字符流
3.字符流
3.1.为什么出现字符流
由于字节流操作中文不是很方便,所以Java就提供了字符流
- 字符流 = 字节流 + 编码表
- 用字节流复制文本文件时,文本文件也会由中文,但是没有问题,原因是最终底层操作会自动进行字节拼接成中文。
- 汉字在存储的时候,无论选择哪种编码存储,第一个字节都是负数
3.2编码表
基础知识:
- 计算机中存储的信息都是用二进制表示的;屏幕上看到的字符都是二进制数转换而来。
- 按照某种规则将字符存储到计算机中叫编码;反之称为解码。
- 注:按照A规则编码必须按照A规则解码,否则会乱码。
- 字符编码:就是一套自然语言的字符与二进制数之间的对应规则(A,65)
字符集
- 是一个系统支持所有字符的集合,
- 包括各国的文字,标点符号,图形符号,数字等
- 为了准确存储和识别各种字符集符号,就需要进行字符编码,
- 一套字符集编码必然有一套字符编码。
- 常见的有:ASCII字符集、GBXXX、Unicode字符集等



3.3字符串中的编码解码问题
package com.guoba.day1222.zifu; import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; import java.util.Arrays; /* UnsupportedEncodingException:不支持字符编码异常 */ public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { String s = "中国"; //byte[] bytes = s.getBytes("UTF-8");//[-28, -72, -83, -27, -101, -67] //byte[] bytes = s.getBytes("GBK");//[-42, -48, -71, -6] byte[] bytes = s.getBytes(); // String ss = new String(bytes,"GBK");//涓浗 // System.out.println(ss); String sss = new String(bytes,"utf-8");//中国 System.out.println(sss); //System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes)); } }
3.4字符流中的编码解码问题
字符流抽象基类
-
Reader: 字符输入流的抽象类
-
InputStreamReader:从字节流到字符流的桥梁
- 读取字节,并使用指定的编码将其解码为字符
- 它使用的字符集可以由名称指定,也可以被明确指定,或者可以接受平台默认的字符集
-
-
Writer:字符输出流的抽象类
- OutputStreamWriter:从字符流到字节流的桥梁
- 使用指定的编码将写入的字符编码为字节
- 使用的字符集可以由名称指定,也可以被明确指定,或者可以接受平台默认的字符集
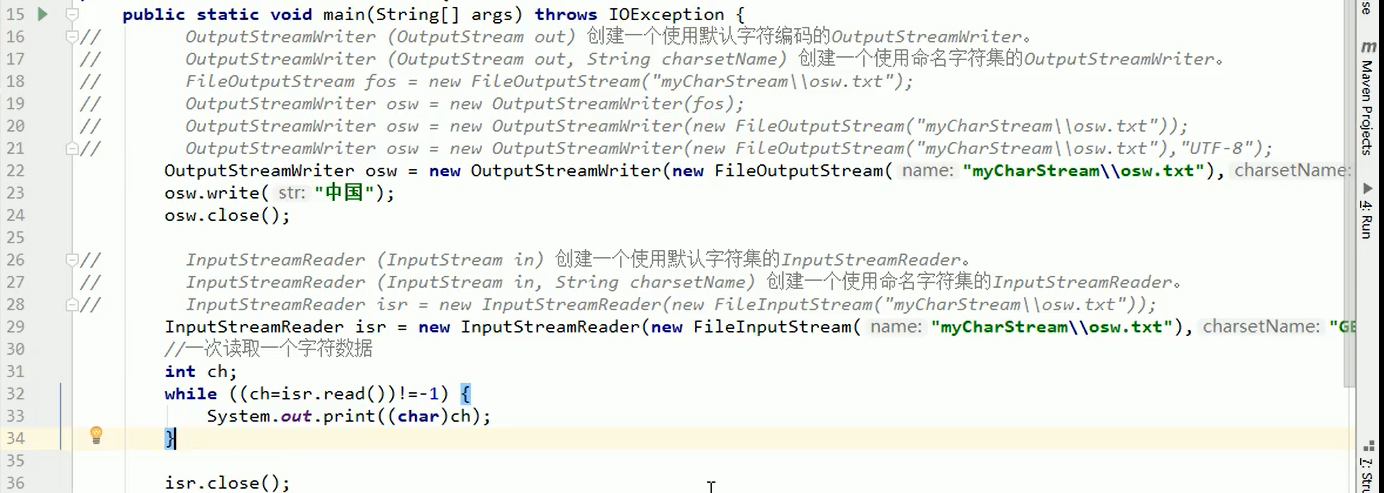
- OutputStreamWriter:从字符流到字节流的桥梁
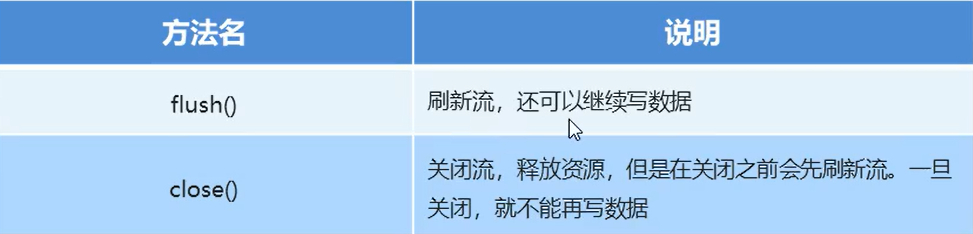
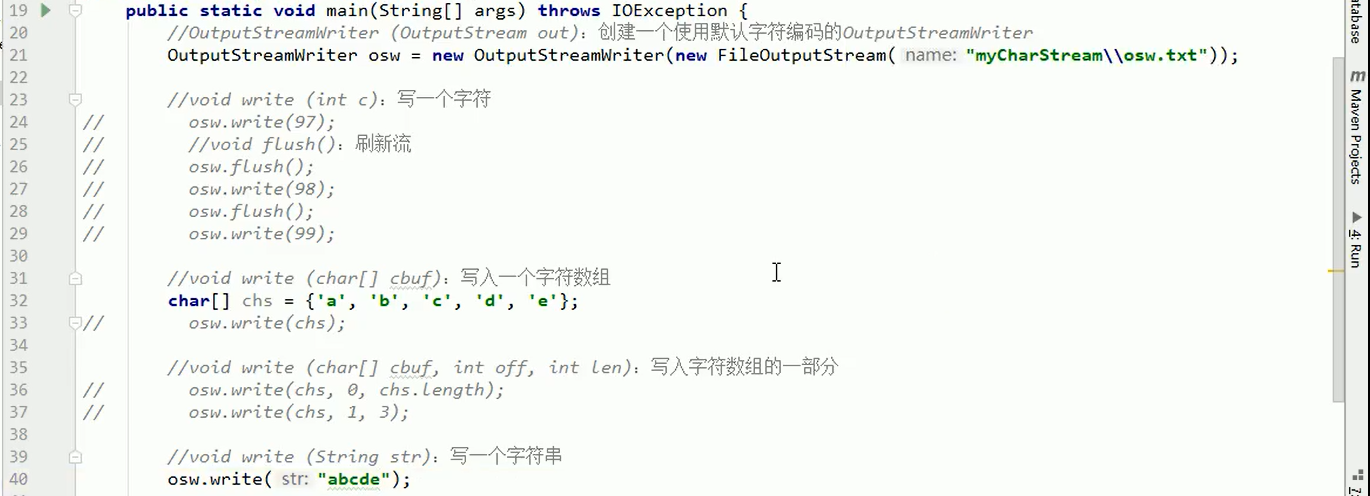
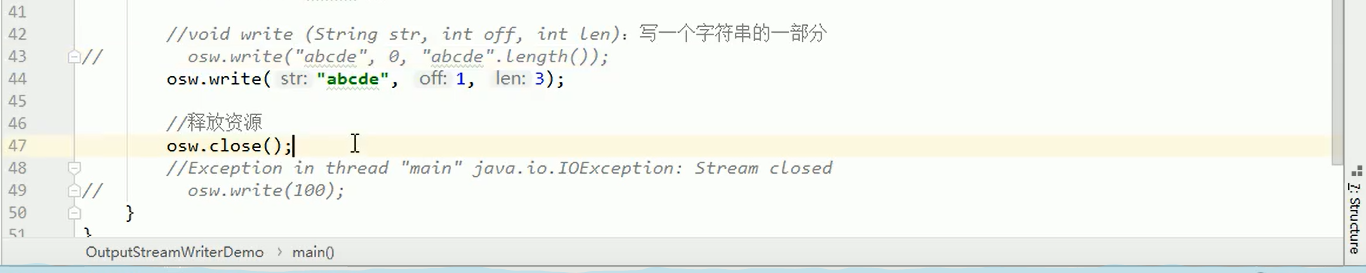
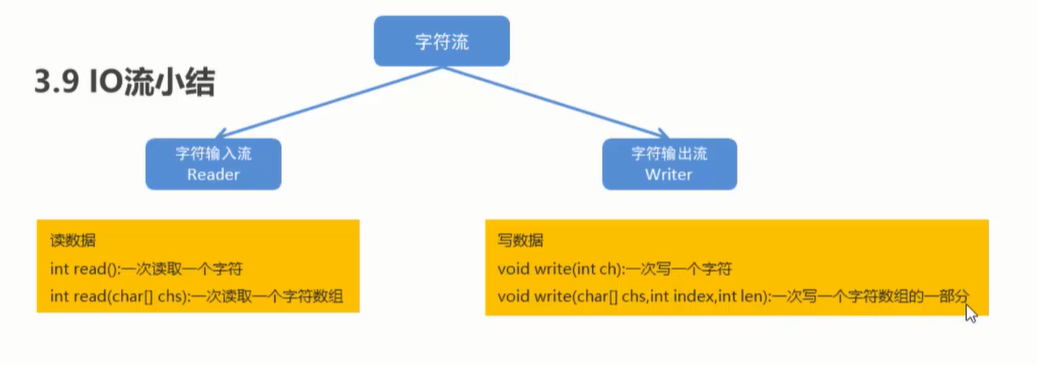
3.5字符流写数据的5种方式

3.6字符流读数据的两种方式

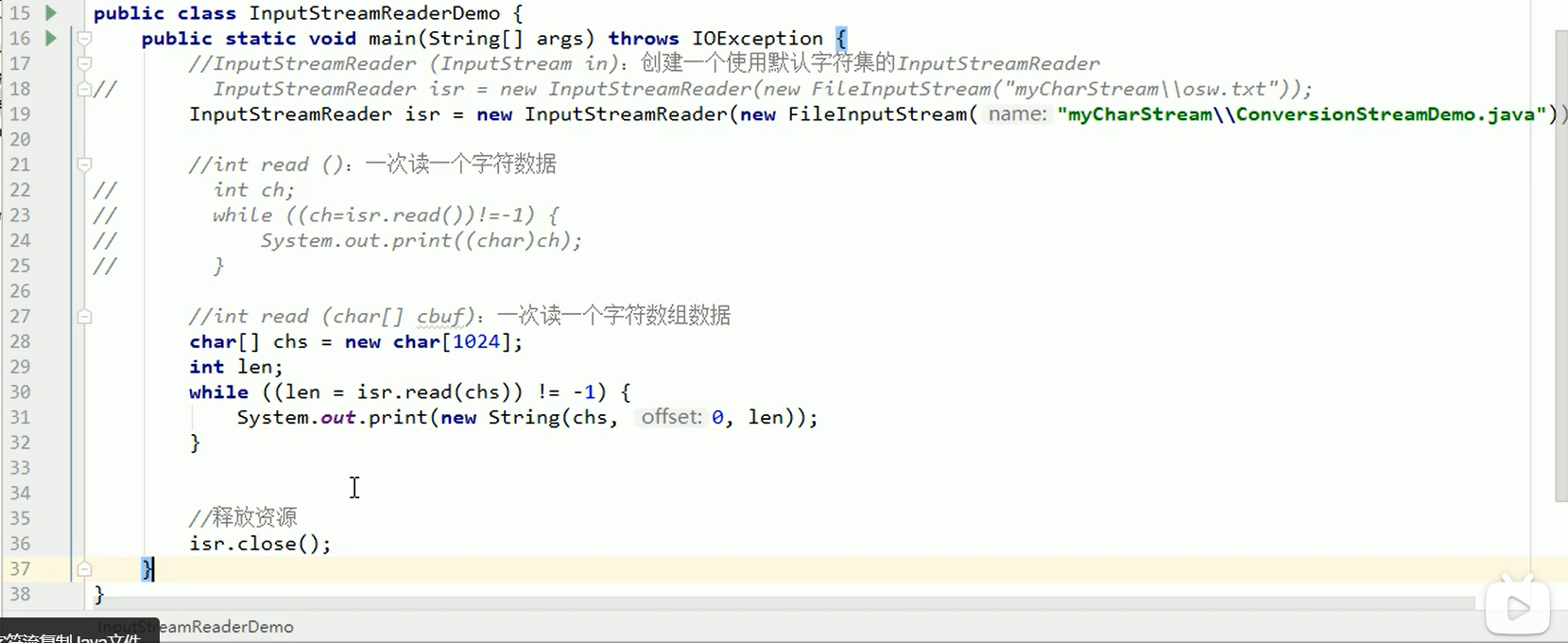

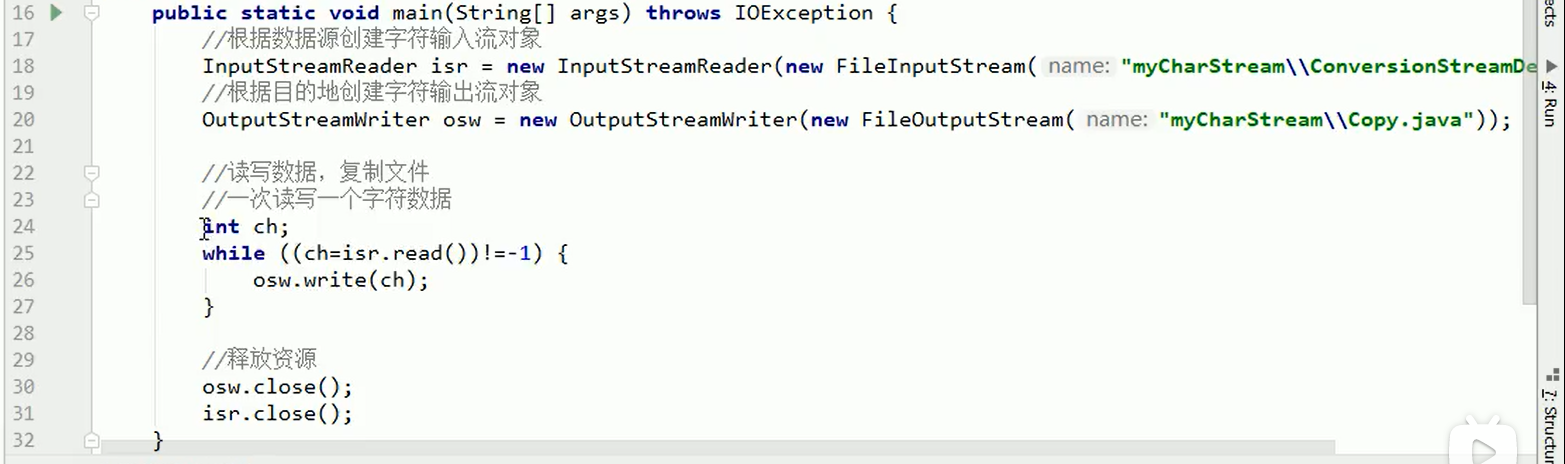

案例:复制Java文件改进版


3.7 字符缓冲流
字符缓冲流:
- BufferedWriter:将文本写入字符输出流,缓冲字符,以提供单个字符,数组和字符串的高效写入,可以指定缓冲区大小,或者可以接受默认大小,默认值大小,默认值足够大,可用于大多数用途
- BufferedReader:从字符输入流读取文本,缓冲字符,以提供字符,数组和行的高效读取,可以指定缓冲区大小,或者可以使用默认大小,默认值足够大,可以用于大多数用途
构造方法:
- BufferedWriter(Writer out)
- BufferedReader(Rerader in)
package com.guoba.day1223; import java.io.*; public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("基础语法\\fw.txt"); // BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("基础语法\\fw.txt")); // bw.write("hello\r\n"); // bw.write("world\r\n"); // bw.write("ccccccccccccc\r\n"); // // //bw.flush(); // // bw.close(); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("基础语法\\\\fw.txt")); // //一次读取一个字符数据 // int by; // while ((by=br.read())!= -1){ // System.out.print((char)by); // } //一次读取一个字符流数组数据 int len; char[] chars =new char[1024]; while ((len=br.read(chars))!= -1){ System.out.print(new String(chars,0,len)); } } }
"D:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_202\bin\java.exe" "... hello world ccccccccccccc Process finished with exit code 0
案例:字符缓冲流创建Java文件
package com.guoba.day1223; import java.io.*; /* 字符缓冲流复制Java文件 思路: 1.根据数据源创建字符缓冲输入流对象 2.根据目标地址创建字符缓冲输出流对象 3.复制文件(两种方式) 4.关闭资源 */ public class Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("基础语法\\Demo01.java")); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("基础语法\\src\\com\\guoba\\day1223\\Demo01.java")); // //一次一个字符 // int ch; // while ((ch=br.read())!= -1){ // bw.write(ch); // } //一次一个字符数组 char[] chars = new char[1024]; int len; while ((len=br.read(chars))!= -1){ bw.write(chars,0,len); } //关闭资源 bw.close(); br.close(); } }
3.8字符缓冲流的特有功能
package com.guoba.day1223; import java.io.BufferedWriter; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; public class Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("基础语法\\ccccc.txt")); for (int i = 0; i <10 ; i++) { bw.write("ccccccccc"+i); bw.newLine();//换行 bw.flush();//刷新流 } bw.close(); } }
package com.guoba.day1223; import java.io.*; public class Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("基础语法\\ccccc.txt")); // //// for (int i = 0; i <10 ; i++) { //// bw.write("ccccccccc"+i); //// bw.newLine();//换行 //// bw.flush();//刷新流 //// } // bw.close(); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("基础语法\\\\ccccc.txt")); // String line = br.readLine();//读一行 // System.out.println(line); String line; while ((line=br.readLine())!=null){ System.out.print(line+"\n"); } br.close(); } }
字符缓冲流特有功能复制文件
package com.guoba.day1223; import java.io.*; public class Demo04 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("基础语法\\ccccc.txt")); BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("基础语法\\copy.txt")); String line; while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { bw.write(line); bw.newLine(); bw.flush(); } bw.close(); br.close(); } }
3.9 IO流小结
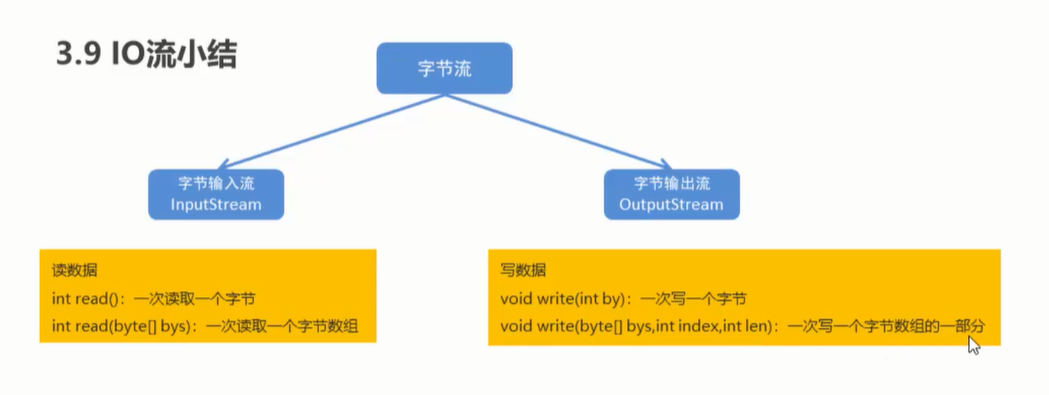
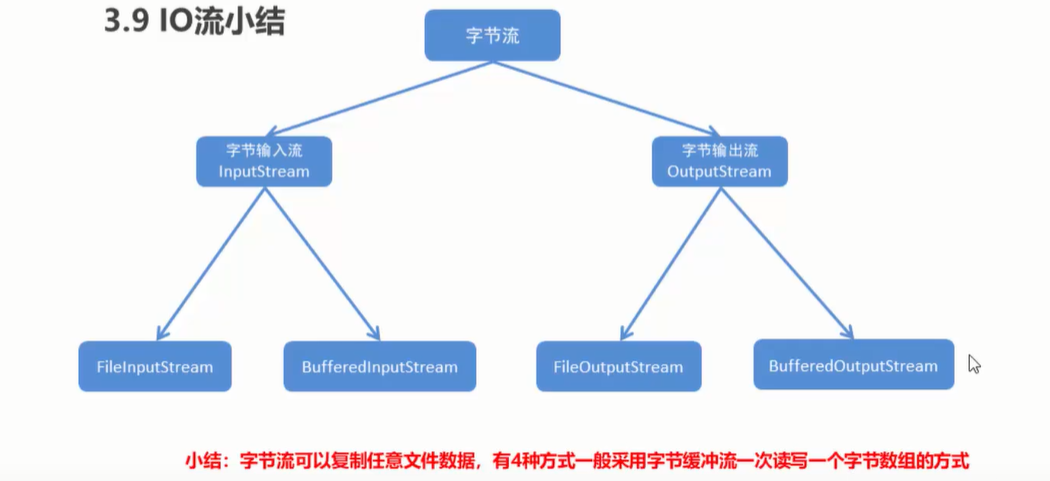
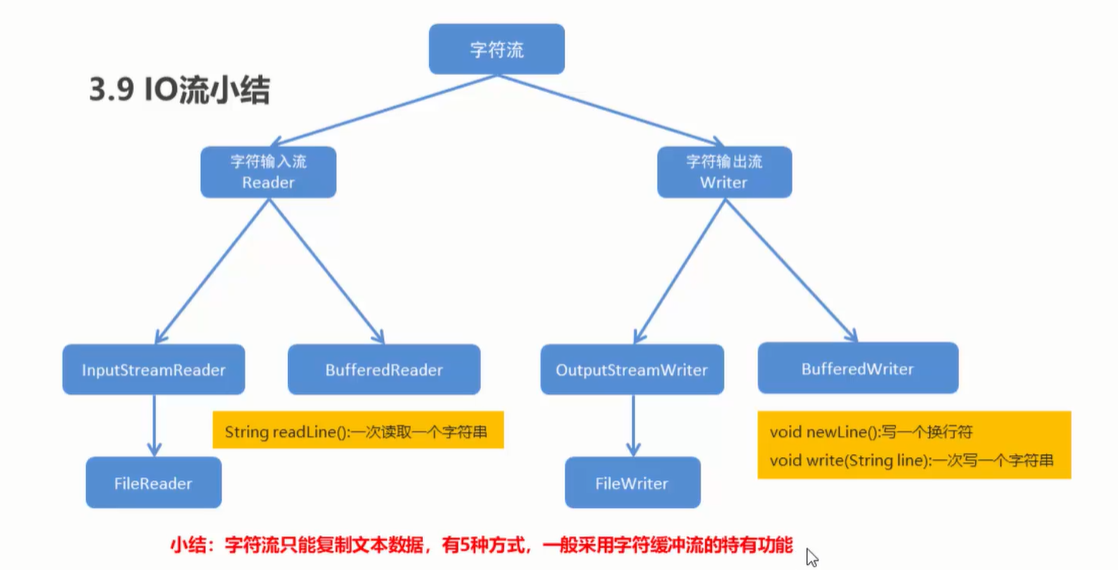
案例:集合到文件
需求:把ArrayList集合中的字符串数据写入到文本文件。
要求:每一个字符串元素作为文件中的一行数据

package com.guoba.day1223; import java.io.*; import java.util.ArrayList; public class Demo05 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); arrayList.add("张三"); arrayList.add("李四"); arrayList.add("王五"); BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("基础语法\\集合到文件.txt")); for (String s: arrayList){ bw.write(s); bw.newLine(); bw.flush(); } bw.close(); } }
案例:文件到集合

package com.guoba.day1223; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.ArrayList; public class Demo06 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("基础语法\\集合到文件.txt")); ArrayList<String> al = new ArrayList<>(); String line; while ((line = br.readLine())!= null){ al.add(line); } br.close(); for (String s : al){ System.out.println(s); } } }
案例:点名器

package com.guoba.day1223; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Random; /* 随机点名 */ public class Demo07 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("基础语法\\集合到文件.txt")); String line; while ((line = br.readLine())!= null){ arrayList.add(line); } br.close(); Random r = new Random(); int index = r.nextInt(arrayList.size()); String name = arrayList.get(index); System.out.println("幸运者是:"+ name); } }
案例:集合到文件(改进版)

package com.guoba.day1223; import java.io.*; import java.util.ArrayList; /* 1.创建集合 2.创建学生对象 3.把学生添加到集合 4.创建字符缓冲输出流对象 5.遍历集合,得到每个学生对象 6.把学生对象的数据拿到且拼接为指定格式的字符表 7.调用字符缓冲流对象的方法写数据 8.关闭资源 */ public class Demo08 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ArrayList<Student> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); Student student1 = new Student(01,"班尼特",18,"男","蒙德"); Student student2 = new Student(02,"重云",18,"女","璃月"); Student student3 = new Student(03,"托马",19,"男","稻妻"); arrayList.add(student1); arrayList.add(student2); arrayList.add(student3); BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("基础语法\\TiWaTe.txt")); for (Student s : arrayList){ StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append(s.getId()).append(",").append(s.getName()).append(",").append(s.getAge()).append(",").append(s.getSex()).append(",").append(s.getAddress()); bw.write(sb.toString()); bw.newLine(); bw.flush(); } bw.close(); } }
package com.guoba.day1223; public class Student { private int id; private int age; private String name; private String sex; private String address; public Student() { } public Student(int id, String name, int age, String sex, String address) { this.id = id; this.age = age; this.name = name; this.sex = sex; this.address = address; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(String sex) { this.sex = sex; } public String getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(String address) { this.address = address; } }
案例:文件到集合(改进版)

package com.guoba.day1223; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.ArrayList; public class Demo09 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("基础语法\\TiWaTe.txt")); ArrayList<Student> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); String line; //从文件获取存入集合 while ((line = br.readLine())!= null){ String[] strarr = line.split(","); Student s = new Student(); s.setId(Integer.parseInt(strarr[0])); s.setName(strarr[1]); s.setAge(Integer.parseInt(strarr[2])); s.setSex(strarr[3]); s.setAddress(strarr[4]); arrayList.add(s); } br.close(); //遍历集合 for (Student s :arrayList){ System.out.println(s.getId()+","+s.getName()+","+s.getAge()+","+s.getSex()+","+s.getAddress()); } } }
集合到文件数据排序改进版
package com.guoba.day1223; import java.io.BufferedWriter; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.TreeSet; public class Demo10 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<Student>(new Comparator<Student>() { @Override public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) { int num1 = s2.getSum() - s1.getSum(); int num2 = num1 == 0 ? s1.getChinese() - s2.getChinese() : num1; int num3 = num1 == 0 ? s1.getMath() - s2.getMath() : num1; int num4 = num1 == 0 ? s1.getMath() - s2.getMath() : num1; return num4; } }); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入第" + (i + 1) + "个学生信息:"); System.out.println("姓名:"); String name = scanner.nextLine(); System.out.println("语文:"); int chinese = scanner.nextInt(); System.out.println("数学:"); int math = scanner.nextInt(); System.out.println("英语:"); int eglish = scanner.nextInt(); Student s = new Student(); s.setChinese(chinese); s.setMath(math); s.setEglish(eglish); s.setName(name); ts.add(s); } BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("基础语法\\成绩.txt")); for (Student s : ts) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append(s.getName()).append(",").append(s.getChinese()).append(",").append(s.getMath()).append(",").append(s.getEglish()).append(",").append(s.getSum()); bw.write(sb.toString()); bw.newLine(); bw.flush(); } bw.close(); } }
案例:复制单极文件夹
package com.guoba.day1223; import java.io.*; public class Demo11 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ //创建数据源目录文件对象 File srcFolder = new File("E:\\2021Study\\test"); //获取数据源目录File对象的名称 String srcFolderName = srcFolder.getName(); //创建目的地文件对象 File destFolder = new File("基础语法",srcFolderName); //判断目的地目录对应文件是否存在 if (!destFolder.exists()){ destFolder.mkdir(); } //获取数据源目录下所有文件的数组 File[] listFiles = srcFolder.listFiles(); //遍历得到每一个对象 for (File srcFile: listFiles){ String srcFilename = srcFile.getName(); File destfile = new File(destFolder, srcFilename); copyFile(srcFile,destfile); } } private static void copyFile(File srcFile,File destFile)throws IOException { BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile)); BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destFile)); byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; int len; while ((len = bis.read())!= -1){ bos.write(bys,0,len); } bos.close(); bis.close(); } }
案例:复制多级文件夹
package com.guoba.day1223; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import static com.sun.deploy.cache.Cache.copyFile; public class Demo12 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File srcFile = new File("E:\\2021Study\\test");//数据源文件对象 File destFile = new File("F:\\");//目的地文件对象 copyFolder(srcFile,destFile);//复制文件夹 } //复制文件夹 private static void copyFolder(File srcFile, File destFile) throws IOException { //判断数据源文件是否是目录 if (srcFile.isDirectory()){ //在目的地创建和数据源文件名称一样的目录 String srcFileName = srcFile.getName(); //使用得到的名称在目的地址创建文件夹 File newFolder = new File(destFile,srcFileName); //判断文件是否存在 if (!newFolder.exists()){ //不存在则创建 newFolder.mkdir(); } //获取数据源文件下所有文件或目录的文件数组 File[] listFiles = srcFile.listFiles(); //遍历 for (File file :listFiles){ copyFolder(file,newFolder); } }else { //不是文件夹则说明是文件,直接用字节缓冲流复制文件 File newFile = new File(destFile,srcFile.getName()); copyFile(srcFile,newFile); } } }
案例:复制文件的异常处理


try/catch/finally





