二叉树
二叉树的基本操作(C++)
1. 首先创建二叉树结构,以及二叉树的类,定义在BinaryTree.h中
1 #ifndef _BINARYTREE_H 2 #define _BINARYTREE_H 3 #include "pch.h" 4 #include <iostream> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 typedef struct TreeNode 9 { 10 char val; //节点的数据类型 11 TreeNode * left; //左子树 12 TreeNode * right; //右子树 13 TreeNode(char x):val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 14 15 }TreeNode, *BiTree; 16 17 class BinaryTree 18 { 19 public: 20 BinaryTree() {} 21 ~BinaryTree() {} 22 void TreeCreate(); //递归的创建二叉树的节点 23 int getSize(); //递归得到树的节点数目 24 int getHeight(); //递归得到树的高度 25 void preOrder(); //前序遍历 26 void inOrder(); //中序遍历 27 void postOrder(); //后序遍历 28 void distroy(); //删除二叉树 29 30 private: 31 BiTree create(); //递归的创建二叉树的节点 32 void preOrder(BiTree root); //前序遍历 33 void inOrder(BiTree root); //中序遍历 34 void postOrder(BiTree root); //后序遍历 35 void distroy(BiTree root); //摧毁树 36 int getHeight(BiTree root); //递归得到树的高度 37 void AddNode(const char key, int direction, BiTree root); //添加节点 38 BiTree m_root; //根节点 39 int size; //节点总数 40 }; 41 42 #endif
2. 具体实现 BinaryTree.cpp
# include "BinaryTree.h"
#pragma region 私有成员函数
//添加节点
//key为要插入的值,direction是从左子树插入还是右子树插入,root为从哪个节点插入
void BinaryTree::AddNode(const char key, int direction, BiTree root)
{
if (direction == 0)
{
//从左子树插入
if (root->left == NULL)
root->left = new TreeNode(key);
else
AddNode(key, direction, root->left);
}
else if (direction == 1)
{
//从右子树插入
if (root->right == NULL)
root->right = new TreeNode(key);
else
AddNode(key, direction, root->right);
}
}
//二叉树的建立,按前序遍历(root->left->right)的方式建立二叉树
BiTree BinaryTree::create()
{
BiTree current = NULL;
char val;
cin >> val;//输入键值
if (val == '#')//标识当前子树为空,转向下一节点
{
return NULL;
}
else
{ //递归的创建左右子树
size++;//记录节点数
current = new TreeNode(val);
current->left = create();
current->right = create();
return current;
}
}
//删除二叉树
void BinaryTree::distroy(BiTree root)
{
if (root)
{
distroy(root->left);
distroy(root->right);
delete root;
root = NULL;
size = 0;
}
}
//递归得到树的高度
int BinaryTree::getHeight(BiTree root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int left_height = getHeight(root->left);
int right_height = getHeight(root->right);
return (left_height > right_height) ? (left_height + 1) : (right_height + 1);
}
//前序遍历 root->left->right
void BinaryTree::preOrder(BiTree root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
else
{
cout << root->val << " --> "; //首先打印根节点
preOrder(root->left); //接着遍历左子树
preOrder(root->right); //接着遍历右子树
}
}
//中序遍历 left->root->right
void BinaryTree::inOrder(BiTree root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
else
{
inOrder(root->left); //首先遍历左子树
cout << root->val << " --> "; //接着打印根节点
inOrder(root->right); //接着遍历右子树
}
}
//后序遍历 left->right->root
void BinaryTree::postOrder(BiTree root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
else
{
postOrder(root->left); //首先遍历左子树
postOrder(root->right); //接着遍历右子树
cout << root->val << " --> "; //接着打印根节点
}
}
#pragma endregion
#pragma region 公有成员函数
//二叉树的建立
void BinaryTree::TreeCreate()
{
size = 0;
m_root =create();
}
//删除二叉树
void BinaryTree::distroy()
{
distroy(m_root);
}
//递归得到树的高度
int BinaryTree::getHeight()
{
return getHeight(m_root);
}
//前序遍历
void BinaryTree::preOrder()
{
cout << "前序遍历的结果如下:" << endl;
preOrder(m_root);
cout << endl;
}
//中序遍历
void BinaryTree::inOrder()
{
cout << "中序遍历的结果如下:" << endl;
inOrder(m_root);
cout << endl;
}
//后序遍历
void BinaryTree::postOrder()
{
cout << "后序遍历的结果如下:" << endl;
postOrder(m_root);
cout << endl;
}
//获取大小
int BinaryTree::getSize()
{
//这里是创建时候直接进行了计数
//也可以利用遍历的方式获取,当节点有值,就加1
return size;
}
#pragma endregion
3.主函数调用
int main() { BinaryTree tree; cout << "按前序遍历方式创建树" << endl; //"ABDG##H###CE#I##F##"; tree.TreeCreate(); cout << "树的高度为:" << tree.getHeight() << endl; cout << "树的节点为:" << tree.getSize() << endl; tree.preOrder(); //前序遍历 tree.inOrder(); //中序遍历 tree.postOrder(); //后序遍历 tree.distroy(); //摧毁树 system("pause"); }
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------分割线-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
输入的树的结构图如下:
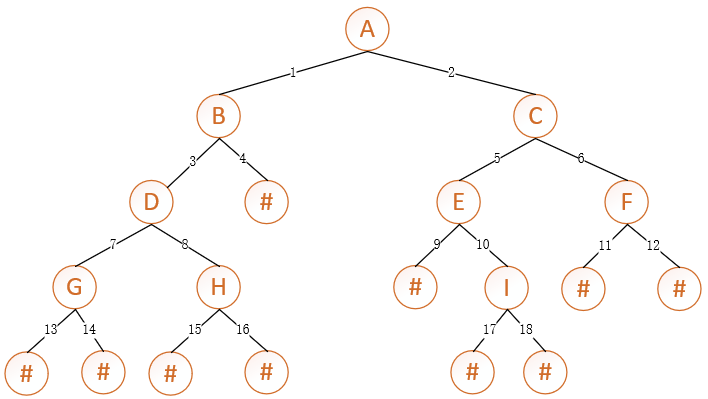
前序遍历:ABDGHCEIF(先是根结点,再前序遍历左子树,再前序遍历右子树)
中序遍历:GDHBAEICF(先中序遍历左子树,再是根结点,再是中序遍历右子树)
后序遍历:GHDBIEFCA(先后序遍历左子树,再是后序遍历右子树,再是根结点)
以该二叉树的创建为例说明递归进行的过程:
BiTree BinaryTree::create() { BiTree current = NULL; char val; cin >> val;//输入键值 if (val == '#')//标识当前子树为空,转向下一节点 { return NULL; } else { //递归的创建左右子树 size++;//记录节点数 current = new TreeNode(val); current->left = create(); current->right = create(); return current; } }
树的建立过程先“递"再"归"。递归可以理解为一个人去楼上拿东西。他沿楼梯上到有东西的楼层,这个可以理解为“递”;拿了东西后,再沿来时的楼梯下来,这个过程叫“归”。
输入 ABDG##H###CE#I##F## (前序遍历建树) 以A的左子树建立过程为例:
(1) “递”的过程:
在建立A后,以A为根节点开始建A的左子树B,然后再以B为根节点建立B的左子树D,按 A->B->D->G 的顺序依次建立。此时都在由左向右执行
current->left = create()
这条语句。但是current却不一样,按从顶层到底层的顺序 即,
- A->left=create B
- B->left=create D
- D->left=create G
- G->left=create()
(2) 当遇到“#”后就进入了“归”(底层到顶层的顺序 )的过程:
- 遇到“#”后,就会return null给G->left(由右向左 return),G->left建立完成;
- 接下来会进入G->right=create() 这条语句,然后遇到“#”后,就会return null给G->right,G->right建立完成;
- 当G->left 、G->right都建立完成后,就会return G 给 D->left,D->left建立完成;
- 接下来进入D->right=create H 这条语句,按照和建立G的过程一样建立完H,然后return H 给 D->right,D->right建立完成;
- 当D->left 、D->right都建立完成后,就会return D 给 B->left,B->left建立完成;
- 接下来会进入B->right=create() 这条语句,然后遇到“#”后,就会return null给B->right,B->right建立完成;
- 当B->left 、B->right都建立完成后,就会return B 给 A->left,A->left建立完成
(3) A的右子树建立也是同样过程
总结:
整个树的建立过程如下列顺序
开始 A-1->B-3->D-7->G-13->#-13->G-14->#-14->G-7->D-8->H-15->#-15->H-16->#-16->H-8->D-3->B-4->#-4->B-1->
A-2->C-5->E-9->#-9->E-10->I-17->#-17->I-18->#-18>I-10->E-5->C-6->F-11->#-11->F-12->#-12>F-6->C-2->A 结束



