uniapp项目实践总结(十四)封装存储和路由方法
导语:在日常 APP 开发过程中,经常要用到数据的存储、获取和删除等操作以及页面导航之间的跳转,为此,封装了一个两个简单的方法来统一调用。
目录
- 原理分析
- 方法实现
- 实战演练
- 案例展示
原理分析
主要是以下 API。
uni.setStorage:保存数据到本地缓存中;uni.getStorage:获取保存的缓存数据;uni.removeStorage:移除保存的数据缓存;uni.clearStorage:清空保存的缓存数据;uni.navigate{type}:跳转页面;
以下方法存于根目录下的scripts文件夹下的utils.js文件中。
方法实现
接下来一一说明如何实现数据缓存操作和路由跳转的封装。
数据缓存
这里是使用一个方法,通过传入不同的类型和参数来实现。
参数如下:
type: 类型,包括设置,获取,删除,清空;isSync: 是否异步;key: 键名;val: 值;
// 存储数据
async function storeage(options) {
try {
let defultOptions = {
type: options.type,
isSync: options.isSync || false,
key: options.key,
data: options.val,
};
let params = { ...options, ...defultOptions };
console.log("数据缓存参数:", params);
let { type, isSync, key, data } = params;
let result = null,
types = {
set: uni[`setStorage${isSync ? "Sync" : ""}`],
get: uni[`getStorage${isSync ? "Sync" : ""}`],
del: uni[`removeStorage${isSync ? "Sync" : ""}`],
clear: uni[`clearStorage${isSync ? "Sync" : ""}`],
};
if (type == "set") {
if (isSync) {
result = await types[type](key, data);
} else {
result = await types[type]({
key,
data,
});
}
}
if (["get", "del"].includes(type)) {
let param = isSync ? key : { key };
result = await types[type](param);
}
if (type == "clear") {
result = await types[type]();
}
return {
code: 1,
data: result,
};
} catch (e) {
return {
code: 2,
data: e,
};
}
}
路由操作
这里是把常用的路由方法装进一个方法里面了,方便调用。
参数如下:
type: 路由类型;url: 路由地址key: 键名;delta: 返回级数;
// 页面跳转
async function navigate(options) {
let res = null,
defultOptions = {
type: options.type || "to",
url: options.url || "",
delta: options.delta || 1,
},
params = { ...options, ...defultOptions };
if (!params.type) return;
if (params.type != "back" && !params.url) return;
let { type, url, delta } = params;
console.log("页面跳转参数:", params);
if (type == "to") {
res = await uni.navigateTo({
url,
});
}
if (type == "back") {
res = await uni.navigateBack({
delta,
});
}
if (type == "redir") {
res = await uni.redirectTo({
url,
});
}
if (type == "tab") {
res = await uni.switchTab({
url,
});
}
if (type == "lanuch") {
res = await uni.reLaunch({
url,
});
}
return res;
}
实战演练
模板内容
- 缓存数据操作
<button class="eg-btn" @click="storeSet('set')">设置数据</button>
<button class="eg-btn" @click="storeSet('get')">获取数据</button>
<button class="eg-btn" @click="storeSet('remove')">删除数据</button>
<button class="eg-btn" @click="storeSet('clear')">清空数据</button>
<view class="eg-res"> 数据:{{ data }} </view>
- 路由操作
<button class="eg-btn" @click="goPage('to', '/pages/test/stand')">去模板</button>
<button class="eg-btn" @click="goPage('back', '', 1)">返回上一页</button>
<button class="eg-btn" @click="goPage('redir', '/pages/index/swiper')">去重定向</button>
<button class="eg-btn" @click="goPage('tab', '/pages/user/index')">去我的</button>
<button class="eg-btn" @click="goPage('lanuch', '/pages/index/list')">去列表</button>
脚本方法
- 定义数据
// 缓存数据
let data = ref("");
- 数据操作
这里为了方便都整合到一起调用了。
async function storeSet(type) {
let id = proxy.$apis.utils.uuid(),
key = "1693991490699-10vrs3hoiv6";
if (type == "set") {
let res = await proxy.$apis.utils.storeage({
type: "set",
isSync: true,
key: id,
val: `id-${id}`,
});
console.log(`数据${type}操作结果:`, res);
}
if (type == "get") {
let res = await proxy.$apis.utils.storeage({
type: "get",
isSync: true,
key,
});
if (res.code == 1) {
data.value = res.data;
}
console.log(`数据${type}操作结果:`, res);
}
if (type == "remove") {
let res = await proxy.$apis.utils.storeage({
type: "del",
isSync: true,
key,
});
console.log(`数据${type}操作结果:`, res);
}
if (type == "clear") {
let res = await proxy.$apis.utils.storeage({
type: "clear",
isSync: true,
});
console.log(`数据${type}操作结果:`, res);
}
}
- 路由方法
这里为了方便都整合到一起调用了。
async function goPage(type, url, delta) {
let data = await proxy.$apis.utils.navigate({
type,
url,
delta,
});
console.log("页面跳转结果:", data);
}
案例展示
-
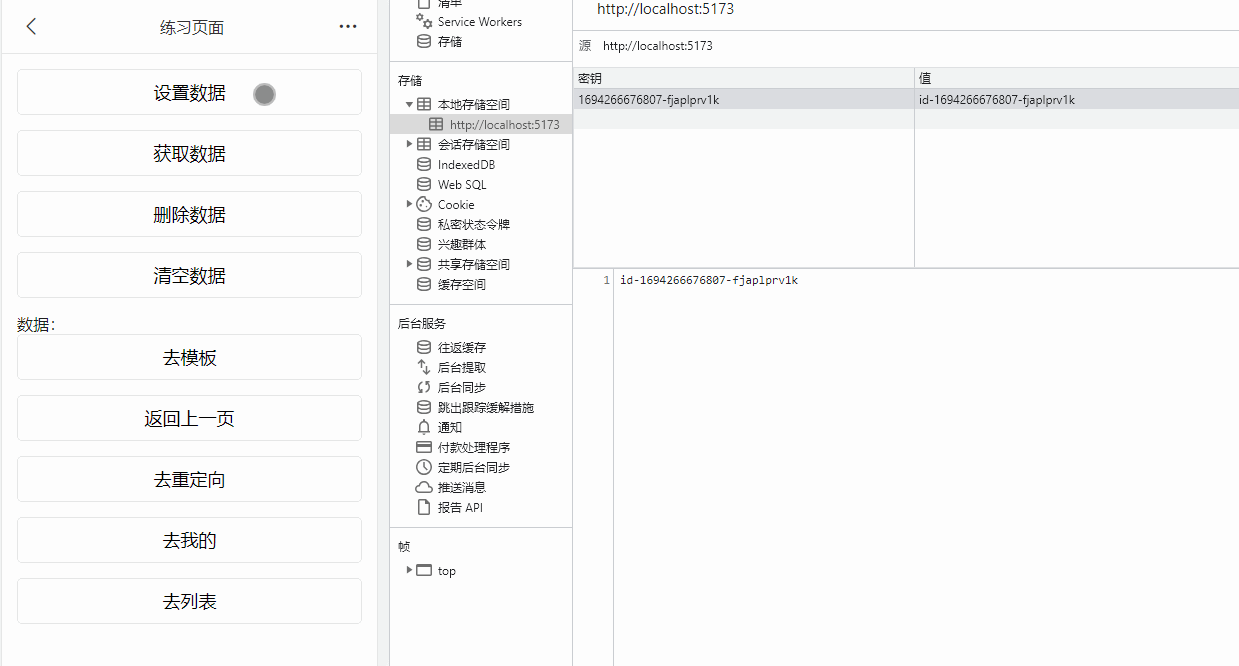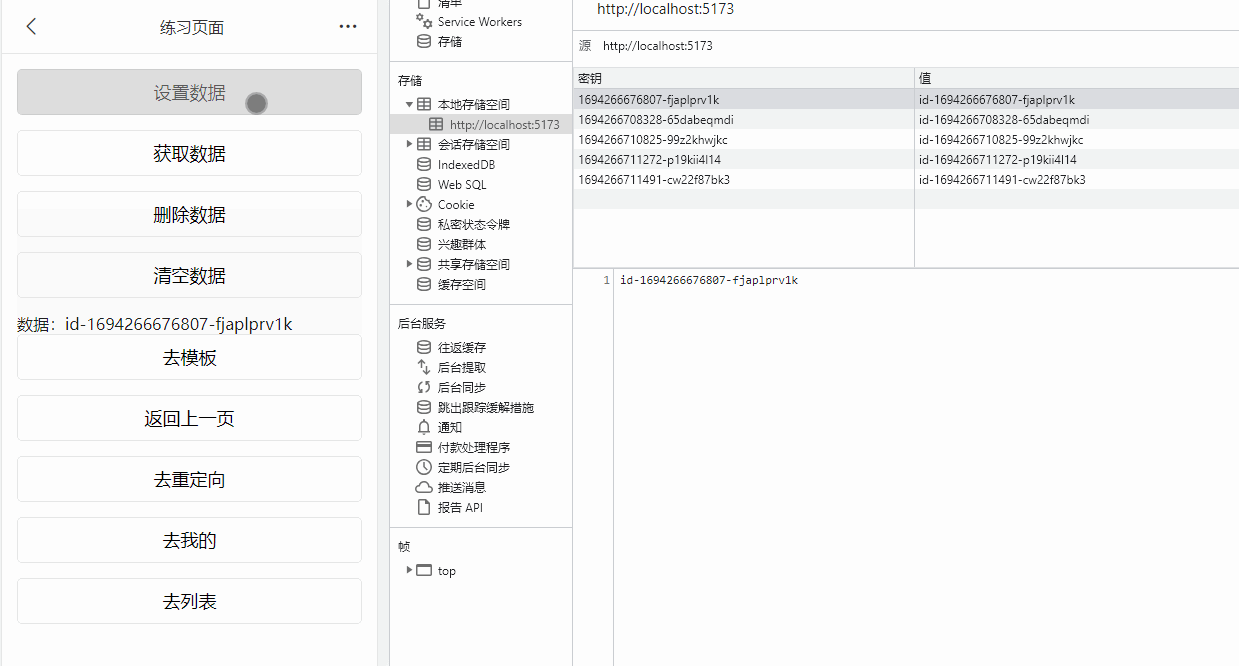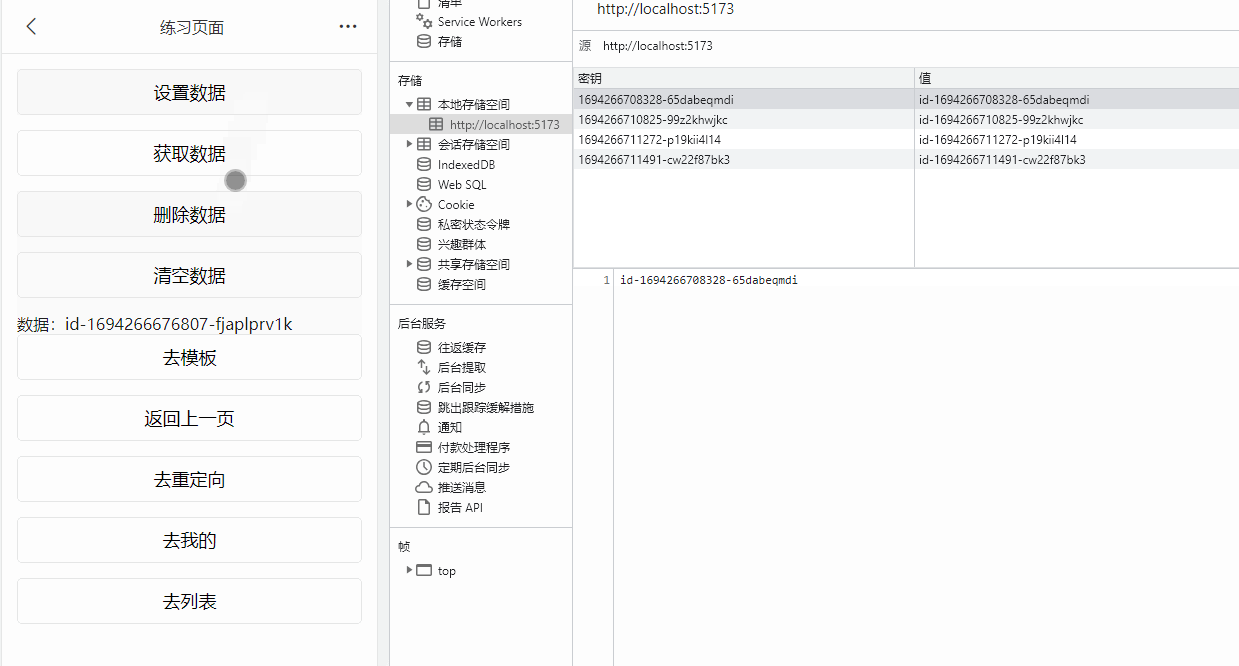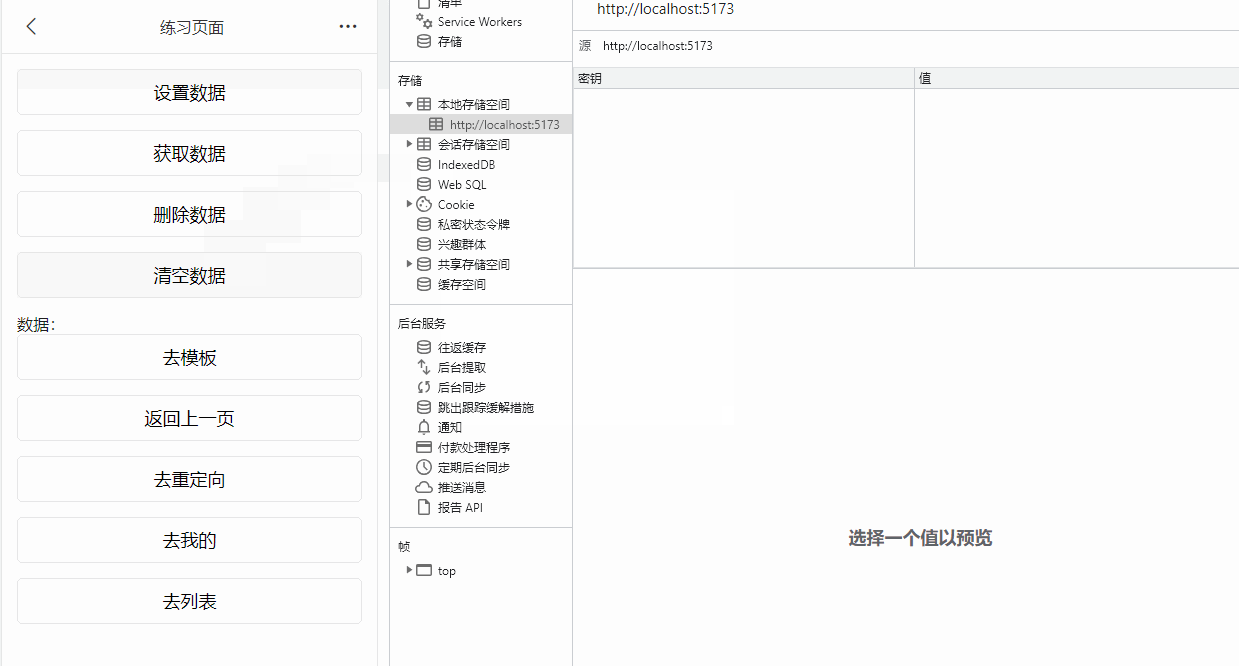
数据缓存
![image]()
-
页面路由
![image]()
最后
以上就是封装存储和路由方法的主要内容,有不足之处,请多多指正。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号