02-方法 ——课程作业01-递归练习
1.使用计算机计算组合数
(1)使用组合数公式利用n!来计算
程序设计思想:
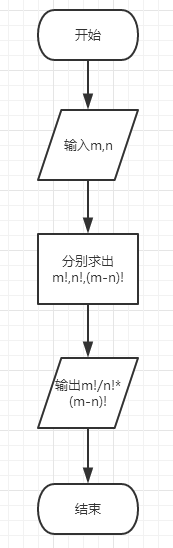
利用递归定义一个方法jiecheng(int n)用来求一个数n的阶乘,当n>1时,返回n*jiecheng(n-1),直到n=1时,返回1。输入底数m和阶数n之后,利用该函数分别求出m和n还有m-n的阶乘,利用公式m!/n!*(m-n)!在main函数中输出结果。
程序流程图:
程序源代码:
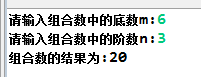
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class ZuHeShu { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 7 System.out.print("请输入组合数中的底数m:"); 8 9 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 10 11 int import_m = input.nextInt(); 12 13 System.out.print("请输入组合数中的阶数n:"); 14 15 int import_n = input.nextInt(); 16 17 System.out.println("组合数的结果为:"+jiecheng(import_m)/(jiecheng(import_n)*jiecheng(import_m-import_n))); 18 19 } 20 21 public static long jiecheng(int i) 22 23 { 24 25 if(i > 1) 26 27 { 28 29 return i * jiecheng(i - 1); 30 31 } 32 33 else 34 35 { 36 37 return 1; 38 39 } 40 41 } 42 43 }
程序测试截图:

(2)使用递推的方法用杨辉三角形计算
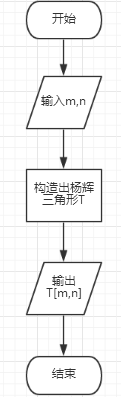
程序设计思想:
定义一个二维数组T存储杨辉三角形,循环赋值构造杨辉三角形:T[i][0] = 1,T[i][i] = 1,(i = 0,1,2……n),其余每个T[i][j] =T[i - 1][j - 1] + T[i - 1][j]。则C(m,n)=T[n][k]。
程序流程图:
程序源代码:
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class ZuHeShu3 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 7 System.out.print("请输入组合数中的底数m:"); 8 9 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 10 11 int m = input.nextInt(); 12 13 System.out.print("请输入组合数中的阶数n:"); 14 15 int n= input.nextInt(); 16 17 System.out.println("组合数的结果为:"+T(m,n)); 18 19 } 20 21 public static int T(int m,int n){ 22 23 int[][] Y = new int[m + 1][m + 1]; 24 25 Y[0][0] = 1; 26 27 for(int i = 0;i < m + 1;i++) 28 29 { 30 31 Y[i][0] = 1; 32 33 Y[i][i] = 1; 34 35 } 36 37 for(int i = 2;i < m + 1;i++) 38 39 { 40 41 for(int j = 1;j < i;j++) 42 43 { 44 45 Y[i][j] = Y[i - 1][j - 1] + Y[i - 1][j]; 46 47 } 48 49 } 50 51 return Y[m][n]; 52 53 } 54 55 }
程序测试截图:

(3)使用递归的方法用组合数递推公式计算
程序设计思想:
定义求组合数函数C(n,k)当k = 0或n = k时,返回1,否则,根据递推公式,C(n,k) = C(n - 1,k - 1) + C(n - 1,k)。
程序流程图:
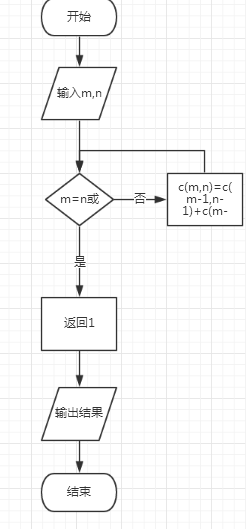
程序源代码:
import java.util.Scanner; public class ZuHeShu2 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.print("请输入组合数中的底数m:"); Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int import_m = input.nextInt(); System.out.print("请输入组合数中的阶数n:"); int import_n = input.nextInt(); System.out.print("组合数的结果为:"+triangle(import_m,import_n)); } public static long triangle(int m,int n) { if(m == n || n == 0) return 1;else return triangle(m - 1,n - 1)+triangle(m - 1,n); } }
程序结果截图:
2.递归编程阶乘解决汉诺塔问题。
程序设计思想:
当盘子的个数n=1时,直接从A移动到C;
n>1时,可将其分为三个步骤:
(1)将上面n-1个盘子从A座移到B座上。
(2)将剩下的一个盘子从A座移到C座上。
(3)将B座上的n-1个盘子从B座移动到C座上。
其中,(1),(3)可用递归函数实现,只是从哪一个座移到哪一个座不同。
程序流程图:
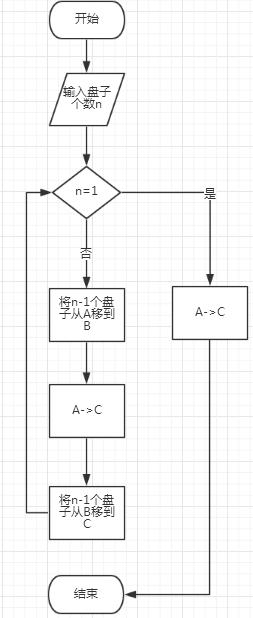
程序源代码:
import java.util.Scanner; public class HanoiTower { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.print("请输入盘子的个数:"); Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int diskes = input.nextInt(); System.out.println("挪动这"+diskes+"盘子的步骤为:"); hanoi(diskes,'A','B','C'); } public static void hanoi(int n, char a, char b, char c) { if(n == 1) { move(a,c); } else { hanoi(n-1,a,c,b); move(a,c); hanoi(n-1,b,a,c); } } public static void move(char a, char c) { System.out.println(a+"-->"+c); } }
程序结果截图:

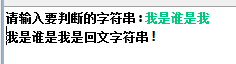
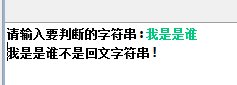
3.使用递归方式判断某个字串是否为回文
程序设计思想:
首先比较第一个字符与最后一个字符的关系,如果相等,利用递归比较第二个与倒数第二个字符的关系,直到比较完,中间如果有一对不相等,直接退出函数并输出不是回文数。
程序流程图:
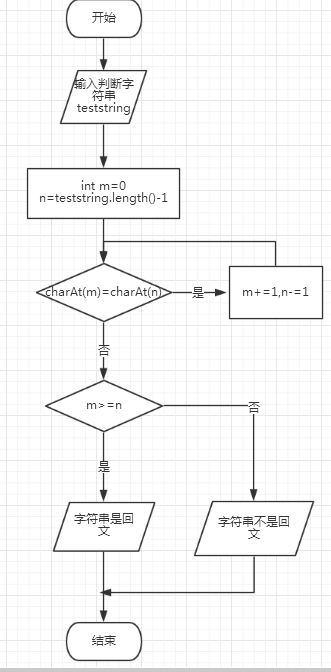
程序源代码:
import java.util.Scanner; public class HuiWen { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.print("请输入要判断的字符串:"); Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String teststring = input.next(); int pre = 0,end = teststring.length() - 1; if(isPalindromestring(teststring,pre,end)) System.out.println(teststring+"是回文字符串!"); else System.out.println(teststring+"不是回文字符串!"); } public static boolean isPalindromestring(String test,int pre, int end) { if(pre >= end) return true; else { if(test.charAt(pre) == test.charAt(end)) return isPalindromestring(test,pre+1,end-1); else return false; } } }
程序测试截图: