IP数据包格式与实际抓包数据总结
IP v4数据包格式总结
要强调的是,理解下图,把它拉成一根直线来理解,别用矩阵来理解。
原因:数据传输时是以二进制(高低电平的形式表示1,0)的形式,在媒介中传输的(如:光缆,电缆,空气等)。
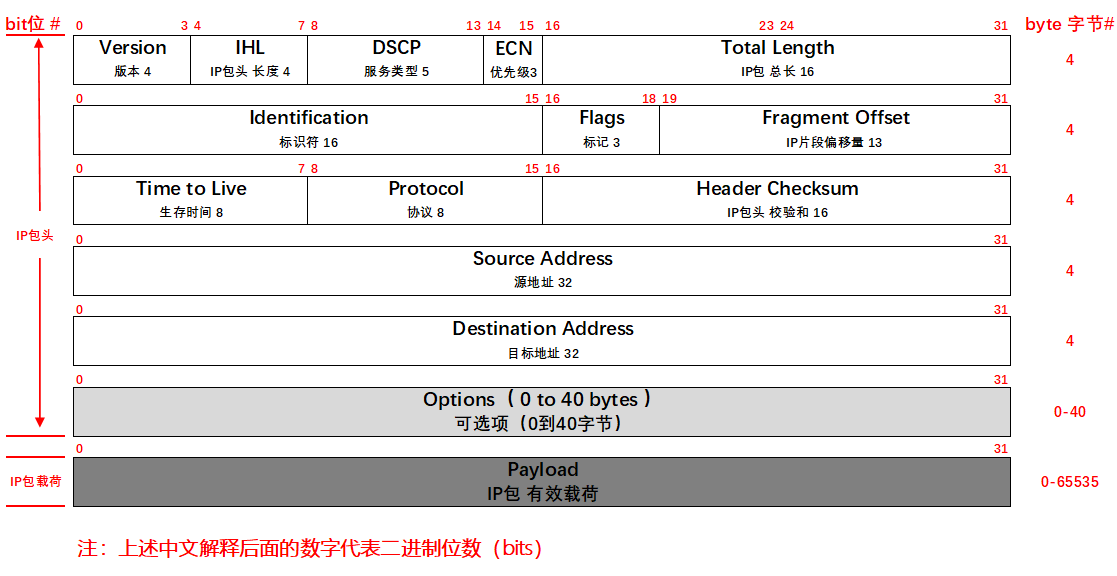
IP包头尺寸(包括可选项): 所以大于或等于20 bytes字节(不含可选项),小于60 bytes字节(含可选项)
IP包尺寸(包括包头和包载荷):所以大于或等于20 bytes字节(只有基本的包头), 小于65536字节(从0开始数,包括0)
以下是抓取到的IP包,顺着看并与上图对照

IPv4 - Packet Structure
Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4)
Internet Protocol is one of the major protocols in the TCP/IP protocols suite. This protocol works at the network layer of the OSI model and at the Internet layer of the TCP/IP model. Thus this protocol has the responsibility of identifying hosts based upon their logical addresses and to route data among them over the underlying network.
IP provides a mechanism to uniquely identify hosts by an IP addressing scheme. IP uses best effort delivery, i.e. it does not guarantee that packets would be delivered to the destined host, but it will do its best to reach the destination. Internet Protocol version 4 uses 32-bit logical address.
Internet Protocol being a layer-3 protocol (OSI) takes data Segments from layer-4 (Transport) and divides it into packets. IP packet encapsulates data unit received from above layer and add to its own header information.
IP Encapsulation
The encapsulated data is referred to as IP Payload. IP header contains all the necessary information to deliver the packet at the other end.
IP Header
IP header includes many relevant information including Version Number, which, in this context, is 4. Other details are as follows −
Version − Version no. of Internet Protocol used (e.g. IPv4:0100, IPV6: 0110).
版本号(Version):长度4比特。标识目前采用的IP协议的版本号。一般的值为0100(IPv4),0110(IPv6)
IHL − Internet Header Length; Length of entire IP header.
IP包头长度(Header Length):长度4比特。这个字段的作用是为了描述IP包头的长度,因为在IP包头中有变长的可选部分。该部分占4个bit位,单位为32bit(4个字节),即本区域值= IP头部长度(单位为bit)/(8*4),因此,一个IP包头的长度最长为“1111”,即15*4=60个字节。IP包头最小长度为20字节。
DSCP − Differentiated Services Code Point; this is Type of Service.
ECN − Explicit Congestion Notification; It carries information about the congestion seen in the route.
服务类型(Type of Service):长度8比特。8位 按位被如下定义 DTRC0 PPP
D 时延: 0:普通 1:延迟尽量小
T 吞吐量: 0:普通 1:流量尽量大
R 可靠性: 0:普通 1:可靠性尽量大
M 传输成本: 0:普通 1:成本尽量小
0 最后一位被保留,恒定为0
PPP:定义包的优先级,取值越大数据越重要
000 普通 (Routine)
001 优先的 (Priority)
010 立即的发送 (Immediate)
011 闪电式的 (Flash)
100 比闪电还闪电式的 (Flash Override)
101 CRI/TIC/ECP(找不到这个词的翻译)
110 网间控制 (Internetwork Control)
111 网络控制 (Network Control)
Total Length − Length of entire IP Packet (including IP header and IP Payload).
IP包总长(Total Length):长度16比特。 以字节为单位计算的IP包的长度 (包括头部和数据),所以IP包最大长度65535字节。
IP包头长度(Header Length):长度4比特。这个字段的作用是为了描述IP包头的长度,因为在IP包头中有变长的可选部分。该部分占4个bit位,单位为32bit(4个字节),即本区域值= IP头部长度(单位为bit)/(8*4),因此,一个IP包头的长度最长为“1111”,即15*4=60个字节。IP包头最小长度为20字节。
Identification − If IP packet is fragmented during the transmission, all the fragments contain same identification number. to identify original IP packet they belong to.
标识符(Identifier):长度16比特。该字段和Flags和Fragment Offest字段联合使用,对较大的上层数据包进行分段(fragment)操作。路由器将一个包拆分后,所有拆分开的小包被标记相同的值,以便目的端设备能够区分哪个包属于被拆分开的包的一部分。
Flags − As required by the network resources, if IP Packet is too large to handle, these ‘flags’ tells if they can be fragmented or not. In this 3-bit flag, the MSB is always set to ‘0’.
标记(Flags):长度3比特。该字段第一位不使用。第二位是DF(Don't Fragment)位,DF位设为1时表明路由器不能对该上层数据包分段。如果一个上层数据包无法在不分段的情况下进行转发,则路由器会丢弃该上层数据包并返回一个错误信息。第三位是MF(More Fragments)位,当路由器对一个上层数据包分段,则路由器会在除了最后一个分段的IP包的包头中将MF位设为1。
Fragment Offset − This offset tells the exact position of the fragment in the original IP Packet.
片偏移(Fragment Offset):长度13比特。表示该IP包在该组分片包中位置,接收端靠此来组装还原IP包。
Time to Live − To avoid looping in the network, every packet is sent with some TTL value set, which tells the network how many routers (hops) this packet can cross. At each hop, its value is decremented by one and when the value reaches zero, the packet is discarded.
生存时间(TTL):长度8比特。当IP包进行传送时,先会对该字段赋予某个特定的值。当IP包经过每一个沿途的路由器的时候,每个沿途的路由器会将IP包的TTL值减少1。如果TTL减少为0,则该IP包会被丢弃。这个字段可以防止由于路由环路而导致IP包在网络中不停被转发。
Protocol − Tells the Network layer at the destination host, to which Protocol this packet belongs to, i.e. the next level Protocol. For example protocol number of ICMP is 1, TCP is 6 and UDP is 17.
协议(Protocol):长度8比特。标识了上层所使用的协议。 例如:协议号1:ICMP, 6:TCP, 17:UDP。
Header Checksum − This field is used to keep checksum value of entire header which is then used to check if the packet is received error-free.
头部校验(Header Checksum):长度16位。用来做IP头部的正确性检测,但不包含数据部分。 因为每个路由器要改变TTL的值,所以路由器会为每个通过的数据包重新计算这个值。
Source Address − 32-bit address of the Sender (or source) of the packet.
Destination Address − 32-bit address of the Receiver (or destination) of the packet.
起源和目标地址(Source and Destination Addresses):这两个地段都是32比特。标识了这个IP包的起源和目标地址。要注意除非使用NAT,否则整个传输的过程中,这两个地址不会改变。
Options − This is optional field, which is used if the value of IHL is greater than 5. These options may contain values for options such as Security, Record Route, Time Stamp, etc.
可选项(Options):这是一个可变长的字段。该字段属于可选项,主要用于测试,由起源设备根据需要改写。可选项目包含以下内容:
松散源路由(Loose source routing):给出一连串路由器接口的IP地址。IP包必须沿着这些IP地址传送,但是允许在相继的两个IP地址之间跳过多个路由器。
严格源路由(Strict source routing):给出一连串路由器接口的IP地址。IP包必须沿着这些IP地址传送,如果下一跳不在IP地址表中则表示发生错误。
路由记录(Record route):当IP包离开每个路由器的时候记录路由器的出站接口的IP地址。
时间戳(Timestamps):当IP包离开每个路由器的时候记录时间。
填充(Padding):因为IP包头长度(Header Length)部分的单位为32bit,所以IP包头的长度必须为32bit的整数倍。因此,在可选项后面,IP协议会填充若干个0,以达到32bit的整数倍。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号