各代移动通讯基站的特点(2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, 6G 的距离,基站,速度,时延)
各代移动通讯的特点(距离,基站,速度,时延)
(2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, 6G)
基站覆盖范围:
2G基站的距离约为10km
3G约为5km
4G约为3km
5G约为500m
6G 目前尚不清楚,相关情况请参考文章后面的附图
4G与5G基站数据对比:
三大运营商都已经做出了自己的大体部署,
联通家的基站密度大概是原来的3到4倍
移动家的达到了六倍左右
电信家的也是三倍以上
网速理论上各是多少
2G理论网速是150Kbps,折合下载速度15-20K/s;2G是第二代手机通信技术规格,以数字语音传输技术为核心。一般定义为无法直接传送如电子邮件、软件等信息;只具有通话和一些如时间日期等传送的手机通信技术规格;
3G理论网速为1-6Mbps,折合下载速度120K/s-600K/s;是指支持高速数据传输的蜂窝移动通讯技术。3G服务能够同时传送声音及数据信息,速率一般在几百kbps以上;
4G理论网速为10-100Mbps,折合下载速度1.5M/s-10M/s;是集3G与WLAN于一体,并能够快速传输数据、高质量、音频、视频和图像等。4G能够以100Mbps以上的速度下载,能够满足几乎所有用户对于无线服务的要求;
5G网络上传速率可以稳定到600Mbps以上,最高可达到1Gbps。
网络时延
1.首先要明白时延与延时的区别:a.时延,Latency,是指一个报文进入一台设备至这个报文出这台设备所经历时间,实际考验的是这个报文在这台设备所消耗的时间。即简言之,从输入要求到响应设备所需的时间,或者称为系统层级的时间的延迟。较低的延迟意味着更快的响应速度,时间越短,此设备性能越高;可以理解为设备固有的特性,设备就这能耐。b.延时,Delay,是指一个操作和另一个操作之间停顿的时间;延时除了设备本身时延外,还有人为操作,技术故障等;
2. 对于2G,3G谈时延没意义,原因不就打个电话啥,了不起发个邮件或文件,时间延迟就延迟呗。但对于工业应用有些就是致命的,如无人驾驶远程操控,0.1秒和0.01秒效果就大有不同,简单计算,汽车每秒30米运行,0.1秒的距离是3米,0.01秒就30厘米了,那就是远程操控的效果就是无人汽车开不开进沟里的区别。 一旦时延大幅降低,通过网络连接进行远程操作,就和本地几乎无差别,即真正的透明化传输。整个社会效率会大幅度提高。
3. 而5G比4G除了速度快很多,更重要的是网络延迟降低了很多。国内外5G研究机构对5G提出了毫秒级的端到端网络延迟要求,理想情况下端到端的网络延迟为1毫秒,典型的端到端网络延迟为5至10毫秒。而我们目前使用的4G网络,端到端的理想网络延迟是10毫秒左右,LTE的端到端典型网络延迟是50至100毫秒。显然,这些数据意味着5G将端到端的网络延迟缩短为4G的十分之一
以上都是理论网速和宽带提供的网速不同,移动蜂窝网络还会受到使用环境人流量、环境是否开阔,基站布局的密度影响。
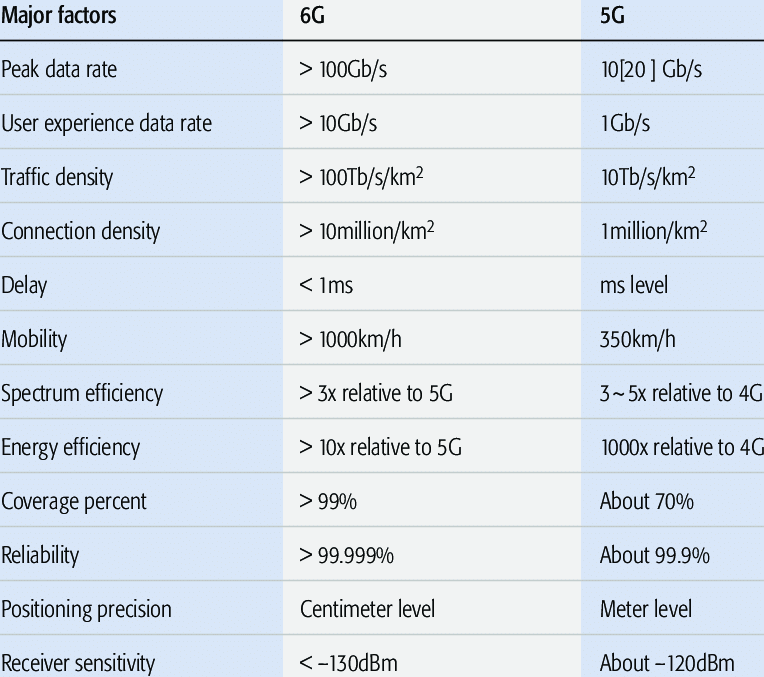
谈谈6G通讯
6G 目前尚不清楚? 但与5G相比,大致分析,6G将使用更先进的无线电设备和更大数量的无线电波,包括使用超高频(EHF)频谱,该频谱可在短距离内提供超高速和巨大容量。在覆盖范围方面,6G可能无处不在。6G卫星技术和能够反射电磁信号的智能表面将向世界上某些地区提供低延迟,几千兆位的连接,而这些地区对于传统移动网络而言太困难或太昂贵。地球的偏远地区,天空和海洋都可以连通。
用人话讲6G:大概是华为5G系统加特斯拉的星链系统,甚至还要远远超越。中国5G很扎实,走稳后上天对中国并非难事。 美国先上天搞星链,走稳后再下地,至少在中国估计机会渺茫。中美合作成本最优!!不合作的话,美方的成本将大于中方!
个人认为,美国地广人稀,发展5G、6G都不划算,所以发展6G先上天,薅全球用户羊毛补贴其国内,重点地方重点铺基站,再走向全球市场是不错的选择。中国是顺其自然,一代一代的发展,不小心就发展到5G踩着她了。他不让我们发展,这怎么挡得住呢?我们国家自己要用啊 !:)
以下信息是外网摘来的,供大家参考(没翻译,将就看):
5 Facts About 5G vs. 6G
5G and 6G exploded into the tech scene at about the same time. Just as 5G rolls out commercially, 6G research and development (R&D) projects have launched. That may lead to some confusion about the difference between the two. Here are five things to know.
1. 5G and 6G Use Two Different Parts of the Spectrum
Both 5G and 6G take advantage of higher frequencies on the wireless spectrum to transmit more data, faster. However, 5G occupies broadband frequencies at sub-6 gigahertz (GHz) and above 24.25 GHz – called low band and high band frequencies respectively. 6G will operate at 95 GHz to 3 terahertz (THz). At those wavelengths, 6G will deliver speeds 1,000 times faster than 5G (which is only four to five times faster than 4G).
2. 5G Makes the Internet of Things Possible. 6G Speeds It Up
Part of the reason 5G is so anticipated lies in the expectation that it will finally make the Internet of Things a practical everyday reality. The frequencies used by 4G are too narrow and too crowded to transmit data at the speeds that smart devices need to function optimally. That’s why they haven’t gained widespread traction. That’s going to change with 5G, and likely again with 6G.
3. 5G Will Not Replace 4G. 6G Will Not Replace 5G
While 4G was 3G but faster, 5G and 6G represent different iterations of wireless connectivity. Many predictions expect 6G will be reserved for business, military, and industrial purposes with some consumer uses such as immersive entertainment. It won’t be practical to have every device streaming with 6G – but other advances may change that.
4. 6G Opens New Frontiers of Connectivity But 5G Doesn’t
5G has struggled to arrive because of its infrastructure requirements. In contrast, 6G will build on the infrastructure we put down for 5G and enhance connectivity – on land, under the sea, or even in space.
5. Both Generations Have Very Low Latency
Latency refers to the time it takes for a packet of information to transmit over a frequency. 4G latency is about 50 milliseconds. In 5G, that drops to 5 milliseconds – about 10 times lower. 6G latency is estimated at 1 millisecond, a latency five times lower than that of 5G. That almost instantaneous speed will help make massive data transmissions possible.
4G vs. 5G vs. 6G: More Than Just Evolutions of Wireless Technology
6G means more than just faster speeds and more data transfer, although those things will exist. When we consider 4G vs. 5G, we can see how wireless technology has evolved. It becomes more nuanced when considering 5G vs. 6G – but that may just be because the technology remains a decade in the future.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号