UDP包格式与实际数据抓包总结
UDP包格式与实际数据抓包总结
UDP 是User Datagram Protocol的简称, 中文名是用户数据报协议,是OSI 参考模型中一种无连接的传输层协议,提供面向事务的简单不可靠信息传送服务。
UDP协议与TCP协议一样用于处理数据包,在OSI模型中,两者都位于传输层,处于IP协议的上一层。
UDP有不提供数据包分组、组装和不能对数据包进行排序的缺点,也就是说,当报文发送之后,是无法得知其是否安全完整到达的。
UDP用来支持那些需要在计算机之间传输数据的网络应用。包括网络视频会议系统在内的众多的客户/服务器模式的网络应用都需要使用UDP协议。

UPD包结构
1.源端口: 主机的应用程序使用的端口号。
2.目的端口:目的主机的应用程序使用的端口号。
3.长度:是指UDP头部和UDP数据的字节长度。因为UDP头 部长度为8字节,所以该字段的最小值为8。
4.校验和:检测UDP数据报在传输中是否有错,有错则丢弃。
UDP header packet structure
UDP wraps datagrams with a UDP header, which contains four fields totaling eight bytes.
The fields in a UDP header are:
1.Source port – The port of the device sending the data. This field can be set to zero if the destination computer doesn’t need to reply to the sender.
2.Destination port – The port of the device receiving the data. UDP port numbers can be between 0 and 65,535.
3.Length – Specifies the number of bytes comprising the UDP header and the UDP payload data. The limit for the UDP length field is determined by the underlying IP protocol used to transmit the data.
4.Checksum – The checksum allows the receiving device to verify the integrity of the packet header and payload. It is optional in IPv4 but was made mandatory in IPv6.
搭建数据测试模型

用UDP发包测试工具发送数据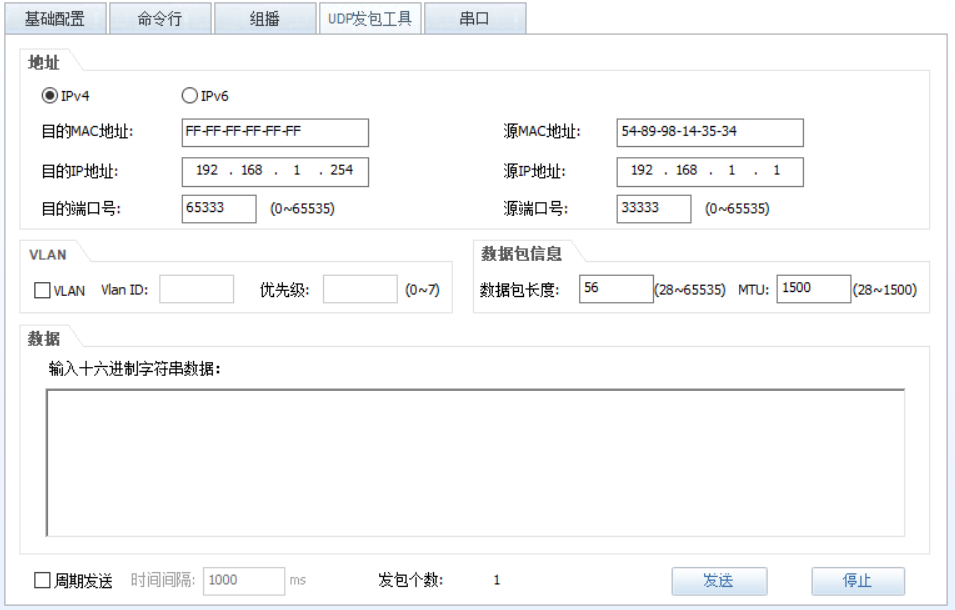
抓取相关UDP数据(总长度36 = 8 + 28)
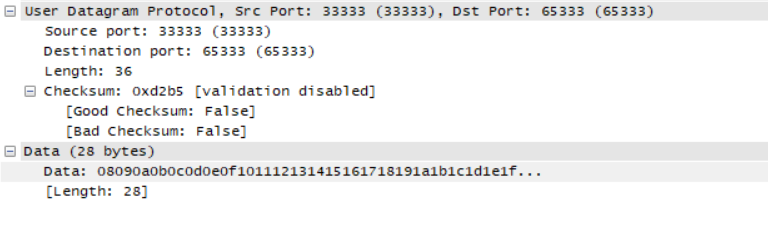
以下是从外网上摘抄的相关信息,进行补充
What is user datagram protocol (UDP)
User datagram protocol (UDP) operates on top of the Internet Protocol (IP) to transmit datagrams over a network. UDP does not require the source and destination to establish a three-way handshake before transmission takes place. Additionally, there is no need for an end-to-end connection.
Since UDP avoids the overhead associated with connections, error checks and the retransmission of missing data, it’s suitable for real-time or high performance applications that don’t require data verification or correction. If verification is needed, it can be performed at the application layer.
UDP is commonly used for Remote Procedure Call (RPC) applications, although RPC can also run on top of TCP. RPC applications need to be aware they are running on UDP, and must then implement their own reliability mechanisms.
The benefits and downsides of UDP
UDP has a number of benefits for different types of applications, including:
No retransmission delays – UDP is suitable for time-sensitive applications that can’t afford retransmission delays for dropped packets. Examples include Voice over IP (VoIP), online games, and media streaming.
Speed – UDP’s speed makes it useful for query-response protocols such as DNS, in which data packets are small and transactional.
Suitable for broadcasts – UDP’s lack of end-to-end communication makes it suitable for broadcasts, in which transmitted data packets are addressed as receivable by all devices on the internet. UDP broadcasts can be received by large numbers of clients without server-side overhead.
At the same time, UDP’s lack of connection requirements and data verification can create a number of issues when transmitting packets. These include:
No guaranteed ordering of packets.
No verification of the readiness of the computer receiving the message.
No protection against duplicate packets.
No guarantee the destination will receive all transmitted bytes. UDP, however, does provide a checksum to verify individual packet integrity.
UDP DDoS threats and vulnerabilities
UDP’s lack of a verification mechanism and end-to-end connections makes it vulnerable to a number of DDoS attacks. Attackers can spoof packets with arbitrary IP addresses, and reach the application directly with those packets.
This is in contrast to TCP, in which a sender must receive packets back from the receiver before communication can start.
UDP specific DDoS attacks include:
UDP Flood
A UDP flood involves large volumes of spoofed UDP packets being sent to multiple ports on a single server, knowing that there is no way to verify the real source of the packets. The server responds to all the requests with ICMP ‘Destination Unreachable’ messages, overwhelming its resources.
In addition to the traditional UDP flood, DDoS perpetrators often stage generic network layer attacks by sending mass amounts of fake UDP packets to create network congestion. These attacks can only be mitigated by scaling up a network’s resources on demand, as is done when using a cloud DDoS mitigation solution.
DNS Amplification
A DNS amplification attack involves a perpetrator sending UDP packets with a spoofed IP address, which corresponds to the IP of the victim, to its DNS resolvers. The DNS resolvers then send their response to the victim. The attack is crafted such that the DNS response is much larger than the original request, which creates amplification of the original attack.
When done on a large scale with many clients and multiple DNS resolvers, it can overwhelm the target system. A DDoS attack with capacity of 27Gbps can be amplified to as much as 300Gbps using amplification.
UDP Port Scan
Attackers send UDP packets to ports on a server to determine which ports are open. If a server responds with an ICMP ‘Destination Unreachable’ message, the port is not open. If there is no such response, the attacker infers that the port is open, and then use this information to plan an attack on the system.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号