Go操作MongoDB
NoSQL泛指非关系型数据库,如mongo,redis,HBase。
mongo使用高效的二进制数据存储,文件存储格式为 BSON ( 一种json的扩展,比json性能更好,功能更强大)。
MySQL中表的概念在mongo里叫集合(collection), MySQL中行的概念在mongo中叫文档(document),一个文档看上去像一个json。
官方
安装mongodb
安装mongo前先配置yum源: vim /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb-org-4.2.repo
[mongodb-org-4.2]
name=MongoDB Repository baseurl=https://repo.mongodb.org/yum/redhat/$releasever/mongodb-org/4.2/x86_64/ gpgcheck=1 enabled=1 gpgkey=https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-4.2.asc
一键安装mongo: sudo yum install -y mongodb-org
启动mongo: systemctl start mongod
mongo常用命令
$ use test; 切换到test库,如果没有则(创建集合时)会自动创建
$ db.createCollection("student"); 创建collection
$ db.createUser({user: "tester",pwd: "123456", roles: [{role: "dbAdmin", db: "test"}]});创建用户
#登录
$ mongo --port 27017 -u "tester" -p "123456" --authenticationDatabase "test"
$ db.student.createIndex({"name":1});在name上创建索引,不是唯一索引
$ db.student.insertOne({name:"张三",city:"北京"});
$ db.student.find({name:"张三"});
$ db.student.update({name:"张三"},{name:"张三",city:"上海"})
$ db.student.deleteOne({name:"张三"});
安装go驱动mongo-driver
go get go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo
连接db
mongodb://[username:password@]host1[:port1][,...hostN[:portN]][/[defaultauthdb][?options]]
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo/options"
"time"
)
func main() {
// 创建一个带有5秒超时的上下文,确保操作不会无限期阻塞
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), time.Second*5)
defer cancel() // 确保在函数结束时取消上下文,释放资源
// 定义MongoDB的连接URI
uri := "mongodb://10.1.0.153:27017/"
// 配置MongoDB客户端选项,包括连接URI、超时时间和认证信息
opt := options.Client().ApplyURI(uri).
SetTimeout(time.Second * 5). // 设置客户端操作超时时间为15秒
SetAuth(
options.Credential{ // 设置认证信息
Username: "root",
Password: "111111",
},
)
// 使用配置选项连接到MongoDB
client, err := mongo.Connect(ctx, opt)
if err != nil {
panic(err) // 如果连接失败,立即终止程序
}
defer func() {
// 确保在函数结束时断开与MongoDB的连接
if err := client.Disconnect(ctx); err != nil {
panic(err) // 如果断开连接失败,立即终止程序
}
}()
// 检查MongoDB连接是否正常
err = client.Ping(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
panic(err) // 如果连接检查失败,立即终止程序
}
// 获取指定数据库和集合的句柄 Test是数据库 User是集合相当于表
coll := client.Database("Test").Collection("User")
}
注意Ping成功才代表连接成功。
操作
初始化连接部分
package main
import (
"context"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo/options"
"time"
)
type User struct {
ID uint
Name string
Age int
Gender int8
BirthDate time.Time
}
var (
coll *mongo.Collection
ctx context.Context
cancel context.CancelFunc
)
func init() {
// 创建一个带有5秒超时的上下文,确保操作不会无限期阻塞
ctx, cancel = context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), time.Second*5)
// 定义MongoDB的连接URI
uri := "mongodb://10.1.0.153:27017/"
// 配置MongoDB客户端选项,包括连接URI、超时时间和认证信息
opt := options.Client().ApplyURI(uri).
SetTimeout(time.Second * 15). // 设置客户端操作超时时间为15秒
SetAuth(
options.Credential{ // 设置认证信息
Username: "root",
Password: "111111",
},
)
// 使用配置选项连接到MongoDB
client, err := mongo.Connect(ctx, opt)
if err != nil {
panic(err) // 如果连接失败,立即终止程序
}
defer func() {
// 确保在函数结束时断开与MongoDB的连接
if err := client.Disconnect(ctx); err != nil {
panic(err) // 如果断开连接失败,立即终止程序
}
}()
// 检查MongoDB连接是否正常
err = client.Ping(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
panic(err) // 如果连接检查失败,立即终止程序
}
// 获取指定数据库和集合的句柄
coll = client.Database("Test").Collection("User")
}
创建
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo/options"
"time"
)
// 定义User结构体,表示用户信息
type User struct {
ID uint // 用户ID
Name string // 用户名
Age int // 用户年龄
Gender int8 // 用户性别(1表示男性,2表示女性等)
BirthDate time.Time // 用户出生日期
}
// 全局变量定义
var (
coll *mongo.Collection // MongoDB集合句柄
client *mongo.Client // MongoDB客户端
ctx context.Context // 上下文
cancel context.CancelFunc // 上下文取消函数
)
func main() {
// 确保在函数结束时取消上下文,释放资源
defer cancel()
// 确保在函数结束时断开与MongoDB的连接
defer func() {
if err := client.Disconnect(ctx); err != nil {
panic(err) // 如果断开连接失败,立即终止程序
}
}()
// 单个创建
// 创建一个User实例
u := User{
ID: 1,
Name: "test",
Age: 18,
Gender: 1,
BirthDate: time.Now(),
}
// 插入单个文档到MongoDB集合
res1, err := coll.InsertOne(ctx, u)
if err != nil {
panic(err) // 如果插入失败,立即终止程序
}
fmt.Println(res1.InsertedID) // 输出插入文档的ObjectID
// ObjectID("6788abe75f41a29b1111dc0f")
// 批量插入
// 创建多个User实例的切片
us := []interface{}{
User{
ID: 2,
Name: "test2",
Age: 18,
Gender: 1,
BirthDate: time.Now(),
},
User{
ID: 3,
Name: "test3",
Age: 18,
Gender: 1,
BirthDate: time.Now(),
},
User{
ID: 4,
Name: "test4",
Age: 18,
Gender: 1,
BirthDate: time.Now(),
},
}
// 批量插入多个文档到MongoDB集合
res2, err := coll.InsertMany(ctx, us)
if err != nil {
panic(err) // 如果插入失败,立即终止程序
}
fmt.Println(res2.InsertedIDs) // 输出插入文档的ObjectID列表
// [ObjectID("6788abe75f41a29b1111dc10") ObjectID("6788abe75f41a29b1111dc11") ObjectID("6788abe75f41a29b1111dc12")]
}
更新
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/bson"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo/options"
"time"
)
// 全局变量定义
var (
coll *mongo.Collection // MongoDB集合句柄
client *mongo.Client // MongoDB客户端
ctx context.Context // 上下文
cancel context.CancelFunc // 上下文取消函数
)
func main() {
// 确保在函数结束时取消上下文,释放资源
defer cancel()
// 确保在函数结束时断开与MongoDB的连接
defer func() {
if err := client.Disconnect(ctx); err != nil {
panic(err) // 如果断开连接失败,立即终止程序
}
}()
// 创建选项,如果文档不存在就插入文档
opts := options.Update().SetUpsert(true)
// 过滤条件
filter := bson.D{{Key: "name", Value: "test"}}
// inc是加 对age的值加222
// update := bson.D{{Key: "$inc", Value: bson.D{{Key: "age", Value: 222}}}}
// set是设置 把age的值设置成222
update := bson.D{{Key: "$set", Value: bson.D{{Key: "age", Value: 666}}}}
// 更新单个文档
// res, err := collection.UpdateOne(ctx, filter, update, opts)
// 更新所有的文档
res, err := coll.UpdateMany(ctx, filter, update, opts)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
// 分别打印匹配到的个数 修改的个数 插入的个数 插入的id
fmt.Println(res.MatchedCount, res.ModifiedCount, res.UpsertedCount, res.UpsertedID)
}
设置SetUpsert(true) 就可以在文档不存在的时候创建文件
不设置,如果条件没匹配到,也不会报错
查询
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/bson"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo/options"
"time"
)
// 定义User结构体,表示用户信息
type User struct {
ID uint // 用户ID
Name string // 用户名
Age int // 用户年龄
Gender int8 // 用户性别(1表示男性,2表示女性等)
BirthDate time.Time // 用户出生日期
}
func main() {
// 确保在函数结束时取消上下文,释放资源
defer cancel()
// 确保在函数结束时断开与MongoDB的连接
defer func() {
if err := client.Disconnect(ctx); err != nil {
panic(err) // 如果断开连接失败,立即终止程序
}
}()
// 创建排序,以id降序排序
sorts := bson.D{{Key: "id", Value: -1}} // 规则必须加上Key Value 不然会有黄线, 排序规则必须得有
// 创建过滤条件
// filter := bson.D{{Key: "name", Value: bson.D{{Key: "$eq", Value: "test"}}}} // name = "test"
filter := bson.D{{}} // 如果没有过滤规则,就需要一个空的
// 创建查询选项
findoption := options.Find()
// 设置排序规则
findoption.SetSort(sorts)
// 设置分页
findoption.SetLimit(2) // 选择2个
findoption.SetSkip(4) // 跳过4个
// 过滤查询 获取游标
cursor, err := coll.Find(ctx, filter, findoption)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
defer cursor.Close(ctx)
// 遍历游标
for cursor.Next(ctx) {
u := User{}
// 读取当前游标数据
err := cursor.Decode(&u)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Printf("%+v\n", u)
}
}
删除
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/bson"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo/options"
"time"
)
func main() {
// 确保在函数结束时取消上下文,释放资源
defer cancel()
// 确保在函数结束时断开与MongoDB的连接
defer func() {
if err := client.Disconnect(ctx); err != nil {
panic(err) // 如果断开连接失败,立即终止程序
}
}()
// 创建过滤条件
filter := bson.D{{Key: "name", Value: bson.D{{Key: "$eq", Value: "test"}}}} // name = "test"
// 或者改写成 bson.M
// filter := bson.M{"name": bson.M{"$eq": "test5"}} // name = "test"
// 删除一条
// res, err := coll.DeleteOne(ctx, filter)
// 删除匹配到的所有
res, err := coll.DeleteMany(ctx, filter)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Println(res.DeletedCount)
}
完整示例
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"time"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/bson"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo/options"
)
type ttt struct {
A int64
B int64
C int64
}
func ReadMongo(collection *mongo.Collection, ctx context.Context) {
//创建排序
sorts := bson.D{{Key: "a", Value: -1}} //规则必须加上Key Value 不然会有黄线, 排序规则必须得有
// filter := bson.D{{Key: "b", Value: bson.D{{Key: "$gt", Value: 2}}}}
filter := bson.D{{}} //如果没有过滤规则,就需要一个空的
findoption := options.Find()
findoption.SetSort(sorts)
findoption.SetLimit(2) //选择2个
findoption.SetSkip(4) //跳过4个
cursor, err := collection.Find(ctx, filter, findoption)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err, "====")
return
}
defer cursor.Close(ctx)
for cursor.Next(ctx) {
t := ttt{}
err := cursor.Decode(&t)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Println(t.A, t.B, t.C, "-----------")
}
}
func CreateMongo(collection *mongo.Collection, ctx context.Context) {
//多个一起插入
catch1 := ttt{A: 61, B: 42, C: 93}
catch2 := ttt{A: 55, B: 66, C: 11}
catch3 := ttt{A: 23, B: 14, C: 77}
catch := []interface{}{catch1, catch2, catch3} //这里必须是interface的切片
fmt.Println(catch)
collection.InsertMany(ctx, catch)
//单个单个得插入
for i := 0; i < 100000; i++ {
t := time.Now().UnixMicro()
catch := ttt{A: t % 100, B: t % 73, C: t % 105}
_, err := collection.InsertOne(ctx, catch)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
}
}
func UpdateMongo(collection *mongo.Collection, ctx context.Context) {
//创建选项,如果文档不存在就插入文档
opts := options.Update().SetUpsert(true)
filter := bson.D{{Key: "a", Value: 88}}
//inc是加 对c的值加222
//update := bson.D{{Key: "$inc", Value: bson.D{{Key: "c", Value: 222}}}}
//set是设置 把c的值设置成222
update := bson.D{{Key: "$set", Value: bson.D{{Key: "c", Value: 666}}}}
//更新单个文档
// res, err := collection.UpdateOne(ctx, filter, update, opts)
//更新所有的文档
res, err := collection.UpdateMany(ctx, filter, update, opts)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
//分别打印匹配到的个数 修改的个数 插入的个数 插入的id
fmt.Println(res.MatchedCount, res.ModifiedCount, res.UpsertedCount, res.UpsertedID)
}
func DeleteMongo(collection *mongo.Collection, ctx context.Context) {
filter := bson.D{{Key: "a", Value: 88}, {Key: "b", Value: 71}}
//删除一条
// res, err := collection.DeleteOne(ctx, filter)
//删除匹配到的所有
res, err := collection.DeleteMany(ctx, filter)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Println(res.DeletedCount)
}
func Mongodb() {
option := options.Client().ApplyURI("mongodb://10.0.0.12:27017").SetConnectTimeout(10 * time.Second)
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := mongo.Connect(ctx, option)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
err = client.Ping(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
defer client.Disconnect(ctx)
//查看所有的库
databases, err := client.ListDatabaseNames(ctx, bson.D{})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
fmt.Println(databases) //[admin config local test]
//连接哪个数据库得哪个集合
collection := client.Database("test").Collection("abc")
// ReadMongo(collection, ctx)
// CreateMongo(collection, ctx)
// UpdateMongo(collection, ctx)
DeleteMongo(collection, ctx)
}
Bson类型
在MongoDB的Go驱动(go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/bson)中,有一些类型用于表示BSON文档或值。
以下是相关类型的对比表格及其用法说明:
BSON 类型对比表格
| 类型 | 定义 | 特点 | 适用场景 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
bson.M |
map[string]interface{} |
无序键值对,简洁高效 | 查询条件、更新操作等 | bson.M{"name": "Alice", "age": 25} |
bson.D |
[]bson.E |
有序键值对,字段顺序固定 | 命令操作、需要保持顺序的场景 | bson.D{{"name", "Alice"}, {"age", 25}} |
bson.A |
[]interface{} |
BSON数组,用于存储一组值 | 存储数组类型的数据 | bson.A{"Alice", 25, true} |
bson.E |
struct { Key string; Value interface{} } |
单个键值对,用于构建 bson.D |
作为 bson.D 的组成部分 |
bson.E{Key: "name", Value: "Alice"} |
详细说明
1. bson.M
- 特点:无序的键值对集合,基于
map实现。 - 适用场景:
- 查询条件(如
filter)。 - 更新操作(如
$set、$inc)。
- 查询条件(如
- 示例:
filter := bson.M{"name": "Alice", "age": bson.M{"$gt": 20}} update := bson.M{"$set": bson.M{"age": 26}}
2. bson.D
- 特点:有序的键值对集合,基于切片实现。
- 适用场景:
- 需要保持字段顺序的场景(如MongoDB命令、聚合管道)。
- 定义复杂的BSON文档结构。
- 示例:
filter := bson.D{{"name", "Alice"}, {"age", bson.D{{"$gt", 20}}}} pipeline := bson.D{ {"$match", bson.D{{"status", "active"}}}, {"$group", bson.D{{"_id", "$category"}, {"total", bson.D{{"$sum", "$quantity"}}}}}, }
3. bson.A
- 特点:BSON数组,用于存储一组值。
- 适用场景:
- 存储数组类型的数据。
- 用于查询条件中的
$in、$all等操作符。
- 示例:
arr := bson.A{"Alice", 25, true} filter := bson.M{"name": bson.M{"$in": bson.A{"Alice", "Bob"}}}
4. bson.E
- 特点:单个键值对,用于构建
bson.D。 - 适用场景:
- 作为
bson.D的组成部分。 - 需要明确键值对的场景。
- 作为
- 示例:
elem := bson.E{Key: "name", Value: "Alice"} doc := bson.D{elem, {"age", 25}}
5. 其他相关类型
bson.RawValue:表示一个BSON值的原始数据,通常用于解析不确定类型的BSON值。bson.Marshal和bson.Unmarshal:用于将Go类型与BSON数据相互转换。bson.MarshalExtJSON和bson.UnmarshalExtJSON:用于将BSON数据与扩展JSON相互转换。
总结
| 类型 | 有序性 | 性能 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
bson.M |
无序 | 高 | 查询条件、更新操作等 |
bson.D |
有序 | 中 | 命令操作、需要保持顺序的场景 |
bson.A |
有序 | 中 | 存储数组类型的数据 |
bson.E |
有序 | 低 | 作为 bson.D 的组成部分 |
根据具体需求选择合适的类型,可以更高效地操作MongoDB数据。
Bson的常用标签
参考 https://www.mongodb.com/zh-cn/docs/drivers/go/current/fundamentals/bson/
在 Go 语言中,使用 bson 标签可以将结构体字段映射到 MongoDB 文档中的字段。以下是一些常见的 bson 标签选项:
- 字段名映射:
bson:"field_name":将结构体字段映射到 MongoDB 文档中的指定字段名。- 例如:
bson:"username"会将结构体字段映射到 MongoDB 中的username字段。
_id字段:_id是 MongoDB 文档的唯一标识符,是将被标记的字段设置成为 唯一标识符,并且需要将类型修改为primitive.ObjectID,其实是一个长整型。- 例如:ID primitive.ObjectID
bson:"_id,omitempty"
- 忽略字段:
bson:"-":忽略该字段,不将其映射到 MongoDB 文档中。- 例如:
bson:"-"会忽略该字段。
- 内嵌文档:
bson:",inline":如果字段类型是结构或映射字段,则字段在编组时将扁平化, 而在解组时将取消扁平化。- 例如:
bson:",inline"会将结构体字段的内容直接内嵌到 MongoDB 文档中。
- 空值处理:
bson:",omitempty":如果字段值为零值(如0、""、nil等),则忽略该字段,不将其映射到 MongoDB 文档中。- 例如:
bson:",omitempty"会在字段为空时忽略该字段。
- 默认值:
bson:"default":在插入文档时,如果字段值为零值,则使用指定的默认值。- 例如:
bson:"default:unknown"会在字段为空时使用unknown作为默认值。
- 数组和切片:
bson:",array":将字段映射为 MongoDB 中的数组。- 例如:
bson:",array"会将字段映射为数组。
- 二进制数据:
bson:",binary":将字段映射为 MongoDB 中的二进制数据。- 例如:
bson:",binary"会将字段映射为二进制数据。
- 时间戳:
bson:",timestamp":将字段映射为 MongoDB 中的时间戳。- 例如:
bson:",timestamp"会将字段映射为时间戳。
示例
type User struct {
ID primitive.ObjectID `bson:"_id,omitempty"`
Username string `bson:"username"`
Password string `bson:"-"`
Email string `bson:"email,omitempty"`
CreatedAt time.Time `bson:"created_at"`
UpdatedAt time.Time `bson:"updated_at,omitempty"`
Metadata map[string]string `bson:"metadata,inline"`
}
在这个示例中:
ID字段映射到 MongoDB 的_id字段,并且在为空时忽略。Username字段映射到username字段。Password字段被忽略,不会映射到 MongoDB 文档中。Email字段映射到email字段,并且在为空时忽略。CreatedAt字段映射到created_at字段。UpdatedAt字段映射到updated_at字段,并且在为空时忽略。Metadata字段的内容会直接内嵌到 MongoDB 文档中,被压平。
这些标签选项可以帮助你更灵活地控制结构体字段与 MongoDB 文档之间的映射关系。
查看效果
https://www.mongodb.com/zh-cn/docs/drivers/go/current/fundamentals/bson/#struct-tags
有标签
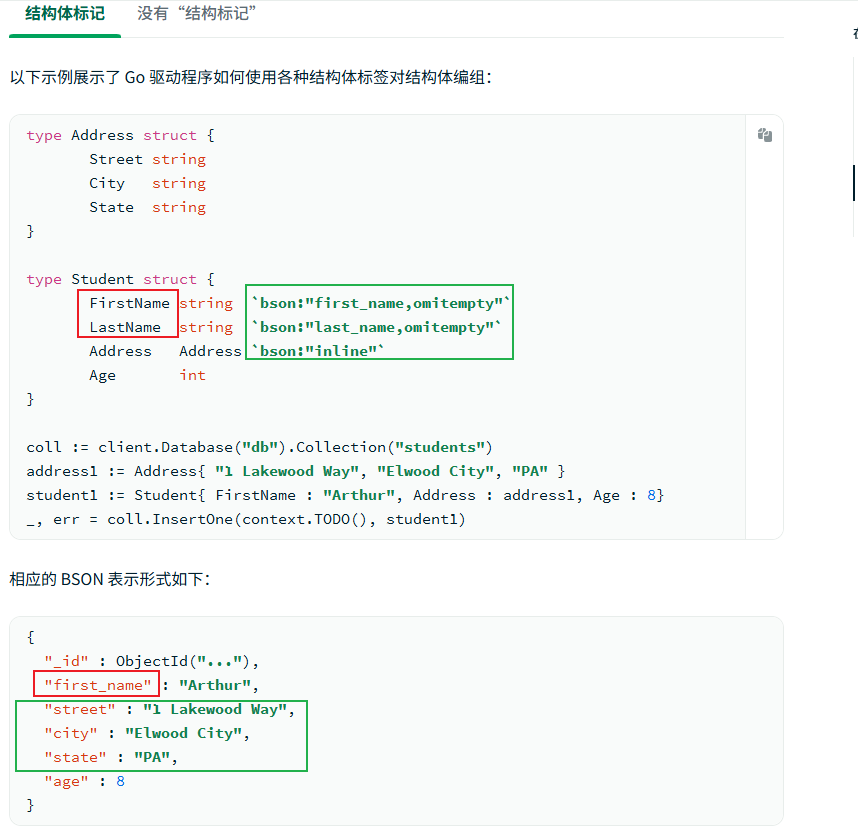
无标签

本文来自博客园,作者:厚礼蝎,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/guangdelw/p/18675211




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
2024-01-16 ubuntu部署fail2ban并配置防止暴力破解