前言
此篇博客讲解Modifier修饰符的使用,Modifier修饰符的作用是快速的修改组件的显示大小、边距、边框、背景颜色、剪裁、点击、旋转、偏移、滚动、焦点等等,Modifier在Compose的全部组件上都有存在,需要熟练的掌握。另外Modifier是可以被扩展函数扩展的,所以此篇博客只举例通用的Modifier,不举例只在某些组件下才能使用的Modifier修饰符(例如Box(align属性)与constraintlayout(constrainAs方法))。
设置背景
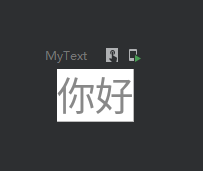
设置背景颜色
代码:
@Preview @Composable fun MyText() { Text( text = "你好", color = Color.Gray, modifier = Modifier.background(Color.White) ) }
效果图:
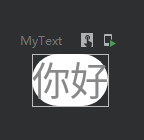
设置圆角背景
@Preview @Composable fun MyText() { Text( text = "你好", color = Color.Gray, modifier = Modifier.background(Color.White, shape = RoundedCornerShape(10.dp)) ) }
效果图:
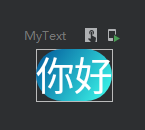
渐变色背景
代码
@Preview @Composable fun MyText() { val colors = listOf(Color(0xFF005599),Color(0xFF3FFFED)) Text( text = "你好", color = Color.White, modifier = Modifier.background(brush = Brush.linearGradient(colors),//设置线性渐变效果 shape = RoundedCornerShape(10.dp), alpha = 1f)//设置透明度 ) }
效果图
设置宽高
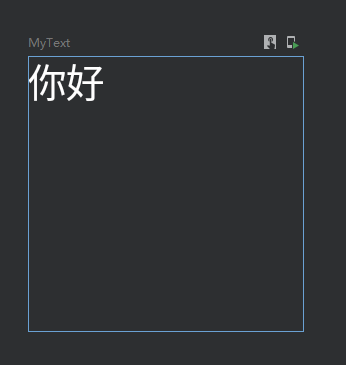
设置指定宽高
代码
@Preview @Composable fun MyText() { Text( text = "你好", color = Color.White, modifier = Modifier .width(100.dp) .height(100.dp) ) }
效果:
填满宽高
代码
@Preview @Composable fun MyText() { Column( modifier = Modifier .width(100.dp) .height(100.dp) .background(Color.Black) ) { Text( text = "你好", color = Color.Black, modifier = Modifier .background(Color.White) .fillMaxSize()//填满宽高 ) } }
效果图:
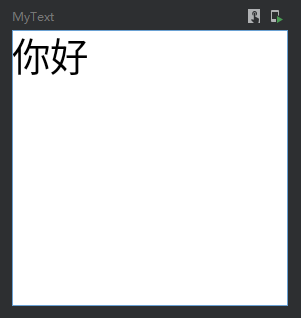
自适应子组件高宽
IntrinsicSize.Min 这个是关键
@Preview @Composable fun MyText() { Box( modifier = Modifier .width(IntrinsicSize.Min) .height(IntrinsicSize.Min) .background(Color.Gray) ) { Text( text = "你好世界", modifier = Modifier.width(60.dp) ) } }
效果图:
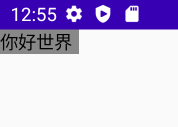
也可以使用wrapContentSize来实现此功能,wrapContentSize会自适应内容大小
Image(painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_test_0), contentDescription = null, modifier = Modifier.wrapContentSize())按比例填充宽高
代码:
@Preview @Composable fun MyText() { Column( modifier = Modifier .width(100.dp) .height(100.dp) .background(Color.Black) ) { Text( text = "你好", color = Color.Black, modifier = Modifier .background(Color.White) .fillMaxSize(0.5f)//以50%比例填满宽高 ) } }
效果:
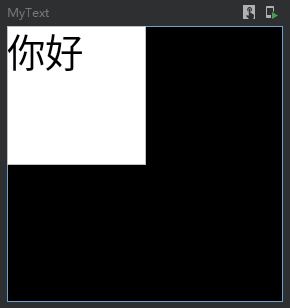
填满宽度或者高度
代码
@Preview @Composable fun MyText() { Column( modifier = Modifier .width(100.dp) .height(100.dp) .background(Color.Black) ) { Text( text = "你好", color = Color.Black, modifier = Modifier .background(Color.Red) .fillMaxWidth() //填满宽度 ) Text( text = "世界", color = Color.Black, modifier = Modifier .background(Color.Yellow) .fillMaxHeight() //填满高度 ) } }
效果:
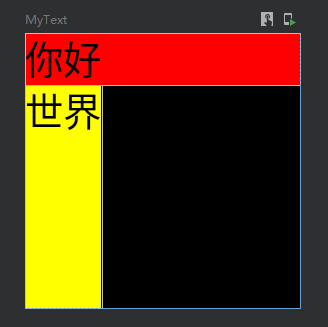
按比例填充宽度与高度
代码
@Preview @Composable fun MyText() { Column( modifier = Modifier .width(100.dp) .height(100.dp) .background(Color.Black) ) { Text( text = "你好", color = Color.Black, modifier = Modifier .background(Color.Red) .fillMaxWidth(0.5f) //填满宽度 ) Text( text = "世界", color = Color.Black, modifier = Modifier .background(Color.Yellow) .fillMaxHeight(0.5f) //填满高度 ) } }
效果图:
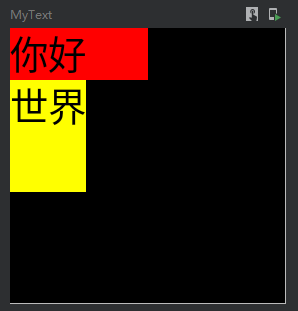
默认最小宽高
@Preview @Composable fun MyText() { Text( text = "你好", color = Color.Black, modifier = Modifier .background(Color.Red) .defaultMinSize(minWidth = 50.dp, minHeight = 50.dp) ) }
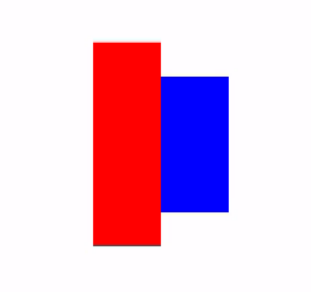
无视父类容器大小强制设置高度与宽度
requiredHeight与requiredWidth
代码:
Box(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()){
//父容器只设置100高度
Row(modifier = Modifier.size(width = 100.dp, height = 100.dp).align(Alignment.Center)) {
//这边使用requiredHeight并且设置150dp,让下面的子元素突破父容器高度
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.requiredHeight(150.dp).width(50.dp).background(color = Color.Red))
//这边同样设置150高度作为对比,实际上这个子元素高度是无法突破父容器的限制
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.size(width = 50.dp, height = 150.dp).background(color = Color.Blue))
}
}效果图:
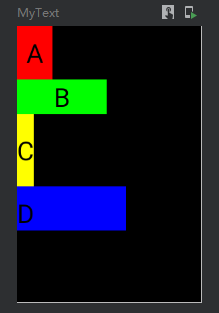
设置边距
代码
@Preview @Composable fun MyText() { Column( modifier = Modifier .width(100.dp) .height(150.dp) .background(Color.Black) ) { Text( text = "A", color = Color.Black, modifier = Modifier .background(Color.Red) .padding(5.dp) //设置全部边距 ) Text( text = "B", color = Color.Black, modifier = Modifier .background(Color.Green) .padding(horizontal = 20.dp) //设置横向边距 ) Text( text = "C", color = Color.Black, modifier = Modifier .background(Color.Yellow) .padding(vertical = 10.dp) //设置竖向边距 ) Text( text = "D", color = Color.Black, modifier = Modifier .background(Color.Blue) .padding(0.dp,5.dp,50.dp,0.dp) //设置指定方向边距 ) } }
效果图:
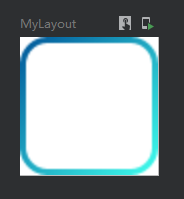
设置边框
一共有三种重载方法
fun Modifier.border(border: BorderStroke, shape: Shape = RectangleShape) = border(width = border.width, brush = border.brush, shape = shape) fun Modifier.border(width: Dp, color: Color, shape: Shape = RectangleShape) = border(width, SolidColor(color), shape) fun Modifier.border(width: Dp, brush: Brush, shape: Shape): Modifier
第一种实现渐变色边框
使用代码:
@Preview @Composable fun MyLayout() { val colors = listOf(Color(0xFF005599), Color(0xFF3FFFED)) Column( modifier = Modifier .width(25.dp) .height(25.dp) .background(Color.White) .border( //设置渐变边框 border = BorderStroke(1.dp, Brush.linearGradient(colors)), //设置边框粗细与边框渐变色 shape = RoundedCornerShape(5.dp) //圆角形状 ) ){ } }
效果图:
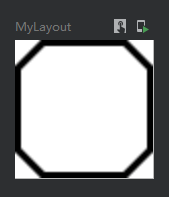
第二种实现单色边框
代码:
@Preview @Composable fun MyLayout() { Column( modifier = Modifier .width(25.dp) .height(25.dp) .background(Color.White) .border( width = 1.dp, //设置边框粗细 color = Color(0xFF000000), //边框颜色 shape = CutCornerShape (5.dp,5.dp,5.dp,5.dp) //切角矩形形状 ) ){ } }
效果图:
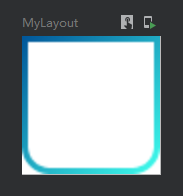
第三种实现渐变色边框
其实与第一种差不多,只是没有了BorderStroke包装
代码:
@Preview @Composable fun MyLayout() { val colors = listOf(Color(0xFF005599), Color(0xFF3FFFED)) Column( modifier = Modifier .width(25.dp) .height(25.dp) .background(Color.White) .border( width = 1.dp, brush = Brush.linearGradient(colors), shape = RoundedCornerShape(0.dp,0.dp,5.dp,5.dp) ) ){ } }
效果图:
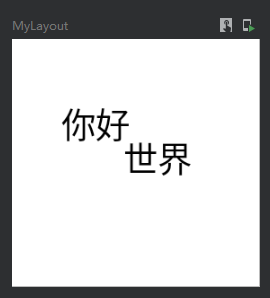
偏移位置
offset这个偏移是偏移自身这个组件
代码:
@Preview @Composable fun MyLayout() { Column( modifier = Modifier .width(100.dp) .height(100.dp) .background(Color.White) ){ Text(text = "你好", color = Color.Black, //相对偏移 这个修改会根据布局方向自动调整水平偏移量(应该是为了阿拉伯语设计的): //当布局方向为从左到右时,正x偏移量会将内容向右移动,当布局方向为从右到左时,正x偏移量会将内容向左移动。 modifier = Modifier.offset(x = 20.dp,y = 25.dp)) Text(text = "世界", color = Color.Black, //绝对偏移 这个修改将不考虑布局方向:正的x偏移总是将内容向右移动 modifier = Modifier.absoluteOffset(x = 45.dp,y = 20.dp)) } }
效果图:
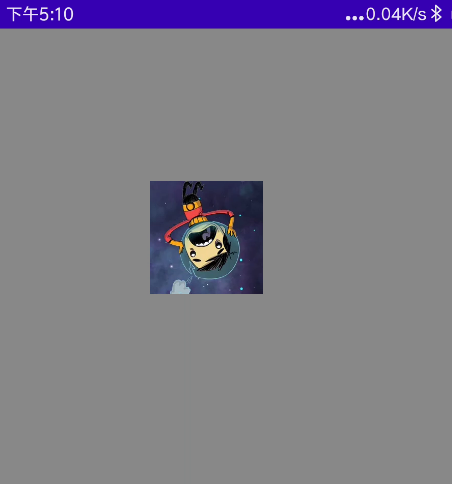
缩放
代码:
@Preview @Composable fun MyScale() { val scale = remember { mutableStateOf(1.5f) } Column( modifier = Modifier .fillMaxSize() .background(Color.Gray) ) { //默认 Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_logo), contentDescription = null, ) //比例缩放 Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_logo), contentDescription = null, modifier = Modifier .padding(top = 30.dp, start = 30.dp) .scale(scale.value) //放大1.5倍 ) //指定宽高缩放 Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_logo), contentDescription = null, modifier = Modifier .padding(top = 70.dp, start = 90.dp) .scale(3f,2f) //宽高缩放 ) } }
效果图:

旋转
代码:
@Preview @Composable fun MyRotate() { val rotate = remember { mutableStateOf(180f) } Column( modifier = Modifier .width(300.dp) .height(300.dp) .background(Color.Gray) ) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_logo), contentDescription = null, modifier = Modifier .padding(100.dp) .rotate(rotate.value) //设置旋转 ) } }
效果图:
旋转与偏移位置的组合
请注意,Modifier一直强调组合的位置不同会出现不同的效果。如果你想实现旋转与拖动功能,那么旋转一定要在前面,否则会出现拖动的时候,实际移动的X轴与Y轴出现相反的问题。
@Composable
fun rotationAndOffset(){
val rotation = remember { mutableStateOf(0f) }
val offsetX = remember { mutableStateOf(0f) }
val offsetY = remember { mutableStateOf(0f) }
AsyncImage(
model = if (mIsUrl.value) mUrl.value else mFile.value,
contentDescription = null,
modifier = Modifier
.rotate(rotation.value) //rotate一定要在前面
.offset { IntOffset(offsetX.value.roundToInt(), offsetY.value.roundToInt()) }
)
}输入操作(点击、双击、长按、拖动、滑动、触控、滚动)
单指操作_单击、按下、双击、长按、触控
@OptIn(ExperimentalFoundationApi::class) @Preview @Composable fun MyClick() { val isEnableClick = remember { mutableStateOf(true) } Column( modifier = Modifier .width(100.dp) .height(150.dp) .background(Color.Black) ) { //方式一 单击监听 Text( text = "A", color = Color.Black, modifier = Modifier .background(Color.White) .clickable(isEnableClick.value) { //设置点击 Log.e("zh", "A单击") } ) //方式二 组合性点击 Text( text = "B", color = Color.Black, modifier = Modifier .background(Color.White) .combinedClickable( //注意!此Api是实验性的 onClick = { Log.e("zh", "B单击") }, onDoubleClick = { Log.e("zh", "B双击") }, onLongClick = { Log.e("zh", "B长按") } ) ) //方式三 输入监听 Text( text = "C", color = Color.Black, modifier = Modifier .background(Color.White) .pointerInput(Unit) { detectTapGestures( onPress = { Log.e("zh", "C按下") }, onDoubleTap = { Log.e("zh", "C双击") }, onLongPress = { Log.e("zh", "C长按") }, onTap = { Log.e("zh", "C触控") } ) } ) } }
多指操作_缩放、旋转、拖动
双指缩放
@Preview @Composable fun MyScale() { val scale = remember { mutableStateOf(1f) } Column( modifier = Modifier .width(300.dp) .height(300.dp) .background(Color.Gray) ) { //多点触控 Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_logo), contentDescription = null, modifier = Modifier .padding(100.dp) .scale(scale.value) .transformable(state = TransformableState { zoomChange, panChange, rotationChange -> scale.value *= zoomChange Log.e("zh", "缩放 ${zoomChange}" ) Log.e("zh", "坐标 ${panChange}") Log.e("zh", "旋转 ${rotationChange}" ) }) ) } }
效果图:
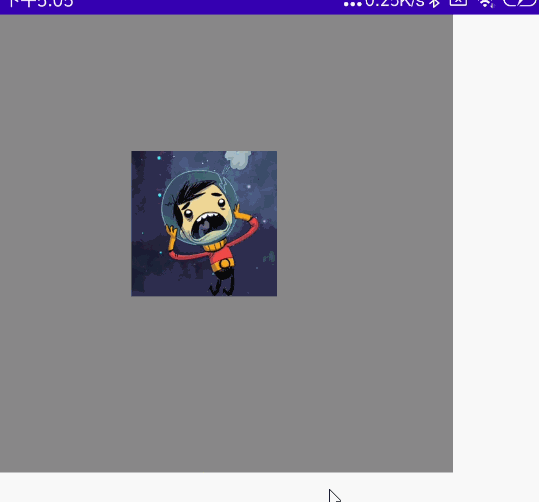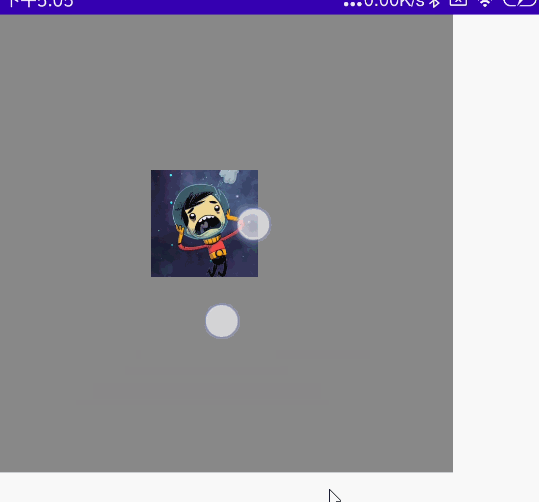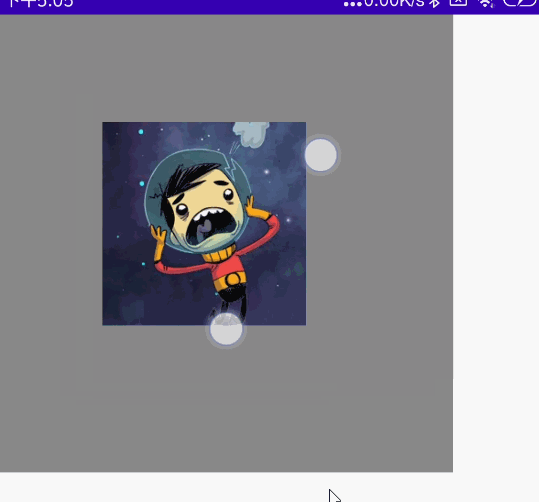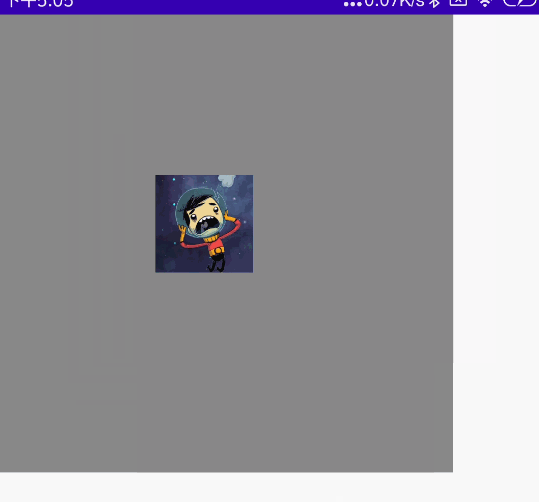
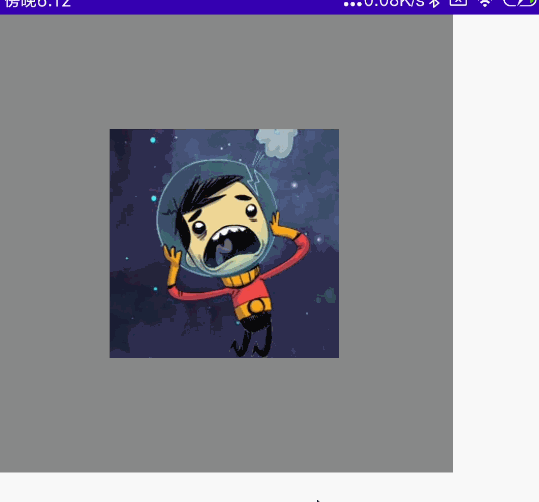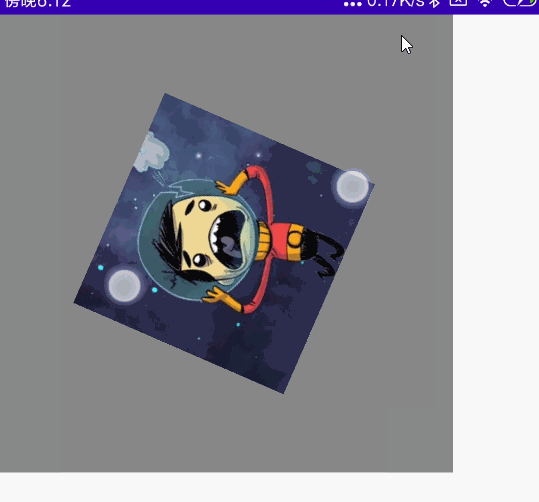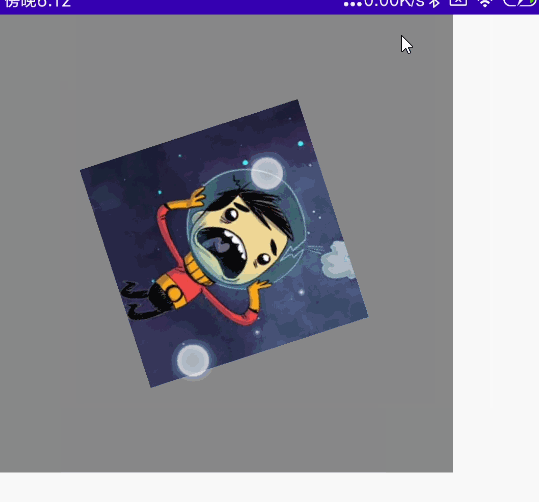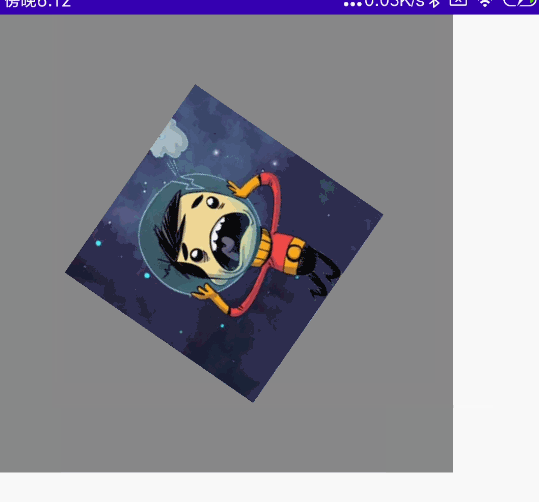
双指旋转
代码:
@Preview @Composable fun MyRotate() { val rotate = remember { mutableStateOf(0f) } Box( modifier = Modifier .width(300.dp) .height(300.dp) .background(Color.Gray), contentAlignment = Alignment.Center ) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_logo), contentDescription = null, modifier = Modifier .fillMaxSize(0.5f) .rotate(rotate.value) //设置旋转 .transformable(state = TransformableState { zoomChange, panChange, rotationChange -> Log.e("zh", "缩放 ${zoomChange}" ) Log.e("zh", "坐标 ${panChange}") rotate.value += rotationChange //旋转变化 Log.e("zh", "旋转 ${rotationChange}" ) }) ) } }
效果图:
双指拖动
@Preview @Composable fun MyOffset() { val offsetX = remember { mutableStateOf(0f) } val offsetY = remember { mutableStateOf(0f) } Box( modifier = Modifier .width(300.dp) .height(300.dp) .background(Color.Gray), contentAlignment = Alignment.Center ) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_logo), contentDescription = null, modifier = Modifier .fillMaxSize(0.5f) .offset { IntOffset(offsetX.value.roundToInt(), offsetY.value.roundToInt()) } //设置偏移 .transformable(state = TransformableState { zoomChange, panChange, rotationChange -> Log.e("zh", "缩放 ${zoomChange}" ) Log.e("zh", "坐标 ${panChange}") offsetX.value += panChange.x offsetY.value += panChange.y Log.e("zh", "旋转 ${rotationChange}" ) }) ) } }
效果图:
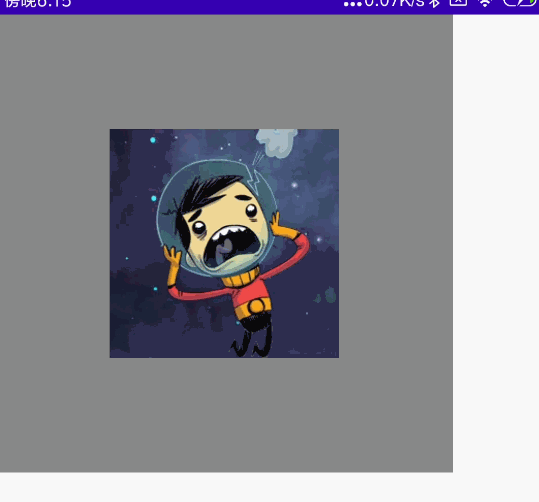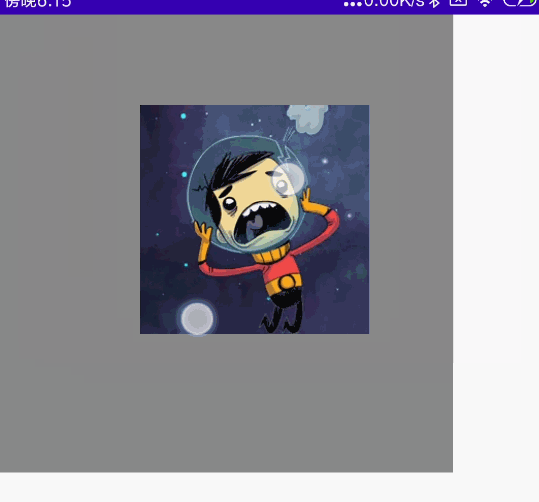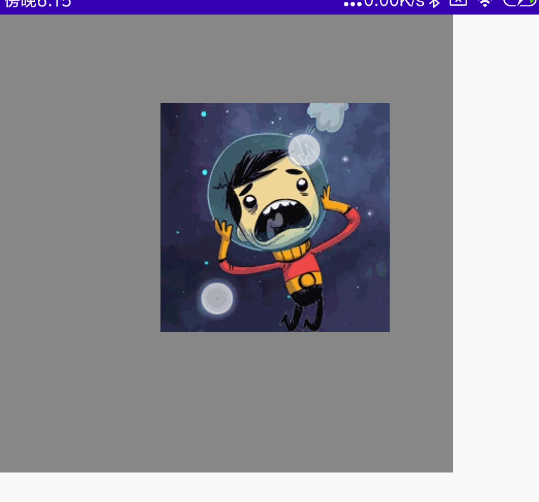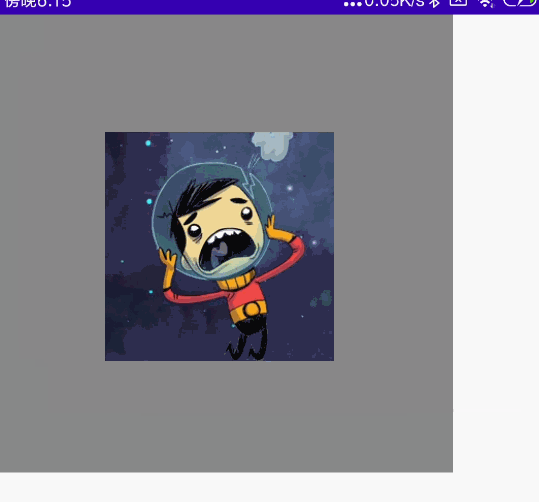
双指多操作组合
同时拖动、旋转、缩放
代码
@Preview @Composable fun MyCombination() { val scale = remember { mutableStateOf(1f) } val offsetX = remember { mutableStateOf(0f) } val offsetY = remember { mutableStateOf(0f) } val rotation = remember { mutableStateOf(0f) } Box( modifier = Modifier .width(300.dp) .height(300.dp) .background(Color.Gray), contentAlignment = Alignment.Center ) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_logo), contentDescription = null, modifier = Modifier .fillMaxSize(0.5f) .graphicsLayer{ scaleX = scale.value scaleY = scale.value translationX = offsetX.value translationY = offsetY.value rotationZ = rotation.value } .transformable(state = TransformableState { zoomChange, panChange, rotationChange -> scale.value *= zoomChange offsetX.value += panChange.x offsetY.value += panChange.y rotation.value += rotationChange }) ) } }
效果图:
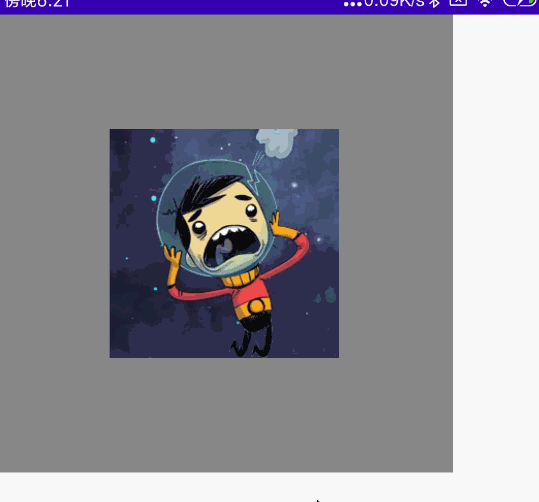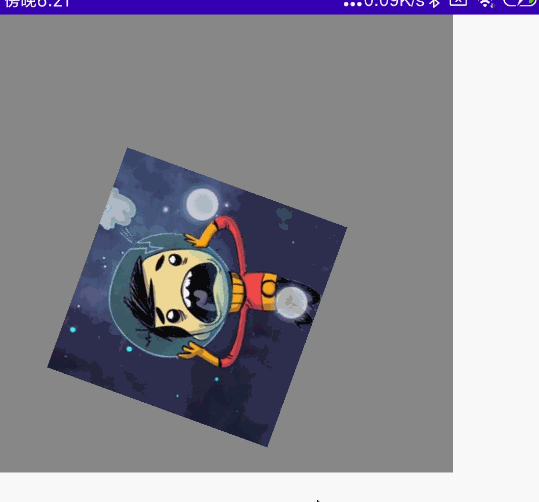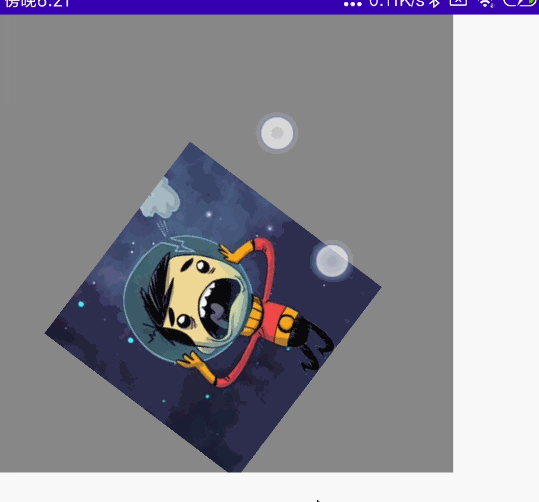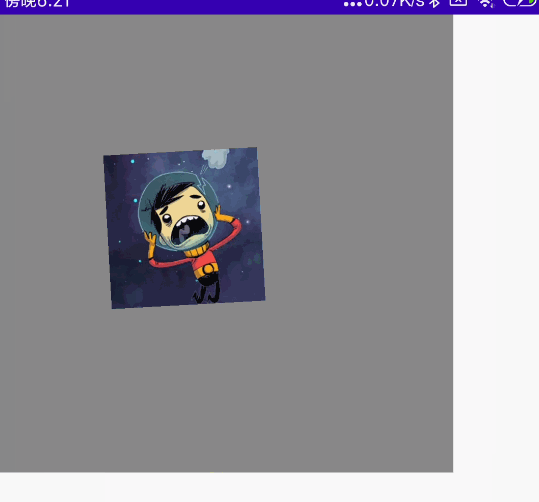
单指拖动
单方向拖动
如果你发现拖动会超出父类布局,但是你希望不超出父类布局,请参考博客下面的 “让子组件不超出当前父组件范围” 内容
@Preview @Composable fun MyImage() { var offset = remember { mutableStateOf(0f) } Column( modifier = Modifier .width(200.dp) .height(200.dp) .background(Color.Gray) ) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_logo), contentDescription = null, contentScale = ContentScale.None, modifier = Modifier .draggable(state = rememberDraggableState() { //设置拖动 offset.value += it }, orientation = Orientation.Vertical) //设置方向 还能设置横向Orientation.Horizontal .offset { IntOffset(0, offset.value.roundToInt()) } ) } }
效果图:

双方向拖动
@Preview @Composable fun MyImage() { val offsetX = remember { mutableStateOf(0f) } val offsetY = remember { mutableStateOf(0f) } Column( modifier = Modifier .width(200.dp) .height(200.dp) .background(color = Color.Gray) ) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_logo), contentDescription = null, modifier = Modifier .offset { IntOffset(offsetX.value.roundToInt(), offsetY.value.roundToInt()) } .pointerInput(Unit) { //检测拖动手势 detectDragGestures { change, dragAmount -> Log.e("zh", "MyImage:检测拖动 当前指针输入数据 = ${change} ") Log.e("zh", "MyImage:检测拖动 每次偏移量 = ${dragAmount} ") offsetX.value += dragAmount.x offsetY.value += dragAmount.y } } ) } }
效果图:

左右滑动
代码
@OptIn(ExperimentalMaterialApi::class)
@Composable
fun APage() {
//滑块的宽度
val slidingBlockWidth = 50.dp
//滑动的最大宽度
val bgWidthDp = 300.dp
//这里是可以滑动的最大距离
val slidingMaxWidthPx = LocalDensity.current.run { (bgWidthDp - slidingBlockWidth).toPx() }
//这里创建一个map,map的第一个值是关闭距离位置与对应key,第二个值是开启距离位置与对应key
val anchors = mapOf(
0f to "close",
slidingMaxWidthPx to "open"
)
var swipeableState = rememberSwipeableState(initialValue = "close")
Box(modifier = Modifier
.width(bgWidthDp)
.height(slidingBlockWidth)
.background(Color.Gray)) {
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.offset { //请注意,offset位置一定要在swipeable的上面,否则会出现无法滑动的问题
//整体移动
IntOffset(swipeableState.offset.value.toInt(), 0)
}
.swipeable(
state = swipeableState,
anchors = anchors,
orientation = Orientation.Horizontal, //移动的方向
thresholds = { from, to ->
//从关闭到开启状态时,滑块移动超过30%距离自动吸附到开启状态
if (from == "close") {
FractionalThreshold(0.3f)
} else {
//从开启状态到关闭状态时,滑块移动超过50%才会自动吸附到关闭状态
FractionalThreshold(0.5f)
}
}
)
.width(slidingBlockWidth) //这个一定要在swipeable下面
.height(slidingBlockWidth) //这个一定要在swipeable下面
.background(Color.Green) //这个一定要在swipeable下面
)
}
}滑动效果图

设置可滚动
横竖两个方向的滚动
代码:
@Preview @Composable fun MyScroll() { Column(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) { //Row横向排列滚动 Row( modifier = Modifier .fillMaxWidth() .horizontalScroll(rememberScrollState()) //设置横向滚动 ) { for (i in 1..10) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_logo), contentDescription = null, ) } } //Column竖向排列滚动 Column( modifier = Modifier .padding(10.dp) .height(250.dp) .verticalScroll(rememberScrollState()) //设置竖向滚动 ) { for (i in 1..10) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_logo), contentDescription = null, ) } } }
效果图:

监听滚动偏移量、滚动位置与滚动位置跳转操作
代码
@Preview @Composable fun MyScroll() { val state = rememberScrollState() val position = remember { derivedStateOf { state.value } } val scope = rememberCoroutineScope() //这个是在Composable调用协程的一种方式 Column() { Text( text = "豫章故郡,洪都新府。星分翼轸,地接衡庐。" + "襟三江而带五湖,控蛮荆而引瓯越。" + "物华天宝,龙光射牛斗之墟;" + "人杰地灵,徐孺下陈蕃之榻。" + "雄州雾列,俊采星驰。" + "台隍枕夷夏之交,宾主尽东南之美。" + "都督阎公之雅望,棨戟遥临;" + "宇文新州之懿范,襜帷暂驻。" + "十旬休假,胜友如云;" + "千里逢迎,高朋满座。" + "腾蛟起凤,孟学士之词宗;" + "紫电青霜,王将军之武库。" + "家君作宰,路出名区;" + "童子何知,躬逢胜饯。", modifier = Modifier .padding(10.dp) .width(100.dp) .height(100.dp) //监听滚动位置 .scrollable(state = rememberScrollableState(consumeScrollDelta = { Log.e("zh", "当前滚动偏移量:${it}") it }), orientation = Orientation.Vertical) .verticalScroll(state) ) Text( color = Color.Red, text = "当前滚动位置${position.value}", ) Button(onClick = { scope.launch { state.scrollTo(0) } }) { Text(text = "回到起点") } } }
效果图:

指针输入
指针输入监听,与上面各色方法类似
代码:
@Preview @Composable fun MyPointerInput() { Box( modifier = Modifier .width(300.dp) .height(300.dp) .background(Color.Gray) ) { Text( text = "你好", color = Color.Black, modifier = Modifier .align(Alignment.Center) .fillMaxSize(0.5f) .background(color = Color.Green) .pointerInput(Unit) { /** * 下面的只能存在一个手势Gestures方法,多了后续的手势方法会不执行,这边是方便观看全部贴出来 */ detectDragGestures { change, dragAmount -> Log.e("zh", "检测拖动手势: change = $change \n dragAmount = $dragAmount") } detectDragGesturesAfterLongPress { change, dragAmount -> Log.e("zh", "检测长按后的拖拽手势: change = $change \n dragAmount = $dragAmount") } detectTapGestures { /** * 检测轻按、双击和长按手势,检测到时分别调用onTap、onDoubleTap和onLongPress。当检测到按压和pressgestuscope时调用onPress。 * tryAwaitRelease PressGestureScope。awaitRelease可以用来检测指针何时被释放或手势何时被取消。 * 第一个向下的指针和最后一个向上的指针被消耗, * 在长按的情况下,检测到长按后的所有更改都被消耗。 */ Log.e("zh", "检测触控: Offset = $it \n") } detectTapGestures( onTap = { Log.e("zh", "单击: Offset = $it \n") }, onDoubleTap = { Log.e("zh", "双击: Offset = $it \n") }, onLongPress = { Log.e("zh", "长按: Offset = $it \n") }, onPress = { Log.e("zh", "按下: Offset = $it \n") }) detectTransformGestures { centroid, pan, zoom, rotation -> Log.e("zh", "旋转、平移和缩放的手势检测器: centroid = $centroid \n pan = $pan \n zoom = $zoom rotation = $rotation") } detectHorizontalDragGestures { change, dragAmount -> Log.e("zh", "检测水平拖动手势: change = $change \n dragAmount = $dragAmount") } detectVerticalDragGestures { change, dragAmount -> Log.e("zh", "检测垂直拖动手势: change = $change \n dragAmount = $dragAmount") } } ) } }
点击效果
效果图
代码
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContent {
Row(
verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically,
modifier = Modifier
.padding(top = 100.dp)
.fillMaxSize()
) {
//默认点击效果
Image(
painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_test_0),
contentDescription = null,
modifier = Modifier
.clickable {
Toast
.makeText(this@DemoActivity, "点击0>默认点击效果", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show()
})
//涟漪点击效果,关键代码是rememberRipple
val interactionSource1 = remember {
MutableInteractionSource()
}
Image(
painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_test_1),
contentDescription = null,
modifier = Modifier
.clickable(onClick = {
Toast
.makeText(this@DemoActivity, "点击1>涟漪点击效果", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show()
}, indication = rememberRipple(), interactionSource = interactionSource1))
//通过修改背景颜色实现自定义点击效果
val interactionSource2 = remember {
MutableInteractionSource()
}
val bgColor = if (interactionSource2.collectIsPressedAsState().value) Color.Blue else Color.Transparent
Image(
painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_test_2),
contentDescription = null,
modifier = Modifier
.clickable(onClick = {
Toast
.makeText(
this@DemoActivity,
"点击2>通过修改背景颜色实现自定义点击效果",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT
)
.show()
}, indication = null, interactionSource = interactionSource2)
.background(bgColor))
//取消点击效果
val interactionSource3 = remember {
MutableInteractionSource()
}
Image(
painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_test_3),
contentDescription = null,
modifier = Modifier
.clickable(onClick = {
Toast
.makeText(this@DemoActivity, "点击3>取消点击效果", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show()
}, indication = null, interactionSource = interactionSource3))
}
}
}graphicsLayer
graphicsLayer可用于对内容应用效果,如缩放、旋转、不透明度、阴影和剪切。当你的层属性由androidx. composition .runtime. state或动画值支持时,最好使用这个版本,因为读取块中的状态只会导致层属性更新,而不会触发重新组合和重新布局。
代码:
@Preview
@Composable
fun MyGraphicsLayer() {
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.width(300.dp)
.height(300.dp)
.background(Color.Gray)
) {
Text(
text = "你好",
color = Color.Black,
modifier = Modifier
.align(Alignment.Center)
.fillMaxSize(0.5f)
.background(color = Color.Green)
.graphicsLayer{
//绘制区域的水平比例尺。默认值为“1”
scaleX = 1f
//绘制区域的垂直比例尺。默认值为“1”。
scaleY = 1f
//绘制区域的alpha。设置为“1”以外的值将导致绘制的内容是半透明的,设置为“0”将使其完全不可见。默认值为' 1 ',取值范围为' 0 ' ~ ' 1 '。
alpha = 1f
//该层相对于其左边界的水平像素偏移量。默认值为' 0 '。
translationX = 0f
//该层相对于其上边界的垂直像素偏移量。默认值为' 0 '
translationY = 0f
//以像素为单位设置阴影的仰角。默认值为“0”,且不能为负值
shadowElevation = 0f
//范围阴影颜色
ambientShadowColor = Color(0xFFFF0000)
//点阴影颜色
spotShadowColor = Color(0xFFFF0000)
//X轴旋转角度
rotationX = 0f
//Y轴旋转角度
rotationY= 0f
//Z轴旋转角度
rotationZ = 0f
//观察相机视角距离
cameraDistance = 0f
//旋转or缩放的中心点
transformOrigin = TransformOrigin.Center
transformOrigin = TransformOrigin(0.1f,0.1f)
//形状
shape = RectangleShape
//设置为' true '将内容剪辑到[shape]。默认值为' false '
clip = false
//渲染效果,比如下面设置的模糊效果
renderEffect = BlurEffect(20f, 0.5f, TileMode.Clamp)
}
)
}
}
裁剪
clip的裁剪
代码:
@Preview @Composable fun MyImage() { Column( modifier = Modifier .width(100.dp) .height(100.dp) .background(Color.White) //clip的剪裁是对当前组件的内部内容进行裁剪,这里使用了CircleShape圆形进行裁剪. //也可以使用RectangleShape 或者 RoundedCornerShape() 矩形进行裁剪 .clip(shape = CircleShape) ) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_logo), contentDescription = null, modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize() ) } }
效果图:
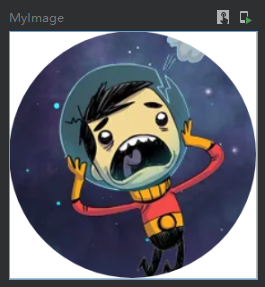
上面是使用常用形状裁剪,这里在举例一个自定义形状的裁剪方式,如下使用path绘制了一个三角形进行裁剪
代码:
/** * 裁剪三角形 */ @Preview @Composable fun MyImage() { val customShape = object : Shape { override fun createOutline(size: Size, layoutDirection: LayoutDirection, density: Density): Outline { val path = Path() path.moveTo(size.width/2, 0f) path.lineTo(0f,size.height) path.lineTo(size.width,size.height) path.close() val outline = Outline.Generic(path) return outline } } Column( modifier = Modifier .width(100.dp) .height(100.dp) .background(Color.White) .clip(shape = customShape) ) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_logo), contentDescription = null, modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize() ) } }
效果图:

让子组件不超出当前父组件范围
clipToBounds 按照指定的边界裁切内容。强制限制当前布局下的子组件不允许超出到外部。另外这个属性与clip属性无关联。
反面例子代码,下面的代码中注释了clipToBounds
@Preview @Composable fun MyImage() { var offset = remember { mutableStateOf(0f) } //必须在套一个布局设置最大范围的父类布局,以展示下面的Image在拖动的时候超出的效果 Column(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize().padding(200.dp)) { Column( modifier = Modifier .width(200.dp) .height(200.dp) .background(Color.Gray) //这里设置背景色为灰色,以观察布局的大小 // .clipToBounds() ) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_logo), contentDescription = null, contentScale = ContentScale.None, modifier = Modifier .draggable(state = rememberDraggableState() { offset.value += it }, orientation = Orientation.Horizontal) .offset { IntOffset(offset.value.roundToInt(), 0) } ) } } }
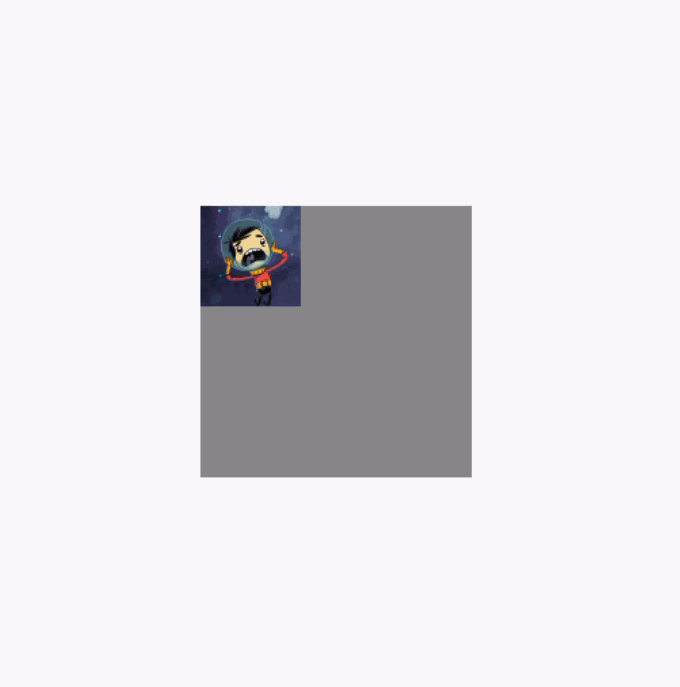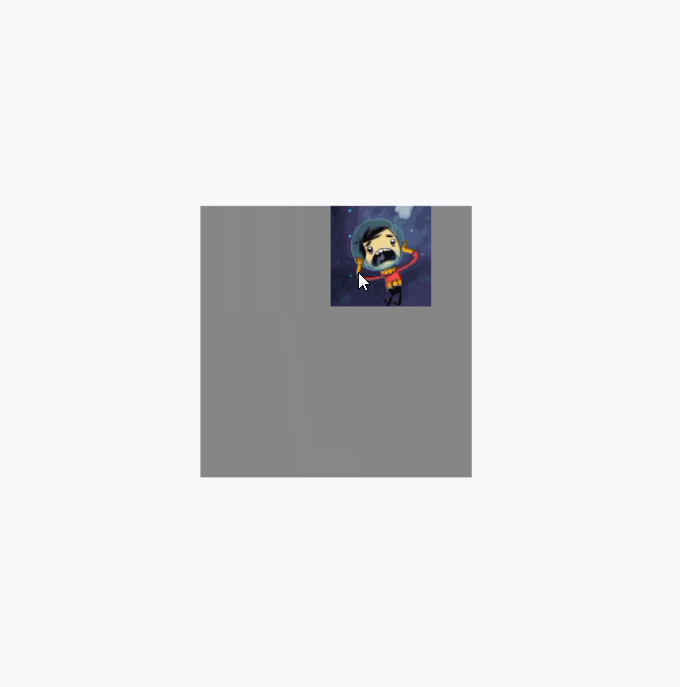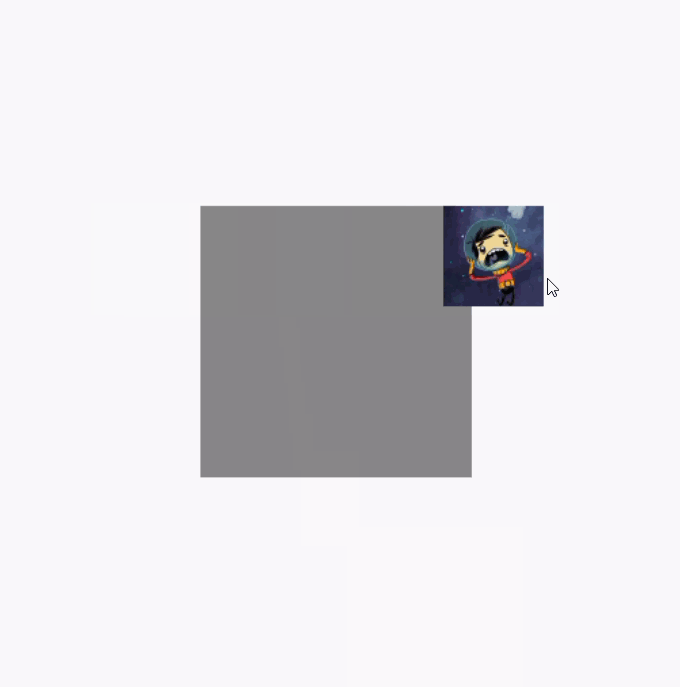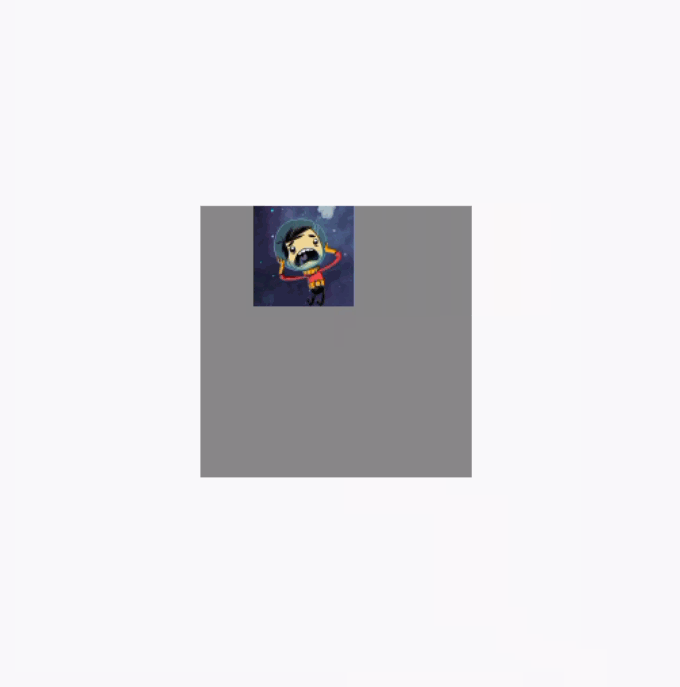
反面例子效果图,图片在拖动的时候可以超出布局范围:
调用clipToBounds 后的效果图(代码就不重复贴了,直接将clipToBounds 注释取消就行):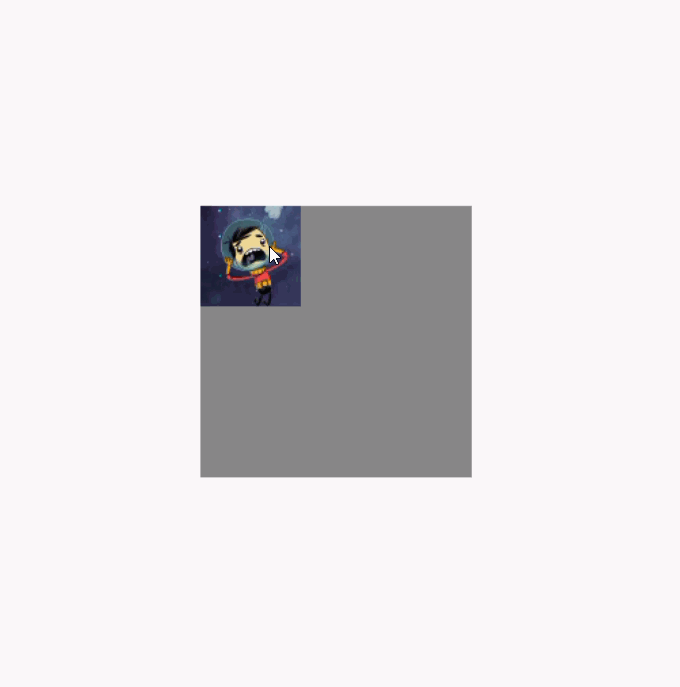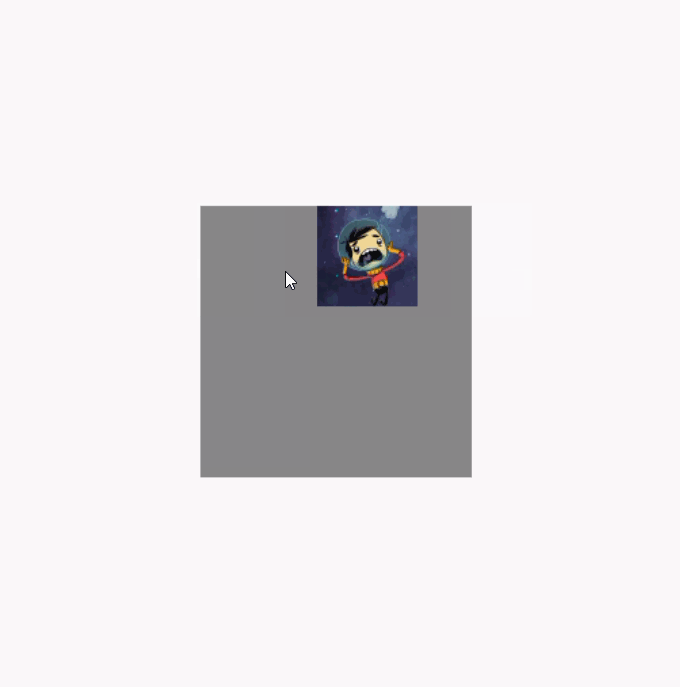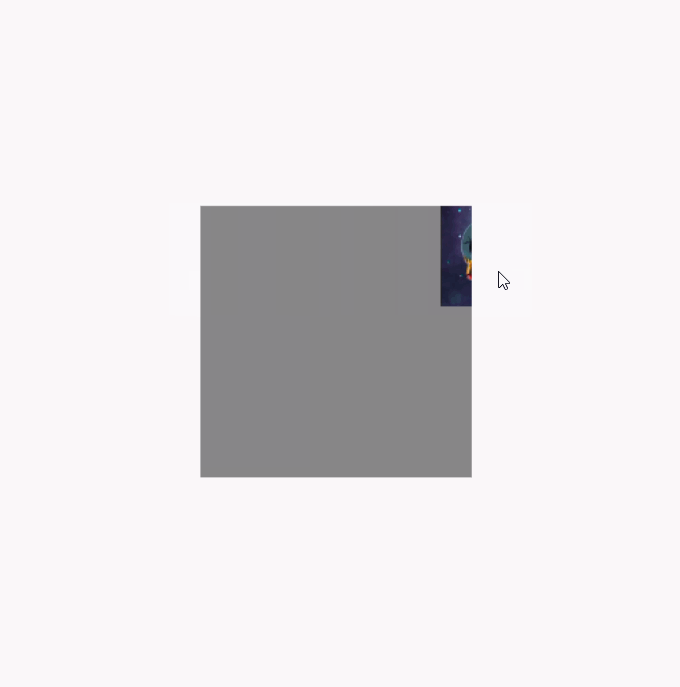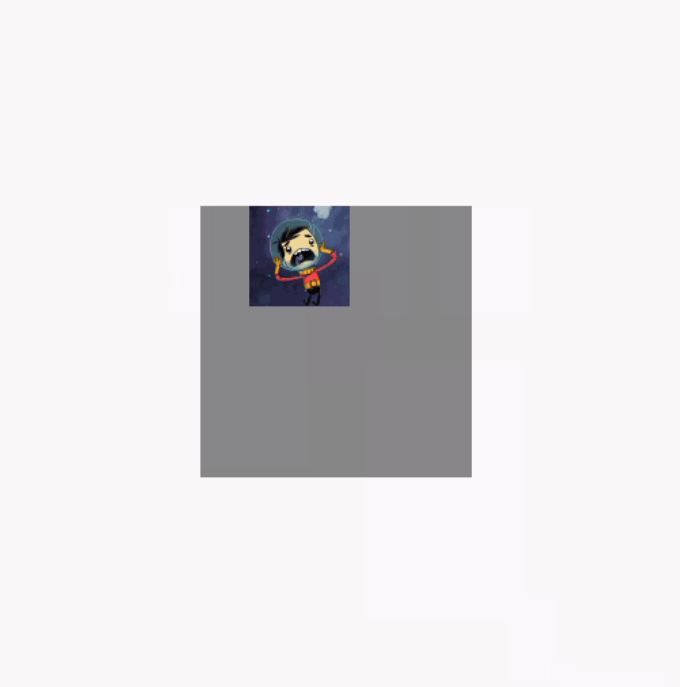
模糊
注意!blur这个api需要Android版本12 31 API的设备上才能生效
代码:
@Preview @Composable fun MyBlur() { Box( modifier = Modifier .width(300.dp) .height(300.dp) .background(Color.Gray) ) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_logo), contentDescription = null, modifier = Modifier .align(Alignment.Center) //注意blur这个api需要Android 12 31 API 才能生效 .blur(radius = 10.dp, edgeTreatment = BlurredEdgeTreatment.Rectangle) //设置模糊 ) } }
效果图:
BlurredEdgeTreatment.Rectangle 是矩形边缘清晰中间模糊

BlurredEdgeTreatment.Unbounded 无边界模糊的效果图:

透明度
代码
@Preview @Composable fun MyAlpha() { Box( modifier = Modifier .width(300.dp) .height(300.dp) .background(Color.Gray) ) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_logo), contentDescription = null, modifier = Modifier .align(Alignment.Center) .alpha(0.1f) //设置透明度 ) } }
效果图:

绘制阴影
注意!shadow这个api需要Android版本10的设备上才能生效
请注意!shadow的使用也是有顺序的,建议放到background前面
代码
@Preview @Composable fun MyShadow() { Box( modifier = Modifier .width(300.dp) .height(300.dp) .background(Color.White) ) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_logo), contentDescription = null, modifier = Modifier .align(Alignment.Center) .shadow( //设置阴影,调用此api需要设备Android版本为10 elevation = 50.dp, //隐藏长度 shape = RectangleShape, //阴影形状 ambientColor = Color.Red, //环境颜色 spotColor = Color.Red, //阴影颜色 clip = true //是否跟随裁剪形状改变阴影形状 ) ) } }
效果图:

绘制
drawBehind绘制,将增加的绘制内容显示到组件图层的最下层
代码:
@Preview @Composable fun MyDrawBehind() { Box( modifier = Modifier .width(300.dp) .height(300.dp) .background(Color.White) ) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_logo), contentDescription = null, modifier = Modifier .align(Alignment.Center) .drawBehind { //绘制到最下面的图层 val radius = size.width / 3 val centerOffset = Offset(size.width, 0f) drawCircle( color = Color.Red, radius = radius, center = centerOffset, style = Fill ) } ) } }
在下面的效果图里,可以看到红圈在图片的下层:

drawWithContent 人为控制绘制内容的顺序
@Preview @Composable fun MyDrawWithContent() { Box( modifier = Modifier .width(300.dp) .height(300.dp) .background(Color.White) ) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_logo), contentDescription = null, modifier = Modifier .align(Alignment.Center) .drawWithContent { /* drawContent()是理解drawWithContent的关键 drawContent这个是这个组件本身需要绘制的内容。 控制这个方法的位置你就可以控制绘制的顺序。 */ drawContent() val radius = size.width / 3 val centerOffset = Offset(size.width, 0f) drawCircle( color = Color.Red, radius = radius, center = centerOffset, style = Stroke(25f) ) } ) } }
因为代码中是先绘制了drawContent()然后在绘制圆环,所以下面的效果图圆环在图片的上层:

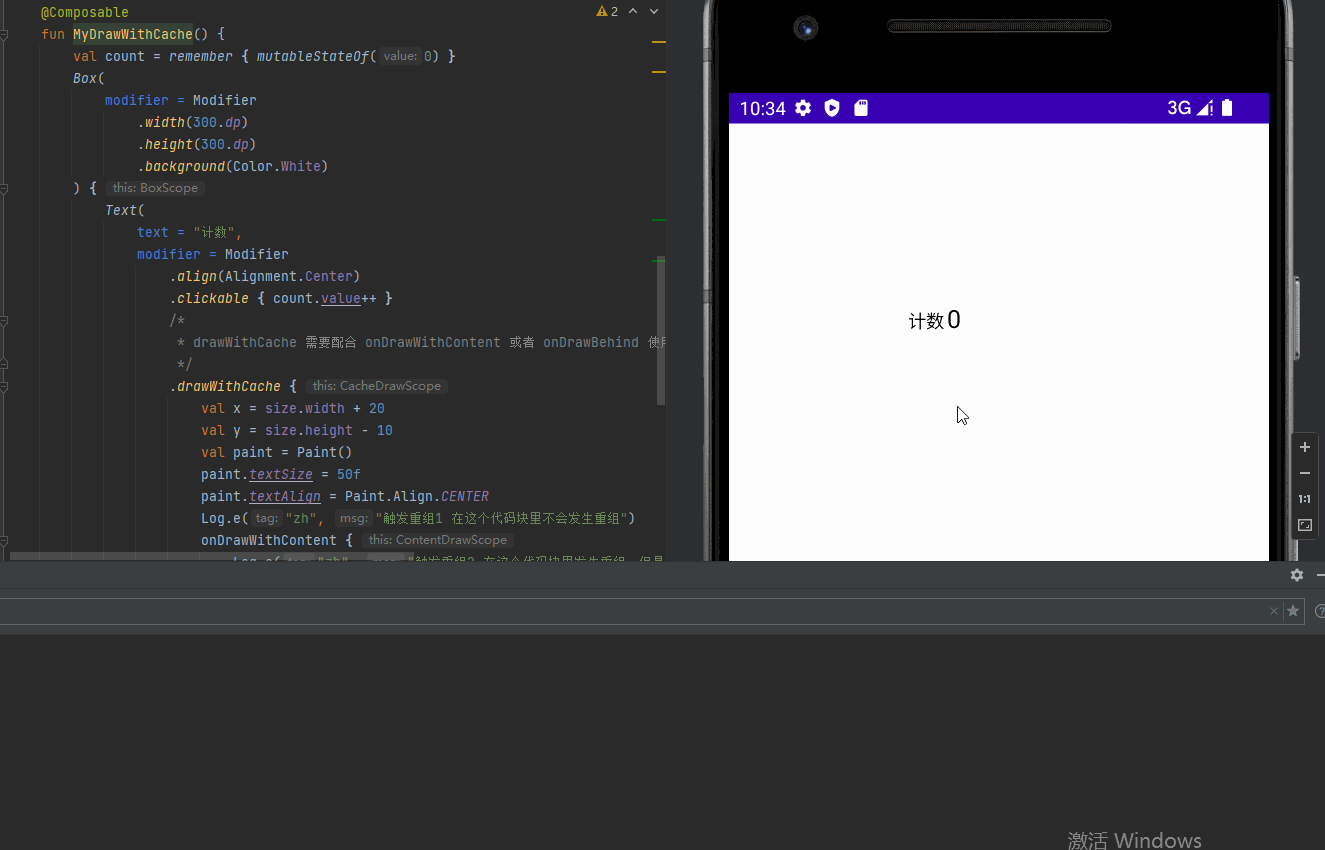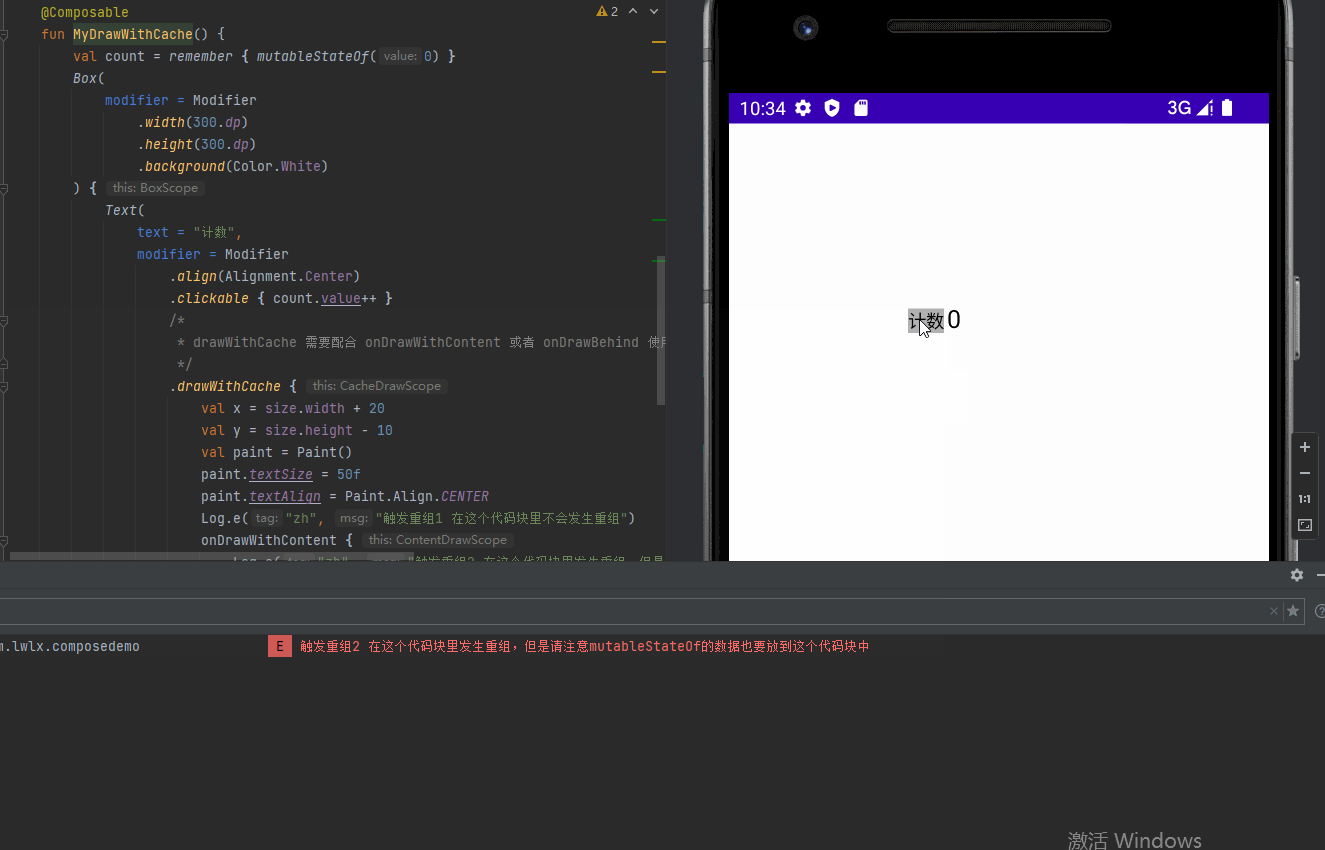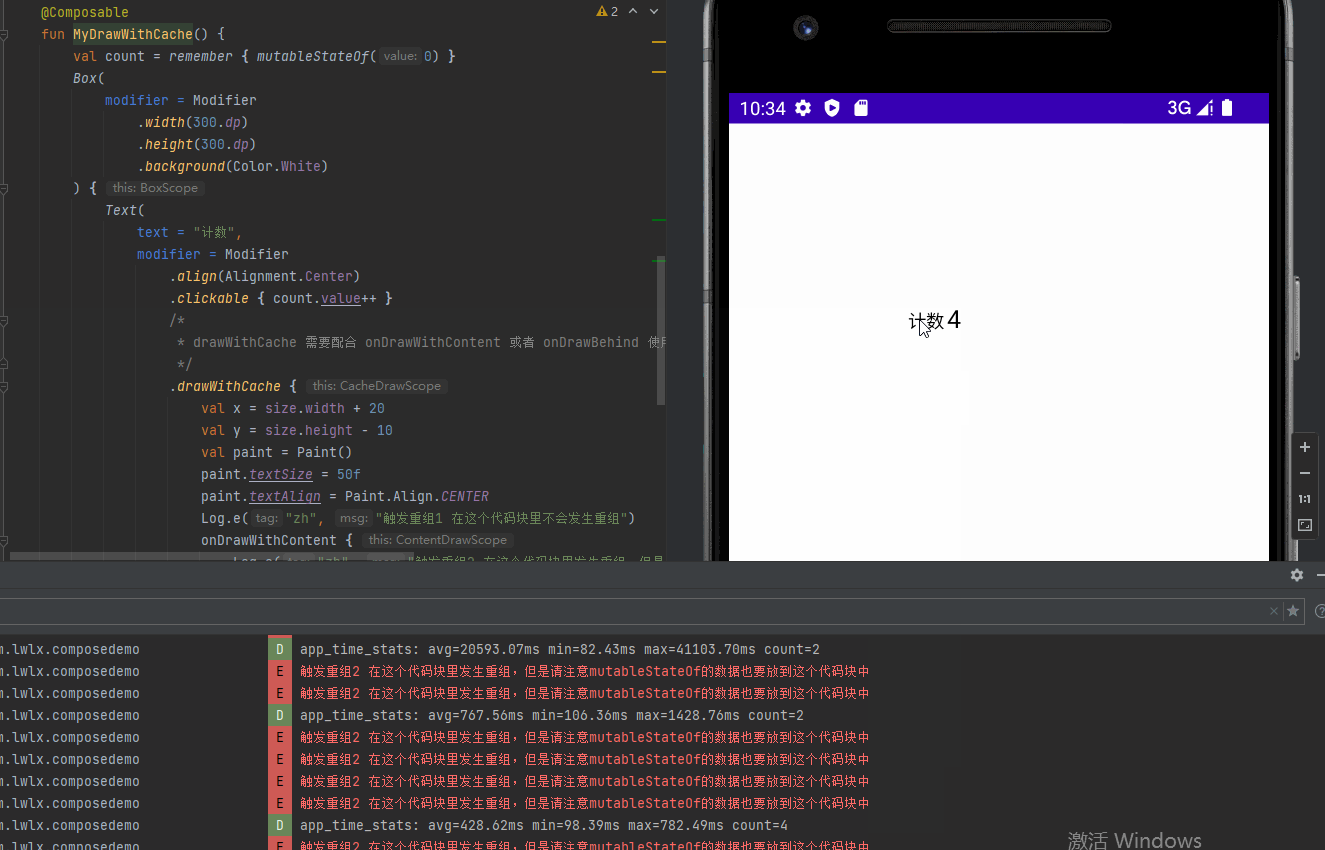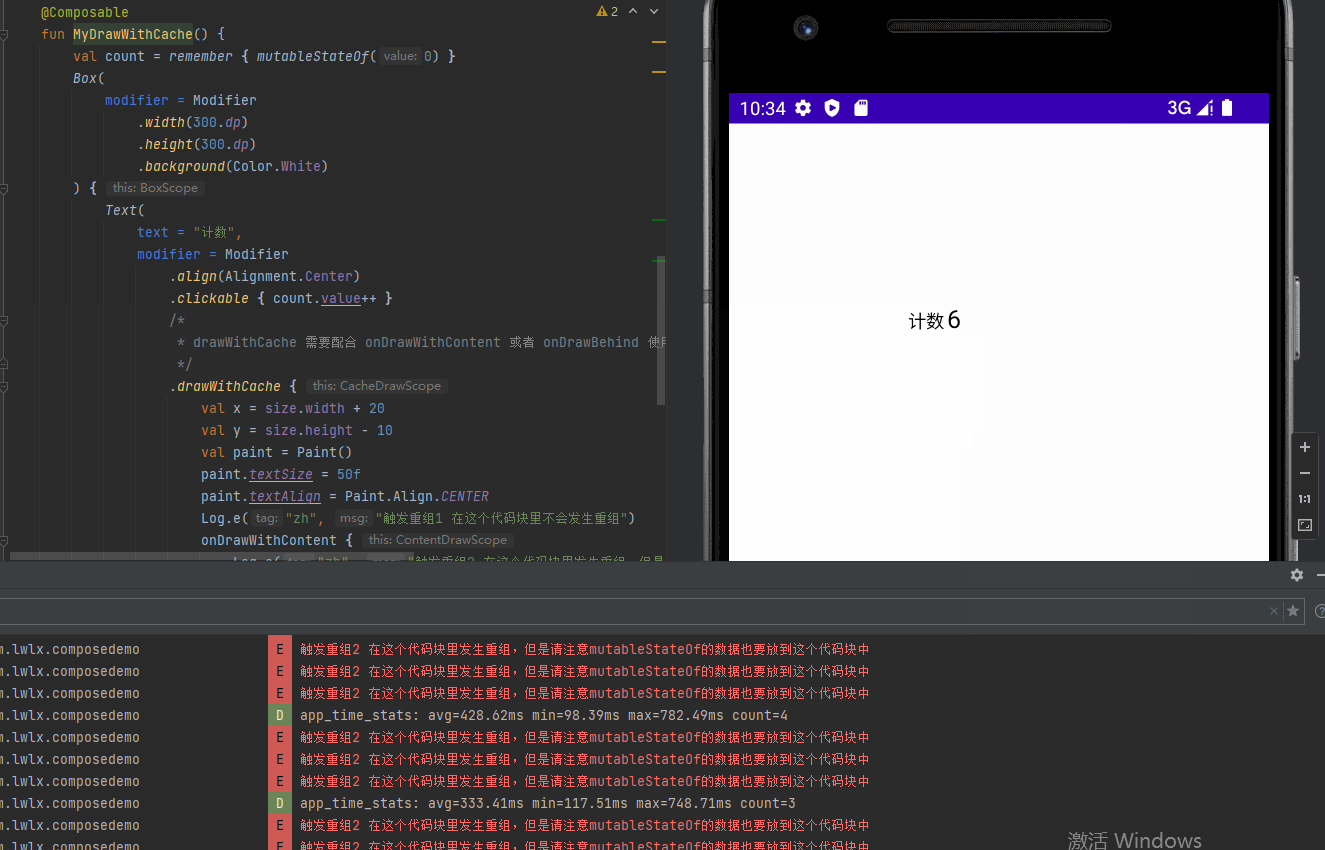
drawWithCache 提供缓存数据避免重组的绘制方式
代码
@Preview @Composable fun MyDrawWithCache() { val count = remember { mutableStateOf(0) } Box( modifier = Modifier .width(300.dp) .height(300.dp) .background(Color.White) ) { Text( text = "计数", modifier = Modifier .align(Alignment.Center) .clickable { count.value++ } /* * drawWithCache 需要配合 onDrawWithContent 或者 onDrawBehind 使用 */ .drawWithCache { val x = size.width + 20 val y = size.height - 10 val paint = Paint() paint.textSize = 50f paint.textAlign = Paint.Align.CENTER Log.e("zh", "触发重组1 在这个代码块里不会发生重组") onDrawWithContent { Log.e("zh", "触发重组2 在这个代码块里发生重组,但是请注意mutableStateOf的数据也要放到这个代码块中") drawIntoCanvas { canvas -> canvas.nativeCanvas.drawText("${count.value}", x, y, paint) } drawContent() } } ) } }
效果图:
Painter绘制
绘制图形
代码:
@Preview @Composable fun MyPaint() { Box( modifier = Modifier .width(100.dp) .height(100.dp) .background(Color.White) ) { Text( text = "你好", modifier = Modifier .align(Alignment.Center) .paint(painter = object : Painter() { override val intrinsicSize: Size get() = Size(50f, 50f) override fun DrawScope.onDraw() { drawLine( color = Color.Red, Offset(0f, 0f), Offset(size.width, size.height), strokeWidth = 10f ) } }) ) } }
效果图:

绘制图像
有一些人会利用这个来绘制组件的背景,的确可以但是个人认为不太妥当...
代码:
@Preview @Composable fun MyPaint() { Box( modifier = Modifier .width(300.dp) .height(300.dp) .background(Color.White) ) { Text( text = "你好", color = Color.White, modifier = Modifier .align(Alignment.Center) .paint(painterResource(id = R.mipmap.ic_logo)) ) } }
效果图:

焦点监听
下面使用TextField输入框来监听焦点的获取
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContent {
Box(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()){
TextField(value = "输入框", onValueChange = {}, modifier = Modifier.onFocusChanged {
val text = if (it.isFocused) "获得焦点" else "失去焦点"
Log.e("zh", "${text}")
}.align(Alignment.Center))
}
}
}焦点的获取与清除
效果图

代码
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContent {
val hasFocus = remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
val focusRequester = remember { FocusRequester() }
val focusManager = LocalFocusManager.current
Box(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()){
TextField(value = "输入框", onValueChange = {}, modifier = Modifier
.focusRequester(focusRequester)
.onFocusChanged {
hasFocus.value = it.isFocused
val text = if (it.isFocused) "获得焦点" else "失去焦点"
Log.e("zh", "${text}")
}
.align(Alignment.Center))
//这边创建按键来控制上面输入框的焦点获取
Button(
modifier = Modifier.padding(bottom = 120.dp).align(Alignment.Center),
onClick = {
if (!hasFocus.value) {
focusRequester.requestFocus() //获取焦点
} else{
focusManager.clearFocus() //清空焦点
}
}
) {
Text(if (!hasFocus.value) "请求焦点" else "取消焦点")
}
}
}
}自定义焦点选中效果
代码
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContent {
val interactionSource = remember { MutableInteractionSource() }
val bg1Color = remember { mutableStateOf(Color.Transparent) }
//collectIsFocusedAsState为焦点状态
if (interactionSource.collectIsFocusedAsState().value){
bg1Color.value = Color(0xFF6FFFFF)
} else {
bg1Color.value = Color.Transparent
}
Column(
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally,
modifier = Modifier
.padding(top = 100.dp)
.fillMaxSize()
) {
Text(
text = "测试1",
fontSize = 20.sp,
textAlign = TextAlign.Center,
modifier = Modifier
.size(100.dp, 100.dp)
.background(color = bg1Color.value, shape = RoundedCornerShape(40.dp))
//需要在clickable上设置interactionSource与indication
.clickable(
interactionSource = interactionSource,
indication = null,
onClick = {
})
)
//默认的自带焦点,作为对比
Text(
text = "测试2",
fontSize = 20.sp,
textAlign = TextAlign.Center,
modifier = Modifier
.size(100.dp, 100.dp)
.clickable(onClick = {
})
)
}
}
}效果图

禁用焦点功能
代码
setContent {
Column(
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally,
modifier = Modifier
.padding(top = 100.dp)
.fillMaxSize()
) {
Text(text = "测试2", textAlign = TextAlign.Center,modifier = Modifier.size(100.dp, 100.dp).focusProperties{
//canFocus设置为false可以禁用焦点
canFocus = false
}.clickable {
})
}
}组合顺序的影响
Modifier的方法组合顺序是会影响到组件的实际效果的,这里使用两段代码演示(可以根据下面2代码看到点击范围发生了改变):
代码1:
@Preview @Composable fun MyText() { Text( text = "你好世界你好世界", color = Color.Black, modifier = Modifier .background(Color.Green) .size(150.dp) .clickable { //点击在前 Log.e("zh", "MyGraphicsLayer: ") } .padding(50.dp) //padding在后 ) }
效果图:

代码2:
@Preview @Composable fun MyText() { Text( text = "你好世界你好世界", color = Color.Black, modifier = Modifier .background(Color.Green) .size(150.dp) .padding(50.dp) //padding在前 .clickable { //点击在后 Log.e("zh", "MyGraphicsLayer: ") } ) }
效果图:

多个Modifier组合
下面的代码种,分别创建了backgroundModifier 与 borderModifier, 并且使用then将他们组合
代码:
@Preview @Composable fun MyText() { val backgroundModifier = Modifier .background(Color.Green) .fillMaxSize(0.2f) val borderModifier = Modifier .border( width = 1.dp, //设置边框粗细 color = Color(0xFF000000), //边框颜色 shape = RoundedCornerShape(5.dp) //切角矩形形状 ) Column { Text( text = "A", color = Color.Black, textAlign = TextAlign.Center, modifier = Modifier .then(backgroundModifier) .then(borderModifier) .clickable { Log.e("zh", "点击A") } ) Text( text = "B", color = Color.Black, textAlign = TextAlign.Center, modifier = Modifier .then(backgroundModifier) .then(borderModifier) .clickable { Log.e("zh", "点击B") } ) } }
扩展Modifier函数
kotlin是支持扩展函数的,所以Modifier也能进行函数扩展,使其可以进行一些风格与功能封装,减少重复代码。
组件风格扩展的例子(一个简单的例子)
假设,现在有一个文本风格有统一的背景与边框,现在希望减少重复代码,我们就可以以下面的方式实现Modifier扩展函数,达到随处使用的目的。
扩展函数代码
then是接续函数,代表myStyle这个函数还可以拼接其他的Modifier的函数
fun Modifier.myStyle() = this.then(
this.padding(10.dp)
.background(color = Color.DarkGray, shape = RoundedCornerShape(5.dp))
.border(5.dp, Color.Red)
)使用函数代码
Column(
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally,
modifier = Modifier
.padding(top = 100.dp)
.fillMaxSize()
) {
Text(
text = "测试1",
fontSize = 20.sp,
textAlign = TextAlign.Center,
modifier = Modifier
.size(100.dp, 100.dp)
.myStyle()
)
Text(
text = "测试2",
fontSize = 20.sp,
textAlign = TextAlign.Center,
modifier = Modifier
.size(100.dp, 100.dp)
.myStyle()
)
}效果图

扩展支持compose的例子
上面的例子非常简单,只是封装了常规的Modifier函数。 但是实际开发中,我们有需求封装各色状态,逻辑等等情况,以达到扩展实现动画效果、焦点选中、按下效果的功能。
实现按下、焦点、鼠标悬浮组件缩放的扩展例子
扩展函数代码
下面关键的是composed函数,这个函数可以让以在compose函数里一样调用,remember状态管理、附带效应等等代码
/**
* 点击和焦点、鼠标悬停的缩放效果
*/
fun Modifier.clickAndFocusHoveredScale(focusedAndHoveredScale: Float, pressedScale: Float, onClick: () -> Unit) =
this.composed(
factory = {
//创建一个缩放效果
val scale = remember {
mutableStateOf(1f)
}
val interactionSource = remember {
MutableInteractionSource()
}
if (interactionSource.collectIsFocusedAsState().value || interactionSource.collectIsHoveredAsState().value) {
//当正在焦点状态与鼠标悬停状态时,这里改变scale的数值
scale.value = focusedAndHoveredScale
} else if (interactionSource.collectIsPressedAsState().value) {
//当按下状态时,这里改变scale的数值
scale.value = pressedScale
} else {
//没有状态默认恢复原来的大小
scale.value = 1.0f
}
return@composed Modifier
.scale(scale.value)
.clickable(interactionSource, indication = null, onClick = onClick)
},
)使用函数代码
Column(
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally,
modifier = Modifier
.padding(top = 100.dp)
.fillMaxSize()
) {
(0..5).forEach {
Text("${it}", color = Color.White, modifier = Modifier.padding(10.dp)
.size(50.dp)
.clickAndFocusHoveredScale(1.3f, 0.7f) {
//点击
}
.background(color = Color.DarkGray)
)
}
}效果图

End
本文来自博客园,作者:观心静 ,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/guanxinjing/p/16807477.html



