python-grpc
目录
1. python下protobuf使用
1.1 安装protobuf
pip3.6 install grpcio #安装grpc
pip3.6 install grpcio-tools #安装grpc tools
1.2 protobuf3定义格式
新建protobuf文件名:hello.proto
syntax = "proto3";
message HelloRequest {
string name = 1;
}
1.3 生成proto的python文件
cd hello.proto文件路径下
命令:python3.6 -m grpc_tools.protoc --python_out=. --grpc_python_out=. -I. hello.proto
注意:只有python生成两个文件
命令解释:
python3.6 -m grpc_tools.protoc:实际需要使用grpc_tools.protoc这里面的命令
--python_out=. :生成的python文件放在当前路径下,这是给rpc用的文件
--grpc_python_out=. :生成的python文件放在当前路径下,这是给grpc用的文件
-I.:指import,当前目录下找hello.proto文件
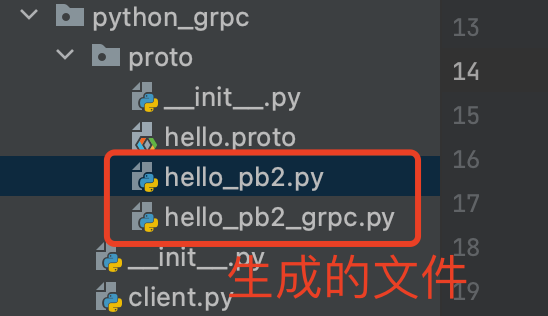
1.4 对比一下protobuf生成的效果
res.SerializeToString() # 序列化二进制
res2.ParseFromString(res_str) # 反序列化二进制
import json
from python_grpc.proto import hello_pb2
def main():
res = hello_pb2.HelloRequest()
res.name = "jeff"
res_str = res.SerializeToString() # 序列化二进制
print(res_str) # b'\n\x04jeff'
print(len((res_str))) # 6,和json对比,josn长度为:16
res2 = hello_pb2.HelloRequest()
res2.ParseFromString(res_str) # 反序列化二进制
print(res2.name) # jeff
res_json = {
"name":"jeff"
}
print(len(json.dumps(res_json))) # 16,json和proto压缩对比,proto压缩后:6
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
2.python下grpc使用
2.1编写hello.proto文件
syntax = "proto3";
package services;
option go_package = "./;proto";
service Greeter {
// 定义SayHello方法
rpc SayHello (HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply);
}
message HelloRequest {
string name = 1; //编号
}
message HelloReply {
string message = 1; //编号
}
2.2 生成proto的python文件
cd hello.proto文件路径下
命令:python3.6 -m grpc_tools.protoc --python_out=. --grpc_python_out=. -I. hello.proto
注意:只有python生成两个文件
命令解释:
python3.6 -m grpc_tools.protoc:实际需要使用grpc_tools.protoc这里面的命令
--python_out=. :生成的python文件放在当前路径下,这是给rpc用的文件
--grpc_python_out=. :生成的python文件放在当前路径下,这是给grpc用的文件
-I.:指import,当前目录下找hello.proto文件
注意:生成的*_grpc.py文件的导包需要修改,否则报错:要让python找到hello_pb2
import hello_pb2 as hello__pb2 改为:
from python_grpc.proto import hello_pb2 as hello__pb2
2.3 编写server端
from concurrent import futures
import grpc
from python_grpc.proto import hello_pb2, hello_pb2_grpc
# 业务处理
class Greeter(hello_pb2_grpc.GreeterServicer):
def SayHello(self, request, context):
return hello_pb2.HelloReply(message=f"你好,{request.name}")
# 启动
def start():
# 1.实例化server
Thread = futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=10) ## 设置线程池,并发大小
server = grpc.server(Thread)
# 2.注册逻辑到server中
hello_pb2_grpc.add_GreeterServicer_to_server(Greeter(), server)
# 3.启动server
server.add_insecure_port("127.0.0.1:8888")
server.start()
server.wait_for_termination()
if __name__ == '__main__':
start()
2.4 编写cilent端
import grpc
from python_grpc.proto import hello_pb2, hello_pb2_grpc
# rpc调用
def main():
# 这里使用with,调用完会自动关闭。优雅写法
with grpc.insecure_channel("127.0.0.1:8888") as channel:
stub = hello_pb2_grpc.GreeterStub(channel)
# 调用定义的SayHello方法
rep = stub.SayHello(
hello_pb2.HelloRequest(name="jeff") # 传递定义的HelloRequest类型参数
)
return rep
# 业务代码
def start():
rep = main()
print(rep.message) # 你好,jeff
if __name__ == '__main__':
start()
选择了IT,必定终身学习
posted @ Jeff的技术栈 阅读 (9999+) 评论 (99) 点赞(99) 编辑 MD 收藏





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构