Java中数据类型可以分为两类
1、基本数据类型(byte,short,char,int,float,double,long,boolean)
2、复合数据类型(类,String等)
Δ在基本数据类型中他们之间的比较,是==比较他们的值,当使用==来判断两个变量是否相等的时候,如果是基本数据类型,值相等,那么就返回true,如下代码:
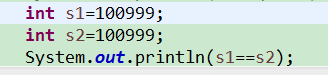
Δ在复合数据类型中当他们用(==)进行比较的时候,比较的是他们在内存中的存放地址,所以除非是同一个new出来的对象,他们的比较后的结果为true,否则比较后结果为false。
JAVA当中所有的类都是继承于Object这个基类的,在Object中的基类中定义了一个equals的方法,这个方法的初始行为是比较对象的内存地址(this==obj),但在一些类库当中这个方法被覆盖掉了,如String,Integer,Date在这些类当中equals有其自身的实现,而不再是比较类在堆内存中的存放地址了。
对于复合数据类型之间进行equals比较,在没有覆写equals方法的情况下,他们之间的比较还是基于他们在内存中的存放位置的地址值的,因为Object的equals方法也是用双等号(==)进行比较的,所以比较后的结果跟双等号(==)的结果相同。如下代码:
class Person{
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person(String name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
public Person() {
super();
}
}
@Test
public void test02(){
Person p1=new Person("张三");
Person p2=new Person("张三");
System.out.println(p1==p2);
System.out.println(p1.equals(p2));
}
返回结果:false,false
那么我们再看一段代码
@Test
public void test03(){
String s1=new String("abc");
String s2=new String("abc");
System.out.println(s1==s2);
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
}
返回结果:false,true
因为String将equals重写了,看重写之后的JDK代码
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
if (this == anObject) {
return true;
}
if (anObject instanceof String) {
String anotherString = (String)anObject;
int n = value.length;
if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = 0;
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i] != v2[i])
return false;
i++;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
因为String底层实际存储是char数组,所以,JDK是while一个个索引的比较值,只要值相等,那么即返回true
那么我们再看这段代码:
@Test
public void test03(){
String s1="abc";
String s2="abc";
System.out.println(s1==s2);
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
}
返回true,true,因为s1,s2都引用同一个String对象abc,内存指向相等故返回true,这里需要解释的是字符串缓存池的概念,在s2="abc"时,程序会先到String缓存池中寻找有相同值的对象,找到之后直接引用!
那么再看一段代码
@Test
public void test03(){
String s1="abc";
String s2=new String("abc");
System.out.println(s1==s2);
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
}
返回,false,true
因为s2创建一个新的abc对象在内存中,值相同但是位置不同!
再看一段代码
@Test
public void test03(){
String s1="abc";
String s2=new String("abc");
s2=s2.intern();
System.out.println(s1==s2);
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
}
返回true,true,看一下intern背后做的哪些工作?,看源码说明:
/**
* Returns a canonical representation for the string object.
* <p>
* A pool of strings, initially empty, is maintained privately by the
* class {@code String}.
* <p>
* When the intern method is invoked, if the pool already contains a
* string equal to this {@code String} object as determined by
* the {@link #equals(Object)} method, then the string from the pool is
* returned. Otherwise, this {@code String} object is added to the
* pool and a reference to this {@code String} object is returned.
* <p>
* It follows that for any two strings {@code s} and {@code t},
* {@code s.intern() == t.intern()} is {@code true}
* if and only if {@code s.equals(t)} is {@code true}.
* <p>
* All literal strings and string-valued constant expressions are
* interned. String literals are defined in section 3.10.5 of the
* <cite>The Java™ Language Specification</cite>.
*
* @return a string that has the same contents as this string, but is
* guaranteed to be from a pool of unique strings.
*/
public native String intern();
* When the intern method is invoked, if the pool already contains a
* string equal to this {@code String} object as determined by
* the {@link #equals(Object)} method, then the string from the pool is
* returned. Otherwise, this {@code String} object is added to the
* pool and a reference to this {@code String} object is returned.
这句话意思:如果池中包含一个字符串等于对象所引用的对象方法,那么直接从池中返回
所以上面代码最后返回true,true!
全文完,感谢您的耐心阅读~
欢迎大家关注我的公众号




