es8.x 版本使用及 java api client
1.为什么不使用High Level REST Client 了
那在 ElasticSearch 7.15.0 版本开始,官方又不建议使用 High Level REST Client 了,为什么呢?因为它是基于原生的 REST API,而这些 API 在某些情况下限制了某些功能的性能优化。与此同时,官方也推出了 Elasticsearch Java 客户端(Java 客户端)作为替代方案。这个新客户端旨在提供更好的性能、更好的稳定性,并且更易于维护和开发。
缺点如下:
1.性能损耗:由于是基于 REST API 的封装,可能存在性能上的一些损耗,比如相比原生的 Java 客户端可能有更高的延迟。
2.功能限制:High Level REST Client 对于一些高级或较新的功能可能提供支持不够或者存在一些限制。
优点如下:
1.易用性高:High Level REST Client 封装了底层的 REST API,提供了了更直观、更易用的开发方法调用 ElasticSearch 的功能。
2.开发效率高
3.较好的兼容性
虽然 High Level REST Client 在易用性和开发效率方面有优势,但是为了获得更好的性能、更好的稳定性,并且获得更多的特性支持,官方建议从 Elasticsearch 7.15.0 版本开始,使用新的 Java 客户端
2.使用 java client 步骤
1. pom 引入
<dependency>
<groupId>co.elastic.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-java</artifactId>
<version>8.14.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.17.0</version>
</dependency>2. 创建 java 客户端
String serverUrl = "http://localhost:9200";
String apiKey = "wM7endtMl1d=U+oJdWFH"; //访问 es 的密钥
// Create the low-level client
RestClient restClient = RestClient
.builder(HttpHost.create(serverUrl))
.setDefaultHeaders(new Header[]{
new BasicHeader("Authorization", "ApiKey " + apiKey)
})
.build();
// Create the transport with a Jackson mapper
ElasticsearchTransport transport = new RestClientTransport(
restClient, new JacksonJsonpMapper());
ElasticsearchClient elasticsearchClient = new ElasticsearchClient(transport);3. 创建索引
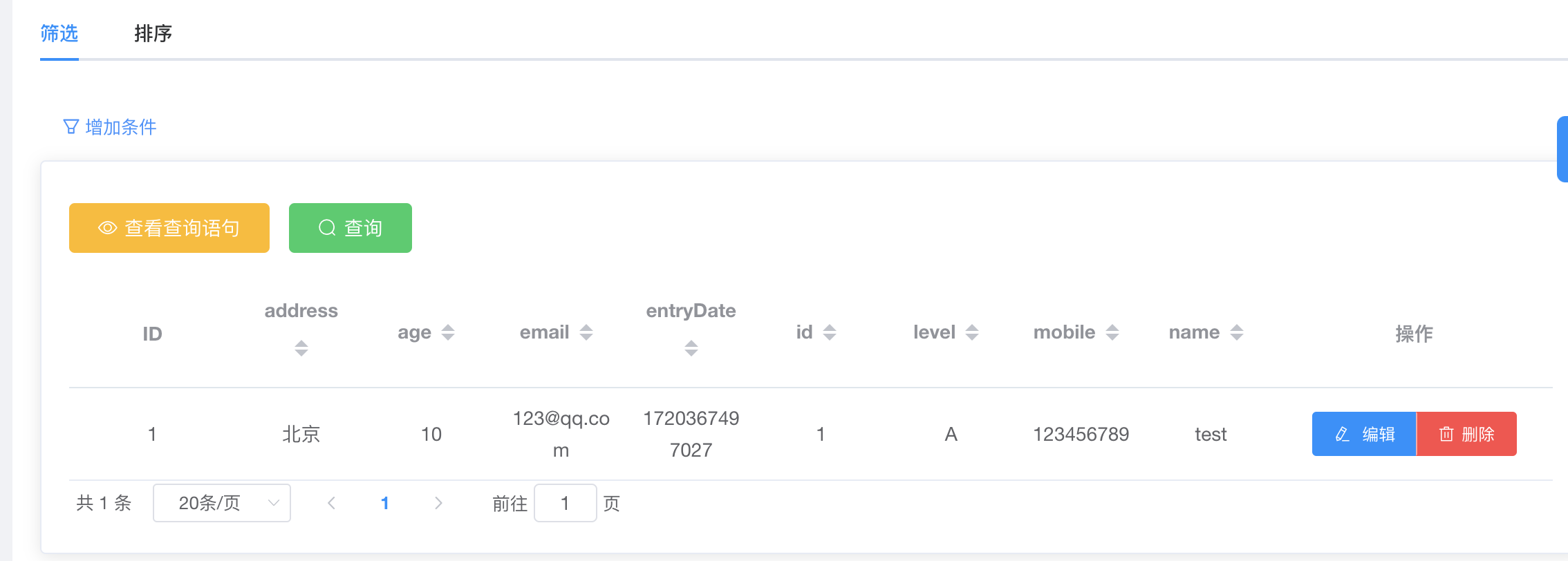
创建一个索引名为“es_2024”的索引
public static void createIndex(ElasticsearchClient esClient) throws IOException {
User user = new User("1", "test", 10, "A", new Date(), "123456789", "123@qq.com", "北京");
IndexResponse response = esClient.index(i -> i
.index("es_2024")
.id(user.getId())
.document(user)
);
System.out.println("Indexed with version " + response.version());
}效果
4. 查询
下面是查询姓名包含李的,且年龄大于等于2岁的人员信息
private static void extracted2(ElasticsearchClient esClient) throws IOException {
String searchText = "李";
int age = 2;
Query byName = MatchQuery.of(m -> m
.field("name")
.query(searchText)
)._toQuery();
Query byMaxPrice = RangeQuery.of(r -> r
.field("age")
.gte(JsonData.of(age))//大于等于
)._toQuery();
SearchResponse<User> response = esClient.search(s -> s
.index("es_2024")
.query(q -> q
.bool(b -> b
.must(byName)
.must(byMaxPrice)
)
),
User.class
);
List<Hit<User>> hits = response.hits().hits();
for (Hit<User> hit : hits) {
User user = hit.source();
System.out.println("Found user " + user.getName() + ", score " + hit.score());
}
}
5. 使用脚本查询
使用脚本模版查询的好处就是,可以不用改代码,直接改模板就好了(前提需要单独创建一个模板的文件,使用时加载该模板)
下面是使用 mustache的一个模板
private static void userScript(ElasticsearchClient esClient) throws IOException {
// Create a script
esClient.putScript(r -> r
.id("query-script")
.script(s -> s
.lang("mustache")// mustache 含义:mustache 模板引擎
.source("{\"query\":{\"match\":{\"{{field}}\":\"{{value}}\"}}}")
));
SearchTemplateResponse<User> response = esClient.searchTemplate(r -> r
.index("es_2024")
.id("query-script")
.params("field", JsonData.of("name"))
.params("value", JsonData.of("李")),
User.class
);
List<Hit<User>> hits = response.hits().hits();
for (Hit<User> hit: hits) {
User user = hit.source();
System.out.println("Found user " + user.getName()+ ", score " + hit.score());
}
}
6. 聚合查询
查询address=南京,并按 age 进行分组查询,此查询只查询结果,所以是 Voild
private static void aggregation(ElasticsearchClient esClient) throws IOException {
String searchText = "南京";
//不使用分词查询,及精确匹配
Query query = TermQuery.of(m -> m
.field("address.keyword")
.value(searchText)
)._toQuery();
SearchResponse<Void> response = esClient.search(b -> b
.index("es_2024")
.size(0)
.query(query)
.aggregations("group_by_age", a -> a
.terms(h -> h
.field("age")
)
),
Void.class
);
List<LongTermsBucket> array = response.aggregations()
.get("group_by_age")
.lterms()
.buckets()
.array();
for (LongTermsBucket bucket: array) {
System.out.println("There are " + bucket.docCount() +
" value " + bucket.key());
}
}
因为address='南京' 且 age=2的只有一个,所以打印出来,bucket 是分组的值,bucket.docCount 是分组值对应的数量
There are 1 value 2 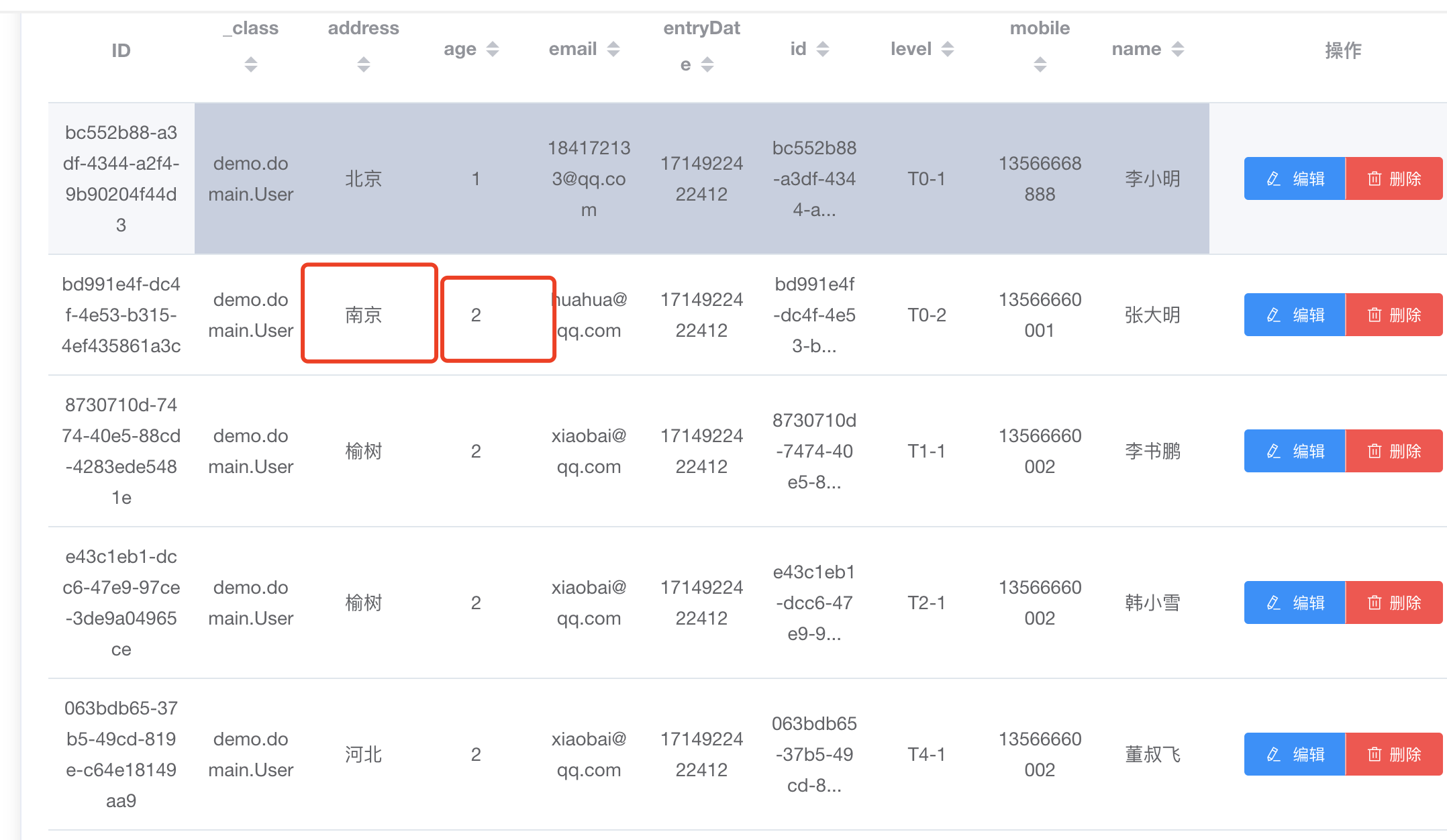
7. 分词查询和不分词查询的注意事项
在Elasticsearch中,查询可以通过多种方式进行,包括全文查询(分词查询)和不分词查询。
全文查询(分词查询):
全文查询通常用于对文本内容进行搜索。它会先分析查询字符串,然后对分析后的词汇进行搜索。这是最常见的搜索方式,也是Elasticsearch默认的搜索方式。
例如,如果你有一个文档,其中包含"Elasticsearch is a great search engine",当你搜索"Elastic search"时,它会将这个查询分解为"Elastic"和"search",然后返回包含这两个词的文档。
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"content": "Elastic search"
}
}
}不分词查询:
不分词查询用于查找完全匹配的词汇。如果你想要查找整个词(例如,整个词汇或短语),你可以使用不分词查询。
例如,如果你有一个文档,其中包含"Elasticsearch is a great search engine",当你搜索"Elasticsearch"时,它会返回包含这个完整词汇的文档。
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"content": "Elasticsearch"
}
}
}在这个例子中,只有包含"Elasticsearch"这个短语的文档会被搜索出来。
另外,如果你不希望Elasticsearch对你的查询进行分析,你可以使用keyword字段进行不分词查询。例如,如果你有一个字段name,它有一个子字段keyword,你可以使用这个字段进行不分词查询。
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"name.keyword": {
"value": "Elasticsearch"
}
}
}
}在这个例子中,只有name.keyword字段完全等于"Elasticsearch"的文档会被搜索出来。
3. es客户端使用工具
找可视化工具,发现支持8.x 的很难找到,这里推荐一个简单好用的ElasticSearch可视化客户端,支持连接6,7,8版本的ES,不妨一试
ElasticView 是一款用来监控ElasticSearch状态和操作ElasticSearch索引的web可视化工具。它由golang开发而成,具有部署方便,占用内存小等优点,官网地址:http://www.elastic-view.cn
- ElasticSearch连接树管理(更方便的切换测试/生产环境)
- 支持权限管理
- 支持sql转换成dsl语法
- 更方便的重建索引
- 任务管理
- 备份管理
- 可将查询内容下载为excel文件
- 可进行索引创建,映射创建,别名创建,索引删除等操作
- 支持版本
6.x,7.x,8.x - 支持类似Navicat功能
- docker部署
- 支持sqlite3(免安装gcc版)
- 数据抽取功能
作者:guanbin —— 纵码万里千山
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/guanbin-529/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。


