任务调度器
1.题目描述
给你一个用字符数组tasks表示的CPU需要执行的任务列表。其中每个字母表示一种不同种类的任务。任务可以以任意顺序执行,并且每个任务都可以在1个单位时间内执行完。在任何一个单位时间,CPU可以完成一个任务,或者处于待命状态。
然而,两个相同种类的任务之间必须有长度为整数n的冷却时间,因此至少有连续n个单位时间内CPU在执行不同的任务,或者在待命状态。
你需要计算完成所有任务所需要的最短时间。
示例 1:
输入:tasks = ["A","A","A","B","B","B"], n = 2
输出:8
解释:A -> B -> (待命) -> A -> B -> (待命) -> A -> B
在本示例中,两个相同类型任务之间必须间隔长度为 n = 2 的冷却时间,而执行一个任务只需要一个单位时间,所以中间出现了(待命)状态。
2.题解
2.1 模拟
public int leastInterval(char[] tasks, int n) {
Map<Character, Integer> freq = new HashMap<Character, Integer>();
for (char ch : tasks) {
freq.put(ch, freq.getOrDefault(ch, 0) + 1);
}
// 任务总数
int m = freq.size();
List<Integer> nextValid = new ArrayList<Integer>();
List<Integer> rest = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Set<Map.Entry<Character, Integer>> entrySet = freq.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Character, Integer> entry : entrySet) {
int value = entry.getValue();
nextValid.add(1);
rest.add(value);
}
int time = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < tasks.length; ++i) {
++time;
int minNextValid = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
if (rest.get(j) != 0) {
minNextValid = Math.min(minNextValid, nextValid.get(j));
}
}
time = Math.max(time, minNextValid);
int best = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
if (rest.get(j) != 0 && nextValid.get(j) <= time) {
if (best == -1 || rest.get(j) > rest.get(best)) {
best = j;
}
}
}
nextValid.set(best, time + n + 1);
rest.set(best, rest.get(best) - 1);
}
return time;
}
需要注意的是,执行任务是需要时间的,这里第一个任务执行完时time为1。
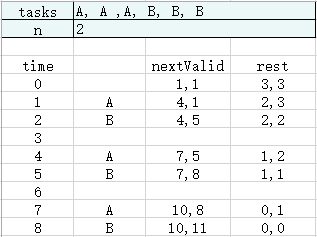
根据我们的策略,我们需要选择不在冷却中并且剩余执行次数最多的那个任务。
这里第一个任务既可以是任务A,也可以是任务B,于是按照遍历的顺序,先执行任务A。
执行完第一个任务A,任务A的执行次数减1,同时任务A的下一次执行的time为4。
当time为2时,只能执行任务B。执行完第二个任务B,任务B的执行次数减1,同时任务A的下一次执行的time为5。
当time为3时,发现任务A和任务B都在冷却中,而任务A的time离现在更近,所以直接跳到任务A的time去执行任务A。
解释代码:
以下代码表示跳到下一个执行任务的time。
// ...
time = Math.max(time, minNextValid);
// ...
以下代码的rest.get(j) > rest.get(best)表示选择不在冷却中并且剩余执行次数最多的那个任务。
int best = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
if (rest.get(j) != 0 && nextValid.get(j) <= time) {
if (best == -1 || rest.get(j) > rest.get(best)) {
best = j;
}
}
}
2.2 构造
public int leastInterval(char[] tasks, int n) {
Map<Character, Integer> freq = new HashMap<Character, Integer>();
// 最多的执行次数
int maxExec = 0;
for (char ch : tasks) {
int exec = freq.getOrDefault(ch, 0) + 1;
freq.put(ch, exec);
maxExec = Math.max(maxExec, exec);
}
// 具有最多执行次数的任务数量
int maxCount = 0;
Set<Map.Entry<Character, Integer>> entrySet = freq.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Character, Integer> entry : entrySet) {
int value = entry.getValue();
if (value == maxExec) {
++maxCount;
}
}
return Math.max((maxExec - 1) * (n + 1) + maxCount, tasks.length);
}
maxExec为最多的执行次数,maxCount为具有最多执行次数的任务数量,n为任务的冷却时间,tasks为任务列表。以tasks = ["A","A","A"], n = 2为例,我们使用一个宽为n+1的矩阵可视化地展现执行任务A的时间点。
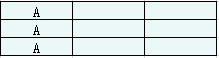
注意到这里两个任务A之间间隔两个格子,任务A正好都在同一列上,计算所需时间为(3 - 1)*(2 + 1) + 1 = 7。
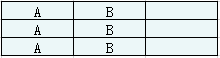
同理,以tasks = ["A","A","A","B","B","B"], n = 2为例,计算所需时间为(3 - 1)*(2 + 1) + 2 = 8。
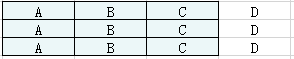
如果maxCount > n + 1,那么计算所需的最短时间为任务的总数tasks.length。
参考:


