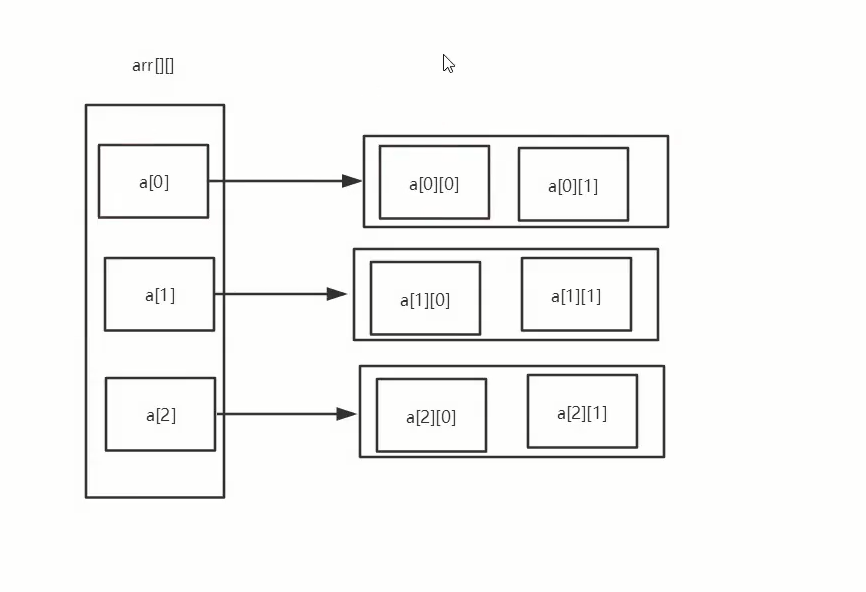
多维数组
- 多维数组可以看成是数组的数组
- 比如二维数组就是一个特殊的一堆数组
- 其中每个元素就是一个数组。
- 二维数组:
| int a[][] = new int[2][5]; |
- 解析:二维数组a可以看成一个两行三列的数组。
- 思考:多维数组的使用?
(
| package com.guoba.Array; |
| |
| public class Demo05 { |
| public static void main(String[] args) { |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| int[][] array = {{1,2},{2,3},{3,4}}; |
| printArray(array[0]); |
| System.out.println(); |
| System.out.println("=========================="); |
| System.out.println(array[0][0]); |
| System.out.println(array[0][1]); |
| } |
| |
| public static void printArray(int[] arr){ |
| for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) { |
| System.out.print(arr[j]+" "); |
| } |
| } |
| } |
| |
| package com.guoba.Array; |
| |
| public class Demo06 { |
| public static void main(String[] args) { |
| |
| int[][] array = {{1,2},{2,3},{3,4}}; |
| for (int i = 0; i < array.length ; i++) { |
| for (int j = 0; j < array[i].length; j++) { |
| System.out.print(array[i][j]+"\t"); |
| } |
| |
| } |
| } |
| } |
| |
Arrays类
Arrays类
- 数组工具类java.util.Arrays
- 由于数组对象本身并没有什么方法可以供我们调用,
- 但API中提供了一个工具类Arrays供我们使用
- 从而可以对数据对象进行一些操作
- 查看JDK帮助文档
- Arrays类中的方法都是static修饰的静态方法
- 在使用的时候可以直接使用类名进行调用
- 功能:
- 》给数组对象赋值:通过fill方法
- 》对数组进行排序:通过short方法,升序
- 》比较数组:通过equals方法比较数组中的元素值是否相等。
- 》查找数组元素:通过binarySearch方法能对排序好的数组进行二分法查找操作
| package com.guoba.Array; |
| |
| import java.util.Arrays; |
| |
| public class Demo07 { |
| public static void main(String[] args) { |
| int[] a = {1,2334,324,54,4,6,546,5,7,7,7,34,34324}; |
| System.out.println(a); |
| |
| System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); |
| |
| arrayPrint(a); |
| Arrays.sort(a); |
| System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); |
| } |
| public static void arrayPrint(int[] a){ |
| for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { |
| if (i == 0){ |
| System.out.println("["); |
| } |
| if (i == a.length){ |
| System.out.println(a[i]+"]"); |
| }else { |
| System.out.println(a[i]+", "); |
| } |
| } |
| } |
| } |
| |
冒泡排序
- 最为出名的排序算法之一
- 代码是两层
- 循环外层冒泡轮数
- 里层依次比较
- 嵌套循环 》时间复杂度为O(n2).
- 思考:如何优化?
- 》加个判断若是排好的则直接跳出循环
代码如下:
| package com.guoba.Array; |
| |
| import java.util.Arrays; |
| |
| public class Demo08_maopao { |
| public static void main(String[] args) { |
| int[] array = {1,2,3,4,5,6}; |
| int[] sort = sort(array); |
| System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sort)); |
| } |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| public static int[] sort(int[] array){ |
| int temp = 0; |
| |
| for (int i = 0; i < array.length-1; i++) { |
| boolean flag = false; |
| for (int j = 0; j < array.length-1-i; j++) { |
| if (array[j+1]>array[j]){ |
| temp =array[j+1]; |
| array[j+1] = array[j]; |
| array[j] = temp; |
| } |
| } |
| if (flag == false){ |
| break; |
| } |
| } |
| return array; |
| } |
| } |
| |
稀疏数组
- 需求:编写五子棋游戏中,有存盘退出和续上盘的功能。
- 分析问题:因为该二维数组很多默认值都为0,因此记录了很多没用的数据。
- 解决:稀疏数组
- 场景:当一个数组中大部分元素为0,或者为同一值的数组时,可以用稀疏数组来保存。
- 处理方式:
- 》记录数组一共有几行几列,有多少个不同值。
- 》把具有不同值的元素及行列及值记录在一个小规模数组中,从而缩小程序规模。
- 如下图,左边为原始数组,右边为稀疏数组。
(![![1638361301175]](https://img2020.cnblogs.com/blog/2647725/202112/2647725-20211202134603750-1432279917.png)
)
代码练习如下:
| package com.guoba.Array; |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| public class Demo09 { |
| public static void main(String[] args) { |
| |
| int[][] array1 = new int[11][11]; |
| array1[1][2] = 1; |
| array1[2][3] = 2; |
| |
| System.out.println("输出这个原始数组"); |
| for (int[] ints:array1) { |
| for (int anInt:ints) { |
| System.out.print(anInt+"\t"); |
| } |
| System.out.println(); |
| } |
| |
| |
| int sum = 0; |
| for (int i = 0; i <11 ; i++) { |
| for (int j = 0; j <11 ; j++) { |
| if (array1[i][j] != 0){ |
| sum++; |
| } |
| } |
| } |
| System.out.println("=================================="); |
| System.out.println("有效值个数:"+sum); |
| |
| int[][] array2 = new int[sum+1][3]; |
| array2[0][0] = 11; |
| array2[0][1] = 11; |
| array2[0][2] = sum; |
| |
| int count = 0; |
| for (int i = 0; i < array1.length; i++) { |
| for (int j = 0; j < array1[i].length; j++) { |
| if (array1[i][j] != 0){ |
| count++; |
| array2[count][0] = i; |
| array2[count][1] = j; |
| array2[count][2] = array1[i][j]; |
| } |
| } |
| } |
| |
| System.out.println("输出稀疏数组"); |
| for (int i = 0; i < array2.length; i++) { |
| System.out.println(array2[i][0]+"\t"+ array2[i][1]+"\t" + array2[i][2]+"\t"); |
| } |
| |
| System.out.println("=================================="); |
| System.out.println("还原"); |
| |
| int[][] array3 = new int[array2[0][0]][array2[0][1]]; |
| |
| for (int i = 1; i < array2.length; i++) { |
| array3[array2[i][0]][array2[i][1]] = array2[i][2]; |
| } |
| |
| System.out.println("输出这个还原数组"); |
| for (int[] ints:array3) { |
| for (int anInt:ints) { |
| System.out.print(anInt+"\t"); |
| } |
| System.out.println(); |
| } |
| } |
| } |
| |

![![1638361301175]](https://img2020.cnblogs.com/blog/2647725/202112/2647725-20211202134603750-1432279917.png)




