IdentityServer4 + SignalR Core +RabbitMQ 构建web即时通讯(二)
IdentityServer4 + SignalR Core +RabbitMQ 构建web即时通讯(二)
IdentityServer4 用户中心生成数据库
上文已经创建了所有的数据库上下文迁移代码,这里开始数据库的迁移和种子数据,EF Core 2.1刚好新增了种子数据的功能,文档地址,一开始的想法是使用这种方式,看起来很简洁与方便,但需要在OnModelCreating中配置,不过IdentityServer4中的2个数据库上下文我不知道怎么配置进去了,所以还是用比较原始的方式吧。
1.在SeedData添加客户端Client ApiResource IdentityRecouse的种子数据;
public static List<Client> Clients() { return new List<Client> { new Client{ // 客户端id ClientId ="chat_client", // 客户端名称 ClientName ="chat client", // TOKEN有效时长 AccessTokenLifetime = 3600, // 配置TOKEN类型,reference为引用类型,数据不会存在TOKEN中 AccessTokenType= AccessTokenType.Jwt, // 配置客户端授权模式 AllowedGrantTypes= GrantTypes.ResourceOwnerPassword, // 配置客户端连接密码 ClientSecrets={ new Secret("123123".Sha256())}, // 客户端允许的请求范围 AllowedScopes={ "chatapi", IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.OfflineAccess, IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.OpenId, IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Profile }, //允许离线,即开启refresh_token AllowOfflineAccess =true, RequireClientSecret=false } }; } public static IEnumerable<ApiResource> ApiResources() { return new List<ApiResource> { // 定义api资源 这里如果使用构造函数传入Name会默认创建一个同名的Scope, // 这点需要注意,因为这个Api如果没有Scope,那根本无法访问 new ApiResource { Name="chatapi", DisplayName="chat api", ApiSecrets= { new Secret("123123".Sha256()) }, Scopes={ new Scope("chatapi","chat api") } } }; } public static IEnumerable<IdentityResource> IdentityResources() { return new List<IdentityResource> { new IdentityResources.OpenId(), new IdentityResources.Profile() }; }
2.StartUp中增加迁移方法,Database.Migrate() 实际就是Update-Database命令,那为什么这样用呢?生产环境总不能让我去执行Update-Database吧?,当我们修改了实体代码与配置时,不用做任何处理,程序运行时就能自动更新数据库结构。Configure中调用 Migration(app).Wait();
public static async Task Migration(IApplicationBuilder app) { using (var scope = app.ApplicationServices.CreateScope()) { // 迁移DemoDbContext上下文 scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<DemoDbContext>().Database.Migrate(); // 迁移PersistedGrantDbContext上下文 scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<PersistedGrantDbContext>().Database.Migrate(); var configurationDbContext = scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<ConfigurationDbContext>(); // 迁移ConfigurationDbContext上下文 configurationDbContext.Database.Migrate(); // 注入用户管理 增加用户 var userManager = scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<UserManager<DemoUser>>(); foreach (var user in SeedData.Users()) { if (userManager.FindByNameAsync(user.UserName).Result == null) { await userManager.CreateAsync(user, "123123"); } } // 增加ApiResources IdentityResources Clients if (!configurationDbContext.ApiResources.Any()) configurationDbContext.ApiResources.AddRange(SeedData.ApiResources().Select(r => r.ToEntity())); if (!configurationDbContext.IdentityResources.Any()) configurationDbContext.IdentityResources.AddRange(SeedData.IdentityResources().Select(r => r.ToEntity())); if (!configurationDbContext.Clients.Any()) configurationDbContext.Clients.AddRange(SeedData.Clients().Select(r => r.ToEntity())); await configurationDbContext.SaveChangesAsync(); } }
这里有个不算坑的坑,Add-Migration命令创建迁移代码时需要把Migration(app).Wait()注释掉,为什么呢?这个命令实际上会启动应用,并执行里面的代码,当首次执行时,数据库并不存在,迁移代码也不存在,所以数据结构都还不存在,如果执行种子数据操作肯定会失败了,当然Add-Migration本身就算是一个代码生成器,属于开发时操作,所以这是一个不算坑的坑。
4.启动程序,控制台能看到迁移信息,
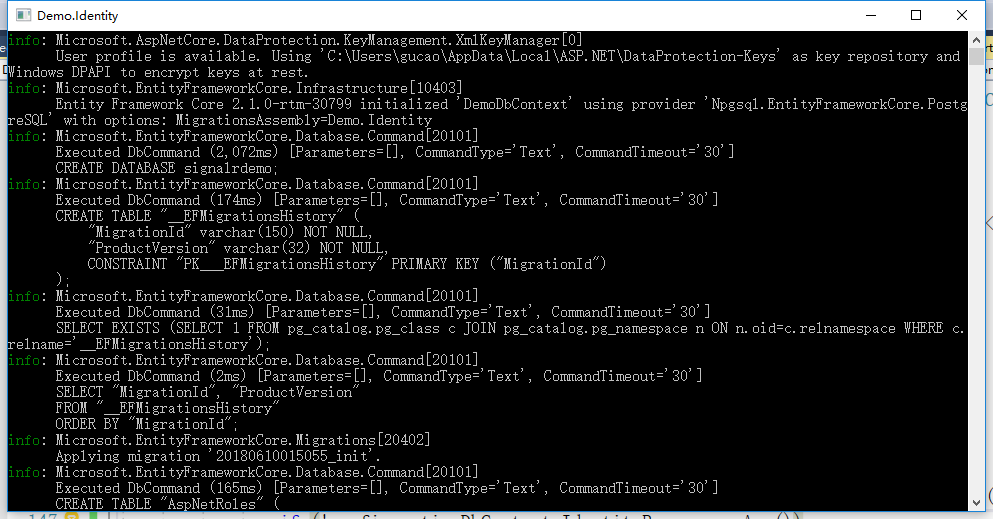
好了,数据库已经给我们创建好了
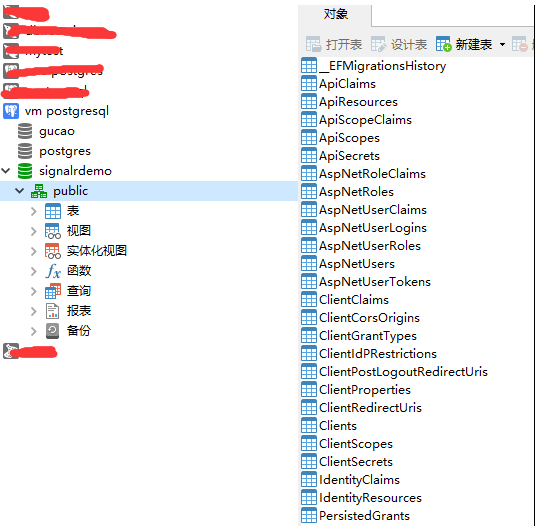
看看AspNetUsers,用户数据也没问题
现在打开Postman,用laowang这个用户试一试token能否拿到,token获取的地址为/connect/token,刷新token也是这个地址
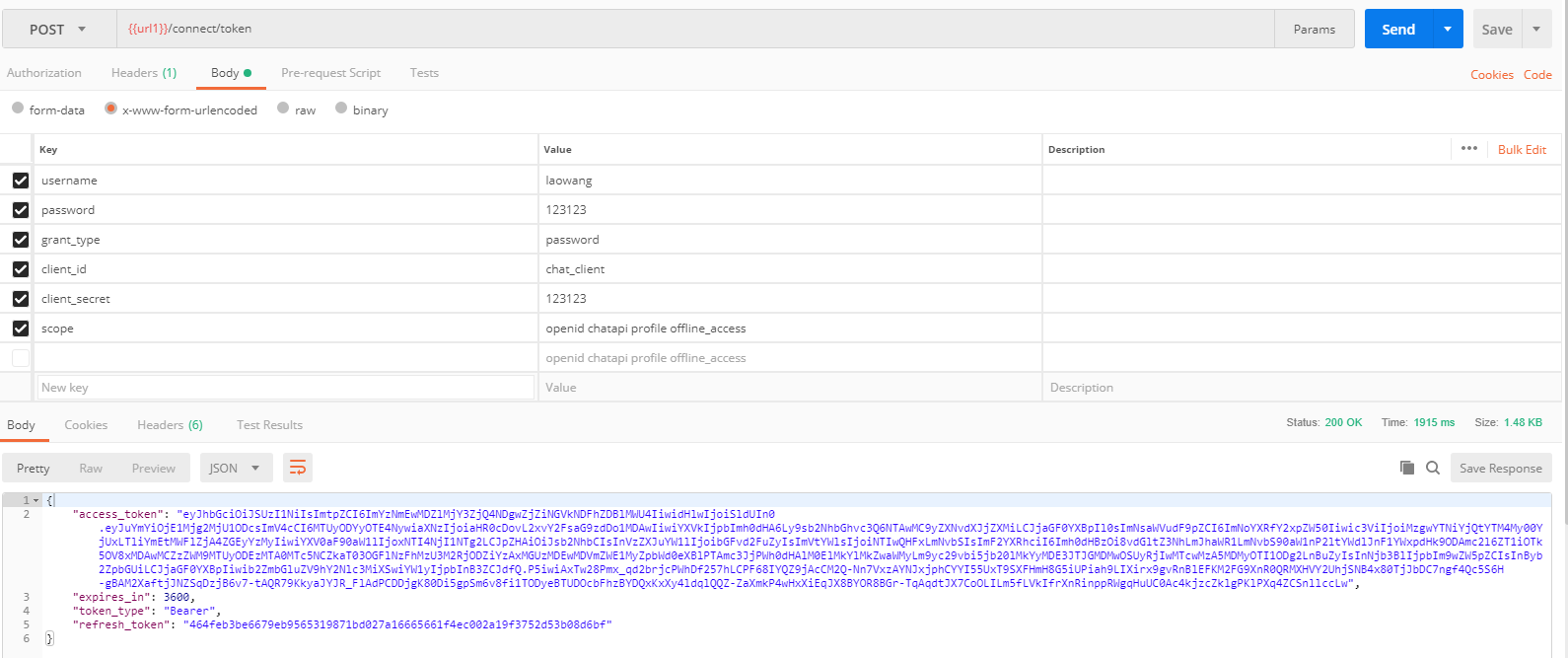
没问题,我们把token复制下拿到jwt.io看看是否带有用户信息,

可以看到username,email,avatar,没有问题。
好了,这篇就到这,下一篇开始写聊天室后端服务。



