Java多线程学习:(wait,notify)--(await,signal)--(park,unpark)
前置Java多线程学习知识点:https://www.cnblogs.com/gzhcsu/p/7674894.html
本文主要对Java.util.concurrent中锁的相关对比学习。
他们分别是:
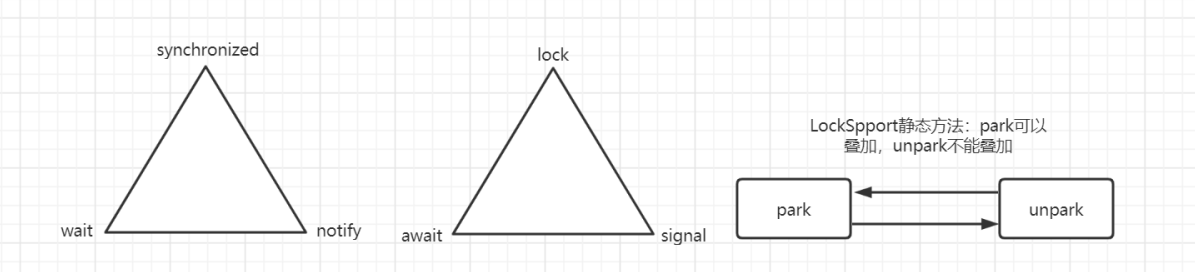
① Object中wait和notify;
② Lock中lock.newCondition:condition.await()和condition.signal();
③ LockSupport中静态方法park和unpark;
一、先上结论:
① 对于Object中wait和notify:必须在锁中使用,这里指synchronized,并且wait方法要先于notify,否则wait方法会一直阻塞该该线程。
② Lock中lock.newCondition:condition.await()和condition.signal():必须在锁中使用,这里指lock.lock()之后,并且await方法要先于singnal,否则await方法会一直阻塞该该线程。
③ LockSupport优势,优势1:不需要再锁中进行;优势二:park方法可以不先于unpark方法。
二、测试代码
1 public class LockAQS { 2 private static Object objectLock = new Object(); 3 private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 4 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 // testWaitAndNotify(); 8 // testLockAndUnLock(); 9 testParkAndUnPark(); 10 } 11 12 static void testParkAndUnPark(){ 13 try { 14 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); 15 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } 18 Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> { 19 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "come in"); 20 LockSupport.park(); 21 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t " + "被唤醒"); 22 }); 23 t1.start(); 24 25 new Thread(()->{ 26 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t " + "通知其他"); 27 LockSupport.unpark(t1); 28 }).start(); 29 30 } 31 32 static void testLockAndUnLock() { 33 Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); 34 new Thread(() -> { 35 try { 36 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); 37 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 38 e.printStackTrace(); 39 } 40 try { 41 lock.lock(); 42 try { 43 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + " come in"); 44 condition.await(); 45 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 46 e.printStackTrace(); 47 } 48 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t " + "被唤醒"); 49 } finally { 50 lock.unlock(); 51 } 52 }, "LockA").start(); 53 54 new Thread(() -> { 55 try { 56 lock.lock(); 57 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t " + "通知其他"); 58 condition.signal(); 59 } finally { 60 lock.unlock(); 61 } 62 }, "LockB").start(); 63 } 64 65 static void testWaitAndNotify() { 66 new Thread(() -> { 67 try { 68 Thread.sleep(2000); 69 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 70 e.printStackTrace(); 71 } 72 synchronized (objectLock) { 73 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "come in"); 74 try { 75 objectLock.wait(); 76 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 77 e.printStackTrace(); 78 } 79 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t " + "被唤醒"); 80 } 81 }, "A").start(); 82 83 new Thread(() -> { 84 synchronized (objectLock) { 85 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "通知其他"); 86 objectLock.notify(); 87 } 88 }, "B").start(); 89 } 90 }
三、分析LockSupport
① 类源码说明:park阻塞当前线程,unpark发放许可证,不同于Semaphores,许可证不可累加计算,至多一个。
/** * Basic thread blocking primitives for creating locks and other * synchronization classes. * * <p>This class associates, with each thread that uses it, a permit * (in the sense of the {@link java.util.concurrent.Semaphore * Semaphore} class). A call to {@code park} will return immediately * if the permit is available, consuming it in the process; otherwise * it <em>may</em> block. A call to {@code unpark} makes the permit * available, if it was not already available. (Unlike with Semaphores * though, permits do not accumulate. There is at most one.)
② LockSupport.parK()方法:阻塞现场直到右许可证。
/** * Disables the current thread for thread scheduling purposes unless the * permit is available. * ... */ public static void park() { UNSAFE.park(false, 0L); }
③ upark方法,给指定的线程发放许可证。
/** * Makes available the permit for the given thread, if it * was not already available. If the thread was blocked on * {@code park} then it will unblock. Otherwise, its next call * to {@code park} is guaranteed not to block. This operation * is not guaranteed to have any effect at all if the given * thread has not been started. * * @param thread the thread to unpark, or {@code null}, in which case * this operation has no effect */ public static void unpark(Thread thread) { if (thread != null) UNSAFE.unpark(thread); }
posted on 2020-12-20 16:49 betterLearing 阅读(995) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?