Springboot整合RabbitMQ---Direct交换机
常用的交换机有以下三种,因为消费者是从队列获取信息的,队列是绑定交换机的(一般),所以对应的消息推送/接收模式也会有以下几种:
Direct Exchange
直连型交换机,根据消息携带的路由键将消息投递给对应队列。
大致流程,有一个队列绑定到一个直连交换机上,同时赋予一个路由键 routing key 。
然后当一个消息携带着路由值为X,这个消息通过生产者发送给交换机时,交换机就会根据这个路由值X去寻找绑定值也是X的队列。
Fanout Exchange
扇型交换机,这个交换机没有路由键概念,就算你绑了路由键也是无视的。 这个交换机在接收到消息后,会直接转发到绑定到它上面的所有队列。
Topic Exchange
主题交换机,这个交换机其实跟直连交换机流程差不多,但是它的特点就是在它的路由键和绑定键之间是有规则的。
简单地介绍下规则:
* (星号) 用来表示一个单词 (必须出现的)
# (井号) 用来表示任意数量(零个或多个)单词
通配的绑定键是跟队列进行绑定的,举个小例子
队列Q1 绑定键为 *.TT.* 队列Q2绑定键为 TT.#
如果一条消息携带的路由键为 A.TT.B,那么队列Q1将会收到;
如果一条消息携带的路由键为TT.AA.BB,那么队列Q2将会收到;
主题交换机是非常强大的,为啥这么膨胀?
当一个队列的绑定键为 "#"(井号) 的时候,这个队列将会无视消息的路由键,接收所有的消息。
当 * (星号) 和 # (井号) 这两个特殊字符都未在绑定键中出现的时候,此时主题交换机就拥有的直连交换机的行为。
所以主题交换机也就实现了扇形交换机的功能,和直连交换机的功能。
另外还有 Header Exchange 头交换机 ,Default Exchange 默认交换机,Dead Letter Exchange 死信交换机
创建2个springboot项目,一个 rabbitmq-provider (生产者),一个rabbitmq-consumer(消费者)
1:创建好springboot项目,pom.xml添加依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency><dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId></dependency> |
2:application.properties文件里面添加mq的配置信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | # amqpspring.rabbitmq.host=127.0.0.1spring.rabbitmq.port=5672spring.rabbitmq.username=adminspring.rabbitmq.password=123456spring.rabbitmq.virtual-host=/# 队列交换机和路由键rabbitmq.queue=my_queuerabbitmq.exchange=my_exchangerabbitmq.routing=my_direct_routing |
3:新建DirectRabbitConfig配置类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 | import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;/** * @Desc Direct交换机配置类 * @User Aiden * @DateTime: 2023-11-08 14:29 * @Project: springboot */@Configurationpublic class DirectRabbitConfig { // 队列名称 @Value("${rabbitmq.queue}") private String QueueName; // 交换机名称 @Value("${rabbitmq.exchange}") private String ExchangeName = "my_exchange"; // 路由匹配键 @Value("${rabbitmq.routing}") private String DirectRoutingKey; /** * 队列 * @return */ @Bean public Queue TestDirectQueue(){ return new Queue(QueueName,true); } /** * 交换机 * @return */ @Bean public DirectExchange TestDirectExchange(){ return new DirectExchange(ExchangeName,true,false); } /** * 通过路由将队列和交换机绑定 * @return */ @Bean public Binding bindDirect(){ return BindingBuilder.bind(TestDirectQueue()).to(TestDirectExchange()).with(DirectRoutingKey); } @Bean DirectExchange lonelyDirectExchange() { return new DirectExchange("lonelyDirectExchange"); }} |
3:编写发送消息的接口,根据业务需要决定;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import java.time.LocalDateTime;import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.UUID;/** * @Desc 发送MQ消息 * @User Aiden * @DateTime: 2023-11-08 14:57 * @Project: springboot */@RestControllerpublic class MessageController { @Autowired private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate; /** * 发送消息 * @return */ @GetMapping("send/msg") public String sendMessage(){ // 数据 HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("msg_id",String.valueOf(UUID.randomUUID())); map.put("msg_body","你好"); map.put("send_time", LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"))); //将消息携带绑定键值:TestDirectRouting 发送到交换机TestDirectExchange rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("my_exchange", "my_direct_routing", map); return "success"; }} |
在安装好的RabbitMQ server端,http://localhost:15672/#/ 就可以看到消息待消费;
5:消费消息,可以创建新项目,同样的配置和信息,创建消费方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import java.util.Map;/** * @Desc 消费MQ消息 * @User Aiden * @DateTime: 2023-11-08 17:35 * @Project: springboot */@Component@RabbitListener(queues = "${rabbitmq.queue}")@RestControllerpublic class ConsumerController { @RabbitHandler public void directReceiver(Map message) { System.out.println(message.toString()); }} |
6:启动项目,根据端口号打开 http://localhost:8082/send/msg 返回OK后,在IDEA控制台就可以看到消息的打印:
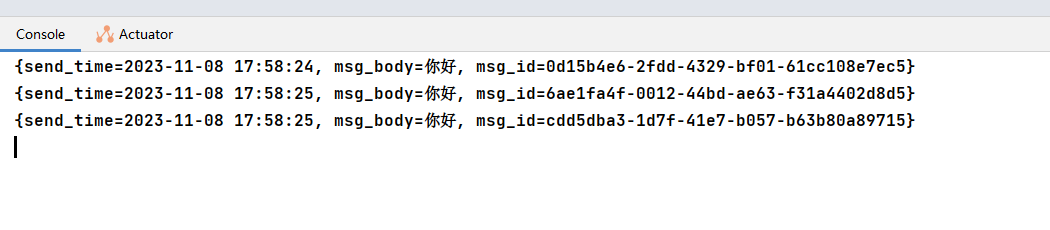
一个简单的整合流程就到此。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术