正文前先来一波福利推荐:
福利一:
百万年薪架构师视频,该视频可以学到很多东西,是本人花钱买的VIP课程,学习消化了一年,为了支持一下女朋友公众号也方便大家学习,共享给大家。
福利二:
毕业答辩以及工作上各种答辩,平时积累了不少精品PPT,现在共享给大家,大大小小加起来有几千套,总有适合你的一款,很多是网上是下载不到。
获取方式:
微信关注 精品3分钟 ,id为 jingpin3mins,关注后回复 百万年薪架构师 ,精品收藏PPT 获取云盘链接,谢谢大家支持!

------------------------正文开始---------------------------
Flink Window机制范例实录:
什么是Window?有哪些用途?
1、window又可以分为基于时间(Time-based)的window
2、基于数量(Count-based)的window。
Flink DataStream API提供了Time和Count的window,同时增加了基于Session的window。
同时,由于某些特殊的需要,DataStream API也提供了定制化的window操作,供用户自定义window。
下面,主要介绍Time-Based window以及Count-Based window,以及自定义的window操作,Session-Based Window操作将会在后续的文章中讲到。
1、Time-Based Window
细分:基于时间的window又分为:
增量聚合;全量聚合。
--------------------------------增量聚合-------------------------------:

类似于 Flink Sql中的 group window,计算结果不断的更新;
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
代码示例:
1.1、Tumbling window(翻滚)
此处的window要在keyed Stream上应用window操作,当输入1个参数时,代表Tumbling window操作,每分钟统计一次,此处用scala语言实现:
增量聚合代码---- 求和操作:
//todo 获得数据源后进行算子操作 DataStream<StartAppCount> windowedData = startupInfoData.keyBy("appId") //以设备id进行分组 .timeWindow(Time.minutes(60)) //指定时间窗口大小为5分钟,指定时间间隔为5分钟 .aggregate(new CountAgg(), new WindowResultFunction()); windowedData.print();
CountAgg自定义的函数,需要实现 AggregateFunction函数
public class CountAgg implements AggregateFunction<StartupInfoData, Long, Long> { @Override public Long createAccumulator() { //初始化算子 return 0L; } @Override public Long add(StartupInfoData startupInfoData, Long acc) { //传入一个入参后,做累加操作,将算子加1 return acc + 1; } @Override public Long getResult(Long acc) { //最输出merge产生的结果 return acc; } @Override public Long merge(Long acc1, Long acc2) { //对算子进行每一个的累和 return acc1 + acc2; } }
输出函数格式:
public class WindowResultFunction implements WindowFunction<Long, StartAppCount, Tuple, TimeWindow> { @Override public void apply( Tuple key, // 窗口的主键,即 appId TimeWindow window, // 窗口 Iterable<Long> aggregateResult, // 聚合函数的结果,即 count 值 Collector<StartAppCount> collector // 输出类型为 StartAppCount ) throws Exception { String appId = ((Tuple1<String>) key).f0; Long count = aggregateResult.iterator().next(); collector.collect(StartAppCount.of(appId, window.getEnd(), count)); }
自定义输出类的类格式:
public class StartAppCount { public String appId; // 商品ID public long windowEnd; // 窗口结束时间戳 public long count; // 商品的点击量 public static StartAppCount of (String appId, long windowEnd, long count) { StartAppCount result = new StartAppCount(); result.appId = appId; result.windowEnd = windowEnd; result.count = count; return result; } @Override public String toString() { return "WordWithCount{" + "appId='" + appId + '\'' + ", count=" + count + '}'; } }
增量聚合代码---- 求平均值操作:
public class AverageAggregate implements AggregateFunction<Tuple2<String,Long>, Tuple2<Long, Long>, Double> { @Override public Tuple2<Long, Long> createAccumulator() { return new Tuple2<>(0L, 0L); } @Override public Tuple2<Long, Long> add(Tuple2<String, Long> value, Tuple2<Long, Long> acc) { //可以理解为缓存的中间值 return new Tuple2<>(acc.f0 + value.f1, acc.f1 + 1L); //传入的值加到acc的第一个值得到传入值, 第二个值为个数 } @Override public Double getResult(Tuple2<Long, Long> acc) { return (double)acc.f0 / acc.f1; } @Override public Tuple2<Long, Long> merge(Tuple2<Long, Long> acc1, Tuple2<Long, Long> acc2) { //进行累和合并 return new Tuple2<>(acc1.f0+acc2.f0, acc1.f1+acc2.f1); } }
使用sum进行求和的代码:
DataStream<WordWithCount> windowCounts = text.flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<String, WordWithCount>() { public void flatMap(String value, Collector<WordWithCount> out) throws Exception { String[] splits = value.split("\\s"); for (String word : splits) { out.collect(new WordWithCount(word, 1L)); } } }).keyBy("word") .timeWindow(Time.seconds(2), Time.seconds(1))//指定时间窗口大小为2秒,指定时间间隔为1秒 .sum("count");//在这里使用sum或者reduce都可以 /*.reduce(new ReduceFunction<WordWithCount>() { public WordWithCount reduce(WordWithCount a, WordWithCount b) throws Exception { return new WordWithCount(a.word,a.count+b.count); } })*/ //把数据打印到控制台并且设置并行度 windowCounts.print().setParallelism(1);
使用reduce进行求和的方法:
DataStream<WordWithCount> windowCounts = text.flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<String, WordWithCount>() { public void flatMap(String value, Collector<WordWithCount> out) throws Exception { String[] splits = value.split("\\s"); for (String word : splits) { out.collect(new WordWithCount(word, 1L)); } } }).keyBy("word") .timeWindow(Time.seconds(2), Time.seconds(1))//指定时间窗口大小为2秒,指定时间间隔为1秒 //.sum("count");//在这里使用sum或者reduce都可以 .reduce(new ReduceFunction<WordWithCount>() { public WordWithCount reduce(WordWithCount a, WordWithCount b) throws Exception { return new WordWithCount(a.word,a.count+b.count); } });
--------------------------------全量的时间窗口操作-------------------------------:

代码示例:
public class MyprocessWindowFunction extends ProcessWindowFunction<Tuple2<String, Long>, String, String, TimeWindow> { @Override public void process(String s, Context context, Iterable<Tuple2<String, Long>> iterable, Collector<String> out) throws Exception { long count = 0; for(Tuple2<String,Long> in : iterable) { count++; } out.collect("Window: " + context.window() + "count: " + count); } }
1.2、Sliding window(滑动)
//todo 获得数据源后进行算子操作 DataStream<StartAppCount> windowedData = startupInfoData.keyBy("appId") //以设备id进行分组 .timeWindow(Time.minutes(60), Time.seconds(5)) //指定时间窗口大小为5分钟,指定时间间隔为5分钟 .aggregate(new CountAgg(), new WindowResultFunction()); windowedData.print();
2、Count-Based Window
2.1、Tumbling Window (滚动计数窗口)
和Time-Based一样,Count-based window同样支持翻滚与滑动窗口,即在Keyed Stream上,统计每100个元素的数量之和
public class FlinkCountWindowDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{ final ParameterTool params = ParameterTool.fromArgs(args); final StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); env.getConfig().setGlobalJobParameters(params); env.setParallelism(1); final int windowSize = params.getInt("window", 100); // read source data DataStreamSource<Tuple2<String, String>> inStream = env.addSource(new StreamDataSource()); // calculate DataStream<Tuple2<String, String>> outStream = inStream .keyBy(0) .countWindow(windowSize) .reduce( new ReduceFunction<Tuple2<String, String>>() { @Override public Tuple2<String, String> reduce(Tuple2<String, String> value1, Tuple2<String, String> value2) throws Exception { return Tuple2.of(value1.f0, value1.f1 + "" + value2.f1); } } ); outStream.print(); env.execute("WindowWordCount"); } }
2.2、Sliding Window
盗用 Flink 原理与实现:Window 机制 中的一张图,假设有一个滑动计数窗口,每2个元素计算一次最近4个元素的总和,那么窗口工作示意图如下所示:
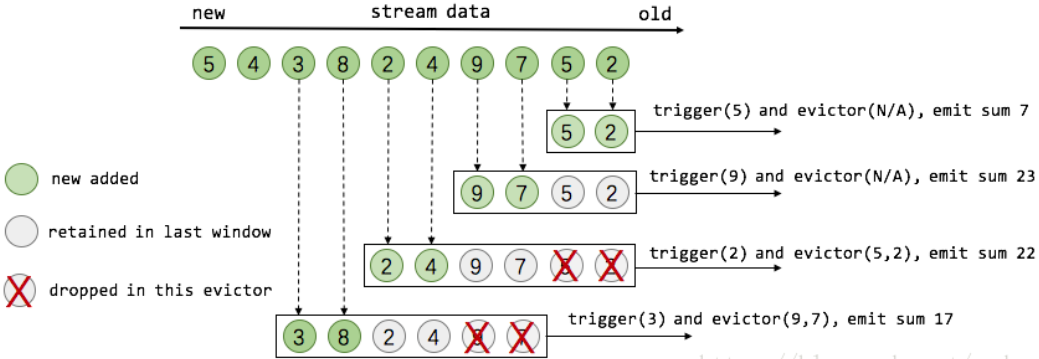
代码示例:
public class FlinkCountWindowDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { final ParameterTool params = ParameterTool.fromArgs(args); final StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); env.getConfig().setGlobalJobParameters(params); env.setParallelism(1); final int windowSize = params.getInt("window", 3); final int slideSize = params.getInt("slide", 2); // read source data DataStreamSource<Tuple2<String, String>> inStream = env.addSource(new StreamDataSource()); // calculate DataStream<Tuple2<String, String>> outStream = inStream .keyBy(0) .countWindow(windowSize, slideSize) .reduce( new ReduceFunction<Tuple2<String, String>>() { @Override public Tuple2<String, String> reduce(Tuple2<String, String> value1, Tuple2<String, String> value2) throws Exception { return Tuple2.of(value1.f0, value1.f1 + "" + value2.f1); } } ); outStream.print(); env.execute("WindowWordCount"); } }
3、Advanced Window(自定义window)
自定义的Window需要指定3个function。
3.1、Window Assigner:负责将元素分配到不同的window。
WindowAPI提供了自定义的WindowAssigner接口,我们可以实现WindowAssigner的public abstract Collection<W> assignWindows(T element, long timestamp)方法。同时,对于基于Count的window而言,默认采用了GlobalWindow的window assigner,例如:keyValue.window(GlobalWindows.create())

