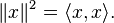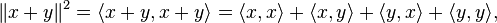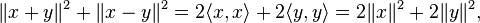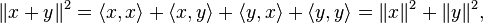parallelogram
The parallelogram law in inner product spaces
In a normed space, the statement of the parallelogram law is an equation relating norms:
In an inner product space, the norm is determined using the inner product:
As a consequence of this definition, in an inner product space the parallelogram law is an algebraic identity, readily established using the properties of the inner product:
Adding these two expressions:
as required.
If x is orthogonal to y, then 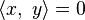 and the above equation for the norm of a sum becomes:
and the above equation for the norm of a sum becomes:
which is Pythagoras' theorem.