是在做知识分享时写的内容,分享给大家,也做个记录。
一、MongoDB介绍
MongoDB 是一个介于关系数据库和非关系数据库之间的产品,是非关系数据库当中功能最丰富,最像关系数据库的。他支持的数据结构非常松散,是类似 json 的 bson 格式,可以存储比较复杂的数据类型。
bson简称Binary JSON,BSON数据格式就是Json数据格式的二进制化,对于开发者而言,在使用及表现形式上两者是一致的。
MongoDB数据结构是由数据库(database)、集合(collection)、文档(document)三部分组成的。
|
Databases(数据库) |
Databases(数据库) |
|
Collection(集合) |
Tables(数据表) |
|
Document(文档) |
Row(行) |
其中,对于开发人员主要面对的是collection和document。其中数据文档(document)是数据载体,其数据格式定义如:{文档名:文档内容, 文档名:文档内容, 文档名:文档内容,….}
网上摘录了一些MongoDB的特点,如下:
- 模式自由。支持动态查询、完全索引,可以方便地对文档中内嵌的对象及数组进行检索。
- 面向文档存储。开发人员可以将现有的序列文档直接导入到MogonDB数据集中。
- 高效的存储机制。MogonDB对数据并没有特殊的限制,任何数据(包括大型的图片、视频等)保存到MogonDB数据库中,最终都将被转换为二进制数据,从而在一定程度上保证读写的搞笑,以及确保数据完整、安全等。
- 支持复制和故障恢复。提供了主-从、主-主模式的数据复制及服务器之间的数据复制。
- 自动分片并支持云级别的伸缩性。支持水平的数据库集群,可以动态添加额外的服务器。
- 支持Python、PHP、Ruby、Java、C、C#、JavaScript、Perl及C++语言的驱动程序。
- 完全支持分布式架构。
- Sphinx1.x开始支持MongoDB驱动。
下来看一下Mongodump导出的数据
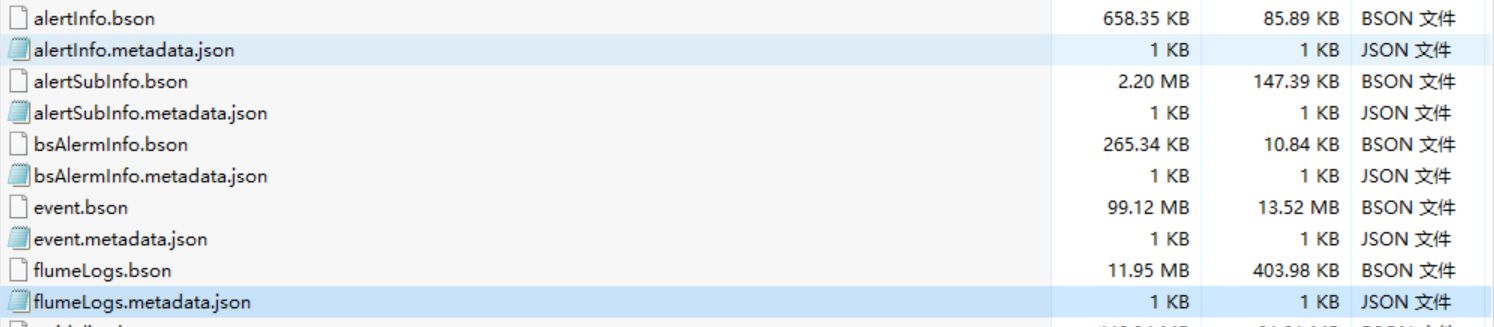
这是从某库导出的数据,有两种文件,bson和metadata.json,bson是数据文件,metadata.json是元数据文件,用来存储表的定义和解释数据,用于数据库本身或用户进行分析,能大概了解数据库系统中的数据对象。
二、MongoDB安装
接下来看一下安装,有windows和linux版本,主要介绍linux的安装和使用,其实在linux下安装也很简单,网上有大量的资料,按照网上介绍的步骤安装就行,可以安装离线文件,也可在线安装。
1、 解压离线文件
tar zxf mongodb-linux-i686-1.8.2.tgz
2、 创建一个用来存储mongo的文件
mkdir /usr/local/mongodb
3、 将解压的文件移动到建好的文件夹中
mv mongodb-linux-i686-1.8.2 /usr/local/mongodb
4、 创建数据库文件和日志文件
cd /usr/local/mongodb
mkdir /usr/local/mongodb/data
mkdir /usr/local/mongodb/logs
上面这些做完后就可以启动了,设置一个开机自启动的设置
5、 开机自启动,将mongodb启动项目追加到系统文件(rc.local)中,保证mongodb在服务器开机时启动
echo "/usr/local/server/mongodb/bin/mongod --dbpath=/usr/local/server/mongodb/data –logpath=/usr/local/server/mongodb/logs –logappend --auth –port=27017" >> /etc/rc.local
6、 启动
./mongod --dbpath=/usr/local/mongodb/data --logpath=/usr/local/mongodb/logs --logappend --port=27017 –fork
加入了fork选项,表示将mongod服务进程推送到后台运行,在看一下启动的其他参数
--dbpath:指定数据库目录,--logpath:指定日志存放目录,--port:指定通信端口,如果这个参数不加,默认是27017,加了就可以指定其他端口,如--port=27018
三、MongoDB使用
然后就可以通过GUI管理工具(mongovue、RockMongo、MongoHub)或命令行进行操作了。
查看有几个数据库:show databases;
切换数据库:uses XXX;
查看有哪些表:show collections;(mongo)
7、 进入mongo安装目录的bin,命令行(windows 和 Linux类似)
mongo 127.0.0.1:27017
l 查询:语法:db.collection.find(query, projection);
query:查询条件,projection:返回的键值对,类似于sql中返回的字段。两个参数都可缺省,如都缺省,则返回所有集合中所有数据。如果要返回格式化数据,使用 pretty()
sql语句中简单查询语句中的查询条件and,or,like,in, not in
and:{“key1”:”value1”,”key2”:”value2”},or:{$or:[{“key1”:”value1”},{“key2”:”value2”}]}
like:{“key1”:/value1/},in:{$in:[value1,value2,value3]},not in: in:{$nin:[value1,value2,value3]}
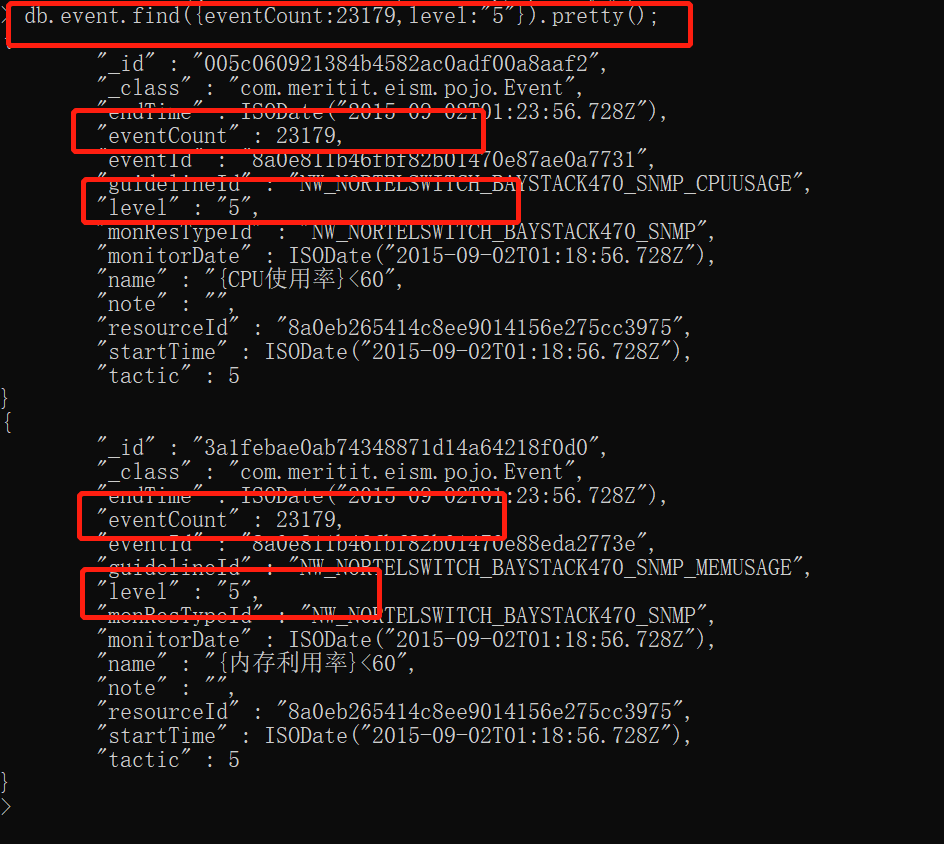
这是and的查询,其他的可自行找资料。再介绍一下projection参数,这个参数用来控制需要返回的键值对,格式为:{key1:1,key2:1} 或者 {key1:0,key2:0}
其实通过这种查询返回的都是游标对象,所以还可以用游标的形式进行遍历。
var cursor = db.envet.find({“key1”:”value1”})
while(cursor.hasNext()) printjson(cursor.next());
这种写法,是javascript shell的方式,还有一种mongo shell,也可以运行游标,这两种对于开发来说,用的非常少,我也不太懂,大家可以自行学习。
还有一种查询db.collection.findOne(),减少了游标操作,只返回一行。
下面看一下mongo常用的操作符如下:

写入:db.collection.save(query),与关系型数据库不同的地方是,不需要提前建好集合(关系型数据库:表),在第一次写入时,会自动创建。每个document都会自动创建一个ID(_id),类似于Oracle中的rowid。
8、 java调用mongodb
java调用其实也比较简单,下载对应驱动文件即可。
- 创建配置文件:mongodb.cfg.properties
#configure threadPool
#Mongodb 数据库地址
mongo.db.address = XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
#Mongodb 数据库IP
mongo.db.port = 27017
#Mongodb 数据库用户名
mongo.db.username = XXX
#Mongodb 数据库密码
mongo.db.password =
#Mongodb 数据库实例
mongo.db.dbname = XXX
#Mongodb 数据库可以建立的最大连接数
mongo.db.connectionsPerHost=20
#Mongodb 与数据库建立连接的超时时间20mins 20*60*1000
mongo.db.connectTimeout=1200000
#Mongodb 一个线程获取到数据库连接的最大阻塞时间 5mins 5*60*1000
mongo.db.maxWaitTime=300000
#Mongodb 线程队列最大值 注:该值和最大连接数的乘积为线程队列最大值
mongo.db.threadsAllowedToBlockForConnectionMultiplier=10
- 编写工具类:MongoDbFactory类(单例)
package dnzl.comman.mongodb; import org.apache.log4j.Logger; import com.mongodb.MongoClient; import com.mongodb.MongoClientOptions; import com.mongodb.ServerAddress; import dnzl.server.SystemName; import dnzl.util.Config; public class MongoFactory { private static final Logger LOGGER = Logger.getLogger(MongoFactory.class); private static MongoClient mongoClient = null; private static String localhost = ""; private static int port = 0; public static String db = ""; private static int connectinsPerHost = 0; private static int connectTimeout = 0; private static int threadsAllowedToBlockForConnectionMultiplier = 0; static { try { Config.conf(SystemName.MONGO); localhost = Config.getString("mongo.db.address"); port = Integer.parseInt(Config.getString("mongo.db.port")); db = Config.getString("mongo.db.dbname"); connectinsPerHost = Integer.parseInt(Config.getString("mongo.db.connectionsPerHost")); connectTimeout = Integer.parseInt(Config.getString("mongo.db.connectTimeout")); threadsAllowedToBlockForConnectionMultiplier = Integer.parseInt(Config.getString("mongo.db.threadsAllowedToBlockForConnectionMultiplier")); LOGGER.info("Mongo configure loaded successfully."); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 获取默认数据库连接 * @return */ public static MongoClient getMongodbInstance() { if (mongoClient == null) { mongoClient = createMongodb(); } return mongoClient; } private static MongoClient createMongodb() { MongoClientOptions.Builder builder = new MongoClientOptions.Builder(); builder.connectionsPerHost(connectinsPerHost); builder.connectTimeout(connectTimeout); builder.threadsAllowedToBlockForConnectionMultiplier(threadsAllowedToBlockForConnectionMultiplier); MongoClientOptions myOptions = builder.build(); // 连接到mongodb MongoClient mongoClient = new MongoClient(new ServerAddress(localhost , port),myOptions); // 打开数据库 // MongoDatabase dbInstance = null; // dbInstance = mongoClient.getDatabase(db); return mongoClient; } public String toString() { StringBuffer strb = new StringBuffer("This MongoDb["); strb.append("ip is:" + localhost); strb.append(", port is : " + port); strb.append(", defaultDB is :" + db +"]"); return strb.toString(); } }
- 应用:MongoDBDaoImpl.java
package dnzl.comman.mongodb.impl; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.regex.Pattern; import org.apache.log4j.Logger; import org.bson.Document; import org.bson.conversions.Bson; import com.mongodb.MongoClient; import com.mongodb.client.FindIterable; import com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection; import com.mongodb.client.MongoCursor; import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase; import com.mongodb.client.model.Filters; import dnzl.comman.mongodb.MogoDBOpertions; import dnzl.comman.mongodb.MongoDBDao; import dnzl.comman.mongodb.MongoFactory; public class MongoDBDaoImpl implements MongoDBDao { private static final Logger LOGGER = Logger.getLogger(MongoDBDaoImpl.class); public MongoDBDaoImpl() { } protected MongoCollection<Document> getCollection(String collectionName) { MongoClient mongoClient = MongoFactory.getMongodbInstance(); MongoDatabase mongodb = mongoClient.getDatabase(MongoFactory.db); return mongodb.getCollection(collectionName.toUpperCase()); } @Override public boolean inSert(String collectionName, String[] keys, Object[] values) { if (keys == null && values == null) { return false; } else { MongoCollection<Document> collection = getCollection(collectionName); Document document = new Document(); for (int i = 0; i < keys.length; i ++) { document.append(keys[i], values[i]); } collection.insertOne(document); return true; } } @Override public boolean insertMany(String collectionName, List<Map<String, Object>> list) { MongoCollection<Document> collection = getCollection(collectionName); ArrayList<Document> lists = new ArrayList<Document>(); for (Map<String,Object> map : list) { Document doc = new Document(); doc.putAll(map); lists.add(doc); } try { collection.insertMany(lists); return true; } catch (Exception e) { LOGGER.error("Mongo write data exception",e); return false; } } @Override public boolean delete(String collectionName, String[] keys, Object[] values) { if (keys == null && values == null) { return false; } else { MongoCollection<Document> collection = getCollection(collectionName); Document document = new Document(); for (int i = 0 ; i < keys.length; i++) { document.append(keys[i], values[i]); } collection.deleteMany(document); return true; } } @Override public boolean drop(String collectionName) { if (collectionName == null || "".equals(collectionName)) { return false; } else { MongoCollection<Document> collection = getCollection(collectionName); collection.drop(); return true; } } @Override public List<Document> find(String collectionName, String[] keys, Object[] values, String [] res) { if (keys == null && values == null) { return null; } else { MongoCollection<Document> collection = getCollection(collectionName); ArrayList<Document> lists = new ArrayList<Document>(); /** * 组装查询条件 */ Document document = new Document(); for (int i = 0 ; i < keys.length; i++) { document.append(keys[i], values[i]); } /** * 根据查询条件获取所有结果 */ FindIterable<Document> findTable = collection.find(document); MongoCursor<Document> mCursor = findTable.iterator(); if (res == null || (res.length > 0 && (res[0] == null || "".equals(res[0])))) { /** * 如果需要查询的字段为空,则返回全部字段(不包含mongoDB自带的_id字段) */ Document rdocument = new Document(); while (mCursor.hasNext()) { Document mc = mCursor.next(); for (String key : mc.keySet()) { /** * 剔除_id字段 */ if ("_id".equals(key)) { continue; } rdocument.append(key, mc.get(key)); } lists.add(rdocument); } } else { /** * 组装指定的查询字段 */ int len = res.length; while (mCursor.hasNext()) { Document mc = mCursor.next(); Document rdocument = new Document(); for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { rdocument.append(res[i], mc.get(res[i])); } lists.add(rdocument); } } return lists; } } public List<Document> find(String collectionName, String[] keys,String [] operations, Object[] values, String [] res) { if (keys == null && values == null) { return null; } else { if (keys.length != operations.length) { return null; } MongoCollection<Document> collection = getCollection(collectionName); ArrayList<Document> lists = new ArrayList<Document>(); /** * 组装查询条件 */ ArrayList<Bson> iterable = new ArrayList<Bson>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < keys.length; i++) { if (MogoDBOpertions.isValidOperater(operations[i])) { Bson operator = null; if ("=".equals(operations[i])) { operator = Filters.eq(keys[i], values[i]); } else if (">".equals(operations[i])) { operator = Filters.gt(keys[i], values[i]); } else if (">=".equals(operations[i])) { operator = Filters.gte(keys[i], values[i]); } else if ("!=".equals(operations[i]) || "<>".equals(operations[i])) { operator = Filters.ne(keys[i], values[i]); } else if ("<".equals(operations[i])) { operator = Filters.lt(keys[i], values[i]); } else if ("<=".equals(operations[i])) { operator = Filters.lte(keys[i], values[i]); } else if ("like".equals(operations[i]) || "LIKE".equals(operations[i])){ /** * MongoDB模糊查询 * 1、完全匹配: * ^name$,相当于key='name' * 2、右匹配: * ^.*name$,相当于key like '%name' * 3、左匹配: * ^name.*$,相当于key like 'name%' * 4、模糊匹配: * ^.*name.*$,相当于 key like '%name%' */ Pattern pattern = null; if (!String.valueOf(values[i]).startsWith("%") && String.valueOf(values[i]).endsWith("%")) { pattern = Pattern.compile("^"+String.valueOf(values[i]).replace("%", "") + ".*$", Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE); } else if (String.valueOf(values[i]).startsWith("%") && !String.valueOf(values[i]).endsWith("%")) { pattern = Pattern.compile("^.*"+String.valueOf(values[i]).replace("%", "") + "$", Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE); } else if (String.valueOf(values[i]).startsWith("%") && String.valueOf(values[i]).endsWith("%")) { pattern = Pattern.compile("^.*"+String.valueOf(values[i]).replace("%", "") + ".*$", Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE); } else { pattern = Pattern.compile("^"+String.valueOf(values[i]).replace("%", "") + ".*$", Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE); } operator = Filters.regex(keys[i], pattern); } else if("in".equals(operations[i]) || "IN".equals(operations[i])) { Object [] inValue = String.valueOf(values[i]).split(","); operator = Filters.in(keys[i], inValue); } iterable.add(operator); } else { LOGGER.info(String.format("invalid operation in condition [%s %s %s]", keys[i],operations[i],values[i])); } } /** * 将所有条件拼接为用and连接 */ Bson query = Filters.and(iterable); /** * 根据查询条件获取所有结果 */ FindIterable<Document> findTable = collection.find(query); MongoCursor<Document> mCursor = findTable.iterator(); if (res == null || (res.length > 0 && (res[0] == null || "".equals(res[0])))) { /** * 如果需要查询的字段为空,则返回全部字段(不包含mongoDB自带的_id字段) */ Document rdocument = new Document(); while (mCursor.hasNext()) { Document mc = mCursor.next(); for (String key : mc.keySet()) { /** * 剔除_id字段 */ if ("_id".equals(key)) { continue; } rdocument.append(key, mc.get(key)); } lists.add(rdocument); } } else { /** * 组装指定的查询字段 */ int len = res.length; while (mCursor.hasNext()) { Document mc = mCursor.next(); Document rdocument = new Document(); for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { rdocument.append(res[i], mc.get(res[i])); } lists.add(rdocument); } } return lists; } } @Override public List<Document> find(String collectionName) { if (collectionName == null || "".equals(collectionName)) { return null; } else { ArrayList<Document> lists = new ArrayList<Document>(); MongoCollection<Document> collection = getCollection(collectionName); FindIterable<Document> findTable = collection.find(); MongoCursor<Document> mCursor = findTable.iterator(); Document rdocument = new Document(); while (mCursor.hasNext()) { Document mc = mCursor.next(); for (String key : mc.keySet()) { /** * 剔除_id字段 */ if ("_id".equals(key)) { continue; } rdocument.append(key, mc.get(key)); } lists.add(rdocument); } return lists; } } @Override public boolean update(String collectionName, String conditionKey, Object conditionValue, String resultKey, Object resultValue) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub MongoCollection<Document> collection = getCollection(collectionName); collection.updateOne(Filters.eq(conditionKey,conditionValue), new Document("$set",new Document(resultKey, resultValue))); //// collection.updateMany(arg0, arg1, arg2); // UpdateOptions u = new UpdateOptions(); // u. return false; } @Override public boolean isExit(String collectionName, String key, Object value) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return false; } @Override public void createIndex(String collectionName, String...keys) { MongoCollection<Document> collection = getCollection(collectionName); Document idoc = new Document(); int keys_len = keys.length; for (int i = 0; i< keys_len; i++) { idoc.append(keys[i], 1); } collection.createIndex(idoc); } }
四、MongoDB 分布式集群和分片
MongoDB 支持在多个机器中通过异步复制达到故障转移和实现冗余。 多机器中同一时刻只有一台是用于写操作。 正是由于这个情况, 为 MongoDB 提供了数据一致性的保障。 担当 Primary 角色的机器能把读操作分发给 slave,实现读写分离 。
MongoDB 在 1.6 版本提供了新功能 replica sets(复制集) , 这比之前的 replication 功能要强大一些, 增加了故障自动切换和自动修复成员节点, 各个 DB 之间数据完全一致, 大大降低了维护成功,replica set 故障切换完全自动,实现了高可用。
MongoDB集群节点的增加和删除均支持热部署,节点同步数据简单。
MongoDB分片是将海量的数据水平扩展的数据库集群系统, 数据分表存储在分片的各个节点上, 使用者通过简单的配置就可以很方便地构建一个分布式 MongoDB 集群。
关于集群和分片,我们下次再分享。



