MyBatis缓存
MyBatis缓存
缓存就是内存中的数据,常常来自对数据库查询结果的保存,使用缓存,我们可以避免频繁的与数据进行交互,进而提高响应速度。
MyBatis也提供两种缓存模式,分为一级缓存和二级缓存。
优点:提供查询效率减少频繁进行I/O操作,从而减少数据库的压力。
适合存放缓存的数据:【1】查询频率比较高的数据 【2】修改频繁低
一级缓存
一级缓存也称为本地缓存,一级缓存是在会话(SqlSession)层面实现,代表着同一个SqlSession 中存在缓存,但是跨SqlSession是没有效果的。
MyBatis的一级缓存是默认开启的,不需要任何配置。我们进行一次实验验证一级缓存是否真的存在?它的作用范围是不是在同一SqlSession有效
例子(验证一级缓存是否存在):
测试代码:
@Test
public void selectByIdTest() throws Exception{
Reader resourceAsReader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsReader);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentDao studentDao = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
Student student = studentDao.selectById(3);
//测试一级缓存是否默认开启
//在同一sqlSession中
Student student1 = studentDao.selectById(3);
System.out.println("student = " + student);
System.out.println("student1 = " + student1);
}
效果展示:

例子(验证作用范围是否在同一SqlSession):
测试代码:
@Test
public void selectByIdTest() throws Exception{
Reader resourceAsReader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsReader);
//开启两个sqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentDao studentDao1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
StudentDao studentDao2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
//不同的会话,根据相同的学生id查询学生信息
Student student1 = studentDao1.selectById(3);
Student student2 = studentDao2.selectById(3);
System.out.println("student1 = " + student1);
System.out.println("student2 = " + student2);
}
效果展示:

例子(同一SqlSession,中间出现增删改语句):
测试代码:
@Test
public void selectByIdTest() throws Exception{
Reader resourceAsReader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsReader);
//开启sqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentDao studentDao = sqlSession1.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
//根据id查询学生信息
Student student1 = studentDao.selectById(3);
//中间进行DQL语句
int row = studentDao.update(new Student(4, "老汪", 18));
//根据相同的id查询学生信息
Student student2 = studentDao.selectById(3);
//查看结果
System.out.println("student1 = " + student1);
System.out.println("student2 = " + student2);
}
效果展示:
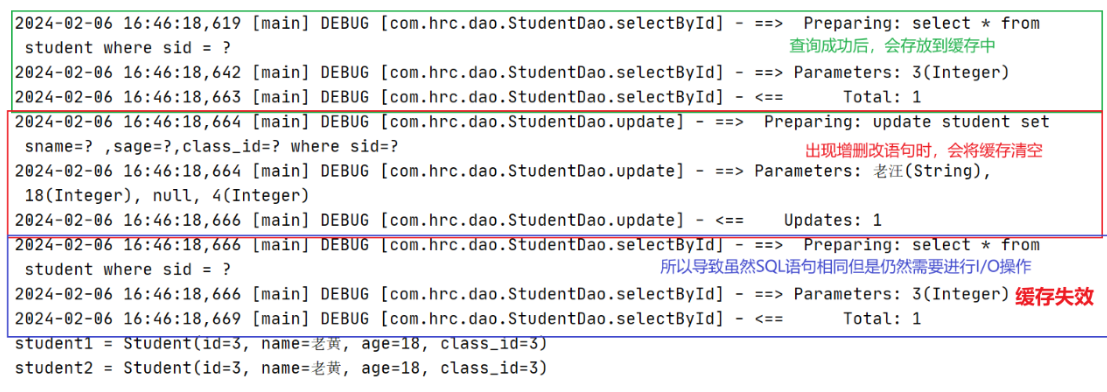
所以中间当出现增删改语句时,缓存会清空所以导致缓存失效。
总结:
(1)什么时候不走缓存?
①不同的SqlSession对象。
②查询条件发生改变。
(2)什么时候缓存是失效?
①第一次查询和第二次查询之间,执行clearCache()方法,手动清空缓存。
②第一次查询和第二次查询之间,执行增、删、改操作。
注意:这个增、删、改操作和哪张表没有关联,只要执行增、删、改操作,一级缓存就会失效!
二级缓存
二级缓存是用来解决一级缓存不能跨会话共享的问题,它的范围在同一个namespace之间,可以被多个SqlSession共享(同一个接口里面的相同方法,都可以共享)
二级缓存在MyBatis中是默认关闭的。
原理:
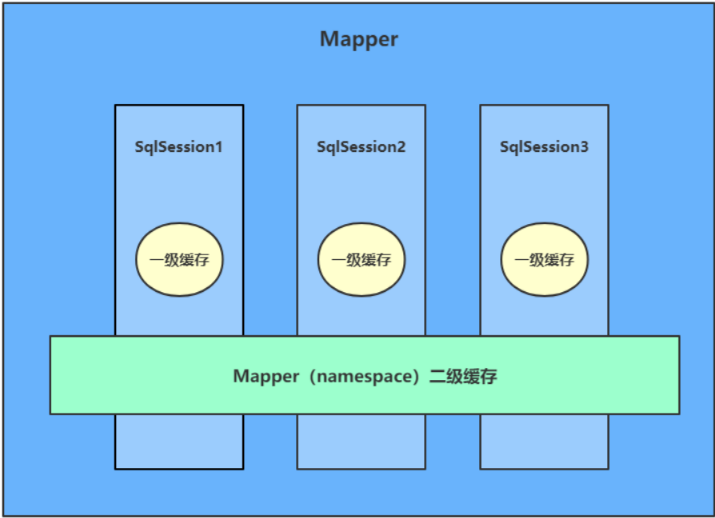
如何开启二级缓存
(1)修改MyBatis配置文件
mybatis-config中有一个全局配置属性,这个可以不用配置,因为默认开启。
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
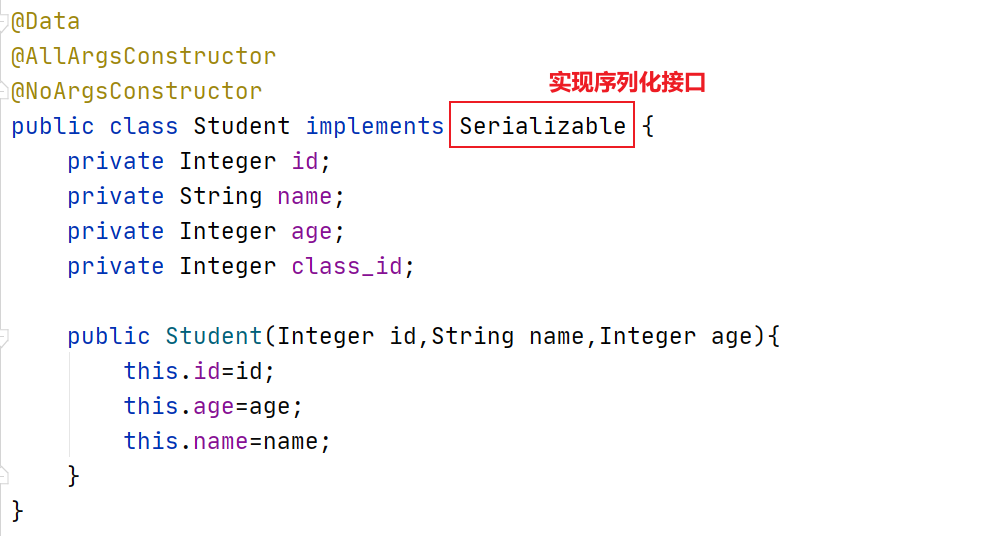
(2)让实体类实现序列化接口
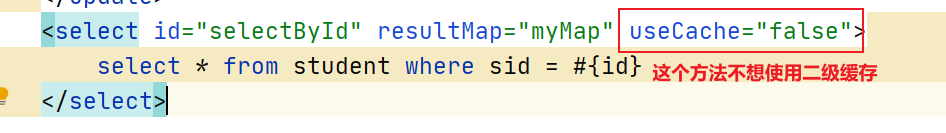
(3)使用二级缓存 映射文件

开启后,默认所有的查询方法都使用二级缓存。
如果不想某些方法使用二级缓存则使用属性useCache="false"
比如:
(4)测试
@Test
public void select() throws Exception {
Reader resourceAsReader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsReader);
//开启两个SqlSession会话
SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentDao studentDao1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
StudentDao studentDao2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
//不同的会话进行相同的查询操作
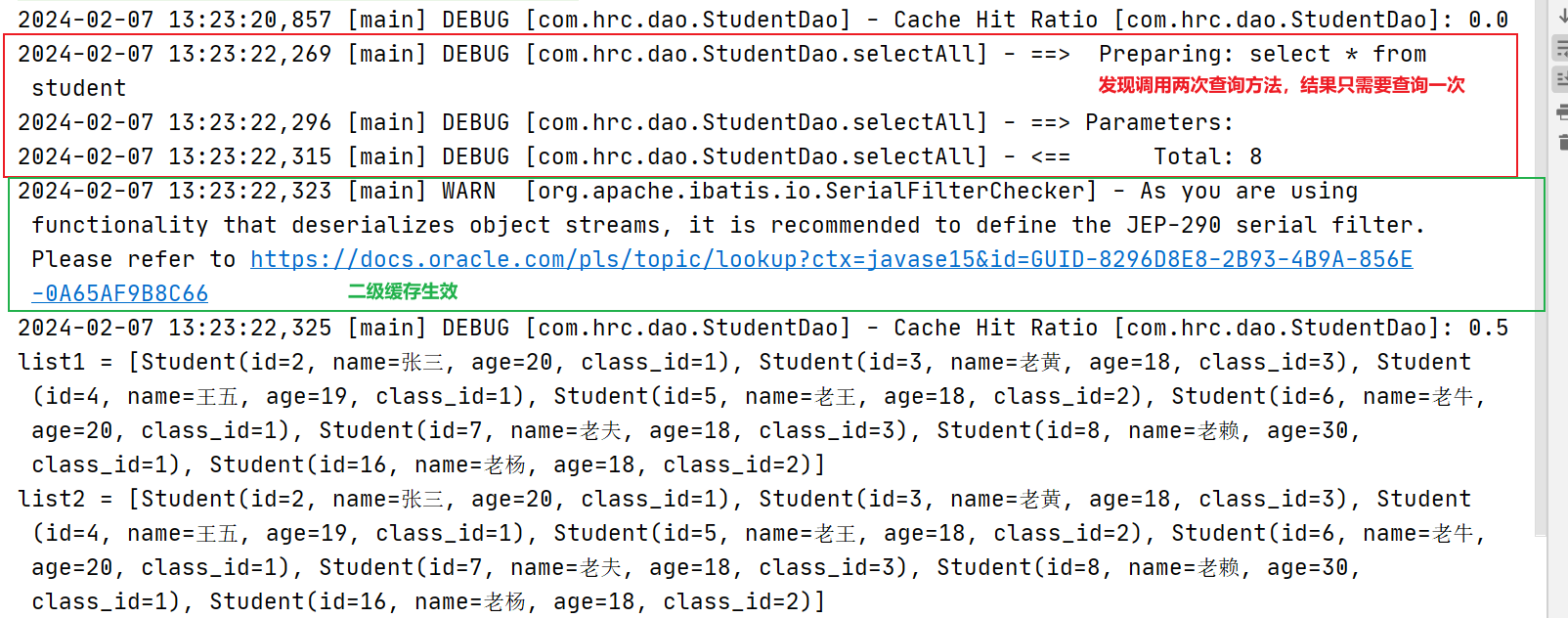
List<Student> list1 = studentDao1.selectAll();
//TODO 注意这里需要提交事务否则缓存失效
sqlSession1.commit();
List<Student> list2 = studentDao2.selectAll();
sqlSession2.commit();
//看结果是否需要二级查询
System.out.println("list1 = " + list1);
System.out.println("list2 = " + list2);
}
效果展示:





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律