4.React生命周期
4.React生命周期
4.1引出生命周期
class Life extends React.Component {
state = {
opacity:0.5
}
death = () => {
// 卸载定时器
// clearInterval(this.timer)
// 卸载组件
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(document.getElementById('test'))
}
// 生命周期钩子函数
// 组件挂载完调用
componentDidMount(){
this.timer = setInterval(()=>{
// 获取原状态
let {opacity} = this.state
// 减小0.1
opacity -= 0.1
// 设置新的透明度
if (opacity <= 0) opacity = 1
this.setState({opacity})
}, 200)
}
// 组件将要卸载操作
componentWillUnmount(){
// 卸载定时器
clearInterval(this.timer)
}
render(){
return (
<div>
<h2 style={{opacity: this.state.opacity}}>yeyang is da hanbi</h2>
<button onClick={this.death}>don't life</button>
</div>
)
}
}
4.2 react生命周期(旧)(17.0版本之前)
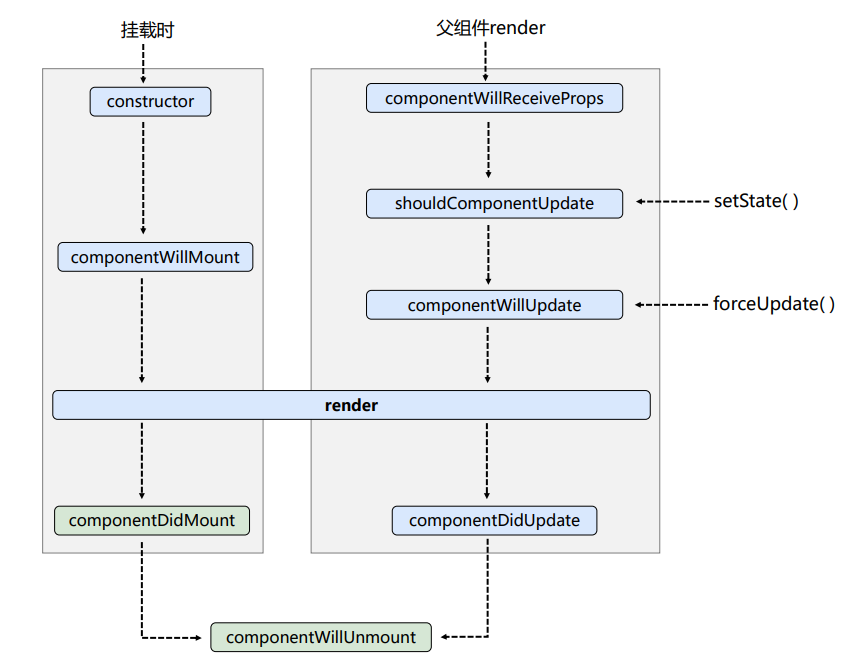
/*
1. 初始化阶段: 由ReactDOM.render()触发---初次渲染
1. constructor()
2. componentWillMount()
3. render()
4. componentDidMount() ====> 常用
--- 一般在这个钩子做一些初始化的事,例如:开启定时器,发送网络请求,订阅消息
2. 更新阶段: 由组件内部this.setSate()或父组件重新render触发
1. shouldComponentUpdate()
2. componentWillUpdate()
3. render() ====> 必须使用的一个
4. componentDidUpdate()
3. 卸载组件: 由ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode()触发
1. componentWillUnmount() ====> 常用
---- 一般在这个钩子中做一些收尾的事,如关闭定时器、取消订阅消息
*/
class Count extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
console.log('Count---constructor')
super(props);
this.state = {
count: 0
}
}
// state = {
// count: 0
// }
add = () => {
const {count} = this.state
this.setState({
count: count+1
})
}
death = () => {
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(document.getElementById('test'))
}
force = () => {
this.forceUpdate() // 强制更新钩子
}
// 组件将要挂载的钩子
componentWillMount(){
console.log('Count---componentWillMount')
}
// 组件挂载完成的钩子
componentDidMount(){
console.log('Count---componentDidMount')
}
// 组件将要卸载时的钩子
componentWillUnmount(){
console.log('Count---componentWillUnmount')
}
// 控制组件更新的阀门: 是否更新组件钩子
shouldComponentUpdate(){
console.log('Count---shouldComponentUpdate')
return true
}
// 组件将要更新的钩子
componentWillUpdate(){
console.log('Count---componentWillUpdate')
}
// 组件更新完的钩子
componentDidUpdate(){
console.log('Count---componentDidUpdate')
}
render(){
console.log('Count---render')
const {count} = this.state
return (
<div>
<h2> 当前求和为{count}</h2>
<button onClick={this.add}>点我+1</button>
<button onClick={this.death}>卸载组件</button>
<button onClick={this.force}>强制更新</button>
</div>
)
}
}
// 父组件A
class A extends React.Component{
state = {
carName: 'benz'
}
changeCar = () => {
this.setState({
carName: 'bmw'
})
}
render(){
return (
<div>
<div>我是A组件</div>
<button onClick={this.changeCar}>换车</button>
<B carName={this.state.carName}/>
</div>
)
}
}
// 子组件B
class B extends React.Component{
// 组件将要接收新的props的钩子
componentWillReceiveProps(props){
console.log('B---componentWillReceiveProps', props)
}
shouldComponentUpdate(){
console.log('B---shouldComponentUpdate')
return true
}
// 组件将要更新的钩子
componentWillUpdate(){
console.log('B---componentWillUpdate')
}
// 组件更新完的钩子
componentDidUpdate(){
console.log('B---componentDidUpdate')
}
render(){
return (
<div>
我是B组件, 接收的车是:{this.props.carName}
</div>
)
}
}
// ReactDOM.render(<Count />, document.getElementById('test'))
ReactDOM.render(<A />, document.getElementById('test'))
4.3 react生命周期(新)(17.0版本之后)
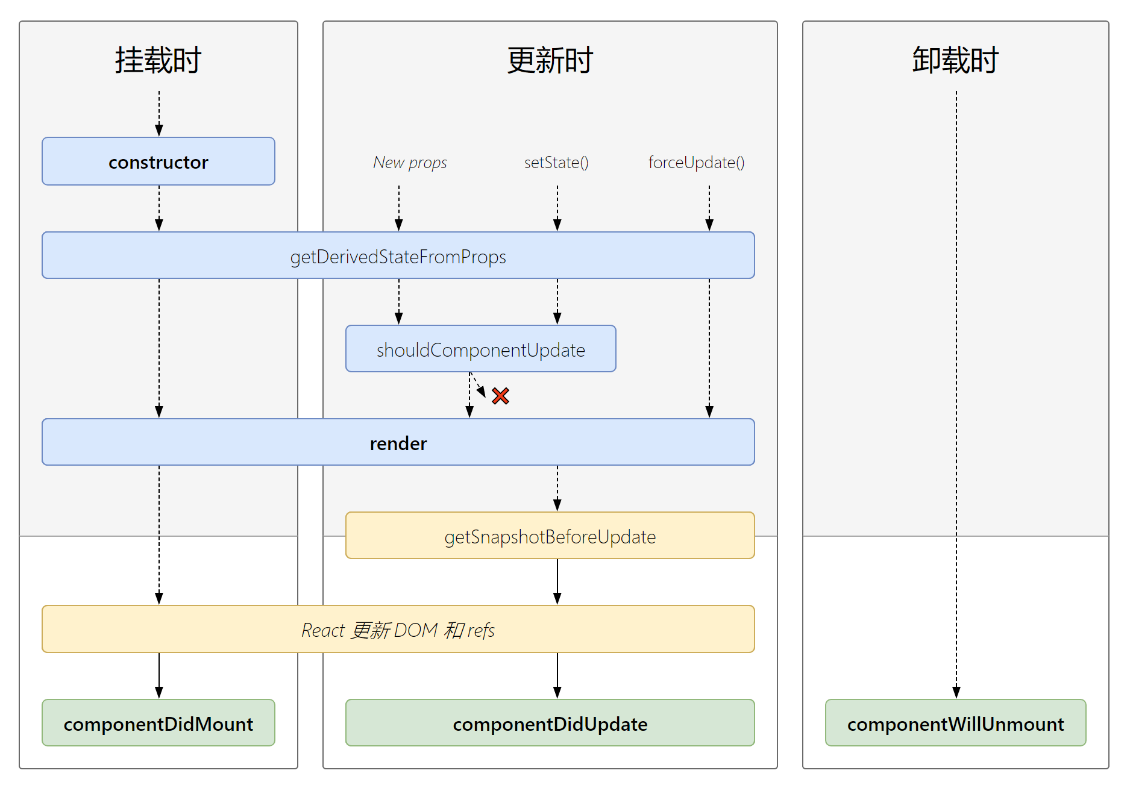
/*
1. 初始化阶段: 由ReactDOM.render()触发---初次渲染
1. constructor()
2. getDerivedStateFromProps
3. render()
4. componentDidMount()
2. 更新阶段: 由组件内部this.setSate()或父组件重新render触发
1. getDerivedStateFromProps
2. shouldComponentUpdate()
3. render()
4. getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
5. componentDidUpdate()
3. 卸载组件: 由ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode()触发
1. componentWillUnmount()
*/
class Count extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
console.log('Count---constructor')
super(props);
this.state = {
count: 0
}
}
// state = {
// count: 0
// }
add = () => {
const {count} = this.state
this.setState({
count: count+1
})
}
death = () => {
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(document.getElementById('test'))
}
force = () => {
this.forceUpdate() // 强制更新钩子
}
// 若state的值在任何时候都取决于props,可以使用该方法
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props ,state){
console.log('Count---getDerivedStateFromProps', props, state)
return null // 返回 state对象或者null
}
// 在更新之前获取快照
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(){
console.log('Count---getSnapshotBeforeUpdate')
return 'abc'
}
// 组件挂载完成的钩子
componentDidMount(){
console.log('Count---componentDidMount')
}
// 组件将要卸载时的钩子
componentWillUnmount(){
console.log('Count---componentWillUnmount')
}
// 控制组件更新的阀门: 是否更新组件钩子
shouldComponentUpdate(){
console.log('Count---shouldComponentUpdate')
return true
}
// 组件更新完的钩子
componentDidUpdate(preProps, preState, snapshotValue){
console.log('Count---componentDidUpdate', preProps, preState, snapshotValue)
}
render(){
console.log('Count---render')
const {count} = this.state
return (
<div>
<h2> 当前求和为{count}</h2>
<button onClick={this.add}>点我+1</button>
<button onClick={this.death}>卸载组件</button>
<button onClick={this.force}>强制更新</button>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Count count={199}/>, document.getElementById('test'))
4.4 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate使用场景
拖动滚动条让滚动条停留在当前数据位置
class NewList extends React.Component {
state = {
newsArr: []
}
componentDidMount() {
setInterval(() => {
// 获取原状态
const {newsArr} = this.state
// 模拟一条新闻
const news = '新闻' + (newsArr.length + 1)
// 更新状态
this.setState({
newsArr: [news, ...newsArr]
})
}, 1000)
}
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate() {
return this.refs.list.scrollHeight
}
componentDidUpdate(preProps, preState, height) {
console.log(preProps, preState, height)
console.log(this.refs.list.scrollTop) // 当前距离滚动条顶端的距离
this.refs.list.scrollTop += (this.refs.list.scrollHeight - height)
// this.refs.list.scrollTop += 30
}
render() {
console.log('NewList---render')
const {newsArr} = this.state
return (
<div className="list" ref='list'>
{
newsArr.map((n, index) => {
return <div key={index} className="news">{n}</div>
})
}
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<NewList/>, document.getElementById('test'))


