GuTianpei-2022-Stochastic Trajectory Prediction via Motion Indeterminacy Diffusion-CVPR
Stochastic Trajectory Prediction via Motion Indeterminacy Diffusion #paper
1. paper-info
1.1 Metadata
- Author:: [[Tianpei Gu]], [[Guangyi Chen]], [[Junlong Li]], [[Chunze Lin]], [[Yongming Rao]], [[Jie Zhou]], [[Jiwen Lu]]
- 作者机构::
- Keywords:: #TrajectoryPrediction, #Diffusion
- Journal:: #CVPR
- Date:: [[6/2022]]
- 状态:: #Done
- 链接:: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9878855/
- 阅读时间:: 2023.01.07
1.2. Abstract
Human behavior has the nature of indeterminacy, which requires the pedestrian trajectory prediction system to model the multi-modality of future motion states. Unlike existing stochastic trajectory prediction methods which usually use a latent variable to represent multi-modality, we explicitly simulate the process of human motion variation from indeterminate to determinate. In this paper, we present a new framework to formulate the trajectory prediction task as a reverse process of motion indeterminacy diffusion (MID), in which we progressively discard indeterminacy from all the walkable areas until reaching the desired trajectory. This process is learned with a parameterized Markov chain conditioned by the observed trajectories. We can adjust the length of the chain to control the degree of indeterminacy and balance the diversity and determinacy of the predictions. Specifically, we encode the history behavior information and the social interactions as a state embedding and devise a Transformer-based diffusion model to capture the temporal dependencies of trajectories. Extensive experiments on the human trajectory prediction benchmarks including the Stanford Drone and ETH/UCY datasets demonstrate the superiority of our method. Code is available at https://github.com/gutianpei/MID.
关键字:轨迹预测, 扩散模型,Transformer
2. Introduction
- 领域:Human trajectory prediction
- 之前的方法:利用生成模型通过潜在变量去表征轨迹的多模态。
- GAN-Based:训练比较困难
- CVAE-Based:生成不自然的轨迹
- 作者的方法:motion indeterminacy diffusion(MID),该方法基于扩散模型。
3. Approach
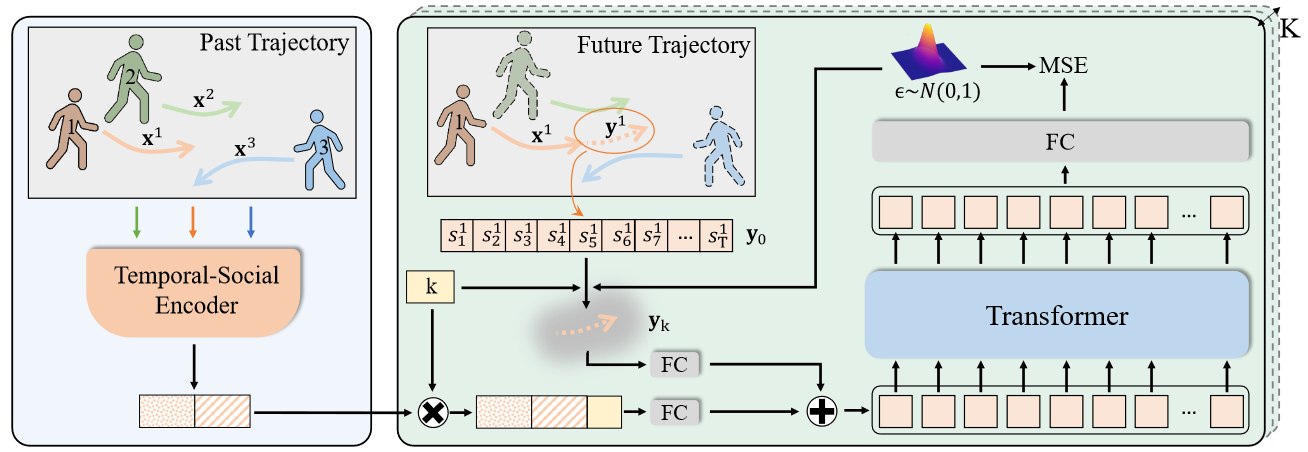
3.1 问题描述
输入:N history trajectories \(X^i=\{s_t^{i\in} \mathbb{R}^{2|t}= -T_{init},...,0 \} \; i\in\{1,..,N\}\)
输出:预测序列 \(y^{i}=\{s_t^i|t=1,2,...,T_{pred}\}\)
3.2 Motion Indeterminacy Diffusion
整体流程就如Fig.1所示,思路很简单,两部分
- 条件的encoder :这里使用的是[1]中的模型
Trajectron++ - 条件扩散模型(除了预测噪声的model不一样,其他于原模型基本一致)
- Transformer-decoder
4. Experiments
- datasets
- Stanford Drone Dataset(SDD)
- UCY/ETH
- Evaluation Metric
- Average Displacement Error (ADE)
- Final Displacement Error (FDE).
5. 总结
该论文的思路很简单,就是将条件扩散模型用于轨迹预测任务。
reference
[1] Tim Salzmann, Boris Ivanovic, Punarjay Chakravarty, and Marco Pavone. Trajectron++: Dynamically-feasible trajectory forecasting with heterogeneous data. In ECCV, 2020.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号