python GUI尝鲜(但当涉猎,见往事耳)
第一步:简单的窗口和内容
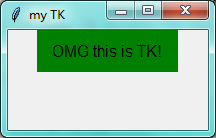

import tkinter as tk window = tk.Tk() # 窗口obj对象 window.title('my TK') # 窗口名字 window.geometry('200x100') # 窗口宽度和高度 # Label对象传入相应参数text:文本内容; bg:背景; font:字体; width、height 内容的宽度、高度 l = tk.Label(window,text='OMG this is TK!',bg='green',font=('Arial',12),width=15,height=2) l.pack() # 例如放在上边、右边、下边、左边(未传参数,随便放置) # l.place() # 例如放在具体某个点 window.mainloop() # 不断的循环循环窗口,保证我们点击窗口后,可以及时执行命令
第二步:增加一个button
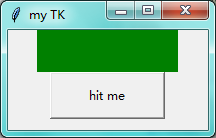
点击hit me 后出现下面这个:
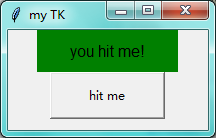

import tkinter as tk window = tk.Tk() # 窗口obj对象 window.title('my TK') # 窗口名字 window.geometry('200x100') # 窗口宽度和高度 var = tk.StringVar() # 创建一个字符串对象 # Label对象传入相应参数textvariable:字符串对象; bg:背景; font:字体; width、height 内容的宽度、高度 l = tk.Label(window,textvariable=var,bg='green',font=('Arial',12),width=15,height=2) l.pack() # 例如放在上边、右边、下边、左边(未传参数,随便放置) on_hit = False # 创建一个标志位 def hit_me(): global on_hit if on_hit: var.set('') on_hit = False else: var.set('you hit me!') on_hit = True # 内容中多加一个button,点击之后执行command所指向的函数 b = tk.Button(window,text='hit me',width=15,height=2,command=hit_me) b.pack() # 每一个对象都要安放 window.mainloop() # 不断的循环循环窗口,保证我们点击窗口后,可以及时执行命令
第三步:Entry对象

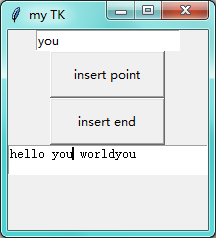
当你点击 insert point 后:会在光标位置插入 you
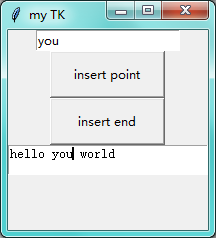
当你点击 insert end 后:会在末尾位置插入 you(无论此时你的光标在哪)

import tkinter as tk window = tk.Tk() # 窗口obj对象 window.title('my TK') # 窗口名字 window.geometry('200x200') # 窗口宽度和高度 e = tk.Entry(window,show=None) # show='*'隐藏所输入的字符为*不可见形式 show=None显示原格式 e.pack() def insert_point(): var = e.get() t.insert('insert',var) def insert_end(): var = e.get() t.insert('end',var) b1 = tk.Button(window,text='insert point',width=15,height=2,command=insert_point) # 执行insert_point函数 光标位置插入 b1.pack() # 每一个对象都要安放 b2 = tk.Button(window,text='insert end',width=15,height=2,command=insert_end) # 执行insert_end函数 末尾插入 b2.pack() # 每一个对象都要安放 t = tk.Text(window,height=2,) # Text 高度是两个字符串的高度 t.pack() window.mainloop() # 不断的循环循环窗口,保证我们点击窗口后,可以及时执行命令
在指定行列插入只需要修改
def insert_end():
var = e.get()
t.insert(2.3,var)
会在第二行,第四列插入(列的话从0算起)

第四步:Listbox


import tkinter as tk window = tk.Tk() # 窗口obj对象 window.title('my TK') # 窗口名字 window.geometry('200x200') # 窗口宽度和高度 var1 = tk.StringVar() l = tk.Label(window,bg='yellow',width=4,textvariable=var1) l.pack() def print_selection(): value = lb.get(lb.curselection()) # 拿到鼠标选中的值 var1.set(value) # 设置给var1对象 b1 = tk.Button(window,text='insert point',width=15,height=2,command=print_selection) # 执行insert_point函数 光标位置插入 b1.pack() # 每一个对象都要安放 var2 = tk.StringVar() var2.set((11,22,33)) # 默认值 lb = tk.Listbox(window,listvariable=var2) # 列表对象 lb.pack() list_item = [77,88,99] for item in list_item: # 循环插入列表值 lb.insert('end',item) lb.insert(1,'first') # 在指定位置插入 lb.insert(2,'second') lb.delete(2) # 在指定位置插入后马上删除 window.mainloop() # 不断的循环循环窗口,保证我们点击窗口后,可以及时执行命令
第五步:Radiobutton
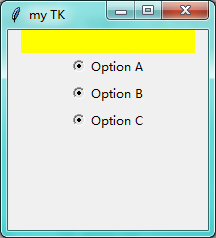
默认全部选中
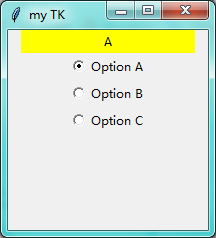
点击Option A后:
点击Option B后


import tkinter as tk window = tk.Tk() # 窗口obj对象 window.title('my TK') # 窗口名字 window.geometry('200x200') # 窗口宽度和高度 var = tk.StringVar() l = tk.Label(window,bg='yellow',width=24,textvariable=var,text='empty') l.pack() def print_selection(): l.config(text='you have select '+ var.get()) # 对 l 对象设置 text 值 r1 = tk.Radiobutton(window,text='Option A',variable=var,value='A',command=print_selection) # 点击执行print_selection函数 r1.pack() r2 = tk.Radiobutton(window,text='Option B',variable=var,value='B',command=print_selection) r2.pack() r3 = tk.Radiobutton(window,text='Option C',variable=var,value='C',command=print_selection) r3.pack() window.mainloop() # 不断的循环循环窗口,保证我们点击窗口后,可以及时执行命令
第六步:Scale
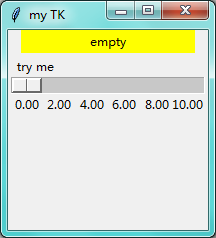
拖动一下后:


import tkinter as tk window = tk.Tk() # 窗口obj对象 window.title('my TK') # 窗口名字 window.geometry('200x200') # 窗口宽度和高度 l = tk.Label(window,bg='yellow',width=24,text='empty') l.pack() def print_selection(v): l.config(text='you have select '+ v) # 对 l 对象设置 text 值 # label 名称; from_ 、to 从0到10; orient 是横向显示(tk.HORIZONTAL)还是竖向显示; tickinterval 间隔2 ; resolution 两位小数 s = tk.Scale(window,label='try me',from_=0,to=10,orient=tk.HORIZONTAL,length=200,showvalue=0,tickinterval=2,resolution=0.01, command=print_selection) s.pack() window.mainloop() # 不断的循环循环窗口,保证我们点击窗口后,可以及时执行命令
第七步:Checkbutton 复选框
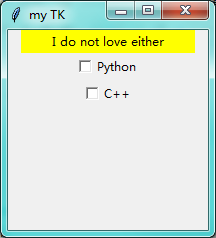
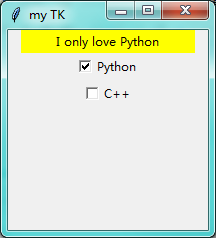


import tkinter as tk window = tk.Tk() # 窗口obj对象 window.title('my TK') # 窗口名字 window.geometry('200x200') # 窗口宽度和高度 l = tk.Label(window,bg='yellow',width=24,text='empty') l.pack() def print_selection(): if (var1.get()==1) and (var2.get()==0): l.config(text='I only love Python') elif (var1.get()==0) and (var2.get()==1): l.config(text='I only love C++') elif (var1.get()==0) and (var2.get()==0): l.config(text='I do not love either') else: l.config(text='I love both') var1 = tk.IntVar() var2 = tk.IntVar() c1 = tk.Checkbutton(window,text='Python',variable=var1,onvalue=1,offvalue=0,command=print_selection) c1.pack() c2 = tk.Checkbutton(window,text='C++',variable=var2,onvalue=1,offvalue=0,command=print_selection) c2.pack() window.mainloop() # 不断的循环循环窗口,保证我们点击窗口后,可以及时执行命令
第八步:画布 canvas
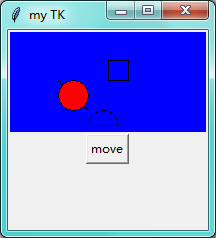
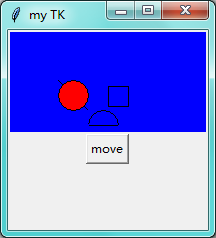

import tkinter as tk window = tk.Tk() # 窗口obj对象 window.title('my TK') # 窗口名字 window.geometry('200x200') # 窗口宽度和高度 canvas = tk.Canvas(window,bg='blue',width=200,height=100) # image_file = tk.PhotoImage(file='hsk.gif') # image = canvas.create_image(0,0,anchor='nw',image=image_file) x0,y0,x1,y1=50,50,80,80 line = canvas.create_line(x0,y0,x1,y1) oval = canvas.create_oval(x0,y0,x1,y1,fill='red') # 圆 填充红色 arc = canvas.create_arc(x0+30,y0+30,x1+30,y1+30,start=0,extent=180) # 扇形 0到180度 rect = canvas.create_rectangle(100,30,120,50) # 正方形 canvas.pack() def moveit(): canvas.move(rect,0,2) # x方向移动0 y方向每次点击移动2 b = tk.Button(window,text='move',command=moveit).pack() window.mainloop() # 不断的循环循环窗口,保证我们点击窗口后,可以及时执行命令
第九步: Menu

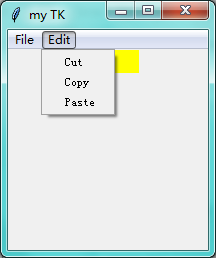

import tkinter as tk window = tk.Tk() # 窗口obj对象 window.title('my TK') # 窗口名字 window.geometry('200x200') # 窗口宽度和高度 l = tk.Label(window,text=' ',bg='yellow') l.pack() counter = 0 def do_job(): global counter l.config(text='do '+ str(counter)) counter+=1 menubar = tk.Menu(window) # 菜单栏 filemenu = tk.Menu(menubar,tearoff=0) menubar.add_cascade(label='File',menu=filemenu) filemenu.add_cascade(label='New',command=do_job) # 给file 加各种功能 filemenu.add_cascade(label='Open',command=do_job) filemenu.add_cascade(label='Save',command=do_job) filemenu.add_separator() # 分割线 filemenu.add_cascade(label='Exit',command=window.quit) # 关掉窗口 editmenu = tk.Menu(menubar,tearoff=0) menubar.add_cascade(label='Edit',menu=editmenu) # 给 edit 加各种功能 editmenu.add_cascade(label='Cut',command=do_job) editmenu.add_cascade(label='Copy',command=do_job) editmenu.add_cascade(label='Paste',command=do_job) window.config(menu=menubar) window.mainloop() # 不断的循环循环窗口,保证我们点击窗口后,可以及时执行命令
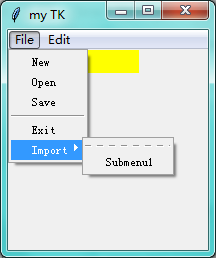

import tkinter as tk window = tk.Tk() # 窗口obj对象 window.title('my TK') # 窗口名字 window.geometry('200x200') # 窗口宽度和高度 l = tk.Label(window,text=' ',bg='yellow') l.pack() counter = 0 def do_job(): global counter l.config(text='do '+ str(counter)) counter+=1 menubar = tk.Menu(window) # 菜单栏 filemenu = tk.Menu(menubar,tearoff=0) menubar.add_cascade(label='File',menu=filemenu) filemenu.add_cascade(label='New',command=do_job) # 给file 加各种功能 filemenu.add_cascade(label='Open',command=do_job) filemenu.add_cascade(label='Save',command=do_job) filemenu.add_separator() # 分割线 filemenu.add_cascade(label='Exit',command=window.quit) # 关掉窗口 editmenu = tk.Menu(menubar,tearoff=0) menubar.add_cascade(label='Edit',menu=editmenu) # 给 edit 加各种功能 editmenu.add_cascade(label='Cut',command=do_job) editmenu.add_cascade(label='Copy',command=do_job) editmenu.add_cascade(label='Paste',command=do_job) submenu = tk.Menu(filemenu) # file 中再嵌套一个 Import 下有 Submenu1 filemenu.add_cascade(label='Import',menu=submenu,underline=0) submenu.add_command(label='Submenu1',) window.config(menu=menubar) window.mainloop() # 不断的循环循环窗口,保证我们点击窗口后,可以及时执行命令
第十步:Frame 窗口布局


import tkinter as tk window = tk.Tk() # 窗口obj对象 window.title('my TK') # 窗口名字 window.geometry('200x200') # 窗口宽度和高度 l = tk.Label(window,text='on the window',bg='yellow') l.pack() frm = tk.Frame(window) # 主frame frm.pack() frm_l = tk.Frame(frm) # 左fram frm_r = tk.Frame(frm) # 右fram frm_l.pack(side='left') frm_r.pack(side='right') tk.Label(frm_l,text='on the frame_l1').pack() tk.Label(frm_l,text='on the frame_l2').pack() tk.Label(frm_r,text='on the frame_r1').pack() window.mainloop() # 不断的循环循环窗口,保证我们点击窗口后,可以及时执行命令
第十一步:messagebox 弹窗
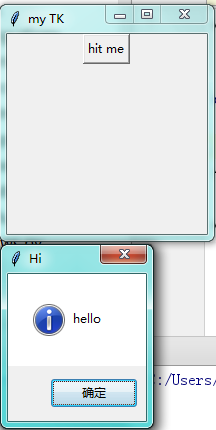

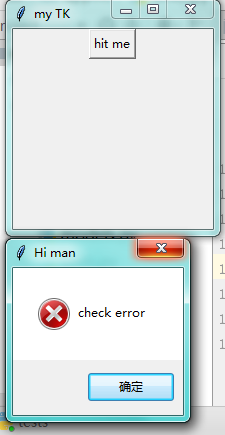

import tkinter as tk from tkinter import messagebox window = tk.Tk() # 窗口obj对象 window.title('my TK') # 窗口名字 window.geometry('200x200') # 窗口宽度和高度 def hit_me(): # messagebox.showinfo(title='Hi',message='hello') # messagebox.showwarning(title='Hi man',message='check warning') # messagebox.showerror(title='Hi man',message='check error') # messagebox.askquestion(title='Hi man',message='hello world') # return yes or no # messagebox.askokcancel(title='Hi man',message='hello world') # return True or False messagebox.askyesno(title='Hi man',message='hello world') # return True or False tk.Button(window,text='hit me',command=hit_me).pack() window.mainloop() # 不断的循环循环窗口,保证我们点击窗口后,可以及时执行命令
第十二步:放置位置

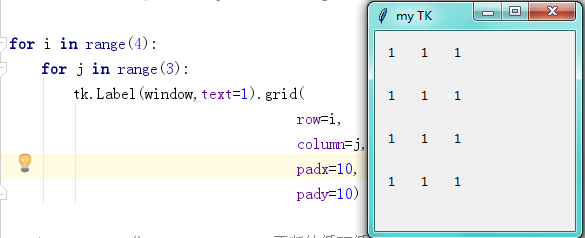
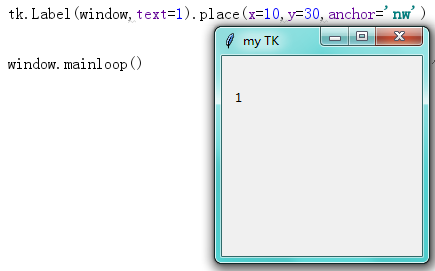

import tkinter as tk from tkinter import messagebox window = tk.Tk() # 窗口obj对象 window.title('my TK') # 窗口名字 window.geometry('200x200') # 窗口宽度和高度 # tk.Label(window,text=1).pack(side='top') # tk.Label(window,text=2).pack(side='left') # tk.Label(window,text=3).pack(side='bottom') # tk.Label(window,text=4).pack(side='right') # for i in range(4): # for j in range(3): # tk.Label(window,text=1).grid(row=i,column=j,padx=10,pady=10) tk.Label(window,text=1).place(x=10,y=30,anchor='nw') window.mainloop() # 不断的循环循环窗口,保证我们点击窗口后,可以及时执行命令
第十三步:登录注册窗口
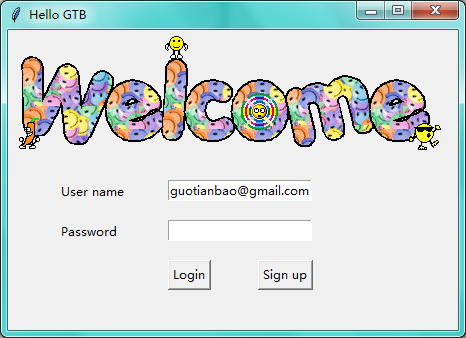
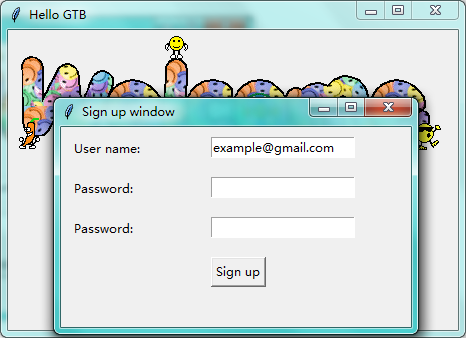

from tkinter import messagebox import tkinter as tk from tkinter import * import pickle window = tk.Tk() # 窗口obj对象 window.title('Hello GTB') # 窗口名字 window.geometry('450x300') # 窗口宽度和高度 # welcome message canvas = tk.Canvas(window,height=200,width=500) image_file = PhotoImage(file='C:\\Users\\mu\\Desktop\\welcome.gif') image = canvas.create_image(0,0,anchor='nw',image=image_file) canvas.pack(side='top') var_user_name = tk.StringVar() var_user_name.set('guotianbao@gmail.com') var_password = tk.StringVar() # userinfo tk.Label(window,text='User name').place(x=50,y=150) tk.Label(window,text='Password').place(x=50,y=190) entry_user_name = tk.Entry(window,textvariable=var_user_name) entry_user_name.place(x=160,y=150) entry_password = tk.Entry(window,textvariable=var_password,show='*') entry_password.place(x=160,y=190) # login and sign up def user_login(): user_name = var_user_name.get() user_password = var_password.get() try: with open('C:\\Users\\mu\\PycharmProjects\\mycrm\\app01\\user_info.txt','rb') as user_file: user_info = pickle.load(user_file) except FileNotFoundError: with open('user_info.txt', 'ab+') as user_file: user_info = {'admin':'admin'} pickle.dump(user_info,user_file) if user_name in user_info: if user_password == user_info[user_name]: messagebox.showinfo(title='Welcome',message='How are you '+user_name) else: messagebox.showerror(title='Hi man',message= 'Your password is wrong, try again. ') else: is_sign_up = messagebox.askyesno('Welcome','You have not sign up yet. Sign up now ?') if is_sign_up: user_sign() def user_sign(): def sign_last(): np = new_pwd.get() # 注册密码 npf = new_pwd_confirm.get() # 确认密码 nn = new_name.get() # 注册的名字 with open('C:\\Users\\mu\\PycharmProjects\\mycrm\\app01\\user_info.txt','rb') as usr_file : exist_usr_info = pickle.load(usr_file) if np != npf: tk.messagebox.showerror('Error', 'Password and confirm password must be the same!') elif nn in exist_usr_info: tk.messagebox.showerror('Error', 'The user has already signed up!') else: exist_usr_info[nn] = np with open('usrs_info.txt', 'ab+') as usr_file: pickle.dump(exist_usr_info, usr_file) tk.messagebox.showinfo('Welcome', 'You have successfully signed up!') window_sign_up.destroy() window_sign_up = tk.Toplevel() window_sign_up.title('Sign up window') window_sign_up.geometry('350x200') new_name = tk.StringVar() new_name.set('example@gmail.com') tk.Label(window_sign_up,text='User name:').place(x=10,y=10) entry_new_name = tk.Entry(window_sign_up,textvariable=new_name) entry_new_name.place(x=150,y=10) new_pwd = tk.StringVar() tk.Label(window_sign_up, text='Password:').place(x=10, y=50) entry_new_pwd = tk.Entry(window_sign_up, textvariable=new_pwd,show='*') entry_new_pwd.place(x=150, y=50) new_pwd_confirm = tk.StringVar() tk.Label(window_sign_up, text='Password:').place(x=10, y=90) entry_new_pwd_confirm = tk.Entry(window_sign_up, textvariable=new_pwd_confirm,show='*') entry_new_pwd_confirm.place(x=150, y=90) btn_comfirm_sign_up = tk.Button(window_sign_up, text='Sign up', command=sign_last) btn_comfirm_sign_up.place(x=150, y=130) btn_login = tk.Button(window,text='Login',command=user_login) btn_login.place(x=160,y=230) btn_login = tk.Button(window,text='Sign up',command=user_sign) btn_login.place(x=250,y=230) window.mainloop() # 不断的循环循环窗口,保证我们点击窗口后,可以及时执行命令
学习: YouTube 莫烦 python GUI 简易教程


