Mybatis-Mapper封装数据类
1.1 项目准备
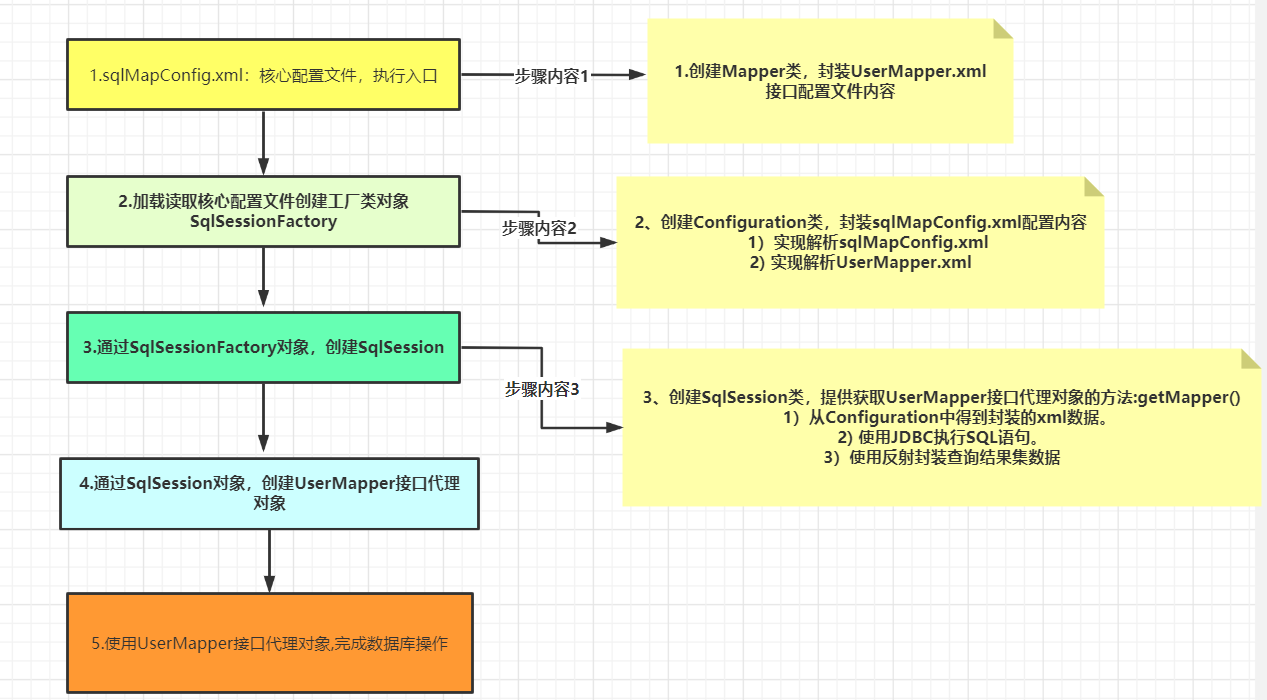
mybatis框架分析
1.1.1 项目环境
- sqlMapConfig.xml核心配置文件,去掉DTD约束。因为dom4j会上网去找dtd文件。
- UserMapper.xml映射配置文件,去掉DTD约束。
- UserMapper接口。
- User实体类。
导入相关jar包
UserMapper.xml

5.1.2 代码实现
- 创建包cn.guardwhy.framework。
- 创建实体类:Mapper包含4个属性:namespace,id,resultType,sql。
- 重写toString()方法,方便后期测试看到封装的结果。
- 生成get和set方法,一个Mapper对象代表一条要操作的查询语句对象。
package cn.guardwhy.framework;
/**
* 封装UserMapper.xml属性
*/
public class Mapper {
private String namespace; // 封装接口名
private String id; // 方法名
private String resultType; // 返回实体类类型
private String sql; // 要执行的SQL语句
/**
* get.set方法
* @return
*/
public String getNamespace() {
return namespace;
}
public void setNamespace(String namespace) {
this.namespace = namespace;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getResultType() {
return resultType;
}
public void setResultType(String resultType) {
this.resultType = resultType;
}
public String getSql() {
return sql;
}
public void setSql(String sql) {
this.sql = sql;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Mapper{" +
"namespace='" + namespace + '\'' +
", id='" + id + '\'' +
", resultType='" + resultType + '\'' +
", sql='" + sql + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
5.2 dom4j方法
解析XML文件,得到Document对象
1. 得到输入流InputStream
2. new SAXReader().read(输入流) 返回Document对象
Document常用方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Element getRootElement() | 得到XML中根元素(标签) |
| List<Node> selectNodes(String xpath) | 通过xpath查询多个节点Node, Node是Element的父接口 |
| Node selectSingleNode(String xpath) | 通过xpath得到一个节点 |
| Element element(String name) | 通过元素的名字得到它的一个子元素 |
属性文本相关方法
| 方法名 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
| String attributeValue(String name) | 通过标签的属性名字,得到属性的值 |
| String getTextTrim() | 得到标签中文本内容,并且去掉前后的空格 |
5.3 核心配置文件
封装核心配置文件:sqlMapConfig.xml文件
- 创建driver,url, username,password四个属性
- 实例化1个空的Map集合:封装其它映射文件的XML信息
- 声明数据源对象DataSource
- 生成get和set方法,生成toString()方法
![]()
loadSqlMapConfig()方法
1、创建loadSqlMapConfig()方法,它的作用
- 解析sqlMapConfig.xml配置文件,给Configuration中的属性赋值。
- 解析UserMapper.xml配置文件,给Mapper中的属性赋值。
2、在构造方法中调用方法: loadSqlMapConfig( )
5.3.1 代码实现
核心配置文件
package cn.guardwhy.framework;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.Node;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import javax.xml.parsers.SAXParser;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 解析XML文件:sqlMapConfig.xml, UserMapper.xml
*/
public class Configuration {
// 1.创建连接池的属性
private String driver;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
// 2.定义连接池
private DataSource dataSource;
// 3.实例化1个空的Map集合:封装其它映射文件的XML信息
private Map<String, Mapper> mappers = new HashMap<>();
// 4.在构造方法中调用方法: loadSqlMapConfig()
public Configuration() {
try {
loadSqlMapConfig();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 5.解析配置文件方法
private void loadSqlMapConfig() throws DocumentException {
// 5.1. 从类路径加载/sqlMapConfig.xml配置文件,创建输入流
InputStream inputStream = Configuration.class.getResourceAsStream("/sqlMapConfig.xml");
// 5.2. 使用dom4j得到文档对象
Document document = new SAXReader().read(inputStream);
// 5.3. 使用XPath读取所有property元素
List<Node> nodes = document.selectNodes("//property");
// 5.4. 遍历每个property元素,读取它的name和value属性值
for(Node node : nodes){
Element propertyElement = (Element) node;
// 得到name属性
String name = propertyElement.attributeValue("name");
// 得到value属性
String value = propertyElement.attributeValue("value");
// 6.判断name的字符串,如果与类中的属性名相同,则赋值到相应属性中
switch (name){
case "driver":
this.driver = value;
break;
case "url":
this.url = value;
break;
case "username":
this.username = value;
break;
case "password":
this.password = value;
break;
}
}
}
/***
* set.get方法
* @return
*/
public String getDriver() {
return driver;
}
public void setDriver(String driver) {
this.driver = driver;
}
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public DataSource getDataSource() {
return dataSource;
}
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
public Map<String, Mapper> getMappers() {
return mappers;
}
public void setMappers(Map<String, Mapper> mappers) {
this.mappers = mappers;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Configuration{" +
"driver='" + driver + '\'' +
", url='" + url + '\'' +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", dataSource=" + dataSource +
", mappers=" + mappers +
'}';
}
}
测试代码
package cn.guardwhy.test;
import cn.guardwhy.framework.Configuration;
public class TestFramework {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
System.out.println(configuration);
}
}
5.4 实体类映射文件
解析UserMapper.xml并且封装到Mapper类中
- 创建新的方法loadMapper(Document document),将当前的文档对象传递给方法
- 读取<mapper>中的resource属性值
- 通过resource读取它对应的XML文件
- 得到namespace,id,resultType,sql的值,封装成Mapper对象
- 在loadSqlMapConfig()中调用此方法
5.4.3 代码实现
解析配置文件
// 解析配置文件方法
private void loadSqlMapConfig() throws DocumentException {
// 解析UserMapper.xml文件
loadMapper(document);
}
/**
* 解析xml实体类映射文件
* @param document
*/
private void loadMapper(Document document) throws DocumentException{
// 1.读取mapper中的resource属性值
// 1.1 读取mapper元素
List<Node> nodes = document.selectNodes("//mapper");
// 1.2 遍历每个mapper元素
for (Node node : nodes){
Element mapperElement = (Element) node;
// 1.3 读取mapper的resource属性值
String resource = mapperElement.attributeValue("resource");
// 2.解析这个XML文件,得到namespace,id,resultType,sql的值
// 2.1 使用类对象,读取输入流下面的resource.
InputStream inputStream = Configuration.class.getResourceAsStream("/" + resource);
// 2.2 创建文档对象
Document doc = new SAXReader().read(inputStream);
// 2.3 得到根元素
Element rootElement = doc.getRootElement();
// 2.4 得到namespace属性
String namespace = rootElement.attributeValue("namespace");
// 2.5 读取根元素下的一个select标签
Element selectElement = rootElement.element("select");
// 2.6 得到id属性
String id = selectElement.attributeValue("id");
// 2.7 resultType属性
String resultType = selectElement.attributeValue("resultType");
// 2.8 SQL属性
String sql = selectElement.getTextTrim();
// 3.封装成Mapper对象
// 3.1 创建一个自定义的Mapper对象,封装上面的三个属性
Mapper mapper = new Mapper();
mapper.setId(id);
mapper.setResultType(resultType);
mapper.setSql(sql);
// 3.2 再封装namespace属性
mapper.setNamespace(namespace);
// 3.3 将封装好的mapper对象添加到this的mappers属性中,其中键是namespace+"."+id,值是自定义的mapper对象。
String key = namespace + "." + id;
this.mappers.put(key, mapper);
}
}
测试代码
package cn.guardwhy.test;
import cn.guardwhy.framework.Configuration;
public class TestFramework {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
System.out.println(configuration);
}
}
5.5 创建数据源
- 创建c3p0的数据源,数据源类:ComboPooledDataSource。
- 设置数据库有关的属性:driver, url,username,password。
- 将this的dataSource设置为上面创建好的数据源对象。
5.5.2 代码实现
/**
* 4.在构造方法中调用方法:
* loadSqlMapConfig()
* 调用createDataSource()方法
*/
public Configuration() {
try {
loadSqlMapConfig();
createDataSource(); //创建数据源
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
创建数据源
*/
private void createDataSource() throws PropertyVetoException {
//使用c3p0连接池
ComboPooledDataSource ds = new ComboPooledDataSource();
//在代码中设置连接池的属性
ds.setUser(this.username);
ds.setPassword(this.password);
ds.setJdbcUrl(this.url);
ds.setDriverClass(this.driver);
//创建好的数据源赋值给成员变量
this.dataSource = ds;
}
5.6 核心组件SqlSession
生成步骤
- 编写SqlSession类,提供一个getMapper()方法,获取接口的实现对象(代理对象)。
- 测试:调用接口中的方法,其中查询数据库的方法,先不从数据库查,而是将模拟的数据写在代码中。
JDK动态代理好处
-
接口的代理对象由程序在执行的过程中动态生成,不用我们自己去写一个类实现接口中所有的方法
-
可以动态生成任意接口的对象
Proxy 类中的方法
Proxy.newProxyInstance( ) :创建UserMapper接口的动态代理对象。
参数列表 : static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h)
作用 : 动态生成代理对象。
| loader | 与真实对象相同的类加载器 |
|---|---|
| interfaces | 代理类所有实现的接口 |
| h | 调用代理对象的接口,使用时传入一个实现类。 需要重写接口中的方法,实现真实对象中每个方法的调用。 |
| 返回 | 生成代理对象 |
InvocationHandler接口
Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
作用:接口中这个方法会调用多次,真实对象中的每个被代理的方法都会调用一次
| proxy | 动态生成的代理对象,不要在方法中直接调用,不然会出现递归死循环的调用。 |
|---|---|
| method | 真实对象的方法 |
| args | 代理对象调用方法时传递的参数 |
| 返回 | 方法的返回值 |
invoke() 方法
| method.invoke(Object obj, Object[] args) | 通过反射调用真实对象中的每个方法 |
|---|---|
| Object obj | 真实对象 |
| Object[] args | 调用真实的方法时传递的参数 |
方法签名
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type)
InvocationHandler匿名类
分析图解

基本功能
- 通过键得到Mapper对象。
- 从Mapper对象中得到SQL语句执行,并且封装成对象返回。
生成步骤
- 实例化Configuration对象,通过类全名+"."+方法名得到键。
- 通过键得到值Mapper对象,得到要执行的sql语句和返回的实体类型。
- 通过数据源得到连接对象,执行数据库操作,通过反射封装结果集并且返回。
5.6.1 SqlSession类
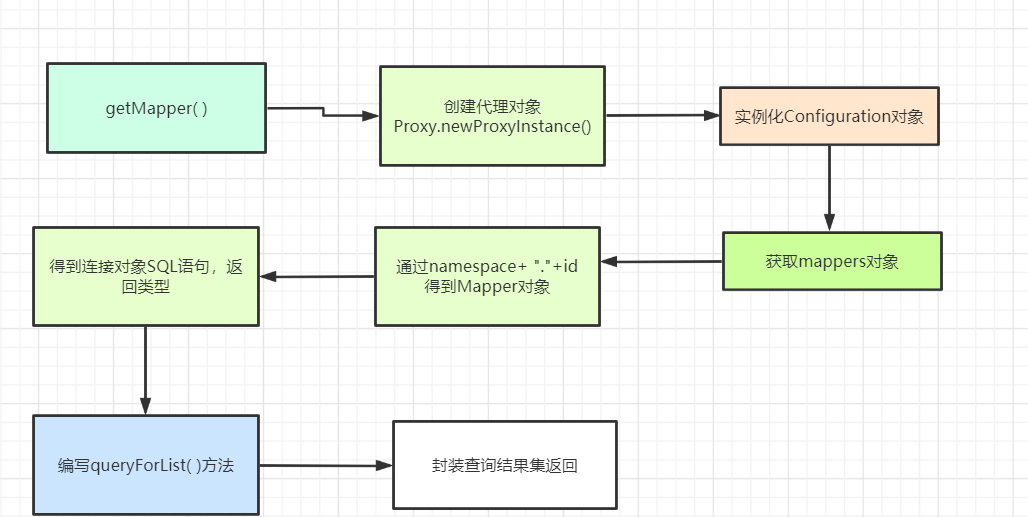
得到SQL语句和返回类型
- 得到Configuration中Map集合
实例化Configuration对象
通过Configuration得到Mapper对象的集合
- 得到Map中的键:类全名.方法名
通过方法对象->得到声明的接口->得到名称:即类全名 com.itheima.dao.UserMapper
获取当前执行的方法名称:findAllUsers
通过类全名+方法名得到键
- 得到Mapper中相应的属性
通过类全名+"."+方法名,从mappers中得到映射的mapper对象
从mapper中获取查询的sql语句
从mapper中获取返回值类型resultType
通过反射将上面的resultType字符串转成类对象,供后面的方法使用
对象访问数据库
- 通过Configuration得到数据源,通过数据源得到连接对象
- 调用List queryForList(Connection connection, String sql, Class clazz)方法
1. 使用JDBC从数据库中查询数据
2. 使用反射来实例化clazz对象,并且封装所有的属性,添加到集合中。
图示:
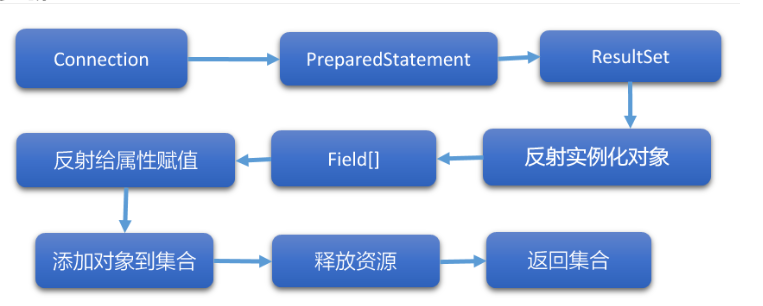
5.6.2 JDBC访问数据库
创建集合List封装结果集,未使用泛型
通过Connection连接对象创建预编译的语句对象
执行查询,得到结果集ResultSet
封装数据成List 对象
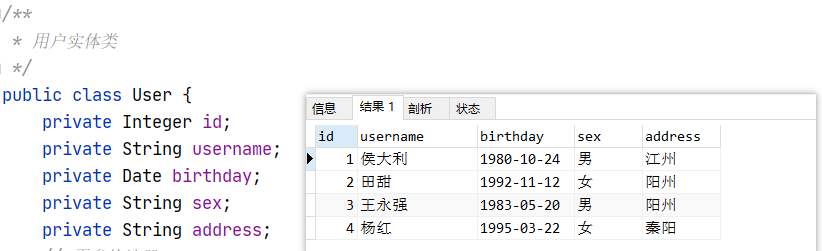
5.6.3 代码示例
Session会话类
package cn.guardwhy.framework;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 会话类
*/
public class SqlSession {
/**
* 创建UserMapper接口的代理对象
* @param mapperClass 接口类对象
* @param <T>
* @return
*/
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> mapperClass){
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(SqlSession.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{mapperClass}, new InvocationHandler() {
/***
*
* @param proxy 生成的代理对象
* @param method 要调用的方法
* @param args 方法的参数
* @return 返回值:方法的返回值
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 1.创建Configuration对象
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
// 2.得到方法的名字
String id = method.getName();
// 3.得到接口的名字
String namespace = method.getDeclaringClass().getName();
// 4.得到key值
String key = namespace + "." + id;
// 5.得到值
Map<String, Mapper> mappers = configuration.getMappers();
Mapper mapper = mappers.get(key);
// 6.SQL语句
String sql = mapper.getSql();
// 7.得到返回数据类型
String resultType = mapper.getResultType();
// 8.得到它的类对象
Class objClass = Class.forName(resultType);
// 9.访问数据库需要Connection对象
DataSource dataSource = configuration.getDataSource();
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
// 使用JDBC来访问数据库,并且封装成List<User>
List list = queryForList(connection, sql, objClass);
return list;
}
});
}
/**
使用JDBC来访问数据库,并且封装成List<User>
*/
private List queryForList(Connection connection, String sql, Class clazz) throws Exception{
List users = new ArrayList<>();
// 1.通过连接对象得到预编译的语句对象
PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 2.执行SQL语句,得到结果集
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
// 3.遍历结果集,将每一行记录封装成一个User对象
while (rs.next()){
Object user = clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();
// 得到类中的所有成员变量
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields){
// 得到成员变量的名字
String name = field.getName();
// 遍历成员变量给每个成员变量赋值
field.setAccessible(true);
// 从结果集取出所有的数据
field.set(user, rs.getObject(name));
}
// 4.添加到集合中
users.add(user);
}
rs.close();
ps.close();
connection.close();
// 5.返回集合
return users;
}
}
测试类
package cn.guardwhy.test;
import cn.guardwhy.dao.UserMapper;
import cn.guardwhy.domain.User;
import cn.guardwhy.framework.Configuration;
import cn.guardwhy.framework.SqlSession;
import java.util.List;
public class TestFramework {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.使用SqlSession类
SqlSession session = new SqlSession();
// 2.调用getMapper(UserMapper.class),返回的就是代理对象
UserMapper userMapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
System.out.println(userMapper.getClass());
// 3.调用代理对象的方法,得到所有的用户
List<User> users = userMapper.findAllUsers();
// 4.输出user
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号