3、Android-全局大喇叭-广播机制
https://www.cnblogs.com/Mrchengs/p/10678609.html
所谓的官博机制可以理解成为1对多的概念
即一个喇叭所有的人都能听到(统一范围内)
为了便于及逆行系统级别的消息通知
Android引入了一套广播机制
而且更容易进行实现。
3.1、广播机制的简介
再Andriod中的广播机制很灵活
因为Android中的每个应用程序都可以对自己感兴趣的广播进行注册
这样该程序就会只接收到自己所关心的广播内容
这些广播肯能来源于系统,也可能来源于其他 程序
Android提供了一套完整的API
允许应用程序自由的发送和接受广播
广播可以分为两种类型:
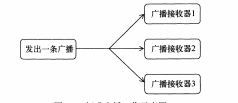
1、标准广播:
是一种完全异步执行的广播,在广播发出之后,所有的广播接收器几乎都会在同一时刻
接受这条广播信息,因此没有任何先后顺序可言。
这种广播的执行效率会高,但是同时也意味着他是无法被截断的
示意图:
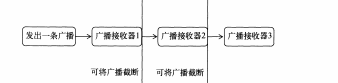
2、有序广播:
是一种同步执行的广播,再广播发出之后,同一时刻只会有一个广播接收器能接收到这条广播信息
当这个广播接器中的逻辑执行完毕后,广播才会继续传递
此种的广播接收器是先后顺序的
优先级较高的接收器可以先接收到消息
前面的广播可以截断正在传递的广播
3.2、接受系统广播
1、动态监听网络变化
广播接收器可以自由的对自己感兴趣的广播进行注册
这样再响应的广播发出时,广播接收器就能接收到该广播
注册广播的方式一把有两种:
1、代码中进行注册
2、AndroidManifest.xml中进行注册
前者动态烛台,后者静态注册
如何创建一个广播接收器:
只需要新建一个类,继承BroadcastReceiver,并且重写父类的onReceive()方法即可
当有广播来时。该方法就会执行
小实例:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private IntentFilter intentFilter;
private NetWorkChengeReceiver netWorkChengeReceiver;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.firstlayout);
ActionBar actionBar = getSupportActionBar();
if (actionBar != null){
actionBar.hide();
}
intentFilter = new IntentFilter();
intentFilter.addAction("android.net.conn.CONNECTIVITY_CHANGE");
netWorkChengeReceiver = new NetWorkChengeReceiver();
registerReceiver(netWorkChengeReceiver,intentFilter);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
unregisterReceiver(netWorkChengeReceiver);
}
class NetWorkChengeReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver{
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Log.d("net:", "onReceive: ");
Toast.makeText(context,"ntework",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
}
自定义的NetWorkChangeReceiver继承BroadCastReceiver
并且实现onReceive()方法
这里如果网络发生变化会进行显示相关的信息
再onCreate()方法中
首先创建一个IntentFilter的实例
为其添加一个值,此时的值时网络发生变化时,系统发出的一条通道信息就是上述的值
也就是说广播接收器想要监听什么广播就需要添加响应的action
然后创建一个NetWorkChangeReceiver的实例
最后调用registerReceiver()方法进行注册,将NetWorkChangeReceiver和IntentFilter的实例都传进去
这样NetWorkChangeReceiver就会接收到值为android.net.conn.CONNECTIVITY_CHANGE的广播
也就实现了监听网络的变化
动态注册的广播接收器一定要取消注册才行,这里需要再onDestroy()方法中通过unregisterReceiver()方法来实现
这里运行程序,进行测试。
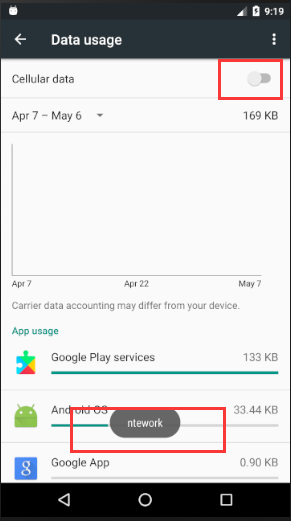
此时只是简单对网络的变化进行提示
此时还能进一步提示是否启动网络的功能
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private IntentFilter intentFilter;
private NetWorkChengeReceiver netWorkChengeReceiver;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.firstlayout);
ActionBar actionBar = getSupportActionBar();
if (actionBar != null){
actionBar.hide();
}
intentFilter = new IntentFilter();
intentFilter.addAction("android.net.conn.CONNECTIVITY_CHANGE");
netWorkChengeReceiver = new NetWorkChengeReceiver();
registerReceiver(netWorkChengeReceiver,intentFilter);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
unregisterReceiver(netWorkChengeReceiver);
}
class NetWorkChengeReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver{
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
ConnectivityManager conn = (ConnectivityManager) getSystemService(Context.CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE);
NetworkInfo net = conn.getActiveNetworkInfo();
if (net !=null && net.isAvailable()){
Toast.makeText(context,"open",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}else {
Toast.makeText(context,"close",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
}
}
再onReceive()方法中
首先通过getSystemService()得到了ConnectivityManager 的实例
这是一个系统服务类,专门用于管理网络连接的。
然后使用getActiveNetworkInfo()方法可以得到NetWorkInfoo的实例
接着调用NetworkInfo的isAvailable()方法,可以判断当前是否有网络了
这里有一个重要的问题:权限
Android为了保护用户设备的安全和隐私
做了严格规定:
如果程序需要进行一些对用户来说比较敏感的操作
就必须再配置文件中进行声明权限
否则程序将会直接崩溃
此时需要在AndroidManifest.xml文件中
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.ccrr.myapplication">
...
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE"/>
</manifest>
这是第一个权限问题
在Android中有许多需要权限才可以进行的
重新执行项目:
此时开启

2、静态注册实现开机启动
动态注册的广播接收器是可以自动的控制注册和注销
在灵活方面有很大的优势
但是也存在缺点:必须要在程序启动之后才能接到广播,因为注册的逻辑是写在onCreate()方法中的
使用静态注册可以在未启动的情况下就能接收到广播
准备一个让程序接受一条开机广播
当收到这条广播时就可以在onReceive()方法这里执行相应的逻辑
从而实现开机启动的功能
右键--new --Other--Broadcast Receiver
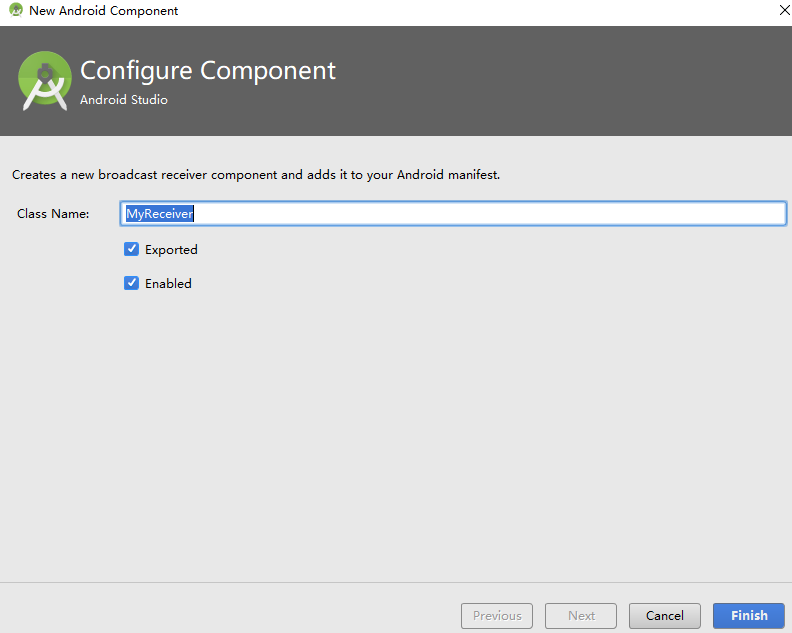
首先写广播的接收器名
Exported属性表示是否允许这个广播接收器接受本程序以外的广播
Enabled属性 表示使用启用这个广播接收器
public class BootCompleteReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
public BootCompleteReceiver() {
}
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Toast.makeText(context,"Boot complete",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
在onReceive()方法中使用其弹出一条信息
静态的广播接收器一定要在AndroidManifest.xml文件中进行注册
此时已经自动进行注册了:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.ccrr.myapplication">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity android:name=".SecondActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<receiver
android:name=".BootCompleteReceiver"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
</manifest>
出现了receiver标签所有的静态广播接收器都是在这里进行住的
通过android:name 来制定具体注册哪一个广播接收器: <action android:name="android.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED" />
同时还需要指定:<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED"/>
否则不能收到开机广播
系统启动之后会发出一条值为:android.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED的广播
可以看到在<intent-filter>标签中加了action
监听系统开机的广播也需要声明权限使用<uses-permission>
重新启动之后:
程序已经可以接受开机广播了
将模拟器关闭重启
在启动之后就会收到开机广播
这可能会失败,需要对程序进行相关的更使用:
详情可见:https://blog.csdn.net/baidu_27196493/article/details/78269674
AndroidManifest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.ccrr.myapplication">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity android:name=".SecondActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<receiver
android:name=".BootCompleteReceiver"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED" />
<action android:name="android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
</manifest>
BootCompleteReceiver.java
public class BootCompleteReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
public BootCompleteReceiver() {
}
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String ation = intent.getAction().toString();
if (ation.equals(Intent.ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED)){
Log.d("ooo","Boot");
Toast.makeText(context,"Boot complete",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
}
此时启动之后就会进行打印在屏幕上!!!
注意:
不要再onReceive()方法中添加过多的逻辑或者任何耗时的操作
因为在广播接收器中不允许开启线程的
当onReceive()方法运行较长时间没有结束时程序就会报错
广播接收器更多的是扮演一种打开程序其他组件的角色
如:创建一条状态栏的通知,或者启动一个服务
3.3、发送自定义广播
主要实践:标准广播和有序广播
1、发送标准广播
发送广播之前首先定义一个广播接收器来准备接受此广播才行
public class MyBroadcastReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
public MyBroadcastReceiver() {
}
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Toast.makeText(context,"MyBroadcastReceiver",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
在收到自定义的广播时就会弹出相关的信息。
<receiver
android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.ccrr.myapplication.MyBroadcastReceiver"></action>
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
这里的代码是自动生成的,此时需要之定义action
这里让自定的MyBroadcastReceiver 接受一条值为com.example.ccrr.myapplication.MyBroadcastReceiver的广播
因此在发送这样一条广播
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button_send"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Send Broadcast"/>
</LinearLayout>
在这里定义一个按钮,用于作为发送广播的触发点
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private IntentFilter intentFilter;
private NetWorkChengeReceiver netWorkChengeReceiver;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.firstlayout);
ActionBar actionBar = getSupportActionBar();
if (actionBar != null){
actionBar.hide();
}
Button button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button_send);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent("com.example.ccrr.myapplication.MyBroadcastReceiver");
sendBroadcast(intent);
}
});
}
}
按钮的点击事件加入自定义广播逻辑
首先构建了一个Intent对象,并且把要发送的广播值传入
然后调用Context的sendBroadcast()方法将广播发送出去com.example.ccrr.myapplication.MyBroadcastReceiver这条广播接收器就会接收到消息
此时发出去的广播就是一条标准广播

由于是使用Intent进行数据传递
因此还可以在Intent中携带数据传递给广播接收器
2、发送有序广播
广播是一种可以跨进程的通信方式
之前程序内发出的广播其他的应用程序也是可以接收到的
此时新建一个项目
新建一个广播接收器用于接收上文中的自定义广播
AnotherBroadcastReceiver.java
public class AnotherBroadcastReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
public AnotherBroadcastReceiver() {
}
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Toast.makeText(context,"AnotherBroadcastReceiver",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not yet implemented");
}
}
此时需要在onReceive()方法中进行显示一部分信息

这里的action是上文中的
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.ccrr.applicationtwo">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<receiver
android:name=".AnotherBroadcastReceiver"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.ccrr.myapplication.MyBroadcastReceiver"></action>
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
</manifest>
这里的action是上文说过的
此时点击上文中的按钮进行显示操作:
此时点击操作可以同时显示两个工程中的打印信息
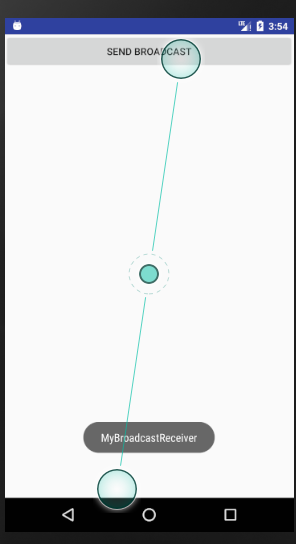

以上均是标准广播!!!
有序广播如下:
此时还是在第一个项目中进行更改

@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.firstlayout);
Button button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button_send);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent("com.example.ccrr.myapplication.MyBroadcastReceiver");
sendOrderedBroadcast(intent,null);
}
});
}
只需要改动一条代码
将sendBroadcast()方法改成sendOrderedBroadcast()
接收两个参数:
1、是Intent
2、是一个与权限相关的字符串
两个程序都可以接收到这条广播


广播接收器是由先后顺序的
前面的广播接收器还可以将广播截断,以阻止其继续传播
如何设置广播接收器的先后顺序呢?
第一个项目
<receiver
android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter android:priority="100">
<action android:name="com.example.ccrr.myapplication.MyBroadcastReceiver"></action>
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
这里指定android:priority属性给广播接收器设置优先级
优先级高的广播接收器可以先收到广播
此时将其设置为100
既然已经获得了优先权,还可以选择是否允许广播继续传递:
第一个项目中:
MyBroadcastReceiver.java
public class MyBroadcastReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
public MyBroadcastReceiver() {
}
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Toast.makeText(context,"MyBroadcastReceiver",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
abortBroadcast();
}
}
在onReceive()方法,就表示这条广播截断
此时后面的广播接收器就无法再接受此条广播
测试:
这里只有一个进行了打印!!!

以上的测试都在第一个项目中
第二个项目只是使用了一个监听
其余的都在第一个项目中进行实现!!!
3.4、使用本地广播
之前的均属于系统全局广播
即发出的广播可以被其他任何应用程序接收到
并且可以接收到来自其他任何程序的广播
这样很容易引起安全性问题
如发送一些携带关键性数据的广播可能被其他应用程序截获
或者其他程序不停的向我们的广播接收器发送各种垃圾广播
为了能够简单的解决安全问题
Android引入了一套本地广播机制
这个广播只能再内部进行
并且广播只能接受来自本地应用程序发出的广播
此时的安全性问题就都不存在了
再MainActivity中:
主要使用LocalBroadcastManager来对广播进行管理
并且提供了发送广播和注册广播接收器的方法
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private IntentFilter intentFilter;
private NetWorkChengeReceiver netWorkChengeReceiver;
//本地广播
private LocalReceiver localReceiver;
private LocalBroadcastManager localBroadcastManager;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.firstlayout);
ActionBar actionBar = getSupportActionBar();
if (actionBar != null){
actionBar.hide();
}//本地广播
//获取实例
localBroadcastManager= localBroadcastManager.getInstance(this);
intentFilter = new IntentFilter();
intentFilter.addAction("com.example.ccrr.myapplication.LocalReceiver");
localReceiver = new LocalReceiver();
//注册本地广播接收器
localBroadcastManager.registerReceiver(localReceiver,intentFilter);
Button button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button_send);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent("com.example.ccrr.myapplication.LocalReceiver");
localBroadcastManager.sendBroadcast(intent);
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();//本地广播
localBroadcastManager.unregisterReceiver(localReceiver);
}
class LocalReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver{
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Toast.makeText(context,"LocalReceiver",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
}
首先通过LocalBroadcastManager的方getInstance()方法得到一个实例
然后再注册广播接收器的时候调用LocalBroadcastManager的registerReceiver()方法
再发送广播的时候调用LocalBroadcastManager的sendBroadcast()方法
此时再按钮的点击事件中发送一条com.example.ccrr.myapplication.LocalReceiver
再LocalReceiver中接收这条消息
此时的广播接收器只能再本地进行接受,其他程序时无法进行接受的,只能在本程序内进行创博
本地广播无法通过静态注册的方式来接受的
静态注册主要是为了程序再未启动的时候也能接受广播
发送本地广播时,程序已经启动了
优点:
1、可以明确知道发送的广播不hi离开我们的程序,不用担心数据的泄露
2、其他程序无法将广播发送到程序的内部,无需担心安全漏洞的隐患
3、发送本地广播比发送系统全局广播将会更加高效


