本章介绍SpringBoot的缓存机制及使用
Spring缓存介绍
Spring从3.1开始定义了org.springframework.cache.Cache 和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术; 并支持使用JCache(JSR-107)注解简化我们开发;
• Cache接口为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合;
• Cache接口下Spring提供了各种xxxCache的实现;如RedisCache,EhCacheCache,ConcurrentMapCache等;
• 每次调用需要缓存功能的方法时,Spring会检查检查指定参数的指定的目标方法是否 已经被调用过;如果有就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果,如果没有就调用方法 并缓存结果后返回给用户。下次调用直接从缓存中获取。
• 使用Spring缓存抽象时我们需要关注以下两点;
1、确定方法需要被缓存以及他们的缓存策略
2、从缓存中读取之前缓存存储的数据
几个重要概念&缓存注解
缓存组件关系图
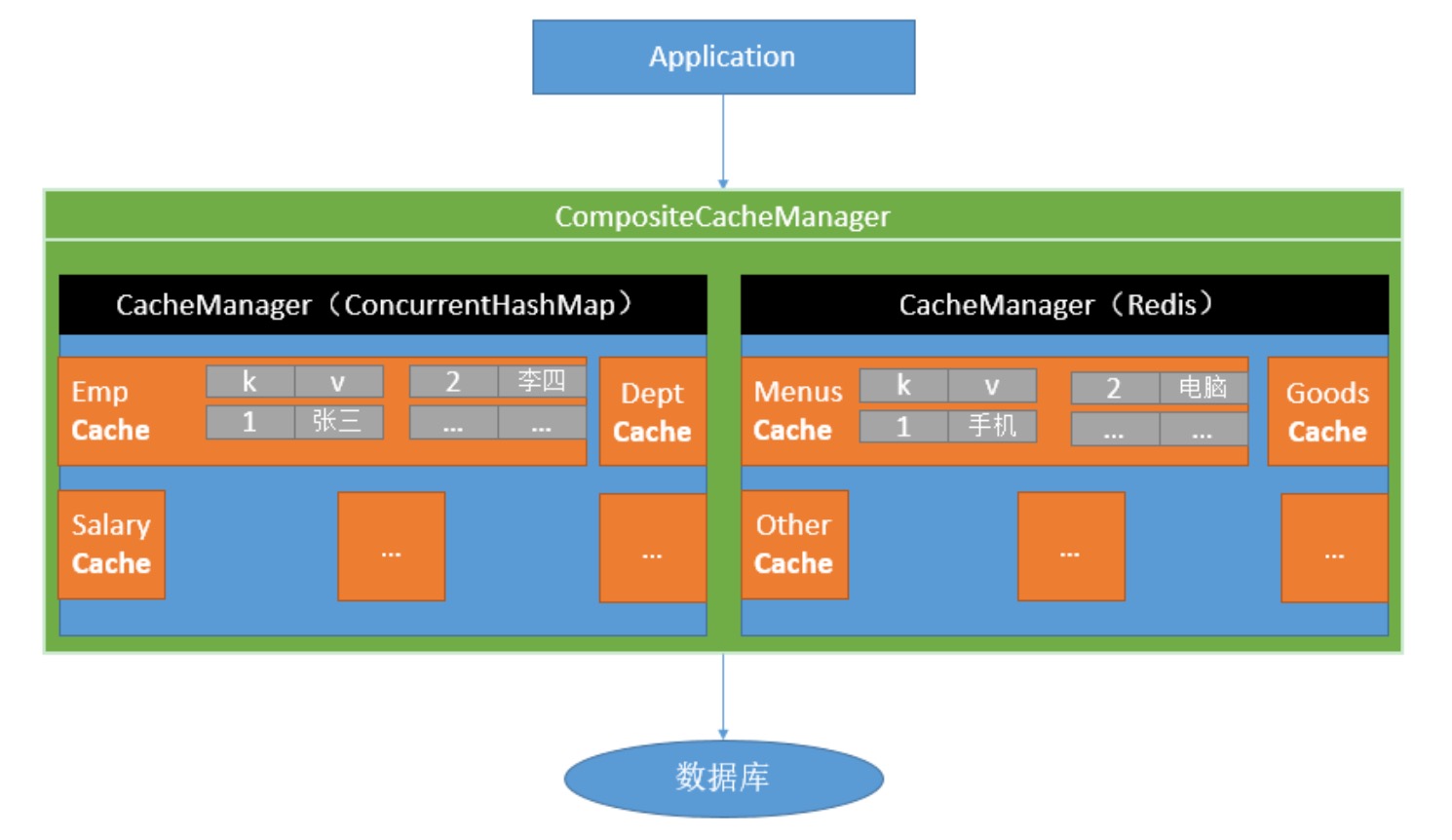
|
Cache |
缓存接口,定义缓存操作。实现有:RedisCache、EhCacheCache、ConcurrentMapCache等 |
|
CacheManager |
缓存管理器,管理各种缓存(Cache)组件 |
|
@Cacheable |
主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存 |
|
@CacheEvict |
清空缓存 |
|
@CachePut |
保证方法被调用,又希望结果被缓存。 |
|
@EnableCaching |
开启基于注解的缓存 |
|
keyGenerator |
缓存数据时key生成策略 |
|
serialize |
缓存数据时value序列化策略 |
缓存注解的主要参数
|
@Cacheable/@CachePut/@CacheEvict 主要的参数 |
||
|
value |
缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定 至少一个 |
例如: @Cacheable(value=”mycache”) 或者 @Cacheable(value={”cache1”,”cache2”} |
|
key |
缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达 式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数 进行组合 |
例如: @Cacheable(value=”testcache”,key=”#userName”) |
|
condition |
缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存/清除缓存,在 调用方法之前之后都能判断 |
例如: @Cacheable(value=”testcache”,condition=”#userNam e.length()>2”) |
|
allEntries (@CacheEvict ) |
是否清空所有缓存内容,缺省为 false,如果指定为 true,则方法调用后将立即清空所有缓存 |
例如: @CachEvict(value=”testcache”,allEntries=true) |
|
beforeInvocation (@CacheEvict) |
是否在方法执行前就清空,缺省为 false,如果指定 为 true,则在方法还没有执行的时候就清空缓存, 缺省情况下,如果方法执行抛出异常,则不会清空 缓存 |
例如: @CachEvict(value=”testcache”, beforeInvocation=true) |
|
unless (@CachePut) (@Cacheable) |
用于否决缓存的,不像condition,该表达式只在方 法执行之后判断,此时可以拿到返回值result进行判 断。条件为true不会缓存,fasle才缓存 |
例如: @Cacheable(value=”testcache”,unless=”#result == null”) |
缓存注解的SpEL(Spring Expression Language)
|
名字 |
位置 |
描述 |
示例 |
|
methodName |
root object |
当前被调用的方法名 |
#root.methodName |
|
method |
root object |
当前被调用的方法 |
#root.method.name |
|
target |
root object |
当前被调用的目标对象 |
#root.target |
|
targetClass |
root object |
当前被调用的目标对象类 |
#root.targetClass |
|
args |
root object |
当前被调用的方法的参数列表 |
#root.args[0] |
|
caches |
root object |
当前方法调用使用的缓存列表(如@Cacheable(value={"cache1", "cache2"})),则有两个cache |
#root.caches[0].name |
|
argument name |
evaluation context |
方法参数的名字. 可以直接 #参数名 ,也可以使用 #p0或#a0 的形式,0代表参数的索引; |
#iban 、 #a0 、 #p0 |
|
result |
evaluation context |
方法执行后的返回值(仅当方法执行之后的判断有效,如‘unless’,’cache put’的表达式 ’cache evict’的表达式beforeInvocation=false) |
#result |
缓存使用
项目搭建
1、新建一个Spring Web工程,整合了mybatis,pom.xml文件如下:

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> 5 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> 6 7 <groupId>com.test</groupId> 8 <artifactId>test-springboot-cache</artifactId> 9 <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> 10 11 <parent> 12 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 13 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> 14 <version>2.1.8.RELEASE</version> 15 </parent> 16 17 <properties> 18 19 <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> 20 <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> 21 <java.version>1.8</java.version> 22 </properties> 23 24 <dependencies> 25 26 <dependency> 27 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 28 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> 29 </dependency> 30 31 <dependency> 32 <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> 33 <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> 34 <version>2.0.1</version> 35 </dependency> 36 37 <!-- mysql --> 38 <dependency> 39 <groupId>mysql</groupId> 40 <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> 41 <version>8.0.12</version> 42 </dependency> 43 44 <dependency> 45 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 46 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> 47 <scope>test</scope> 48 </dependency> 49 50 </dependencies> 51 52 53 <!-- SpringBoot打包插件,可以将代码打包成一个可执行的jar包 --> 54 <build> 55 <plugins> 56 <plugin> 57 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 58 <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> 59 </plugin> 60 </plugins> 61 </build> 62 63 </project>
application.yml文件如下:

spring:
datasource:
username: admin
password: 123456
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test_mybatis
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
mybatis:
configuration:
# 下划线转大写映射
mapUnderscoreToCamelCase: true
logging:
level:
com:
test:
springboot:
cache:
mapper: debug
debug: true
目录结构
2、编写实体类Employee.java和Department.java

1 package com.test.springboot.cache.bean; 2 3 import java.io.Serializable; 4 5 public class Employee implements Serializable { 6 7 private Integer id; 8 private String lastName; 9 private String gender; 10 private String email; 11 private Integer deptId; 12 13 public Integer getDeptId() { 14 return deptId; 15 } 16 17 public void setDeptId(Integer deptId) { 18 this.deptId = deptId; 19 } 20 21 public Integer getId() { 22 return id; 23 } 24 25 public void setId(Integer id) { 26 this.id = id; 27 } 28 29 public String getLastName() { 30 return lastName; 31 } 32 33 public void setLastName(String lastName) { 34 this.lastName = lastName; 35 } 36 37 public String getGender() { 38 return gender; 39 } 40 41 public void setGender(String gender) { 42 this.gender = gender; 43 } 44 45 public String getEmail() { 46 return email; 47 } 48 49 public void setEmail(String email) { 50 this.email = email; 51 } 52 53 @Override 54 public String toString() { 55 return "Employee{" + 56 "id=" + id + 57 ", lastName='" + lastName + '\'' + 58 ", gender='" + gender + '\'' + 59 ", email='" + email + '\'' + 60 ", deptId=" + deptId + 61 '}'; 62 } 63 }

1 package com.test.springboot.cache.bean; 2 3 import java.io.Serializable; 4 5 public class Department implements Serializable { 6 7 private Integer id; 8 private String depName; 9 10 public Integer getId() { 11 return id; 12 } 13 14 public void setId(Integer id) { 15 this.id = id; 16 } 17 18 public String getDepName() { 19 return depName; 20 } 21 22 public void setDepName(String depName) { 23 this.depName = depName; 24 } 25 }
3、编写EmployeeMapper.java

1 package com.test.springboot.cache.mapper; 2 3 import com.test.springboot.cache.bean.Employee; 4 import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*; 5 6 @Mapper 7 public interface EmployeeMapper { 8 9 @Select("SELECT * FROM employee WHERE id = #{id}") 10 public Employee getEmpById(Integer id); 11 12 @Update("UPDATE employee SET last_name = #{lastName}, email=#{email},gender=#{gender},dept_id=#{deptId} WHERE id = #{id}") 13 public void updateEmp(Employee employee); 14 15 @Delete("DELETE FROM employee WHERE id = #{id}") 16 public void deleteEmpById(Integer id); 17 18 @Insert("INSERT INTO employee(last_name, email, gender, dept_id) VALUES(#{lastName},#{email},#{gender},#{deptId})") 19 public void insertEmp(Employee emp); 20 }
4、编写EmployeeService.java

1 package com.test.springboot.cache.service; 2 3 import com.test.springboot.cache.bean.Employee; 4 import com.test.springboot.cache.mapper.EmployeeMapper; 5 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; 6 import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; 7 8 @Service 9 public class EmployeeService { 10 11 @Autowired 12 EmployeeMapper employeeMapper; 13 14 public Employee getEmp(Integer id){ 15 System.out.println("===查询" + id + "号员工"); 16 return employeeMapper.getEmpById(id); 17 } 18 }
5、编写EmployeeController.java

1 package com.test.springboot.cache.controller; 2 3 import com.test.springboot.cache.bean.Employee; 4 import com.test.springboot.cache.service.EmployeeService; 5 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; 6 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; 7 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; 8 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; 9 10 @RestController 11 public class EmployeeController { 12 13 @Autowired 14 EmployeeService employeeService; 15 16 @GetMapping("emp/{id}") 17 public Employee getEmployee(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { 18 19 return employeeService.getEmp(id); 20 } 21 }
7、编写启动类Application.java

1 package com.test.springboot.cache; 2 3 4 import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan; 5 import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; 6 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; 7 8 /** 9 * 一、搭建基本环境 10 * 1、创建数据库,创建department和employee表 11 * 2、创建JavaBean封装数据 12 * 3、整合MyBatis操作数据库 13 * a、配置数据源信息 14 * b、使用注解版的MyBatis: 15 * 1)、@MapperScan指定需要扫描的mapper接口所在的包 16 * 二、快速体验缓存 17 * 步骤: 18 * 1、开启基于注解的缓存 @EnableCaching 19 * 2、标注缓存注解即可 @Cacheable、@CacheEvict、@CachePut 20 */ 21 22 @MapperScan("com.test.springboot.cache.mapper") 23 @SpringBootApplication 24 public class Application { 25 26 public static void main(String[] args) { 27 SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); 28 } 29 30 }
8、启动项目,浏览器访问地址:http://localhost:8080/emp/1,测试能否正常获取数据
使用缓存
1、开启基于注解的缓存 @EnableCaching
1 @EnableCaching 2 @MapperScan("com.test.springboot.cache.mapper") 3 @SpringBootApplication 4 public class Application { 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); 8 } 9 10 }
2、标注缓存注解即可 @Cacheable、@CacheEvict、@CachePut,在EmployeeService的getEmp方法上注解
1 @Cacheable(cacheNames="emp") 2 public Employee getEmp(Integer id){ 3 System.out.println("===查询" + id + "号员工"); 4 return employeeMapper.getEmpById(id); 5 }
3、启动项目,浏览器访问地址:http://localhost:8080/emp/1,连续2个请求,看第二次是否有查数据库(通过日志可以体现)
缓存原理
缓存自动配置原理
1、分析自动配置类:CacheAutoConfiguration
2、在CacheAutoConfiguration类中,自动导入了类CacheConfigurationImportSelector.class
1 @Import(CacheConfigurationImportSelector.class) 2 public class CacheAutoConfiguration {
CacheConfigurationImportSelector.class
1 static class CacheConfigurationImportSelector implements ImportSelector { 2 3 @Override 4 public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) { 5 CacheType[] types = CacheType.values(); 6 String[] imports = new String[types.length]; 7 for (int i = 0; i < types.length; i++) { 8 imports[i] = CacheConfigurations.getConfigurationClass(types[i]); 9 } 10 return imports; 11 } 12 13
而CacheConfigurationImportSelector会根据条件自动导入以下缓存的配置类,以下配置类不完全生效,要在一定条件下配置类才会生效
GenericCacheConfiguration.class EhCacheCacheConfiguration.class HazelcastCacheConfiguration.class InfinispanCacheConfiguration.class JCacheCacheConfiguration.class CouchbaseCacheConfiguration.class RedisCacheConfiguration.class CaffeineCacheConfiguration.class SimpleCacheConfiguration.class NoOpCacheConfiguration.class
3、测试项目,在项目配置文件中配置(debug: true),配置调试模式,然后启动项目通过在控制查看输出日志,可以看到SimpleCacheConfiguration配置上了

而SimpleCacheConfiguration,的内容如下;它在容器中注入了一个ConcurrentMapCacheManager,用来管理缓存
1 @Configuration 2 @ConditionalOnMissingBean(CacheManager.class) 3 @Conditional(CacheCondition.class) 4 class SimpleCacheConfiguration { 5 6 private final CacheProperties cacheProperties; 7 8 private final CacheManagerCustomizers customizerInvoker; 9 10 SimpleCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties, CacheManagerCustomizers customizerInvoker) { 11 this.cacheProperties = cacheProperties; 12 this.customizerInvoker = customizerInvoker; 13 } 14 15 @Bean 16 public ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager() { 17 ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager = new ConcurrentMapCacheManager(); 18 List<String> cacheNames = this.cacheProperties.getCacheNames(); 19 if (!cacheNames.isEmpty()) { 20 cacheManager.setCacheNames(cacheNames); 21 } 22 return this.customizerInvoker.customize(cacheManager); 23 } 24 25 }
4、分析ConcurrentMapCacheManager类,它是实现了CacheManager接口
1 public class ConcurrentMapCacheManager implements CacheManager, BeanClassLoaderAware { 2 3 private final ConcurrentMap<String, Cache> cacheMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16); 4 5 private boolean dynamic = true; 6 7 private boolean allowNullValues = true; 8 9 private boolean storeByValue = false; 10 11 ... 12 13 // 根据名字获取一个Cache 14 @Override 15 @Nullable 16 public Cache getCache(String name) { 17 Cache cache = this.cacheMap.get(name); 18 if (cache == null && this.dynamic) { 19 synchronized (this.cacheMap) { 20 cache = this.cacheMap.get(name); 21 if (cache == null) { 22 // cache为空时,创建一个Cache 23 cache = createConcurrentMapCache(name); 24 this.cacheMap.put(name, cache); 25 } 26 } 27 } 28 return cache; 29 } 30 31 32 // 根据名字创建一个Cache,实际上是ConcurrentMapCache 33 protected Cache createConcurrentMapCache(String name) { 34 SerializationDelegate actualSerialization = (isStoreByValue() ? this.serialization : null); 35 return new ConcurrentMapCache(name, new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256), 36 isAllowNullValues(), actualSerialization); 37 38 } 39 40 }
在ConcurrentMapCacheManager类中的getCache上打断点,然后页面做请求访问,可以看到调用被@Cacheable注解的方法时;会在方法调用前,调用getCache方法,而第一次调用getCache方法时,会去创建一个ConcurrentMapCache,而ConcurrentMapCache它的构造方法中,有ConcurrentHashMap参数,所以缓存键值对实际是放在ConcurrentHashMap中。
缓存运行步骤
@Cacheable注解的方法运行步骤
1、方法运行之前,先去查询Cache(缓存组件),按照cacheNames指定的名字获取(CacheManager先获取相应的缓存),第一次获取缓存如果没有Cache组件会自动创建
2、去Cache中查找缓存的内容,使用一个key,默认就是方法的参数,key是按照某种策略生成的,默认使用SimpleKeyGenerator生成key
通过调试运行方法,可以看到会调用抽象类CacheAspectSupport的findCachedItem方法,其中通过generateKey方法生成key的

而generateKey方法如下:其中keyGenerator就是SimpleKeyGenerator
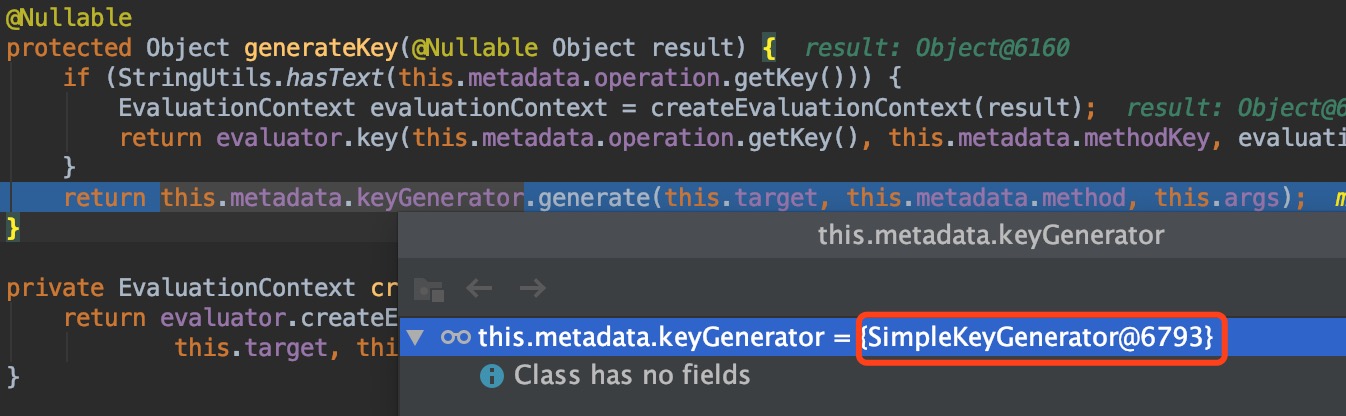
查看SimpleKeyGenerator类,可以知道其中key的生成策略
1 public class SimpleKeyGenerator implements KeyGenerator { 2 3 @Override 4 public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) { 5 return generateKey(params); 6 } 7 8 /** 9 * Generate a key based on the specified parameters. 10 */ 11 public static Object generateKey(Object... params) { 12 if (params.length == 0) { 13 return SimpleKey.EMPTY; 14 } 15 if (params.length == 1) { 16 Object param = params[0]; 17 if (param != null && !param.getClass().isArray()) { 18 return param; 19 } 20 } 21 return new SimpleKey(params); 22 } 23 24 }
分析SimpleKeyGenerator生成key的默认策略:
-
-
- 如果没有参数:key= new SimpleKey();
- 如果有一个参数:key=参数的值
- 如果有多个参数:key=new SimpleKey(params);
-
3、没有查到缓存就调用目标方法
4、将目标方法返回的结果,放入缓存中
缓存标签
1、@Cacheable
使用场景:@Cacheable标注的方法执行之前先检查缓存中有没有这个数据,默认按照参数的值作为key去查询缓存,如果没有就运行方法并将结果放入缓存;以后再来调用就可以直接使用缓存中的数据
几个属性:
-
- cacheNames/value:指定缓存组件的名字
- key:缓存数据使用key;可以用它来指定。默认是使用方法参数的值 1-方法的返回值
-
@Cacheable(cacheNames="emp", key = "#id")
-
- 编写SpEL:
- #id;参数id的值
- #a0 #p0 #root.args[0]
- keyGenerator:key的生成器;可以自己指定key的生成器的组件id
- key/keyGenerator:二选一使用
- cacheManager:指定缓存管理器;
- condition:指定符合条件的情况下才缓存
- unless:否定缓存;当unless指定的条件为true,方法的返回值就不会被缓存;可以获取到结果进行判断 unless = "#result == null"
- sync: 是否使用异步模式
keyGenerator使用
a、先编辑一个MyCacheConfig类,注入自己的KeyGenerator
1 @Configuration 2 public class MyCacheConfig { 3 4 @Bean("myKeyGenerator") 5 public KeyGenerator keyGenerator(){ 6 return new KeyGenerator(){ 7 @Override 8 public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) { 9 return method.getName()+ "-" + Arrays.asList(params); 10 } 11 }; 12 } 13 }
b、使用如下:
@Cacheable(cacheNames="emp", keyGenerator = "myKeyGenerator")
2、@CachePut
使用场景:@CachePut标注的方法执行之后执行,即调用方法,又更新缓存数据,如:修改了数据库的某个数据,同时更新缓存
运行时机:先调用目标方法,将目标方法缓存起来
使用如下:@CachePut(cacheNames = "emp", key = "#p0.id")
3、@CacheEvict
使用场景:指定要删除的缓存数据
allEntries = true:指定清楚这个缓存中的所有数据
beforeInvocation = false:缓存的清楚在方法之后执行,默认是在方法执行之后执行,如果方法出现异常,缓存不会清除
beforeInvocation = false:缓存的清除在方法之前执行,无论方法是否出现异常,缓存都会清除
使用如下:
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "emp", key = "#id" ) //指定缓存删
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "emp", allEntries = true) // 删emp所有的缓存
4、@Caching
使用场景:定义复杂规则缓存
使用如下:
1 @Caching( 2 cacheable = { 3 @Cacheable(value = "emp", key = "#lastName") 4 }, 5 put = { 6 @CachePut(value = "emp", key = "#result.id+100"), 7 @CachePut(value = "emp", key = "#result.email") 8 } 9 )
5、@CacheConfig
使用场景:抽取缓存的公共配置
使用如下:
1 @CacheConfig(cacheNames = {"emp"}) 2 @Service 3 public class EmployeeService { 4 5 .... 6 7 }




