[USACO12FEB]附近的牛Nearby Cows
题目概述
题目描述
Farmer John has noticed that his cows often move between nearby fields. Taking this into account, he wants to plant enough grass in each of his fields not only for the cows situated initially in that field, but also for cows visiting from nearby fields. Specifically, FJ's farm consists of N fields (1 <= N <= 100,000), where some pairs of fields are connected with bi-directional trails (N-1 of them in total). FJ has designed the farm so that between any two fields i and j, there is a unique path made up of trails connecting between i and j. Field i is home to C(i) cows, although cows sometimes move to a different field by crossing up to K trails (1 <= K <= 20). FJ wants to plant enough grass in each field i to feed the maximum number of cows, M(i), that could possibly end up in that field -- that is, the number of cows that can potentially reach field i by following at most K trails. Given the structure of FJ's farm and the value of C(i) for each field i, please help FJ compute M(i) for every field i.
给你一棵 n 个点的树,点带权,对于每个节点求出距离它不超过 k 的所有节点权值和 mi。
输入输出格式
输入格式
* Line 1: Two space-separated integers, N and K. * Lines 2..N: Each line contains two space-separated integers, i and j (1 <= i,j <= N) indicating that fields i and j are directly connected by a trail. * Lines N+1..2N: Line N+i contains the integer C(i). (0 <= C(i) <= 1000)
第一行两个正整数 n,k。 接下来 n−1 行,每行两个正整数 u,v,表示 u,v 之间有一条边。
最后 n 行,每行一个非负整数 ci,表示点权。
输出格式
* Lines 1..N: Line i should contain the value of M(i).
输出 n 行,第 i 行一个整数表示 mi。
输入输出样例
输入样例 #1
6 2
5 1
3 6
2 4
2 1
3 2
1
2
3
4
5
6
输出样例 #1
15
21
16
10
8
11
数据范围
样例解释
There are 6 fields, with trails connecting (5,1), (3,6), (2,4), (2,1), and (3,2). Field i has C(i) = i cows. Field 1 has M(1) = 15 cows within a distance of 2 trails, etc.
对于 100% 的数据:1≤n≤105,1≤k≤20,0≤ci≤1000
解题报告
题意理解
给你一棵 n 个点的树,点带权,对于每个节点求出距离它不超过 k 的所有节点权值和 mi。
算法解析
- 树形结构
- 统计一定距离的点权和
- 树上节点特别多,基本上要线性复杂度
- 程序员的第六感
综上所述,我们得知这道题目需要使用,树形DP算法。
然后我们不难设计出,状态表示
因此,我们不难发现,在这个状态表示中,状态转移,只会从儿子节点中转移过来。
利用儿子节点,更新父亲节点。
但是,题目并没有如此简单。
在本题中,对于一个树上节点,他可以被那些节点转移过来呢
- 子辈节点(儿子,子树,兄弟的子树)
- 同辈节点(兄弟)
- 祖辈节点(父亲,祖先)
对于,子辈,同辈,这些节点的转移,显然都是满足,树形DP的自下而上的转移方式。
但是,祖辈节点们,可就是完全违背,我们树形DP的转移方式。
怎么办?
我们不妨,再来一次转移,而且本次转移,自上而下
因此,我们利用父亲节点,更新儿子节点
那么这里的
我们根据这张图片,分析一波
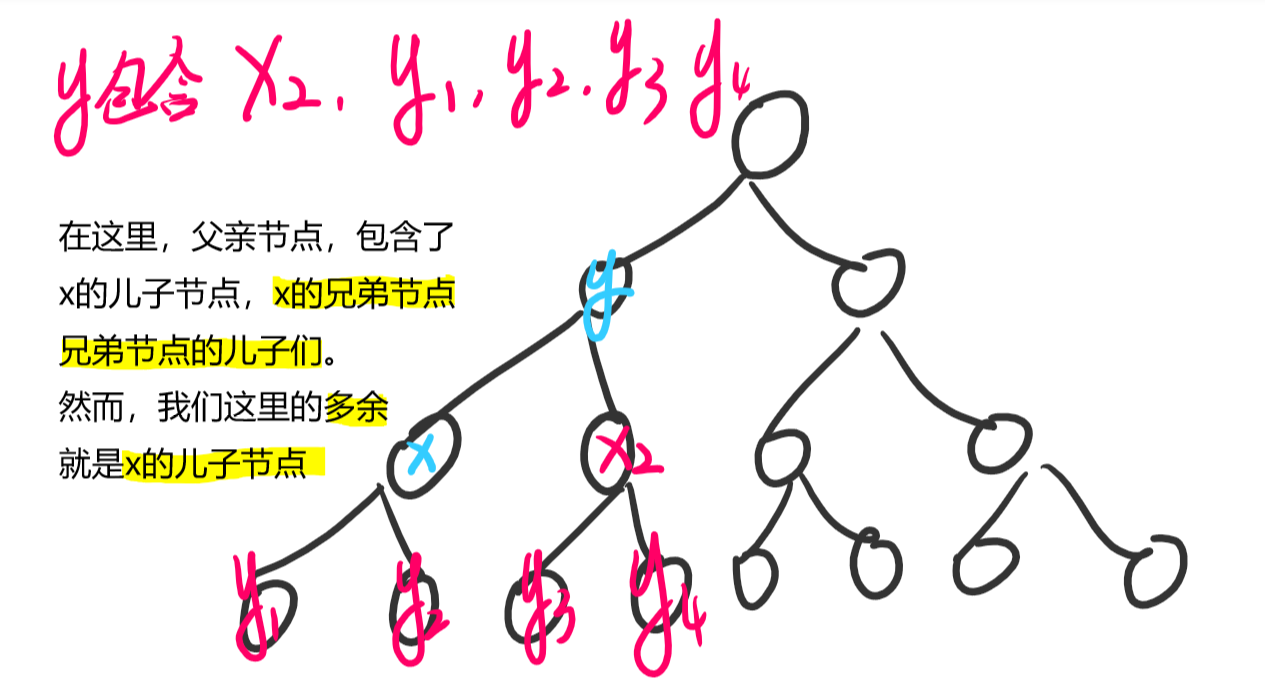
父亲的转移,让我们的同辈节点,和同辈的儿子节点都累加了。
此时,我们发现
- 子辈节点,多。
- 同辈节点,刚好
- 父辈节点,刚好
我们发现,x的距离为2的点,包含到k距离为1的k的儿子们.
而这些点位于k的子树中的点已经在第一次转移,加入到里面去了。
因此,我们不得不,容斥原理,处理多余的子辈节点
推到出来,就是
代码解析
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=110000,K=21;
int n,k,a[N],f[N][K],deep[N];
vector<int> g[N];
void dfs(int x,int s)
{
deep[x]=deep[s]+1;
for(int y:g[x])
{
if (y==s)
continue;
dfs(y,x);
for(int p=1; p<=k; p++)
f[x][p]+=f[y][p-1];
}
}
void dfs2(int x)
{
for(int y:g[x])
{
if (deep[y]<=deep[x])
continue;
for(int p=k; p>=2; p--)
f[y][p]-=f[y][p-2];
for(int p=1; p<=k; p++)
f[y][p]+=f[x][p-1];
dfs2(y);
}
}
inline void init()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);
for(int i=1; i<n; i++)
{
int a,b;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
g[a].push_back(b);
g[b].push_back(a);
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
scanf("%d",&f[i][0]);
dfs(1,0);
dfs2(1);
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
int ans=0;
for(int j=0; j<=k; j++)
ans+=f[i][j];
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
}
signed main()
{
init();
return 0;
}
本文作者:秦淮岸灯火阑珊
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/gzh-red/p/11844919.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。




【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 智能桌面机器人:用.NET IoT库控制舵机并多方法播放表情
· Linux glibc自带哈希表的用例及性能测试
· 深入理解 Mybatis 分库分表执行原理
· 如何打造一个高并发系统?
· .NET Core GC压缩(compact_phase)底层原理浅谈
· 新年开篇:在本地部署DeepSeek大模型实现联网增强的AI应用
· DeepSeek火爆全网,官网宕机?本地部署一个随便玩「LLM探索」
· Janus Pro:DeepSeek 开源革新,多模态 AI 的未来
· 互联网不景气了那就玩玩嵌入式吧,用纯.NET开发并制作一个智能桌面机器人(三):用.NET IoT库
· 上周热点回顾(1.20-1.26)