Java 使用线程池执行耗时方法
1.添加线程池管理工具
package group.hound.interfaces.infra.threadpool; import com.google.common.util.concurrent.ThreadFactoryBuilder; import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; /** * 线程池管理(线程统一调度管理) * * @author jinliang 2020/02/19 19:43 */ public class ThreadPoolManager { private static ThreadPoolManager sThreadPoolManager = new ThreadPoolManager(); /** * 线程池基本大小 */ private static final int SIZE_CORE_POOL = 15; /** * 线程池最大数量 */ private static final int SIZE_MAX_POOL = 15; /** * 线程池单例创建方法 * @return sThreadPoolManager */ public static ThreadPoolManager newInstance() { return sThreadPoolManager; } /** * 线程工厂 */ ThreadFactory namedThreadFactory = new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("cleanRecord-pool-%d").build(); /************************************************************************************************************** * 常见的几种线程技术 ************************************************************************************************************** * Java通过Executors提供四种线程池,分别为: * newCachedThreadPool创建一个可缓存线程池,如果线程池长度超过处理需要,可灵活回收空闲线程,若无可回收,则新建线程。 * newFixedThreadPool 创建一个定长线程池,可控制线程最大并发数,超出的线程会在队列中等待。 * newScheduledThreadPool 创建一个定长线程池,支持定时及周期性任务执行。 newSingleThreadExecutor * 创建一个单线程化的线程池,它只会用唯一的工作线程来执行任务,保证所有任务按照指定顺序(FIFO, LIFO, 优先级)执行。 * * 1、public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) { * return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()); } * * 2、 public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() { * return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService (new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>())); } * * 3、public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() { * return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>()); } ****************************************************************************************************************/ /** * 创建一个定长线程池,可控制线程最大并发数,超出的线程会在队列中等待 * @param corePoolSize - 池中所保存的线程数,包括空闲线程。 * @param maximumPoolSize - 池中允许的最大线程数。 * @param keepAliveTime - 当线程数大于核心时,此为终止前多余的空闲线程等待新任务的最长时间。 * @param unit - keepAliveTime 参数的时间单位。 * @param workQueue - 执行前用于保持任务的队列。此队列仅由保持 execute 方法提交的 Runnable 任务。 * @param handler - 由于超出线程范围和队列容量而使执行被阻塞时所使用的处理程序。 */ private final ThreadPoolExecutor mThreadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(SIZE_CORE_POOL, SIZE_MAX_POOL, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(),namedThreadFactory, new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()); /** * 将构造方法访问修饰符设为私有,禁止任意实例化。 */ private ThreadPoolManager() { } /** * 将线程池初始化,核心线程数量 */ public void perpare() { if (mThreadPool.isShutdown() && !mThreadPool.prestartCoreThread()) { @SuppressWarnings("unused") int startThread = mThreadPool.prestartAllCoreThreads(); } } /** * 向线程池中添加任务方法 */ public void addExecuteTask(Runnable task) { if (task != null) { mThreadPool.execute(task); } } /** * 判断是否是最后一个任务 */ protected boolean isTaskEnd() { if (mThreadPool.getActiveCount() == 0) { return true; } else { return false; } } /** * 获取缓存大小 */ public int getQueue(){ return mThreadPool.getQueue().size(); } /** * 获取线程池中的线程数目 */ public int getPoolSize(){ return mThreadPool.getPoolSize(); } /** * 获取已完成的任务数 */ public long getCompletedTaskCount(){ return mThreadPool.getCompletedTaskCount(); } /** * 关闭线程池,不在接受新的任务,会把已接受的任务执行完 */ public void shutdown() { mThreadPool.shutdown(); } }
2.使用线程池执行方法
package com.mybatis.plus.utils; import cn.hutool.core.lang.Console; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.HttpURLConnection; import java.net.URL; import java.net.URLConnection; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadPoolManager threadPoolManager = ThreadPoolManager.newInstance(); for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) { final Integer s = i; threadPoolManager.addExecuteTask(() -> testThread(s)); } } public static void testThread(int i){ Console.log("=======正在执行>>>>>>" + i); for (int q = 1; q < 10; q++) { Console.log(i + ">>>>>>>>>" + q); } } }
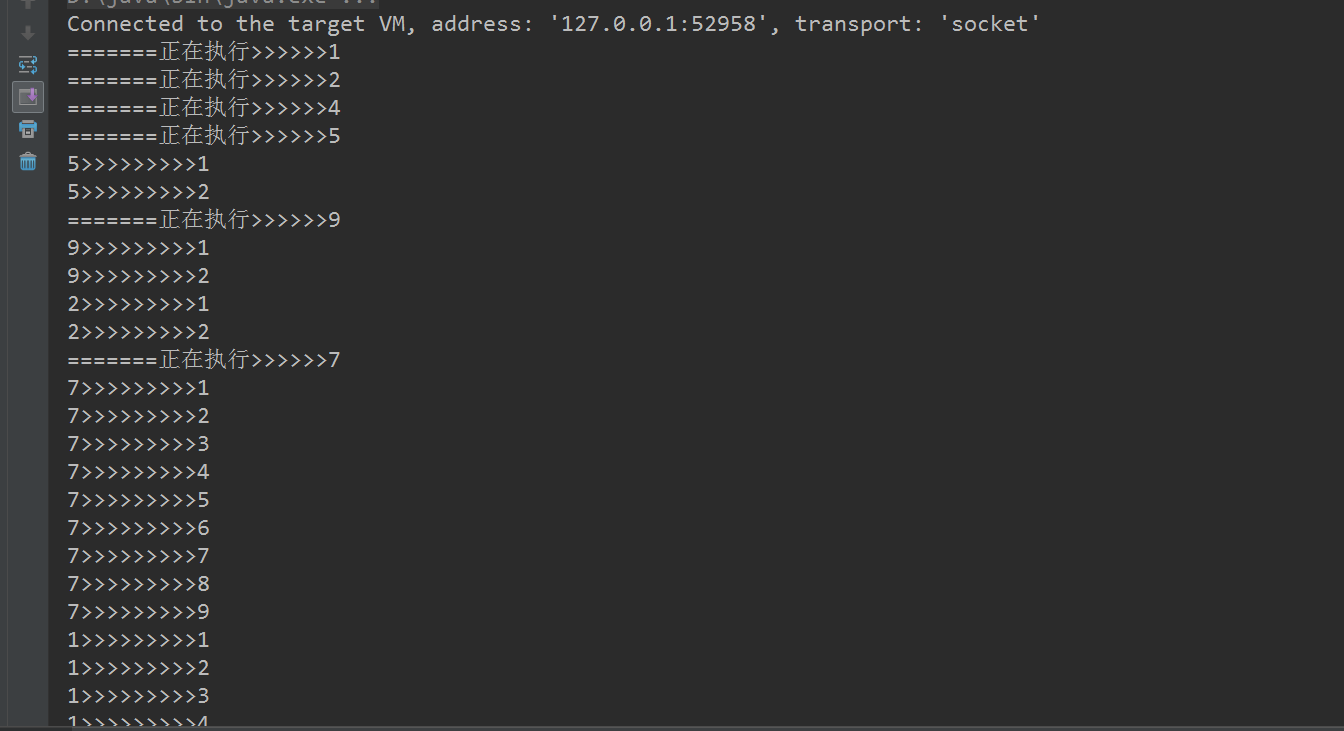
打印效果:
⎛⎝官萧何⎠⎞一只快乐的爪哇程序猿;邮箱:1570608034@qq.com


