前言
在大型分布式集群系统中由于日志是分布在不同服务器上,在排错过程中需要登录不同服务器grep | tail 查看日志是非常不方便,所以需要统一的日志管理平台聚合收集日志。比如阿里的sls(收费产品)…
但是一般实际开发过程中存在4套环境,dev(开发),test(测试),pre(预发验证),和prod(生产)。如果你的生产环境使用的是全套云服务且忽略成本,那你可以直接使用云服务厂商的日志组件。单如果你想节约成本,有没有不收费又好用的日志组件呢?有,ELK。
ELK是目前最流行的日志搜索组合组件,分别是Elasticsearch+Logstash+Kibana组件的简称,但是FileBeat又是什么玩意儿呢?请往下看。
本文环境:
Windows10+(Elasticsearch+Logstash+Kibana+FileBeat)7.8.0
为什么是windows环境,首先在搭建ELK环境过程中需要大量编写测试一些配置文件要不停调试,配置文件在(Linux | windows)环境是通用的,为了方便且更好的写好这篇文章,所以直接用我本地环境。本文以实战为主,拒绝花里胡巧没用的。ok,在动手搭建之前先简单介绍一下这4个组件到底是干什么的。
1、ElasticSearch
1、基于Lucene的分布式全文搜索引擎,2、基于rest接口,3、java语言开发,源码开放。从这3点可以看出,1、扩展方便为分布式而生,2、基于rest接口访问,无关对接语言,3、开源免费,研发实力足够强可以自己定制。es天生适合做大数据搜索存储
2、Logstash
Logstash是一个开源的服务器端数据处理管道,可以同时从多个数据源获取数据,并对其进行转换,然后将其发送到你最喜欢的“存储
简单解释下,这个组件是专门收集日志,并且对日志进行加工处理格式化,然后分发到你指定的地方(mysql,mq,nosql)的一个数据处理管道。基于java环境,但是特别占用内存
3、Kibana
开源的分析和可视化web平台,主要是和es搭配使用。
4、FileBeat
轻量级的日志采集工具,它和Logstash是同一个作者,因为Logstash太笨重且吃内存,所有作者新出了这么一个组件,FileBeat可以一个进程搜集服务器中所有指定的多个日志文件。Logstash做不到的,但是Logstash强大的数据处理和数据分发能力比FileBeat做的好。
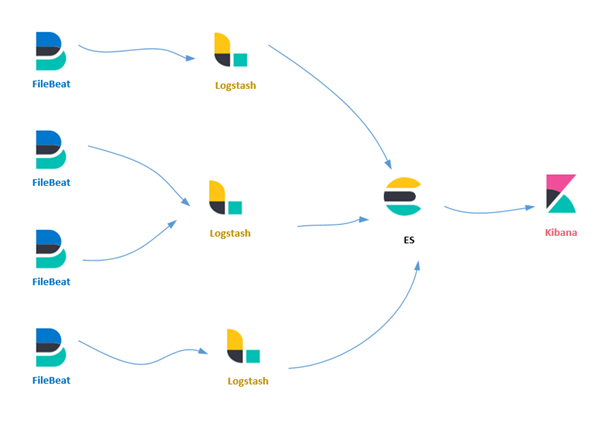
下面是这4个组件简单的逻辑关系图
在搭建之前先下载这4个组件,https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/
1、启动Elasticsearch
如果你是Linux,请异步 这里
修改es配置文件
以下是我的配置:
# ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration ========================= # # NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings. # Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you # understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences. # # The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists # the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster. # # Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options: # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html # # ---------------------------------- Cluster ----------------------------------- # # Use a descriptive name for your cluster: # #cluster.name: my-application # # ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------ # # Use a descriptive name for the node: #节点,名字自定义 node.name: node-1 # # Add custom attributes to the node: # #node.attr.rack: r1 # ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------ # # Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma): #数据存储位置 path.data: E:\elk\elasticsearch-7.8.0-windows-x86_64\elasticsearch-7.8.0\data # # Path to log files: #日志存储位置 path.logs: E:\elk\elasticsearch-7.8.0-windows-x86_64\elasticsearch-7.8.0\logs # # ----------------------------------- Memory ----------------------------------- # # Lock the memory on startup: # #bootstrap.memory_lock: true # # Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available # on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this # limit. # # Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory. # # ---------------------------------- Network ----------------------------------- # # Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6): #绑定访问的主机ip,0.0.0.0 是不限制 network.host: 0.0.0.0 # # Set a custom port for HTTP: #绑定的访问端口,默认就是9200 http.port: 9200 # # For more information, consult the network module documentation. # # --------------------------------- Discovery ---------------------------------- # # Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when this node is started: # The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"] # #discovery.seed_hosts: ["host1", "host2"] # # Bootstrap the cluster using an initial set of master-eligible nodes: #集群初始化的主节点,这个需要包含node.name 否则会报错 cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"] # # For more information, consult the discovery and cluster formation module documentation. # # ---------------------------------- Gateway ----------------------------------- # # Block initial recovery after a full cluster restart until N nodes are started: # #gateway.recover_after_nodes: 3 # # For more information, consult the gateway module documentation. # # ---------------------------------- Various ----------------------------------- # # Require explicit names when deleting indices: # #action.destructive_requires_name: true # 这些是es-head需要的配置 http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*" node.master: true node.data: true
修改完成直接双击启动
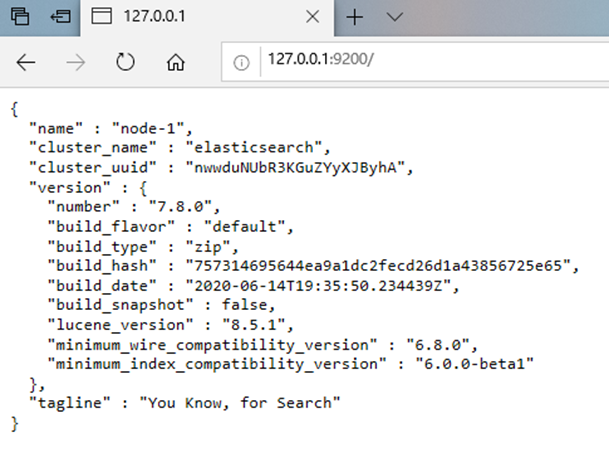
浏览器访问如下,则启动成功。
2、Kibana启动
修改Kibana配置文件
# Kibana is served by a back end server. This setting specifies the port to use. #访问端口,默认就是5601 server.port: 5601 # Specifies the address to which the Kibana server will bind. IP addresses and host names are both valid values. # The default is 'localhost', which usually means remote machines will not be able to connect. # To allow connections from remote users, set this parameter to a non-loopback address. server.host: "0.0.0.0" # Enables you to specify a path to mount Kibana at if you are running behind a proxy. # Use the `server.rewriteBasePath` setting to tell Kibana if it should remove the basePath # from requests it receives, and to prevent a deprecation warning at startup. # This setting cannot end in a slash. #server.basePath: "" # Specifies whether Kibana should rewrite requests that are prefixed with # `server.basePath` or require that they are rewritten by your reverse proxy. # This setting was effectively always `false` before Kibana 6.3 and will # default to `true` starting in Kibana 7.0. #server.rewriteBasePath: false # The maximum payload size in bytes for incoming server requests. #server.maxPayloadBytes: 1048576 # The Kibana server's name. This is used for display purposes. #server.name: "your-hostname" # The URLs of the Elasticsearch instances to use for all your queries. elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://localhost:9200"]
双击启动即可
启动成功页面
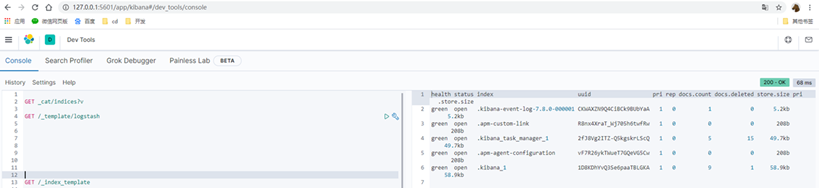
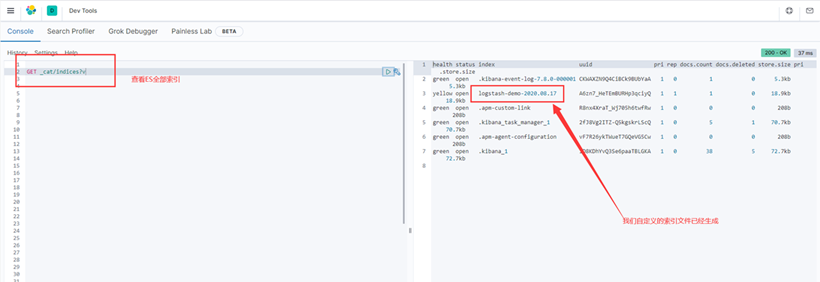
启动成功之后可以在Kibana中查看一下当前es中存在的索引
3、启动logstash
编写一个logstash_test.conf配置文件,体验一下Logstash
input {
stdin {}
}
output {
stdout{ }
}
启动命令
.\bin\logstash.bat -f .\config\logstash_test.conf
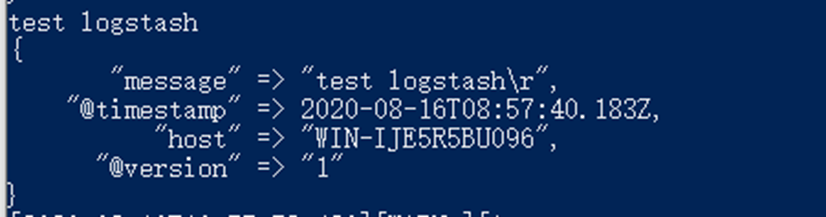
直接在控制台输入test logstash,控制台输出我们输入的内容
换一种输出数据的格式,以json | rubydebug
stdout{ codec => rubydebug }
stdout{ codec => json}
大家可以自己测试,看一下输出的效果
Logstash接入FileBeat
配置文件做一下改动,多了inpu插件配置,监听一个5044端口,这个就是FileBeat网络端口
# Sample Logstash configuration for creating a simple # Beats -> Logstash -> Elasticsearch pipeline. input { beats { port => 5044 } } output { stdout{ codec => rubydebug } }
4、启动FileBeat
新建FileBeat配置文件filebeat_test.yml
# ============================== Filebeat inputs =============================== filebeat.inputs: - type: log #开启日志读取 enabled: true #日志路径 paths: - D:\data\logs\demo\*.log #额外的字段 fields: app: demo review: 1 #匹配多行,按照时间正则匹配 yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS multiline.pattern: ^\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2} \d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2}.\d{3} multiline.negate: true #日期之后匹配 multiline.match: after #tail_files = true 不收集存量日志 tail_files: true #额外增加的标签字段 tags: ["demo"] # ============================== Filebeat modules ============================== filebeat.config.modules: # Glob pattern for configuration loading path: ${path.config}/modules.d/*.yml # Set to true to enable config reloading reload.enabled: false # Period on which files under path should be checked for changes #reload.period: 10s # ======================= Elasticsearch template setting ======================= #es 索引模板 setup.template.settings: index.number_of_shards: 1 #index.codec: best_compression #_source.enabled: false # ------------------------------ Logstash Output ------------------------------- #输出到logstash output.logstash: #The Logstash hosts hosts: ["localhost:5044"] processors: - add_host_metadata: ~ - add_cloud_metadata: ~ - add_docker_metadata: ~ - add_kubernetes_metadata: ~
启动FileBeat
.\filebeat.exe -e -c .\filebeat_test.yml
访问demo项目,打印一些日志,让FileBeta读取
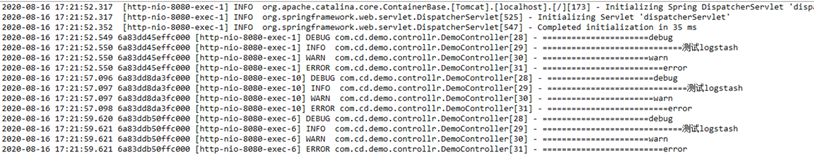
Logstash控制台,这是json形式打印出来的
我们挑一条日志格式化看看FileBeat采集的日志通过Logstash打印出来之后是什么样子。
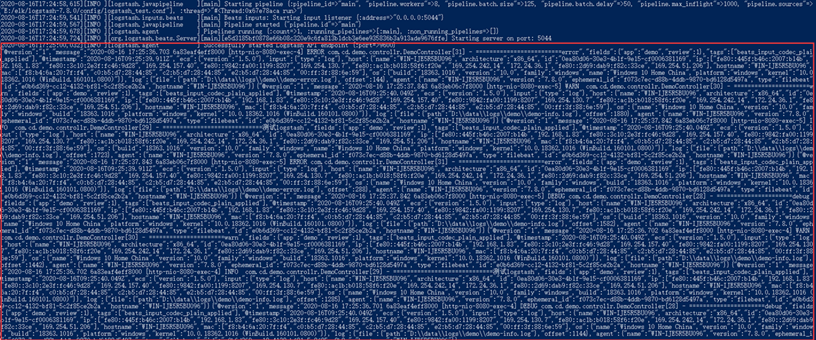
{ "@version":"1", "message":"2020-08-16 17:29:13.138 6a83f82acbf8000 [http-nio-8080-exec-9] DEBUG com.cd.demo.controllr.DemoController[28] - ======================debug", "fields":{ "app":"demo", "review":1 }, "tags":[ "demo", "beats_input_codec_plain_applied" ], "@timestamp":"2020-08-16T09:29:15.075Z", "ecs":{ "version":"1.5.0" }, "input":{ "type":"log" }, "host":{ "name":"WIN-IJE5R5BU096", "architecture":"x86_64", "id":"0ea80d06-30e3-4b1f-9e15-cf0006381169", "ip":[ "fe80::445f:b46c:2007:b14b", "192.168.1.83", "fe80::3c10:2e3f:fc46:9d28", "169.254.157.40", "fe80::9842:fa00:1199:8207", "169.254.130.7", "fe80::ac1b:b018:58f6:f20e", "169.254.242.14", "172.24.36.1", "fe80::2d69:dab9:f82c:33ce", "169.254.51.206" ], "hostname":"WIN-IJE5R5BU096", "mac":[ "f8:b4:6a:20:7f:f4", "c0:b5:d7:28:44:85", "c2:b5:d7:28:44:85", "e2:b5:d7:28:44:85", "00:ff:3f:88:6e:59" ], "os":{ "name":"Windows 10 Home China", "version":"10.0", "family":"windows", "build":"18363.1016", "platform":"windows", "kernel":"10.0.18362.1016 (WinBuild.160101.0800)" } }, "log":{ "file":{ "path":"D:\data\logs\demo\demo-info.log" }, "offset":2020 }, "agent":{ "name":"WIN-IJE5R5BU096", "version":"7.8.0", "ephemeral_id":"f073c7ec-d88b-4ddb-9870-bd6128d5497a", "type":"filebeat", "id":"e0b6d369-cc12-4132-bf81-5c2f85ce2b2a", "hostname":"WIN-IJE5R5BU096" } }
以上就是FileBeat收集通过Logstash未经过滤打印在控制台的数据,可以看到FileBeat收集的日志还是很全面(软件,硬件,网络),这些日志我们并不全部需要,我们仅把自己需要的字段存储即可,这就需要格式化数据。格式化数据需要借助Logstash的Filter插件,https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/filter-plugins.html
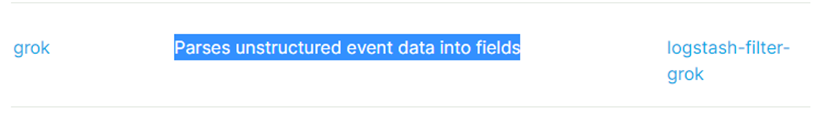
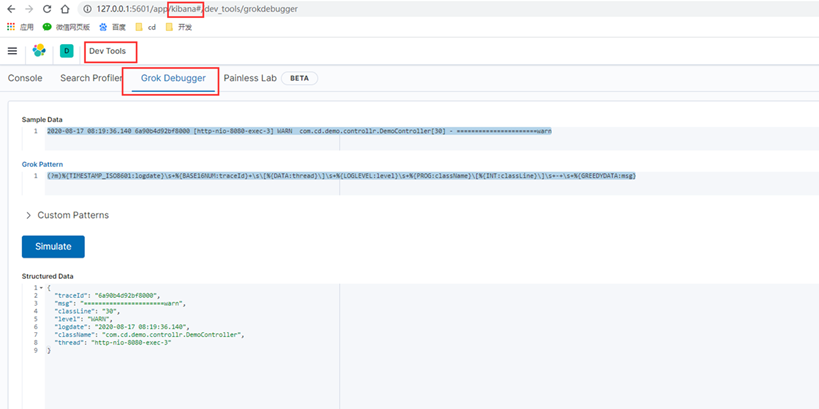
找到grok插件,它的意思是将非结构化事件数据转为字段,转为字段之后我们方便存储统计
我们真正要提取的是message字段,这个字段是我们实际的业务日志,使用grok编写正则去提取message字段,可以用Kibana自带的grok工具或者是 http://grokdebug.herokuapp.com/?#(grokdebug并不好用,时常无法访问)
来测试编写正则,匹配提取我们的日志,下图就展示了将message抽取为一个个单独的字段
完整的Logasth配置
# Sample Logstash configuration for creating a simple # Beats -> Logstash -> Elasticsearch pipeline. input { beats { port => 5044 } } filter { #提取message字段,这个字段是业务日志,使用正则匹配的形式将message提取为一个个字段,为什么有两个message呢?假如你的日志格式不统一就需要多个正则去匹配,但是尽量避免这种情况的出现 #多个正则匹配,如果日志量比较大,会降低Logstash的处理效率, grok{ match => [ "message" , "(?m)%{TIMESTAMP_ISO8601:logdate}\s+%{BASE16NUM:traceId}+\s\[%{DATA:thread}\]\s+%{LOGLEVEL:level}\s+%{PROG:className}\[%{INT:classLine}\]\s+-+\s+%{GREEDYDATA:msg}", "message" , "(?m)%{TIMESTAMP_ISO8601:logdate}\s\s+\[%{DATA:thread}\]\s+%{LOGLEVEL:level}\s\s++%{PROG:className}\[%{INT:classLine}\]\s+-+\s+%{GREEDYDATA:msg}" ] } #使用业务日志时间替换Logstash的@timestamp时间,避免两个时间不同步 date { match => ["logdate", "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS"] target => "@timestamp" remove_field => ["logdate"] } #去除一些不需要的字段,注意一定要保留@timestamp字段否则无法按照日期维度建立索引,同时也保留message字段方便我们查看 #同时将额外添加的fields字段当作一个新的字段添加,这样以便我们知道是哪个应用日志,也可以使用tags字段来做定义 mutate{ remove_field => ["@version","@metadata","input","agent","ecs","fields"] add_field => { "appName" => "%{[fields][app]}" } } } #经过filter过滤之后的字段继续输出到控制台 output { stdout{ codec => json } }
重启Logstash观察控制台日志
{ "tags":[ "demo", "beats_input_codec_plain_applied" ], "log":{ "file":{ "path":"D:\data\logs\demo\demo-info.log" }, "offset":2020 }, "host":{ "mac":[ "f8:b4:6a:20:7f:f4", "c0:b5:d7:28:44:85", "c2:b5:d7:28:44:85", "e2:b5:d7:28:44:85", "00:ff:3f:88:6e:59" ], "os":{ "build":"18363.1016", "platform":"windows", "name":"Windows 10 Home China", "kernel":"10.0.18362.1016 (WinBuild.160101.0800)", "family":"windows", "version":"10.0" }, "id":"0ea80d06-30e3-4b1f-9e15-cf0006381169", "name":"WIN-IJE5R5BU096", "ip":[ "fe80::445f:b46c:2007:b14b", "192.168.1.83", "fe80::3c10:2e3f:fc46:9d28", "169.254.157.40", "fe80::9842:fa00:1199:8207", "169.254.130.7", "fe80::ac1b:b018:58f6:f20e", "169.254.242.14", "172.24.36.1", "fe80::2d69:dab9:f82c:33ce", "169.254.51.206" ], "hostname":"WIN-IJE5R5BU096", "architecture":"x86_64" }, "level":"DEBUG", "traceId":"6a91634313f7000", "className":"com.cd.demo.controllr.DemoController", "msg":"======================debug", "appName":"demo", "classLine":"28", "message":"2020-08-17 09:07:13.761 6a91634313f7000 [http-nio-8080-exec-1] DEBUG com.cd.demo.controllr.DemoController[28] - ======================debug", "thread":"http-nio-8080-exec-1", "@timestamp":"2020-08-17T01:07:13.761Z" }
现在看这个日志基本上已经是我们想要的,包括,日志路径,应用名,业务日志,主机信息等核心日志信息。
接着我们将日志结果输出到ES中去 文档地址:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/plugins-outputs-elasticsearch.html#plugins-outputs-elasticsearch-index
高版本的Logstash日志索引默认建立方式是{now/d}-000001 格式,例如:logstash-2020.02.10-000001,如果想自己定义指定 ilm_enabled => false即可
Logstash配置输出到ES完整配置,加了详细配置说明
# Sample Logstash configuration for creating a simple # Beats -> Logstash -> Elasticsearch pipeline. input { beats { port => 5044 } } filter { #提取message字段,这个字段是业务日志,使用正则匹配的形式将message提取为一个个字段,为什么有两个message呢?假如你的日志格式不统一就需要多个正则去匹配,但是尽量避免这种情况的出现 #多个正则匹配,如果日志量比较大,会降低Logstash的处理效率, grok{ match => [ "message" , "(?m)%{TIMESTAMP_ISO8601:logdate}\s+%{BASE16NUM:traceId}+\s\[%{DATA:thread}\]\s+%{LOGLEVEL:level}\s+%{PROG:className}\[%{INT:classLine}\]\s+-+\s+%{GREEDYDATA:msg}", "message" , "(?m)%{TIMESTAMP_ISO8601:logdate}\s\s+\[%{DATA:thread}\]\s+%{LOGLEVEL:level}\s\s++%{PROG:className}\[%{INT:classLine}\]\s+-+\s+%{GREEDYDATA:msg}" ] } #使用业务日志时间替换Logstash的@timestamp时间,避免两个时间不同步 date { match => ["logdate", "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS"] target => "@timestamp" remove_field => ["logdate"] } #去除一些不需要的字段,注意一定要保留@timestamp字段否则无法按照日期维度建立索引,同时也保留message字段方便我们查看 #同时将额外添加的fields字段当作一个新的字段添加,这样以便我们知道是哪个应用日志,也可以使用tags字段来做定义 mutate{ remove_field => ["@version","@metadata","input","agent","ecs","fields"] add_field => { "appName" => "%{[fields][app]}" } } } #经过filter过滤之后的字段继续输出到控制台 和 ES output { stdout{ codec => rubydebug } elasticsearch { hosts => ["127.0.0.1:9200"] #按照每天一个日志索引建立 index => "logstash-demo-%{+yyyy.MM.dd}" #关闭Logstash的ilm_enabled,否则会按照{now/d}-000001 方式创建索引文件 #ilm_enabled => false } }
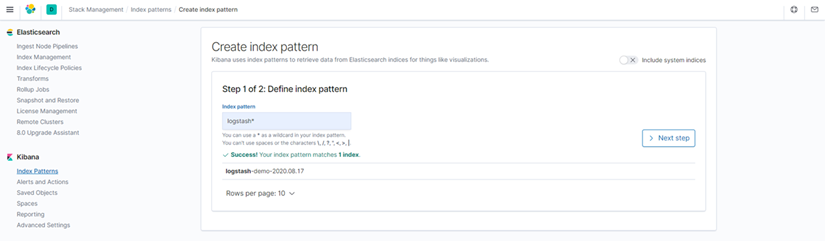
Kibana展示日志数据,Kibane读取ES的数据索引
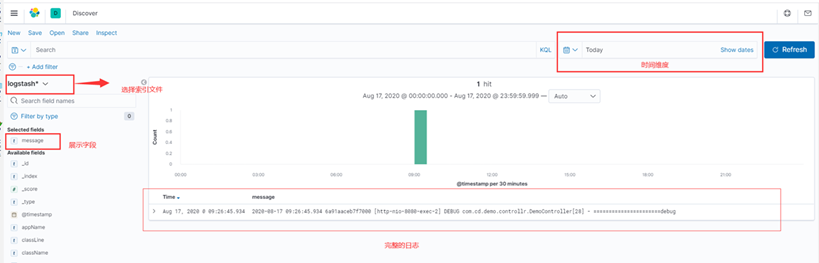
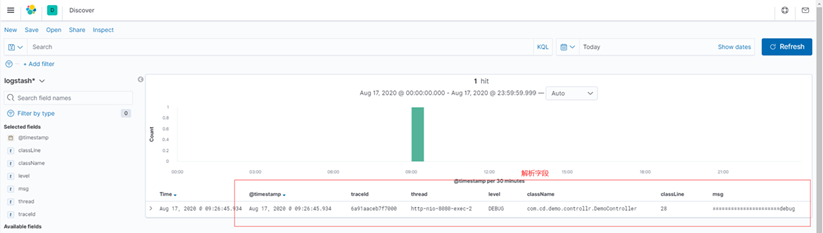
Kibana->Discover展示数据
全量message
message字段解析之后的字段展示
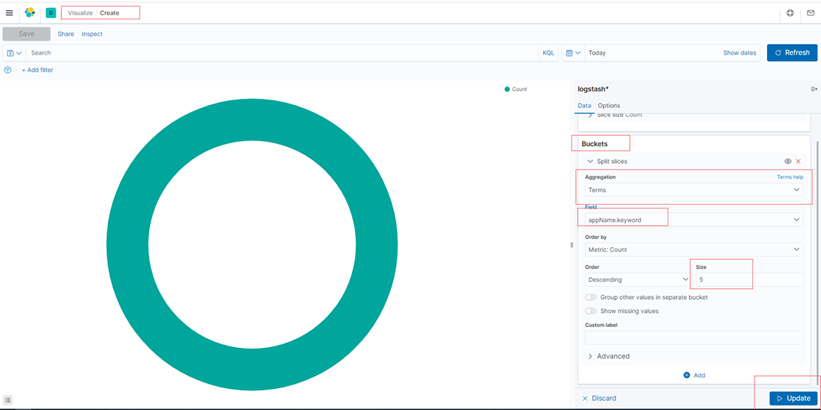
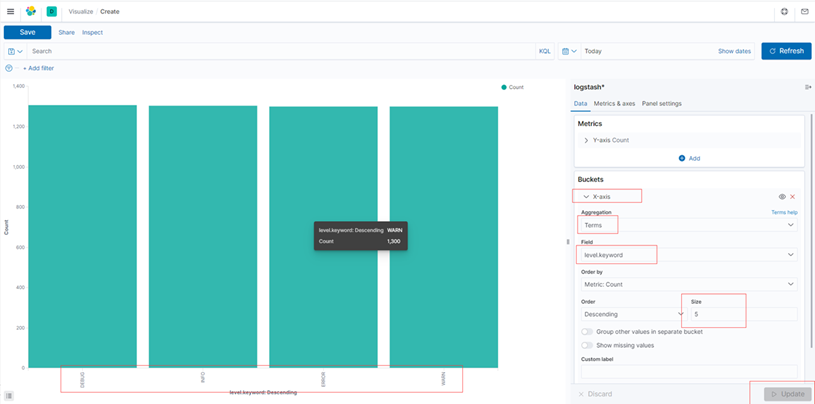
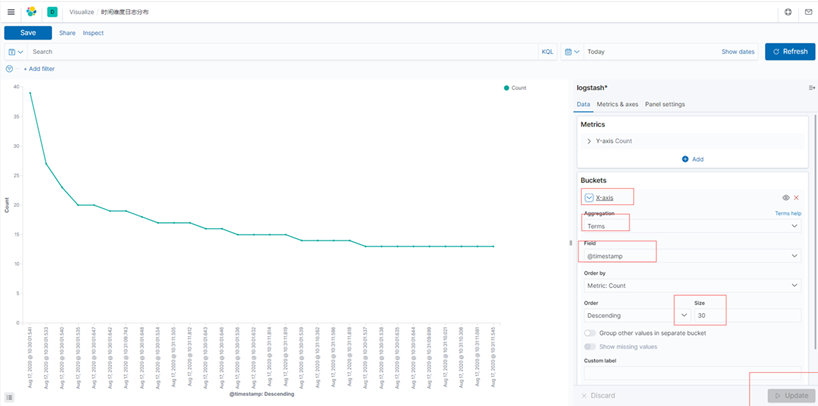
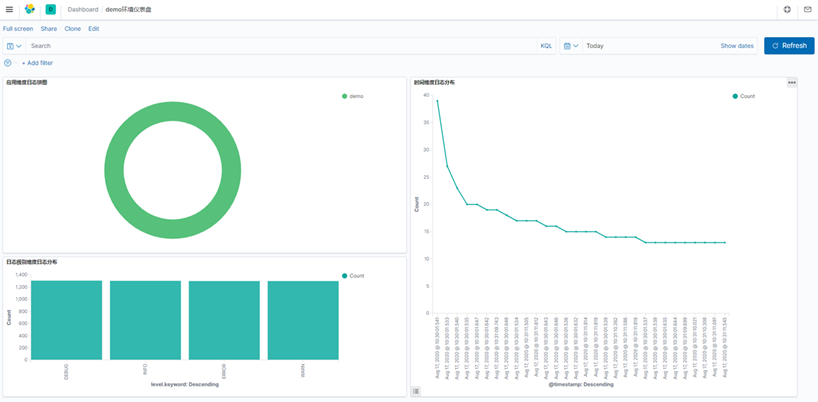
建立日志分析图
饼图,按照应用维度创建
柱形图,按照日志级别维度创建
时间维度,最近30次日志分布
创建仪表盘
注意,如果你想改图示名字,点击save重新保存即可,图示改名也是如此。
以上就是ELK+FileBeat全量配置,如果日志量太大可以优化Logsasth,比如加Logstash集群,不使用正则匹配日志等,本文ELK虽然是基于windows搭建,但配置信息在Linux是可以使用。
linux环境下后台启动
nohup filebeat -e -c filebeat_pre.yml &
nohup ./bin/logstash -f config/logstash_pre.conf &
nohup ./bin/kibana --allow-root &
参考材料:
官方文档:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/index.html
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/index.html
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/index.html
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/libbeat/current/index.html
Kibana中文文档:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/kibana/current/index.html
全文完,感谢您的耐心阅读~
欢迎大家关注我的公众号