架构模式
本人已迁移博客至掘进,以后会在掘进平台更新最新的文章也会有更多的干货,欢迎大家关注!!!https://juejin.im/user/588993965333309
今天讨论这个话题是比较大的,是关于iOS的架构方面的问题,随着开发的时间的不断增加,经过的项目也会不断地增加。很多时候会看到同事说,这是哪一个sb写的代码,为什么要放到这里,等等话语。说的这些问题,本篇博客我们来讲解MVC代码存在的耦合性慢慢衍生出MVP架构模式,然后再讲述MVVM模式以及RAC的介绍,主要是带着代码去讲解,希望通过这篇博客,大家可以增加对架构模式的理解,以及可以自由的选择架构模式。
- MVC架构思路
- MVC封装和解耦
- MVP架构思路
- MVVM架构思路
一、MVC架构思路
在MVC,MVP以及MVVM中,大家可能对MVC架构模式更熟悉!下面是大家非常熟悉的一张图。
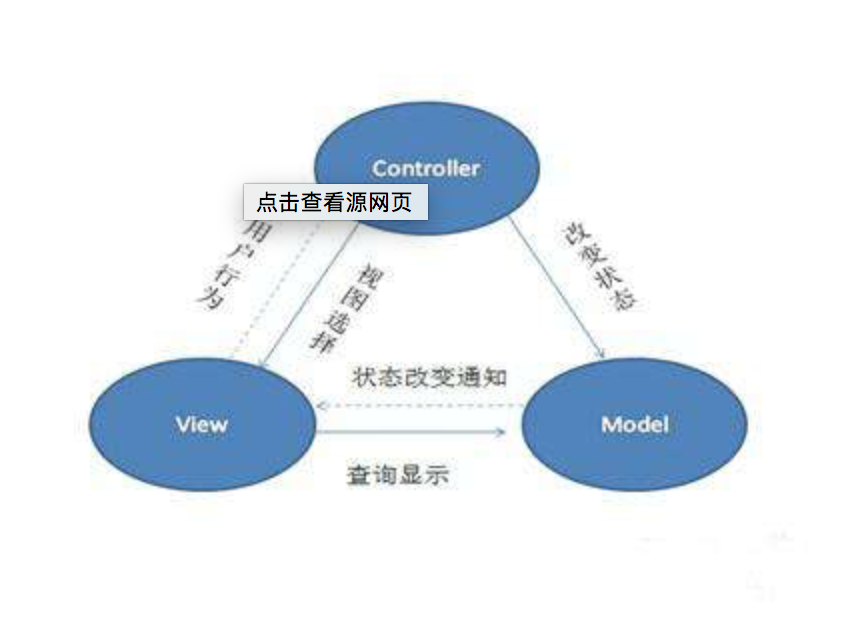
在代码里面体验可能是这样,下面我们以一个列表展示MVC方式的显示。
举例:下面我们要实现下面的简单界面!
1.1 Controller
在控制器Controller中,完成对数据的请求,以及数据源的展示!
- (void)loadData{ NSArray *temArray = @[ @{@"name":@"zxy1",@"imageUrl":@"http://hello",@"num":@"99"}, @{@"name":@"zxy2",@"imageUrl":@"http://hello",@"num":@"99"}, @{@"name":@"zxy3",@"imageUrl":@"http://hello",@"num":@"99"}, @{@"name":@"zxy4",@"imageUrl":@"http://hello",@"num":@"59"}, @{@"name":@"zxy5",@"imageUrl":@"http://hello ",@"num":@"49"}]; for (int i = 0; i<temArray.count; i++) { Model *m = [Model modelWithDictionary:temArray[i]]; [self.dataArray addObject:m]; } } #pragma mark - tableViewDataSource - (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section{ return self.dataArray.count; }
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath{
MVCTableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:reuserId forIndexPath:indexPath];
cell.model = self.dataArray[indexPath.row];
return cell;
}
在viewDidload里面完成初始化!
- (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; [self loadData]; [self.view addSubview:self.tableView]; self.tableView.delegate = self; self.tableView.dataSource = self; }
上面的cell的cell.model = self.dataArray[indexPath.row]会出发view的setModel方法,进行赋值!
1.2 View
view里面包括数据model,完成对显示层的赋值!
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h> #import "Model.h" @interface MVCTableViewCell : UITableViewCell @property (nonatomic, strong) UIButton *subBtn; @property (nonatomic, strong) UILabel *nameLabel; @property (nonatomic, strong) UILabel *numLabel; @property (nonatomic, strong) UIButton *addBtn; @property (nonatomic, assign) int num; @property (nonatomic, strong) NSIndexPath *indexPath; @property (nonatomic, strong) Model *model; @end
在view通过setModel:进行赋值
- (void)setupUI{ [self.contentView addSubview:self.nameLabel]; [self.contentView addSubview:self.subBtn]; [self.contentView addSubview:self.numLabel]; [self.contentView addSubview:self.addBtn]; self.num = 0; } - (void)setModel:(Model *)model{ _model = model; self.nameLabel.text = model.name; self.numLabel.text = model.num; }
1.3 Model
在请求的数据中,声明属性
@interface Model : NSObject @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name; @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *imageUrl; @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *num; @end
上面就是简单的MVC的代码结构,我相信很多人都写过类似的代码!但是上面的代码对于大工程项目来说,耦合性太高,下面来讲述MVC封装和解耦!
二、MVC封装和解耦
而苹果愿景中的MVC是这样的。
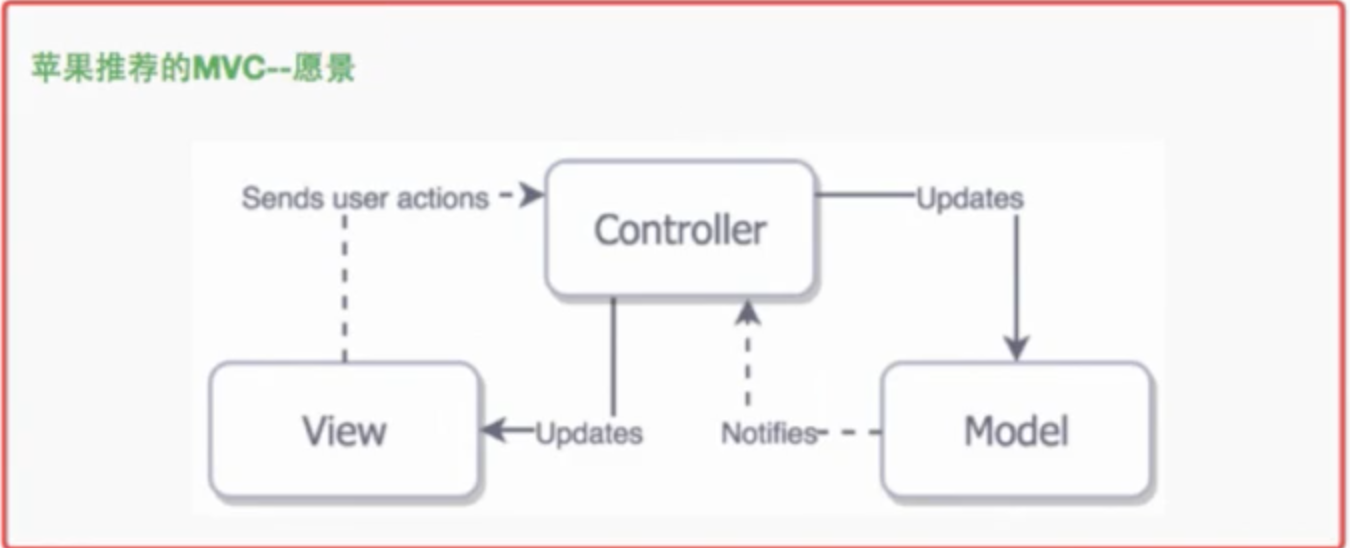
但在上面实际的MVC操作中,比如上面
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath{ MVCTableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:reuserId forIndexPath:indexPath]; cell.model = self.dataArray[indexPath.row]; return cell; }
cell.model = self.dataArray[indexPath.row];这句代码不是不对,而是不好,cell---Model造成了强引用,耦合性特别高。
仔细看上面MVC结构的代码,数据还是自己自定义数据,还没有加入网络请求以及业务处理,就看出来Controller就会变得非常臃肿,如下图:
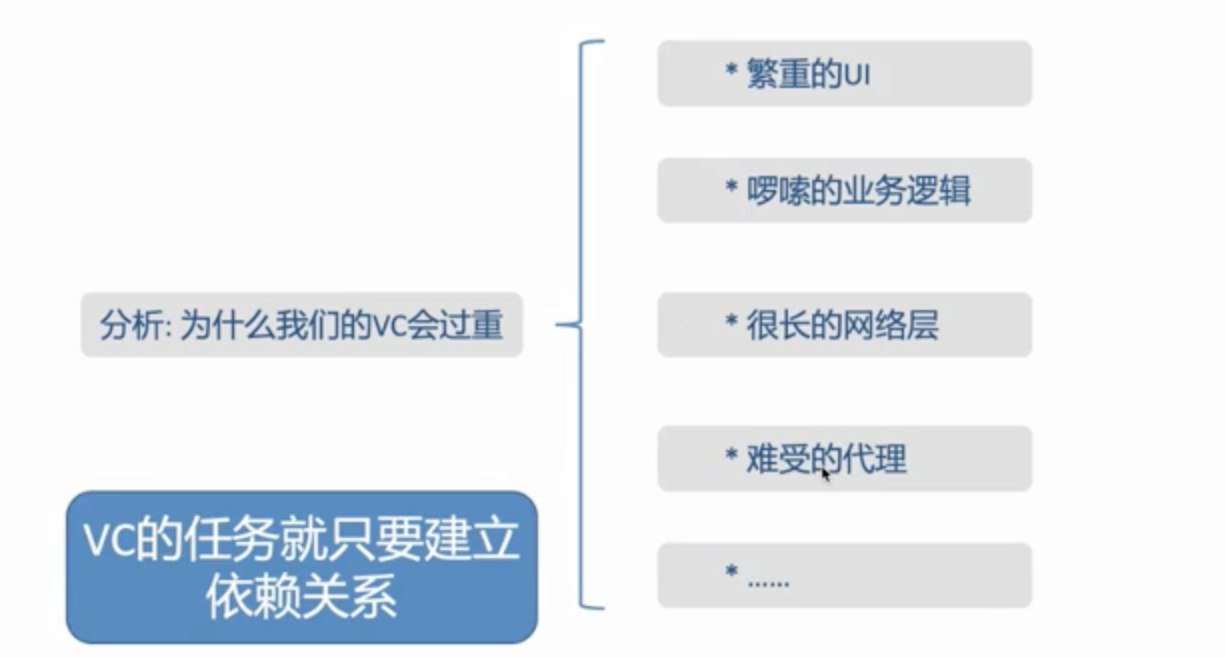
对于tableView或者CollectionView的数据源代码看起来非常臃肿,下面我们针对数据源进行封装以及解耦。
针对数据源方法,我们新建立一个LMDataSource类,用于数据源方法的封装
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> #import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
//声明一个block,用于回调cell,model,下标 typedef void (^CellConfigureBefore)(id cell, id model, NSIndexPath * indexPath); @interface LMDataSource : NSObject<UITableViewDataSource,UICollectionViewDataSource> @property (nonatomic, strong) NSMutableArray *dataArray;; //自定义 - (id)initWithIdentifier:(NSString *)identifier configureBlock:(CellConfigureBefore)before; // @property (nonatomic, strong) IBInspectable NSString *cellIdentifier; @property (nonatomic, copy) CellConfigureBefore cellConfigureBefore; - (void)addDataArray:(NSArray *)datas; - (id)modelsAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath; @end
在LMDataSource.m中进行实现相应代码:
#import "LMDataSource.h" @implementation LMDataSource - (id)initWithIdentifier:(NSString *)identifier configureBlock:(CellConfigureBefore)before { if(self = [super init]) { _cellIdentifier = identifier; _cellConfigureBefore = [before copy]; } return self; } - (void)addDataArray:(NSArray *)datas{ if(!datas) return; if (self.dataArray.count>0) { [self.dataArray removeAllObjects]; } [self.dataArray addObjectsFromArray:datas]; } - (id)modelsAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { return self.dataArray.count > indexPath.row ? self.dataArray[indexPath.row] : nil; } #pragma mark UITableViewDataSource
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section { return !self.dataArray ? 0: self.dataArray.count; } - (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:self.cellIdentifier forIndexPath:indexPath]; id model = [self modelsAtIndexPath:indexPath]; if(self.cellConfigureBefore) { self.cellConfigureBefore(cell, model,indexPath); } return cell; } #pragma mark UICollectionViewDataSource
- (NSInteger)collectionView:(UICollectionView *)collectionView numberOfItemsInSection:(NSInteger)section{ return !self.dataArray ? 0: self.dataArray.count; } - (UICollectionViewCell *)collectionView:(UICollectionView *)collectionView cellForItemAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { UICollectionViewCell *cell = [collectionView dequeueReusableCellWithReuseIdentifier:self.cellIdentifier forIndexPath:indexPath]; id model = [self modelsAtIndexPath:indexPath]; if(self.cellConfigureBefore) { self.cellConfigureBefore(cell, model,indexPath); } return cell; } - (NSMutableArray *)dataArray{ if (!_dataArray) { _dataArray = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:5]; } return _dataArray; } @end
然后我们针对请求数据进行封装到另一个类Util中
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> #import "Model.h" #import <YYKit.h> @interface Util : NSObject @property (nonatomic, strong) NSMutableArray *dataArray; @end
实现方法
#import "Util.h" @implementation Util - (instancetype)init{ self = [super init]; if (self) { [self loadData]; } return self; } - (void)loadData{ NSArray *temArray = @[ @{@"name":@"zxy1",@"imageUrl":@"http://hello",@"num":@"99"}, @{@"name":@"zxy2",@"imageUrl":@"http://hello",@"num":@"99"}, @{@"name":@"zxy3",@"imageUrl":@"http://hello",@"num":@"99"}, @{@"name":@"zxy4",@"imageUrl":@"http://hello",@"num":@"59"}, @{@"name":@"zxy5",@"imageUrl":@"http://hello ",@"num":@"49"}]; for (int i = 0; i<temArray.count; i++) { Model *m = [Model modelWithDictionary:temArray[i]]; [self.dataArray addObject:m]; } } #pragma mark - lazy - (NSMutableArray *)dataArray{ if (!_dataArray) { _dataArray = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:10]; } return _dataArray; } @end
上面已经将数据源方法和请求数据封装了,所以在Controller就会变成
#import "MVCViewController.h" #import "LMDataSource.h" #import "MVCTableViewCell.h" #import "Util.h" #import "Model.h" #import <YYKit.h> static NSString *const reuserId = @"reuserId"; @interface MVCViewController ()<UITableViewDelegate,UITableViewDataSource> @property (nonatomic, strong) UITableView *tableView; @property (nonatomic, strong) NSMutableArray *dataArray; @property (nonatomic, strong) LMDataSource *dataSource; @property (nonatomic, strong) Util *pt; @end @implementation MVCViewController /** 1: 耦合性强 2: cell服用 UI <---> model (双向绑定) 3: VC 好重 : adapter */ - (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; // [self loadData]; self.dataSource = [[LMDataSource alloc] initWithIdentifier:reuserId configureBlock:^(MVCTableViewCell *cell, Model *model, NSIndexPath *indexPath) { cell.model = model;
//cell.numLabel.text = model.num;
//cell.nameLabel.text = model.name;
}]; self.pt = [[Util alloc] init]; [self.dataSource addDataArray:self.pt.dataArray]; self.view.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor]; [self.view addSubview:self.tableView]; self.tableView.dataSource = self.dataSource; // self.tableView.delegate = self; // self.tableView.dataSource = self; // } //- (void)loadData{ // // NSArray *temArray = // @[ // @{@"name":@"zxy1",@"imageUrl":@"http://hello",@"num":@"99"}, // @{@"name":@"zxy2",@"imageUrl":@"http://hello",@"num":@"99"}, // @{@"name":@"zxy3",@"imageUrl":@"http://hello",@"num":@"99"}, // @{@"name":@"zxy4",@"imageUrl":@"http://hello",@"num":@"59"}, // @{@"name":@"zxy5",@"imageUrl":@"http://hello ",@"num":@"49"}]; // for (int i = 0; i<temArray.count; i++) { // Model *m = [Model modelWithDictionary:temArray[i]]; // [self.dataArray addObject:m]; // } //} #pragma mark - tableViewDataSource //- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section{ // return self.dataArray.count; //} // // //- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath{ // MVCTableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:reuserId forIndexPath:indexPath]; // cell.model = self.dataArray[indexPath.row]; // return cell; //} // // //#pragma mark - tableViewDelegate // //- (void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView didSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath{ // [tableView deselectRowAtIndexPath:indexPath animated:YES]; //}
发现原本Controller很繁杂的代码,现在就会变得非常少。但是发现View和Model还是没有彻底解耦。
下面我们讲述另外一种架构模式。
三、MVP架构思路
3.1 MVP概括(面向协议(接口)编程)
MVP(Model-View-Presenter),是MVC架构模式的变形。因为UI是经常变化的,同样的数据可能有很多种显示方式,业务层也是比较容易变化的,我们希望UI的逻辑及业务逻辑和数据隔离出来,而MVP就是个很好地选择。
Presenter代替了Controller,但是比Controller担任更多的任务。Presenter处理事件,执行相应的逻辑而这些逻辑映射到Model的Command用来操作Model,处理UI如何工作的代码都会放到了Utiler上。
Model和View使用Observer观察者模式进行通信;而Presenter和View是使用Mediator模式进行沟通;Presenter使用Command模式来操作Model。
对待处理流程中:
MVC中,用户的请求会先到达控制器Controller,控制器Controller从Model里面获取数据,然后选中合适的View,将数据呈现在View上;但是在MVP中,用户的请求首先会到达View中,View进行传递请求到指定的Presenter,Presenter从Model获取后,再把处理结果通过接口传到View上。
下面是MVP(Model-View-Utiler)交互图
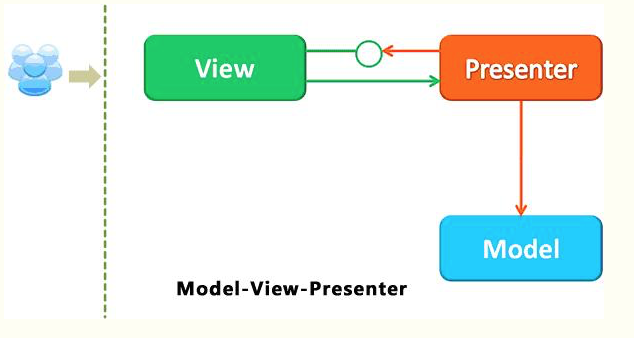
在上面的MVC 中,数据库以及网络都会交给UIViewController,这样不便于团队开发,耦合性很高;MVP的诞生也是为了解决这个问题,将模块独立,数据是数据,UI是UI,完全隔离,做UI开发的专心做UI开发,数据库维护的专门维护数据库,我们就通过P层(中介将UI层和数据层关联),类似于下面:
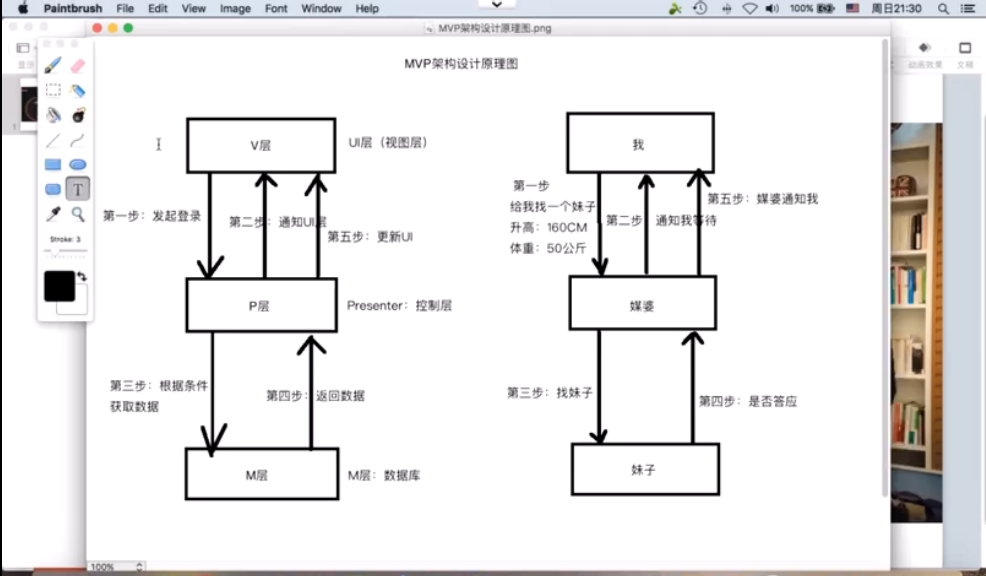
3.2 下面将讲述项目MVP架构
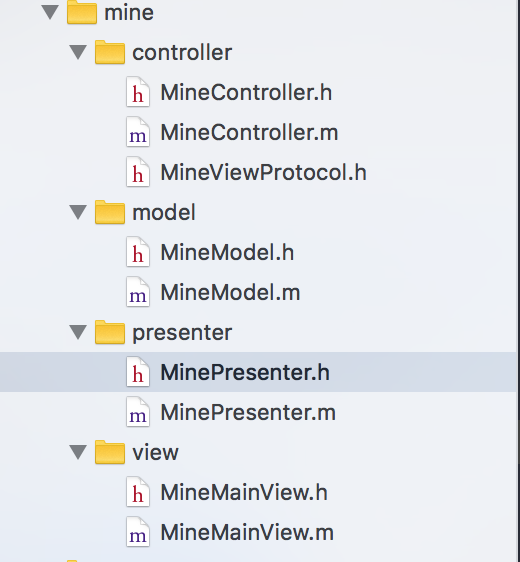
3.2.1 Controller
在控制器里面完成主要view的加载。
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h> @interface MineController : UIViewController @end #import "MineController.h" #import "MineMainView.h" @interface MineController () @property (nonatomic,strong)MineMainView *mainView; @end @implementation MineController - (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; [self.view addSubview:self.mainView]; } #pragma mark - lazy load - (MineMainView *)mainView{ if (!_mainView) { _mainView = [[MineMainView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectZero]; } return _mainView; } @end
声明一个协议MineViewProtocol,完成成功或者失败赋值
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> #import "MineModel.h" @protocol MineViewProtocol <NSObject> - (void)onGetMineInfoSuccess:(MineModel *)model; - (void)onGetMineInfoFail:(NSInteger) errorCode des:(NSString *)des; @end
3.2.2 Model
Model和MVC的Model一样,声明属性。
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> @interface MineModel : NSObject @property (nonatomic,copy) NSString *name; @property (nonatomic,copy) NSString *address; @property (nonatomic,copy) NSString *birthday; @end #import "MineModel.h" @implementation MineModel @end
3.2.3 View
View进行UI的显示,拿到数据之后,可以实现接口完成对UI界面的赋值。
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h> /** 如果MineMainView是一个共用页面,并且需要其他数据资源,可以将presenter写在view里面 */ @interface MineMainView : UIView @end #import "MineMainView.h" #import "MinePresenter.h" @interface MineMainView()<MineViewProtocol> @property (nonatomic,strong)MinePresenter *presenter; @end @implementation MineMainView - (instancetype)init { self = [super init]; if (self) { [self.presenter getMineInfoWithURLString:@"mine" param:@{}]; } return self; } #pragma mark - lazy load - (MinePresenter *)presenter{ if (!_presenter) { _presenter = [[MinePresenter alloc] initWithView:self]; } return _presenter; } #pragma MineViewProtocol
- (void)onGetMineInfoSuccess:(MineModel *)model{ //这里做一些与UI相关的事情,完成对UI的赋值,避免了view与model的强依赖 } - (void)onGetMineInfoFail:(NSInteger) errorCode des:(NSString *)des{ } @end
3.2.4 presenter
#import "HttpPresenter.h" #import "MineViewProtocol.h" @interface MinePresenter : HttpPresenter <id<MineViewProtocol>> //用于请求数据 - (void)getMineInfoWithURLString:(NSString *)URLString param:(NSDictionary *)param; @end
在相应的实现中
#import "MinePresenter.h" #import "MineModel.h" #import "HKHttpResponse.h" @implementation MinePresenter - (void)getMineInfoWithURLString:(NSString *)URLString param:(NSDictionary *)param{ [self.httpClient get:URLString parameters:param]; } #pragma mark - HttpResponseHandle //用来回调,触发view代理,完成赋值 - (void)onSuccess:(id )responseObject{ HKHttpResponse * responseObj = (HKHttpResponse *)responseObject; MineModel *model = [MineModel yy_modelWithJSON:responseObj.content]; if ([_view respondsToSelector:@selector(onGetMineInfoSuccess:)]) { [_view onGetMineInfoSuccess:model]; } } - (void)onFail:(id)clientInfo errCode:(NSInteger)errCode errInfo:(NSString *)errInfo{ if ([_view respondsToSelector:@selector(onGetMineInfoFail:des:)]) { [_view onGetMineInfoFail:errCode des:errInfo]; } } @end
上面就是简单的MVP的项目使用和简单的架构结构。如果嵌套层次比较多,页面比较复杂,传值比较频繁,不推荐用MVP架构方式,而需求非常清晰,嵌套层次比较少可以尝试用MVP。
四、MVVM架构思路(双向绑定)
MVVM架构中,组件就会随之变成Model-View-ViewModel,如下图:
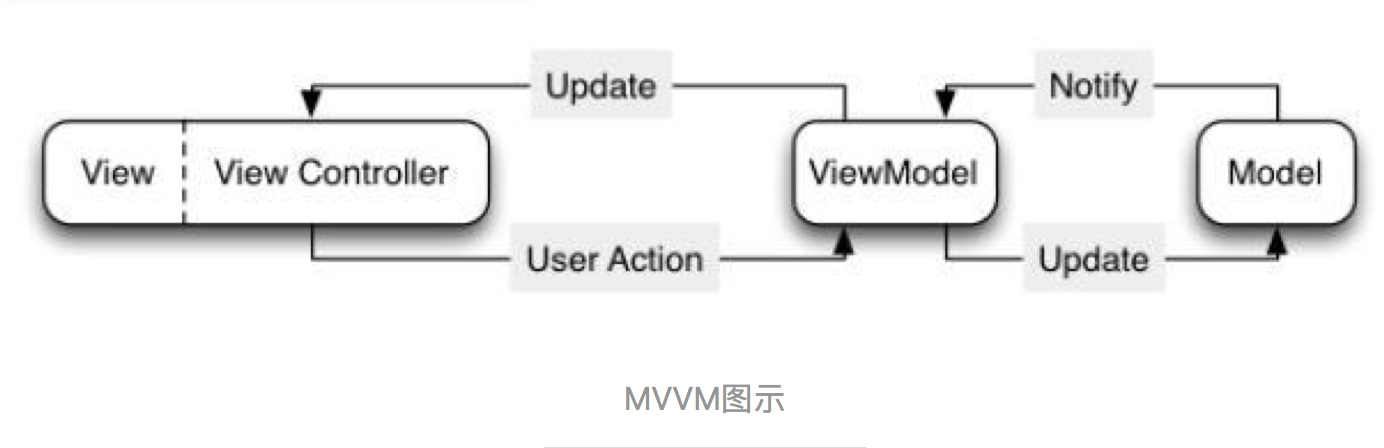
ViewModel是MVC新引入的视图模型,用于显示逻辑,验证逻辑和网络请求存放的地方。但需要注意的是视图本身不应该放在VM中,换句话说就是VM代码中不要引入UIKit.h,这样解决了VC臃肿的问题,然后VM包含所有的展示逻辑但不会引用V,所以这样是可以通过编程充分测试。
我们来一起看一下在具体代码中的使用:
下面我们一一讲解各个文件夹的使用:
4.1 IOAMeAddressApi
对于Api文件夹,我们首先看一下此类包含的内容:请求参数的配置
#import "IOARequest.h" #import "IOAMeAddressModel.h" // 新增地址 @interface IOAMeAddAddressRequest: IOARequest @property (nonatomic, strong) IOAMeAddressModel *addressModel; @end // 设置默认收货地址 @interface IOAMeSetDefaultAddressRequest: IOARequest @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *addressId; @end // 收货地址列表 @interface IOAMeAddressListRequest: IOARequest @end // 删除收货地址 @interface IOAMeDeleteAddressRequest: IOAMeSetDefaultAddressRequest //@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *addressId; @end
然后IOAMeAddressApi.m中
#import "IOAMeAddressApi.h" // 新增地址 @implementation IOAMeAddAddressRequest - (id)requestArgument { NSMutableDictionary *dic = [IOAApiManager getParametersWithService:@"App.Users...."]; self.addressModel.province = self.addressModel.pId; self.addressModel.city = self.addressModel.cId; self.addressModel.district = self.addressModel.aId; if (self.addressModel.city == nil) { self.addressModel.city = @""; } if (self.addressModel.district == nil) { self.addressModel.district = @""; } NSDictionary *temp = [self.addressModel yy_modelToJSONObject]; [dic addEntriesFromDictionary:temp]; return dic; } @end // 设置默认收货地址 @implementation IOAMeSetDefaultAddressRequest - (id)requestArgument { NSMutableDictionary *dic = [IOAApiManager getParametersWithService:@"App.Users......"]; if (self.addressId) { [dic setObject:self.addressId forKey:@"address_id"]; } return dic; } @end // 收货地址列表 @implementation IOAMeAddressListRequest - (id)requestArgument { NSMutableDictionary *dic = [IOAApiManager getParametersWithService:@"App.Users......"]; return dic; } @end // 删除收货地址 @implementation IOAMeDeleteAddressRequest - (id)requestArgument { NSMutableDictionary *dic = [IOAApiManager getParametersWithService:@"App.Users....."]; if (self.addressId) { [dic setObject:self.addressId forKey:@"address_id"]; } return dic; } @end
这个类IOAMeAddressApi用于ViewModel中发送请求的请求体参数的配置,没有太多的难度,仅仅为了防止ViewModel臃肿。
4.2 IOAMeAddressModel
Model用于请求数据属性的声明(IOAMeAddressModel继承于IOAUserAddressBaseModel)
/* address_id 地址ID consignee 收货人 country 国家 province 省份 city 城市 district 地区 twon 乡镇 address 地址 zipcode 邮政编码 name 姓名 mobile 手机 telephone 电话号码 address_alias 地址别名 is_default 默认收货地址 */ @interface IOAMeAddressModel : IOAUserAddressBaseModel @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *consignee; @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *zipcode; @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *address_id; @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *twon; @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *address_alias; @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *is_default; @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *telephone; @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *country; @end
在上面声明了属性,如果有需要特殊处理的属性,看一下实现方法
#import "IOAMeAddressModel.h" @implementation IOAMeAddressModel + (NSDictionary *)modelCustomPropertyMapper { return @{ @"pId" : @"p_id", @"cId" : @"c_id", @"aId" : @"d_id" }; } // 根据code获取地址 - (NSString *)getAddress { NSMutableString *address = [NSMutableString string]; if (self.province.length) { [address appendString:self.province]; } if (self.city.length && ![self.city isEqualToString:@"0"]) { [address appendString:@"-"]; [address appendString:self.city]; } if (self.district.length && ![self.district isEqualToString:@"0"]) { [address appendString:@"-"]; [address appendString:self.district]; } return address; } @end
上面红色方法modelCustomPropertyMapper是yyModel中的,用于解决json解析文件中关键字和定义声明的属性不一致的问题。
4.3 ViewModel
ViewModel在这个项目中用于完成对数据的请求和解析。就以新增收获地址接口来说:
@interface IOAMeAddressViewModel : NSObject // 新增修改收货地址 - (void)requestForAddAddress:(IOAMeAddressModel *)addressModel callback:(void (^)(IOAResponse *response))callback; @end
看一下实现方法
#import "IOAMeAddressViewModel.h" @implementation IOAMeAddressViewModel // 新增收货地址 - (void)requestForAddAddress:(IOAMeAddressModel *)addressModel callback:(void (^)(IOAResponse *response))callback { IOAMeAddAddressRequest *api = [[IOAMeAddAddressRequest alloc] init]; api.addressModel = addressModel; [api startWithCompletionBlockWithSuccess:^(IOARequest *request) { id dic = request.responseObject[@"data"]; IOAResponse *response = [IOAResponse responseWithRequest:request]; if (!dic) { if (callback) { callback(response); } return; } if ([dic isKindOfClass:[NSNumber class]] || [dic isKindOfClass:[NSString class]]) { if (![dic boolValue]) { if (callback) { callback(response); } return; } } response.success = YES; if (callback) { callback(response); } } failure:^(IOARequest *request) { IOAResponse *response = [IOAResponse responseWithRequest:request]; if (callback) { callback(response); } }]; }
上面startWithCompletionBlockWithSuccess方法是自己对网络第三方框架YTKNetwork的封装,大家想用本项目封装网络框架可以在下面地方下载。https://github.com/zxy1829760/YTKNetwork-
4.4 ViewController
ViewController完成对整个布局的初始化以及触发请求。
NSString *kCellIdentifier = @"IOAReceiveAddressTableViewCell"; @interface IOAReceiveAddressViewController () <IOACellDelegate> @property (nonatomic, strong) UIButton *addAddress; //@property (nonatomic, assign) NSUInteger select; @property (nonatomic, strong) IOAMeAddressViewModel *viewModel; @end @implementation IOAReceiveAddressViewController - (void)dealloc { } - (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; self.title = @"管理收货地址"; self.view.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor]; [self.dataSource removeAllObjects]; } - (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning { [super didReceiveMemoryWarning]; } - (void)viewWillAppear:(BOOL)animated { [super viewWillAppear:animated]; [self requestForAddressList]; } - (void)viewDidAppear:(BOOL)animated { [super viewDidAppear:animated]; } #pragma mark - IOAProtocol - (void)addSubViews { [super addSubViews]; [self.view addSubview:self.addAddress]; } - (void)prepare { CGFloat height = 44; [self.addAddress mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) { make.left.right.equalTo(self.view); make.bottom.equalTo(self.view).offset(-BottomHeightOffset); // make.bottom.equalTo(self.view.mas_safeAreaLayoutGuideBottom); // make.bottom.equalTo(self.view); make.height.mas_equalTo(height); }]; [self.tableView mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) { make.left.right.equalTo(self.view); make.bottom.equalTo(self.addAddress.mas_top); make.top.equalTo(self.view).offset(TopHeightOffset); // make.top.equalTo(self.view); // make.top.equalTo(self.view.mas_safeAreaLayoutGuideTop); }]; } #pragma mark - UITableViewDataSource - (NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInTableView:(UITableView *)tableView { return self.dataSource.count; } - (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section { return 1; } - (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { IOAReceiveAddressTableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:kCellIdentifier forIndexPath:indexPath]; cell.cellDelegate = self; cell.selectionStyle = UITableViewCellSelectionStyleNone; [cell update:self.dataSource[indexPath.section]]; return cell; } - (void)registerClasses { [self.tableView registerClass:[IOAReceiveAddressTableViewCell class] forCellReuseIdentifier:kCellIdentifier]; } - (void)clickedEmptyPage:(id)object { [self requestForAddressList]; } #pragma mark - IOARefreshAndLoadMoreDelegate - (void)refresh:(id<IOARefreshAndLoadMoreDelegate>)collection { [self requestForAddressList]; } #pragma mark - CellDelegate - (void)clickOn:(id)sender { IOAInfoTableViewCell *cell = sender; NSIndexPath *indexPath = [self.tableView indexPathForCell:cell]; IOAMeAddressModel *model = self.dataSource[indexPath.section]; if (cell.clickType == kInfoCellClickDelete) { [self requestForDeleteAddress:model.address_id withIndexPaht:indexPath]; } else if (cell.clickType == kInfoCellClickEdit) { IOAAddReceiveAddressViewController *vc = [IOAAddReceiveAddressViewController new]; vc.isEdit = YES; vc.addressModel = model; [self.navigationController pushViewController:vc animated:YES]; } else { // IOAMeAddressModel *model = self.dataSource[indexPath.section]; if ([model.is_default boolValue]) { [self.tableView reloadData]; return; } model.is_default = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%d", 1]; [self requestForSetDefaultAddress:model]; } } #pragma mark - Actions - (void)clickAddAdress:(UIButton *)sender { IOAAddReceiveAddressViewController *vc = [IOAAddReceiveAddressViewController new]; [self.navigationController pushViewController:vc animated:YES]; } #pragma mark - Api - (void)requestForAddressList { [self dismissEmptyPage]; [self startProgress]; [self.viewModel requestForAddressList:^(IOAResponse *response) { dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{ [self stopProgress]; NSArray<IOAMeAddressModel *> *addressList = response.responseObject; if (addressList) { [self.dataSource removeAllObjects]; [self.dataSource addObjectsFromArray:addressList]; [self.tableView reloadData]; if (self.dataSource.count == 0) { [self showNoDatasPage]; return ; } } else { if ([response isNoNetwork] && self.dataSource.count == 0) { [self showNoNetworkPage]; return; } if ([response isExpiryToken]) { [self showLoginViewController]; return; } if ([response alertOrNot]) { if (response.responseMessage.length > 0) { [self.view makeToast:response.responseMessage]; return; } [self.view makeToast:@"获取失败"]; } } }); }]; }
上面就是MVVM代码在实际项目中的使用。本篇博客会不断更新,因为框架的东西很难学完,慢慢优化。
下一篇我们将讲述MVVM+RAC的结合使用,以及了解RAC底层实现逻辑。



