Django入门项目实践(中)
4.用户账户
4.1 让用户能够输入数据
添加新主题
# untitled/learning_logs/forms.py
from django import forms
from .models import Topic, Entry
class TopicForm(forms.ModelForm):
class Meta:
model = Topic
fields = ['text']
labels = {'text':''}
"""定义learning_logs的URL模式"""
# untitled/learning_logs/urls.py
from django.conf.urls import url
from . import views
app_name = 'learning_logs'
urlpatterns = [
# 主页
url(r'^$', views.index, name='index'),
url(r'^topics/$', views.topics, name='topics'),
url(r'^topics/(?P<topic_id>\d+)/$', views.topic, name='topic'),
url(r'^new_topic/$', views.new_topic, name='new_topic'),
]
# untitled/learning_logs/views.py
from django.http import HttpResponseRedirect
from django.shortcuts import render
from django.urls import reverse
from learning_logs.forms import TopicForm
from learning_logs.models import Topic
#···
def new_topic(request):
"""添加新主题"""
if request.method != 'POST':
form = TopicForm()
else:
form = TopicForm(request.POST)
if form.is_valid():
form.save()
return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse('learning_logs:topics'))
context = {'form':form}
return render(request, 'learning_logs/new_topic.html', context)
#···
<!-- untitled/templates/learning_logs/new_topic.html -->
{% extends "learning_logs/base.html" %}
{% block content %}
<p>Add a new topic:</p>
<form action="{% url 'learning_logs:new_topic' %}" method='post'>
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_p }}
<button name="submit">add topic</button>
</form>
{% endblock content %}
添加新条目
(略)
编辑新条目
(略)
4.2 创建用户账户
应用程序users
# untitled/untitled/settings.py
# ···
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
# 我的应用程序
'learning_logs',
'users'
]
# ···
# untitled/untitled/urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from django.conf.urls import include, url
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
url(r'^users/', include('users.urls', namespace='users')),
url(r'', include('learning_logs.urls', namespace='learning_logs')),
]
4.2.1 登录
由于Django版本的问题,下面的URL模式跟《Python编程从入门到实践》的示例有点不一样。
"""为应用程序users定义URL模式"""
# untitled/users/urls.py
from django.contrib.auth.views import LoginView
from django.urls import path
app_name = 'users'
urlpatterns = [
path('login/', LoginView.as_view(template_name='users/login.html'), name="login"),
]
<!-- untitled/templates/users/login.html -->
{% extends "learning_logs/base.html" %}
{% block content %}
{% if form.errors %}
<p>Your username and password didn't match. Please try again.</p>
{% endif %}
<form method="post" action="{% url 'users:login' %}">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_p }}
<button name="submit">log in</button>
<input type="hidden" name="next" value="{% url 'learning_logs:index' %}" />
</form>
{% endblock content %}
<!-- untitled/templates/learning_logs/base.html -->
<p>
<a href="{% url 'learning_logs:index' %}">Learning Log</a> -
<a href="{% url 'learning_logs:topics' %}">Topics</a> -
{% if user.is_authenticated %}
Hello, {{ user.username }}.
{% else %}
<a href="{% url 'users:login' %}">log in</a>
{% endif %}
</p>
{% block content %}{% endblock %}
4.2.2 注销
# untitled/users/urls.py
from django.contrib.auth.views import LoginView
from django.urls import path
from django.conf.urls import url
from . import views
app_name = 'users'
urlpatterns = [
path('login/', LoginView.as_view(template_name='users/login.html'), name="login"),
url(r'^logout/$', views.logout_view, name='logout'),
]
注意下面导入的是from django.urls import reverse,而不是from django.core.urlresolvers import reverse。
# untitled/users/views.py
from django.http import HttpResponseRedirect
from django.urls import reverse
from django.contrib.auth import logout
def logout_view(request):
"""Log the user out."""
logout(request)
return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse('learning_logs:index'))
4.2.3 注册
# untitled/users/views.py
from django.contrib.auth.forms import UserCreationForm
from django.http import HttpResponseRedirect
from django.shortcuts import render
from django.urls import reverse
from django.contrib.auth import logout, authenticate, login
# ···
def register(request):
if request.method != 'POST':
form = UserCreationForm()
else:
form = UserCreationForm(data=request.POST)
if form.is_valid():
new_user = form.save()
authenticated_user = authenticate(username=new_user.username, password=request.POST['password1'])
login(request, authenticated_user)
return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse('learning_logs:index'))
context = {'form':form}
return render(request, "users/register.html", context)
<!-- untitled/templates/users/register.html -->
{% extends "learning_logs/base.html" %}
{% block content %}
<form method="post" action="{% url 'users:register' %}">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_p }}
<button name="submit">register</button>
<input type="hidden" name="next" value="{% url 'learning_logs:index' %}" />
</form>
{% endblock content %}
4.3 让用户拥有自己的数据
使用@login_required限制访问
# untitled/learning_logs/views.py
from django.contrib.auth.decorators import login_required
from django.http import HttpResponseRedirect
from django.shortcuts import render
# ···
@login_required
def topics(request):
topics = Topic.objects.order_by('date_added')
context = {'topics' : topics}
return render(request, 'learning_logs/topics.html', context)
# ···
# untitled/untitled/settings.py
# ···
LOGIN_URL = '/users/login/'
将数据关联到用户
注意这行代码owner = models.ForeignKey('auth.User', on_delete=models.CASCADE)的写法。
# untitled/learning_logs/models.py
from django.db import models
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
class Topic(models.Model):
"""A topic the user is learning about."""
text = models.CharField(max_length=200)
date_added = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True)
owner = models.ForeignKey('auth.User', on_delete=models.CASCADE)
def __str__(self):
"""Return a string representation of the model."""
return self.text
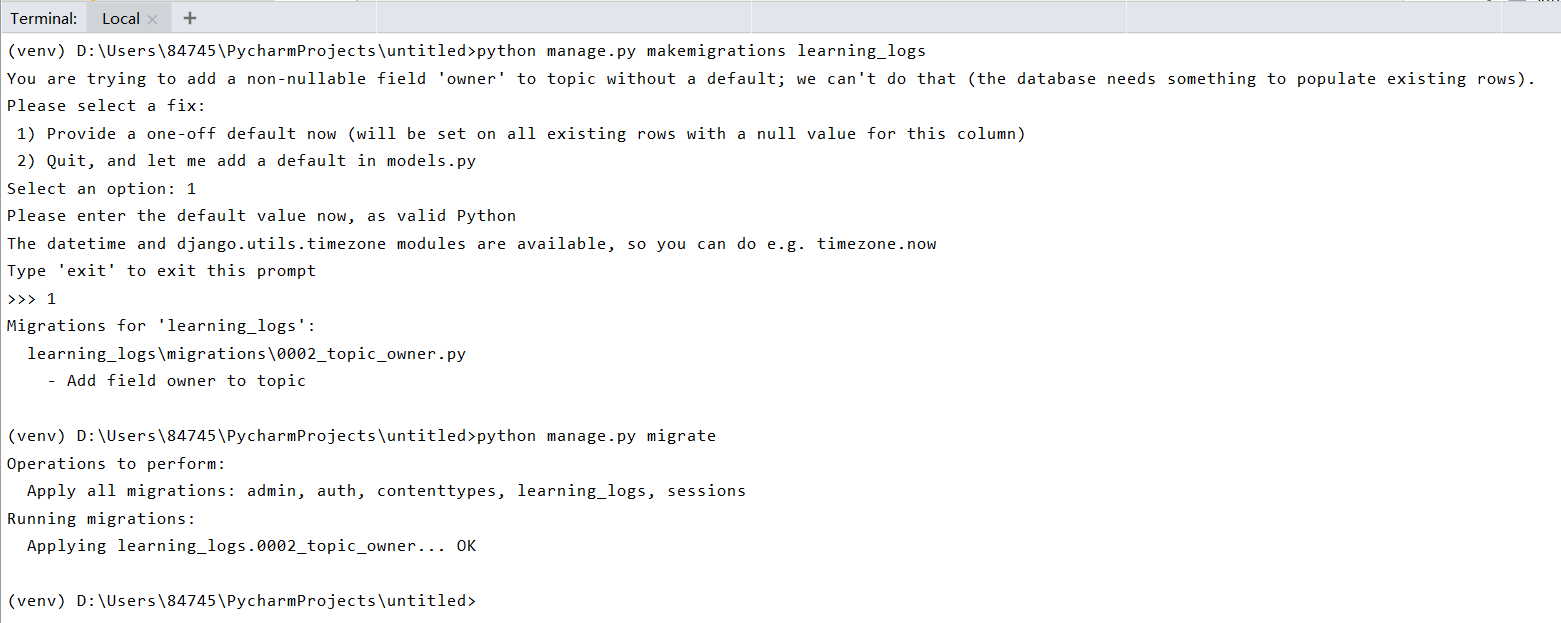
我们迁移数据库时,Django将对数据库进行修改,使其能够存储主题和用户之间的关联。
执行python manage.py makemigrations learning_logs时,我们为外键值指定默认值。
只允许用户访问自己的主题
# untitled/learning_logs/views.py
# ···
@login_required
def topics(request):
topics = Topic.objects.filter(owner=request.user).order_by('date_added')
context = {'topics' : topics}
return render(request, 'learning_logs/topics.html', context)
# ···
保护用户的主题
# untitled/learning_logs/views.py
# ···
@login_required
def topic(request, topic_id):
topic = Topic.objects.get(id=topic_id)
if topic.owner != request.user:
raise Http404
entries = topic.entry_set.order_by('-date_added')
context = {'topic': topic, 'entries': entries}
return render(request, 'learning_logs/topic.html', context)
# ···
保护页面edit_entry
# untitled/learning_logs/views.py
# ···
@login_required
def edit_entry(request, entry_id):
"""Edit an existing entry."""
entry = Entry.objects.get(id=entry_id)
topic = entry.topic
if topic.owner != request.user:
raise Http404
if request.method != 'POST':
# Initial request; pre-fill form with the current entry.
form = EntryForm(instance=entry)
else:
# POST data submitted; process data.
form = EntryForm(instance=entry, data=request.POST)
if form.is_valid():
form.save()
return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse('learning_logs:topic',
args=[topic.id]))
context = {'entry': entry, 'topic': topic, 'form': form}
return render(request, 'learning_logs/edit_entry.html', context)
将新主题关联到当前用户
# untitled/learning_logs/views.py
# ···
@login_required
def new_topic(request):
"""添加新主题"""
if request.method != 'POST':
form = TopicForm()
else:
form = TopicForm(request.POST)
if form.is_valid():
new_topic = form.save(commit=False)
new_topic.owner = request.user
new_topic.save()
return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse('learning_logs:topics'))
context = {'form':form}
return render(request, 'learning_logs/new_topic.html', context)
# ···
参考资料:《Python编程从入门到实践》—【美】Eric Matthes 著


