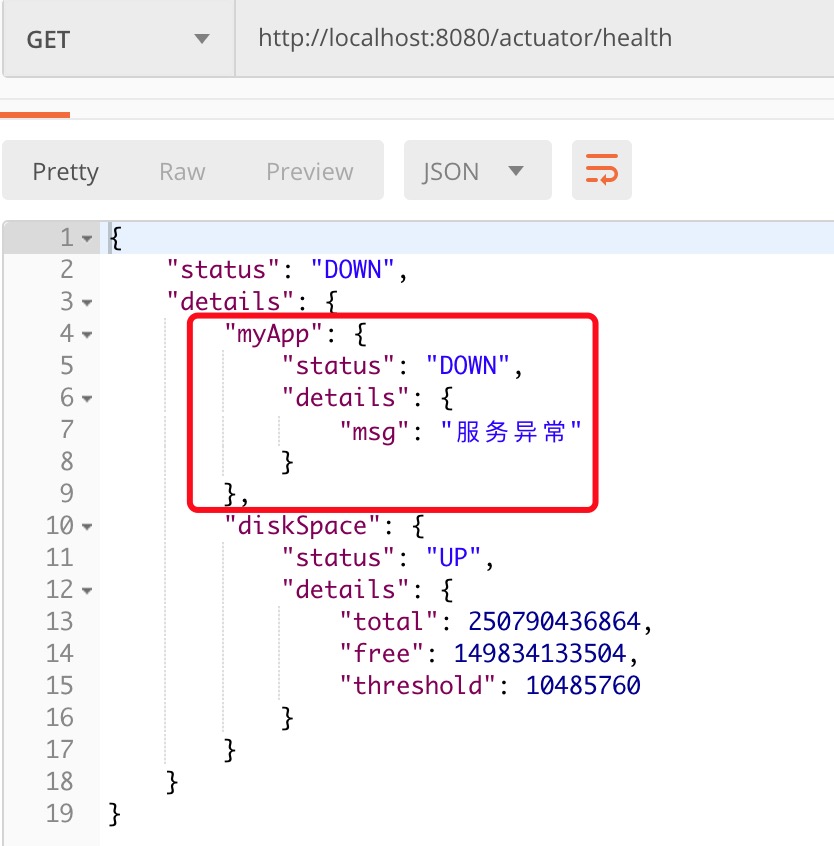
1 // 注入Spring容器中 2 @Component 3 public class MyAppHealthIndicator implements HealthIndicator { 4 @Override 5 public Health health() { 6 // 自定义的检查方法 7 // Health build = Health.up().build(); 8 return Health.down().withDetail("msg", "服务异常").build(); 9 } 10 }
4、重启项目,效果如下:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号