(1)前言:
这次blog内容是第6-8次pta,主要是成绩计算系列,第6次pta是只有一道题,是成绩计算系列的开始,和菜单第一次加大难度一样,有点无从下手,但相对菜单简单一些,主要就是课程性质的分别计算。课程成绩统计程序2是在课程成绩统计程序1的基础上增加了实验以及新的成绩计算方式,课程成绩统计程序3是在课程成绩统计程序2的基础上增加了对于实验课程计算成绩时候的比重分配以及课程成绩计算的方式,总之就是难度逐渐加大,但都是在一个模块上添加。
(2)设计与分析:
第六次题目集
某高校课程从性质上分为:必修课、选修课,从考核方式上分为:考试、考察。
考试的总成绩由平时成绩、期末成绩分别乘以权重值得出,比如平时成绩权重0.3,期末成绩权重0.7,总成绩=平时成绩*0.3+期末成绩*0.7。
考察的总成绩直接等于期末成绩
必修课的考核方式必须为考试,选修课可以选择考试、考察任一考核方式。
1、输入:
包括课程、课程成绩两类信息。
课程信息包括:课程名称、课程性质、考核方式(可选,如果性质是必修课,考核方式可以没有)三个数据项。
课程信息格式:课程名称+英文空格+课程性质+英文空格+考核方式
课程性质输入项:必修、选修
考核方式输入选项:考试、考察
课程成绩信息包括:学号、姓名、课程名称、平时成绩(可选)、期末成绩
课程信息格式:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+课程名称+英文空格+平时成绩+英文空格+期末成绩
以上信息的相关约束:
1)平时成绩和期末成绩的权重默认为0.3、0.7
2)成绩是整数,不包含小数部分,成绩的取值范围是【0,100】
3)学号由8位数字组成
4)姓名不超过10个字符
5)课程名称不超过10个字符
6)不特别输入班级信息,班级号是学号的前6位。
2、输出:
输出包含三个部分,包括学生所有课程总成绩的平均分、单门课程成绩平均分、单门课程总成绩平均分、班级所有课程总成绩平均分。
为避免误差,平均分的计算方法为累加所有符合条件的单个成绩,最后除以总数。
1)学生课程总成绩平均分按学号由低到高排序输出
格式:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+总成绩平均分
如果某个学生没有任何成绩信息,输出:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+"did not take any exams"
2)单门课程成绩平均分分为三个分值:平时成绩平均分(可选)、期末考试平均分、总成绩平均分,按课程名称的字符顺序输出
格式:课程名称+英文空格+平时成绩平均分+英文空格+期末考试平均分+英文空格+总成绩平均分
如果某门课程没有任何成绩信息,输出:课程名称+英文空格+"has no grades yet"
3)班级所有课程总成绩平均分按班级由低到高排序输出
格式:班级号+英文空格+总成绩平均分
如果某个班级没有任何成绩信息,输出:班级名称+英文空格+ "has no grades yet"
异常情况:
1)如果解析某个成绩信息时,课程名称不在已输入的课程列表中,输出:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+":"+课程名称+英文空格+"does not exist"
2)如果解析某个成绩信息时,输入的成绩数量和课程的考核方式不匹配,输出:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+": access mode mismatch"
以上两种情况如果同时出现,按第一种情况输出结果。
3)如果解析某个课程信息时,输入的课程性质和课程的考核方式不匹配,输出:课程名称+" : course type & access mode mismatch"
4)格式错误以及其他信息异常如成绩超出范围等,均按格式错误处理,输出"wrong format"
5)若出现重复的课程/成绩信息,只保留第一个课程信息,忽略后面输入的。
信息约束:
1)成绩平均分只取整数部分,小数部分丢弃
参考类图:

输入样例1:
仅有课程。例如:
java 必修 考试
数据结构 选修 考试
形式与政治 选修 考察
end
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
java has no grades yet
数据结构 has no grades yet
形式与政治 has no grades yet
输入样例2:
单门考试课程 单个学生。例如:
java 必修 考试
20201103 张三 java 20 40
end
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
20201103 张三 34
java 20 40 34
202011 34
输入样例3:
单门考察课程 单个学生。例如:
java 选修 考察
20201103 张三 java 40
end
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
20201103 张三 40
java 40 40
202011 40
输入样例4:
考试课程 单个学生 不匹配的考核方式。例如:
java 必修 考试
20201103 张三 java 20
end
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
20201103 张三 : access mode mismatch
20201103 张三 did not take any exams
java has no grades yet
202011 has no grades yet
输入样例5:
单门课程,单个学生,课程类型与考核类型不匹配。例如:
java 必修 考察
20201103 张三 java 40
end
输出样例5:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
java : course type & access mode mismatch
java does not exist
20201103 张三 did not take any exams
202011 has no grades yet
输入样例6:
单门课程,多个学生。例如:
java 选修 考察
20201103 李四 java 60
20201104 王五 java 60
20201101 张三 java 40
end
输出样例6:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
20201101 张三 40
20201103 李四 60
20201104 王五 60
java 53 53
202011 53
输入样例7:
单门课程,单个学生,课程类型与考核类型不匹配。例如:
形式与政治 必修 考试
数据库 选修 考试
java 选修 考察
数据结构 选修 考察
20201103 李四 数据结构 70
20201103 李四 形式与政治 80 90
20201103 李四 java 60
20201103 李四 数据库 70 78
end
输出样例7:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
20201103 李四 73
java 60 60
数据结构 70 70
数据库 70 78 75
形式与政治 80 90 87
202011 73
输入样例8:
单门课程,单个学生,成绩越界。例如:
数据结构 选修 考察
20201103 李四 数据结构 101
end
输出样例8:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
wrong format
数据结构 has no grades yet
输入样例9:
多门课程,多个学生,多个成绩。例如:
形式与政治 必修 考试
数据库 选修 考试
java 选修 考察
数据结构 选修 考察
20201205 李四 数据结构 70
20201103 李四 形式与政治 80 90
20201102 王五 java 60
20201211 张三 数据库 70 78
end
输出样例9:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
20201102 王五 60
20201103 李四 87
20201205 李四 70
20201211 张三 75
java 60 60
数据结构 70 70
数据库 70 78 75
形式与政治 80 90 87
202011 73
202012 72
2.类图
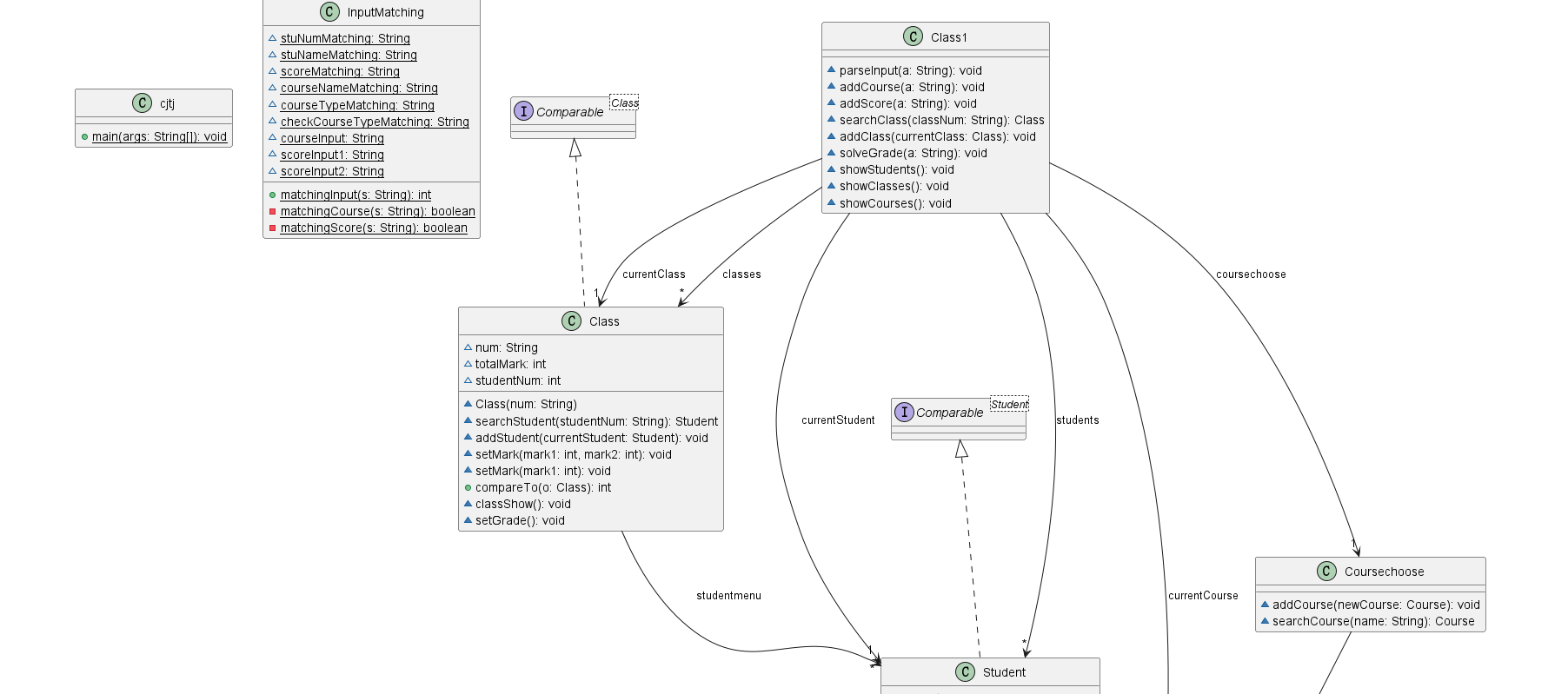
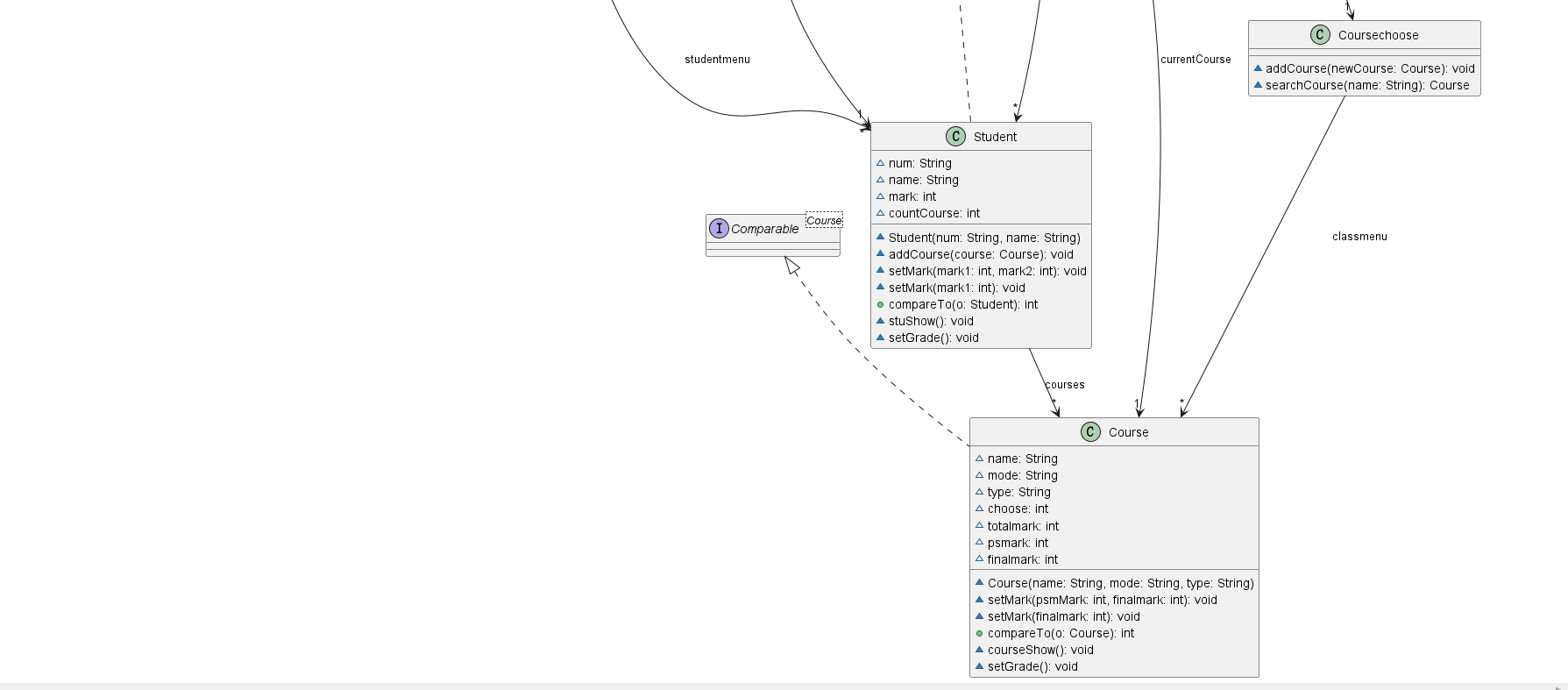
3.题目分析
由题目要求,首先要创建相关的几个类,进行大致架构,分别是InputMatching类,Class类,Class1类,Course类,Coursechoose类,Student类,.然后再对应的类里细化。
-
首先在
Main类中,通过Scanner类获取用户输入的信息,并使用Class1类的parseInput()方法解析输入的信息,并调用相应的方法进行处理。 -
InputMatching类定义了一些用于匹配输入格式的正则表达式,并提供了一个静态方法matchingInput()用于判断输入的类型。 -
Course类表示一门课程,包含了课程的名称、性质、考查方式以及成绩信息。其中,setMark()方法用于设置课程的平时成绩和最后成绩,并计算总成绩。 -
Coursechoose类表示所有课程的集合,可以添加课程和根据课程名称进行查找。 -
Class类表示一个班级,包含班级编号、总分和学生数量的信息,以及学生的集合。其中,setMark()方法用于设置班级的总分。 -
Student类表示一个学生,包含学号、姓名和成绩的信息,以及所选课程的集合。其中,setMark()方法用于设置学生的成绩。 -
Class1类是主要的业务逻辑类,包含了班级、学生和课程的集合,以及一些操作这些集合的方法。其中,parseInput()方法根据输入的内容调用相应的方法进行处理,addCourse()方法用于添加课程,addScore()方法用于添加成绩,searchClass()方法用于根据班级编号查找班级,addClass()方法用于添加班级,solveGrade()方法用于处理成绩信息,showStudents()方法用于展示学生的成绩,showClasses()方法用于展示班级的成绩,showCourses()方法用于展示课程的成绩。 -
在
Main类的main方法中,通过循环读取用户输入的信息,并调用parseInput()方法进行处理,直到用户输入"end"结束。最后调用class1对象的showStudents()、showClasses()和showCourses()方法展示学生、班级和课程的成绩情况。
4.源代码
import java.text.Collator; import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner into = new Scanner(System.in); Class1 class1 = new Class1(); String a; while(!(a=into.nextLine()).equals("end")) { class1.parseInput(a); } class1.showStudents(); class1.showCourses(); class1.showClasses(); } } class InputMatching { static String stuNumMatching = "[0-9]{8}";//8个0-9的数字 static String stuNameMatching = "\\S{1,10}";//1到10个非空格(TAB)字符 static String scoreMatching = "([1-9]?[0-9]|100)"; static String courseNameMatching = "\\S{1,10}";//1到10个非空格(TAB)字符 static String courseTypeMatching = "(选修|必修)"; static String checkCourseTypeMatching = "(考试|考察)"; //courseInput用于定义课程信息模式(正则表达式) static String courseInput = courseNameMatching + " " + courseTypeMatching + " " + checkCourseTypeMatching; //scoreInput用于定义成绩信息模式(正则表达式) static String scoreInput1 = stuNumMatching + " " + stuNameMatching + " " + courseNameMatching + " " + scoreMatching + " "+scoreMatching; static String scoreInput2 = stuNumMatching + " " + stuNameMatching + " " + courseNameMatching + " " + scoreMatching ; public static int matchingInput(String s) { if (matchingCourse(s)) { return 1; } if (matchingScore(s)) { return 2; } return 0; } private static boolean matchingCourse(String s) { return s.matches(courseInput); } private static boolean matchingScore(String s) { return s.matches(scoreInput1)||s.matches(scoreInput2); } } class Course implements Comparable<Course> { String name;//课程名字 String mode;//课程性质 String type;//考查方式 int choose; int totalmark;//这门课的分数 int psmark;//总的平时成绩 int finalmark;//最后的成绩 Course(String name, String mode, String type) { this.name = name; this.mode = mode; this.type = type; this.totalmark = 0; this.psmark = 0; this.finalmark = 0; this.choose = 0; } void setMark(int psmMark,int finalmark) { this.psmark +=psmark; this.finalmark +=finalmark; this.choose++; } void setMark(int finalmark) { this.finalmark+=finalmark; this.choose++; } @Override public int compareTo(Course o) { Collator collator= Collator.getInstance(Locale.CHINA); return collator.compare(this.name,o.name); } void courseShow() { setGrade(); if(this.choose==0) { System.out.println(this.name+" has no grades yet"); } else { if(this.psmark == 0) { System.out.println(this.name+" "+this.finalmark+" "+this.finalmark); } else { System.out.println(this.name+" "+this.psmark+" "+this.finalmark+" "+this.totalmark); } } } void setGrade() { if(this.choose==0){} else { this.psmark = this.psmark/this.choose; this.finalmark = this.finalmark / this.choose; this.totalmark = (int) (this.psmark*0.3+this.finalmark*0.7); } } } class Coursechoose { ArrayList<Course> classmenu= new ArrayList<>(); void addCourse(Course newCourse) { classmenu.add(newCourse); } Course searchCourse(String name) { for (Course c : classmenu) { if (c.name.equals(name)) return c; } return null; } } class Class implements Comparable<Class> { String num; int totalMark; int studentNum; Class(String num) { this.num = num; this.studentNum=0; this.totalMark=0; } ArrayList <Student> studentmenu = new ArrayList<>(); Student searchStudent(String studentNum) { for (Student student : this.studentmenu) { if (student.num.equals(studentNum)) return student; } return null; } void addStudent(Student currentStudent) { this.studentmenu.add(currentStudent); this.studentNum++; } void setMark(int mark1,int mark2) { this.totalMark += mark1*0.3 +mark2 *0.7; } void setMark(int mark1) { this.totalMark += mark1; } @Override public int compareTo(Class o) { return this.num.compareTo(o.num); } void classShow() { setGrade(); if(this.studentNum==0||this.totalMark==0) { System.out.println(this.num + " has no grades yet"); } else { System.out.println(this.num+" "+this.totalMark); } } void setGrade() { if(this.studentNum == 0){} else { for(int i=0 ;i<this.studentmenu.size() ;i++) { if(this.studentmenu.get(i).countCourse>1) { this.studentNum += this.studentmenu.get(i).countCourse-1; } } this.totalMark = this.totalMark/this.studentNum; } } } class Student implements Comparable<Student> { String num; String name; int mark; int countCourse; ArrayList<Course> courses = new ArrayList<>(); Student(String num,String name) { this.num = num; this.name = name; this.mark = 0; this.countCourse = 0; } void addCourse(Course course) { this.courses.add(course); this.countCourse++; } void setMark(int mark1,int mark2) { this.mark += (int) (mark1*0.3 + mark2*0.7); } void setMark(int mark1) { this.mark += mark1; } @Override public int compareTo(Student o) { return this.num.compareTo(o.num); } void stuShow() { setGrade(); if(this.mark==-1) { System.out.println(this.num+" "+this.name+" did not take any exams"); } else { System.out.println(this.num+" "+this.name+" "+this.mark); } } void setGrade() { if(this.countCourse==0) { this.mark=-1; } else { this.mark=this.mark/this.countCourse; } } } class Class1 { Class currentClass ; Student currentStudent ; Course currentCourse; ArrayList<Class> classes = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<>(); Coursechoose coursechoose=new Coursechoose(); void parseInput(String a) { switch (InputMatching.matchingInput(a)) { case 0 : System.out.println("wrong format"); break; case 1 : addCourse(a); break; case 2 : addScore(a); break; } } void addCourse(String a) { String [] b = a.split(" "); currentCourse = coursechoose.searchCourse(b[0]); if(currentCourse == null) { if (a.matches("\\S* 必修* 考察")) { System.out.println(b[0] + " : course type & access mode mismatch"); } else { if (a.matches("\\S* 必修* 考试")) { currentCourse = new Course(b[0],b[1],b[2]); } else if (a.matches("\\S* 选修* 考试")) { currentCourse = new Course(b[0],b[1],b[2]); } else if (a.matches("\\S* 选修* 考察")) { currentCourse = new Course(b[0],b[1],b[2]); } coursechoose.addCourse(currentCourse); } } } void addScore(String a) { String[] s=a.split(" "); String classNum = s[0].substring(0, 6); String studentNum = s[0]; String studentName = s[1]; if(searchClass(classNum)==null) { currentClass = new Class(classNum); addClass(currentClass); currentStudent = new Student(studentNum, studentName); currentClass.addStudent(currentStudent); students.add(currentStudent); solveGrade(a); } else { currentClass = searchClass(classNum); if(currentClass.searchStudent(studentNum) == null) { currentStudent = new Student(studentNum,studentName); currentClass.addStudent(currentStudent); if(students.contains(currentStudent)){} else{ students.add(currentStudent); } } else { currentStudent = currentClass.searchStudent(studentNum); if(students.contains(currentStudent)){} else{ students.add(currentStudent); } } solveGrade(a); } } Class searchClass(String classNum) { for (Class aClass : classes) { if (aClass.num.equals(classNum)) return aClass; } return null; } void addClass(Class currentClass) { classes.add(currentClass); } void solveGrade(String a) { String [] b = a.split(" "); if(b.length==5) { int pscore = Integer.parseInt(b[3]); int examScore = Integer.parseInt(b[4]); if( coursechoose.searchCourse(b[2])!=null) { currentCourse = coursechoose.searchCourse(b[2]); if(currentCourse.type.equals("考试")) { if(currentStudent.courses.contains(currentCourse)){} else { currentStudent.addCourse(currentCourse); currentStudent.setMark(pscore, examScore); currentClass.setMark(pscore, examScore); currentCourse.setMark(pscore, examScore); } } else { System.out.println(b[0] + " " + b[1] + " : access mode mismatch"); } } else { System.out.println(b[2] + " does not exist"); } } else { int normalScore = Integer.parseInt(b[3]); if( coursechoose.searchCourse(b[2])!=null) { currentCourse = coursechoose.searchCourse(b[2]); if(currentCourse.type.equals("考察")) { if(currentStudent.courses.contains(currentCourse)){} else { currentStudent.addCourse(currentCourse); currentStudent.setMark(normalScore); currentClass.setMark(normalScore); currentCourse.setMark(normalScore); } } else { System.out.println(b[0] + " " + b[1] + " : access mode mismatch"); } } else { System.out.println(b[2] + "dose not exist"); } } } void showStudents() { Collections.sort(students); for(Student s : students) { s.stuShow(); } } void showClasses() { Collections.sort(classes); for(Class s : classes) { s.classShow(); } } void showCourses() { Collections.sort( coursechoose.classmenu); for(Course s : coursechoose.classmenu) { s.courseShow(); } } }
第七次题目集

输入多个学生的成绩信息,包括:学号、姓名、成绩。
学号是每个学生的唯一识别号,互不相同。
姓名可能会存在重复。
使用HashMap存储学生信息,并实现根据学号的检索功能
输入格式:
输入多个学生的成绩信息,每个学生的成绩信息格式:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+成绩
以“end”为输入结束标志
end之后输入某个学号,执行程序输出该生的详细信息
输出格式:
输出查询到的学生信息格式:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+成绩
如果没有查询到,则输出:"The student "+查询的学号+" does not exist"
源代码
import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); Map<String, Student> studentMap = new HashMap<>(); String input = ""; while (!input.equals("end")) { // System.out.print("请输入学生信息(学号 姓名 分数)(输入end结束录入):"); input = sc.nextLine(); if (!input.equals("end")) { String[] inputArray = input.split(" "); if (inputArray.length == 3) { String studentId = inputArray[0]; String name = inputArray[1]; int grade = Integer.parseInt(inputArray[2]); Student student = new Student(name, grade); studentMap.put(studentId, student); } else { System.out.println("wrong format!"); } } } // 查询学生信息 // System.out.print("请输入要查询的学生学号:"); String queryId = sc.nextLine(); Student queryResult = queryStudentInfo(queryId, studentMap); if (queryResult != null) { System.out.println(queryId + " " + queryResult.getName() + " " + queryResult.getGrade()); } else { System.out.println("The student "+queryId+ " does not exist"); } } private static Student queryStudentInfo(String studentId, Map<String, Student> studentMap) { return studentMap.get(studentId); } } class Student { private String name; private int grade; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int grade) { this.name = name; this.grade = grade; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getGrade() { return grade; } public void setGrade(int grade) { this.grade = grade; } }
输入多个学生的成绩信息,包括:学号、姓名、成绩。
学号是每个学生的唯一识别号,互不相同。
姓名可能会存在重复。
要求:使用HashMap存储学生信息。
输入格式:
输入多个学生的成绩信息,每个学生的成绩信息格式:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+成绩
以“end”为输入结束标志
输出格式:
按学号从大到小的顺序输出所有学生信息,每个学生信息的输出格式:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+成绩
源代码
import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Set; import java.util.TreeMap; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); Map<String, Student> studentMap = new HashMap<>(); String input = ""; while (!input.equals("end")) { input = sc.nextLine(); if (!input.equals("end")) { String[] inputArray = input.split(" "); if (inputArray.length == 3) { String studentId = inputArray[0]; String name = inputArray[1]; int grade = Integer.parseInt(inputArray[2]); Student student = new Student(name, grade); studentMap.put(studentId, student); } else { System.out.println("wrong format!"); } } } TreeMap<String, Student> sortedMap = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<String>() { @Override public int compare(String o1, String o2) { return o2.compareTo(o1); } }); sortedMap.putAll(studentMap); Set<Map.Entry<String, Student>> entrySet = sortedMap.entrySet(); for (Map.Entry<String, Student> entry : entrySet) { String key = entry.getKey(); Student value = entry.getValue(); System.out.println(key + " " + value.getName() + " " + value.getGrade()); } } } class Student { private String name; private int grade; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int grade) { this.name = name; this.grade = grade; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getGrade() { return grade; } public void setGrade(int grade) { this.grade = grade; } }
设计一个动物发生模拟器,用于模拟不同动物的叫声。比如狮吼、虎啸、狗旺旺、猫喵喵……。
定义抽象类Animal,包含两个抽象方法:获取动物类别getAnimalClass()、动物叫shout();
然后基于抽象类Animal定义狗类Dog、猫类Cat和山羊Goat,用getAnimalClass()方法返回不同的动物类别(比如猫,狗,山羊),用shout()方法分别输出不同的叫声(比如喵喵、汪汪、咩咩)。
最后编写AnimalShoutTest类测试,输出:
猫的叫声:喵喵
狗的叫声:汪汪
山羊的叫声:咩咩
其中,在AnimalShoutTestMain类中,用speak(Animal animal){}方法输出动物animal的叫声,在main()方法中调用speak()方法,分别输出猫、狗和山羊对象的叫声。
请在下面的【】处添加代码。
//动物发生模拟器. 请在下面的【】处添加代码。
public class AnimalShoutTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat cat = new Cat();
Dog dog = new Dog();
Goat goat = new Goat();
speak(cat);
speak(dog);
speak(goat);
}
//定义静态方法speak()
【】
}
//定义抽象类Animal
【】class Animal{
【】
}
//基于Animal类,定义猫类Cat,并重写两个抽象方法
class Cat 【】{
【】
【】
}
//基于Animal类,定义狗类Dog,并重写两个抽象方法
class Dog 【】{
【】
【】
}
//基于Animal类,定义山羊类Goat,并重写两个抽象方法
class Goat 【】{
【】
【】
}
源代码
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Cat cat = new Cat(); Dog dog = new Dog(); Goat goat = new Goat(); speak(cat); speak(dog); speak(goat); } //定义静态方法speak() public static void speak(Animal animal){ System.out.println(animal.getAnimalClass()+"的叫声:"+animal.shout()); } } //定义抽象类Animal abstract class Animal{ public abstract String getAnimalClass(); public abstract String shout(); } //基于Animal类,定义猫类Cat,并重写两个抽象方法 class Cat extends Animal{ public String getAnimalClass(){ return "猫"; } public String shout(){ return "喵喵"; } } //基于Animal类,定义狗类Dog,并重写两个抽象方法 class Dog extends Animal{ public String getAnimalClass(){ return "狗"; } public String shout(){ return "汪汪"; } } //基于Animal类,定义山羊类Goat,并重写两个抽象方法 class Goat extends Animal{ public String getAnimalClass(){ return "山羊"; } public String shout(){ return "咩咩"; } }
课程成绩统计程序-2在第一次的基础上增加了实验课,以下加粗字体显示为本次新增的内容。
某高校课程从性质上分为:必修课、选修课、实验课,从考核方式上分为:考试、考察、实验。
考试的总成绩由平时成绩、期末成绩分别乘以权重值得出,比如平时成绩权重0.3,期末成绩权重0.7,总成绩=平时成绩*0.3+期末成绩*0.7。
考察的总成绩直接等于期末成绩
实验的总成绩等于课程每次实验成绩的平均分
必修课的考核方式必须为考试,选修课可以选择考试、考察任一考核方式。实验课的成绩必须为实验。
1、输入:
包括课程、课程成绩两类信息。
课程信息包括:课程名称、课程性质、考核方式(可选,如果性质是必修课,考核方式可以没有)三个数据项。
课程信息格式:课程名称+英文空格+课程性质+英文空格+考核方式
课程性质输入项:必修、选修、实验
考核方式输入选项:考试、考察、实验
考试/考查课程成绩信息包括:学号、姓名、课程名称、平时成绩(可选)、期末成绩
考试/考查课程信息格式:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+课程名称+英文空格+平时成绩+英文空格+期末成绩
实验课程成绩信息包括:学号、姓名、课程名称、实验次数、每次成绩
实验次数至少4次,不超过9次
实验课程信息格式:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+课程名称+英文空格+实验次数+英文空格+第一次实验成绩+...+英文空格+最后一次实验成绩
以上信息的相关约束:
1)平时成绩和期末成绩的权重默认为0.3、0.7
2)成绩是整数,不包含小数部分,成绩的取值范围是【0,100】
3)学号由8位数字组成
4)姓名不超过10个字符
5)课程名称不超过10个字符
6)不特别输入班级信息,班级号是学号的前6位。
2、输出:
输出包含三个部分,包括学生所有课程总成绩的平均分、单门课程成绩平均分、单门课程总成绩平均分、班级所有课程总成绩平均分。
为避免误差,平均分的计算方法为累加所有符合条件的单个成绩,最后除以总数。
1)学生课程总成绩平均分按学号由低到高排序输出
格式:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+总成绩平均分
如果某个学生没有任何成绩信息,输出:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+"did not take any exams"
2)单门课程成绩平均分分为三个分值:平时成绩平均分(可选)、期末考试平均分、总成绩平均分,按课程名称的字符顺序输出
考试/考察课程成绩格式:课程名称+英文空格+平时成绩平均分+英文空格+期末考试平均分+英文空格+总成绩平均分
实验课成绩格式:课程名称+英文空格+总成绩平均分
如果某门课程没有任何成绩信息,输出:课程名称+英文空格+"has no grades yet"
3)班级所有课程总成绩平均分按班级由低到高排序输出
格式:班级号+英文空格+总成绩平均分
如果某个班级没有任何成绩信息,输出:班级名称+英文空格+ "has no grades yet"
异常情况:
1)如果解析某个成绩信息时,课程名称不在已输入的课程列表中,输出:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+":"+课程名称+英文空格+"does not exist"
2)如果解析某个成绩信息时,输入的成绩数量和课程的考核方式不匹配,输出:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+": access mode mismatch"
以上两种情况如果同时出现,按第一种情况输出结果。
3)如果解析某个课程信息时,输入的课程性质和课程的考核方式不匹配,输出:课程名称+" : course type & access mode mismatch"
4)格式错误以及其他信息异常如成绩超出范围等,均按格式错误处理,输出"wrong format"
5)若出现重复的课程/成绩信息,只保留第一个课程信息,忽略后面输入的。
信息约束:
1)成绩平均分只取整数部分,小数部分丢弃
参考类图(与第一次相同,其余内容自行补充):
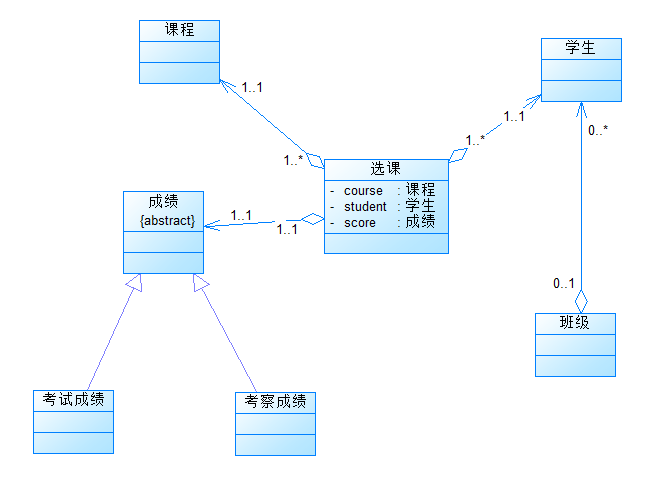
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
java 实验 实验
20201103 张三 java 4 70 80 90
end
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
20201103 张三 : access mode mismatch
20201103 张三 did not take any exams
java has no grades yet
202011 has no grades yet
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
java 实验 实验
20201103 张三 java 3 70 80 90
end
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
wrong format
java has no grades yet
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
java 必修 实验
20201103 张三 java 3 70 80 90 100
end
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
java : course type & access mode mismatch
wrong format
输入样例4:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
java 必修 实验
20201103 张三 java 4 70 80 90 105
end
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
java : course type & access mode mismatch
wrong format
输入样例5:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
java 选修 考察
C语言 选修 考察
java实验 实验 实验
编译原理 必修 考试
20201101 王五 C语言 76
20201216 李四 C语言 78
20201307 张少军 编译原理 82 84
20201103 张三 java实验 4 70 80 90 100
20201118 郑觉先 java 80
20201328 刘和宇 java 77
20201220 朱重九 java实验 4 60 60 80 80
20201132 王萍 C语言 40
20201302 李梦涵 C语言 68
20201325 崔瑾 编译原理 80 84
20201213 黄红 java 82
20201209 赵仙芝 java 76
end
输出样例5:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
20201101 王五 76
20201103 张三 85
20201118 郑觉先 80
20201132 王萍 40
20201209 赵仙芝 76
20201213 黄红 82
20201216 李四 78
20201220 朱重九 70
20201302 李梦涵 68
20201307 张少军 83
20201325 崔瑾 82
20201328 刘和宇 77
C语言 65 65
java 78 78
java实验 77
编译原理 81 84 82
202011 70
202012 76
202013 77
2.类图


3.题目分析
对比成绩统计1,增加了一个实验课程,首先还是包括了学生、课程和班级三个类,以及一个主类用于输入和输出。
在主类Main中,使用Scanner类读取用户输入,并通过while循环不断解析输入,直到输入为"end"为止。然后调用Class1类的方法解析输入,并最终输出学生、课程和班级的成绩信息。
InputMatching类用于匹配输入的字符串是否符合指定的格式,包括学生学号、学生姓名、课程名称、课程性质等。
Course类表示课程,包括课程名称、课程性质、考查方式等属性,以及设置和获取成绩的方法。
Coursechoose类表示课程选择,包括一个课程列表,可以添加课程和查找课程。
Class类表示班级,包括班级编号、总成绩、学生数量等属性,以及添加学生和设置成绩的方法。
Student类表示学生,包括学生学号、姓名、成绩等属性,以及添加课程和设置成绩的方法。
Class1类是主要的逻辑处理类,包括解析输入、添加课程和成绩、查找班级和学生等方法,以及展示学生、课程和班级的成绩信息的方法。
在解析输入时,根据输入的格式,判断是添加课程还是添加成绩,并根据课程和学生的信息进行相应的操作。
最后,在主类的main方法中,创建一个Class1对象,然后通过循环读取用户输入,调用Class1对象的方法进行处理,并最终输出成绩信息。
4.源代码
import java.text.Collator; import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner into = new Scanner(System.in); Class1 class1 = new Class1(); String a; while(!(a=into.nextLine()).equals("end")) { class1.parseInput(a); } class1.showStudents(); class1.showCourses(); class1.showClasses(); } } class InputMatching { static String stuNumMatching = "[0-9]{8}";//8个0-9的数字 static String stuNameMatching = "\\S{1,10}";//1到10个非空格(TAB)字符 static String scoreMatching = "([1-9]?[0-9]|100)"; static String courseNameMatching = "\\S{1,10}";//1到10个非空格(TAB)字符 static String courseTypeMatching = "(选修|必修|实验)"; static String checkCourseTypeMatching = "(考试|考察|实验)"; //courseInput用于定义课程信息模式(正则表达式) static String courseInput = courseNameMatching + " " + courseTypeMatching + " " + checkCourseTypeMatching; //scoreInput用于定义成绩信息模式(正则表达式) static String scoreInput1 = stuNumMatching + " " + stuNameMatching + " " + courseNameMatching + " " + scoreMatching + " " + scoreMatching; static String scoreInput2 = stuNumMatching + " " + stuNameMatching + " " + courseNameMatching + " " + scoreMatching; static String expInput = stuNumMatching + " " + stuNameMatching + " " + courseNameMatching + " " + "([4-9]|[1-9][0-9])" + "( (" + scoreMatching + "){4,9}){1,}"; public static int matchingInput(String s) { if (matchingCourse(s)) { return 1; } if (matchingScore(s)) { return 2; } if (matchingExp(s)) { return 2; } return 0; } private static boolean matchingCourse(String s) { return s.matches(courseInput); } private static boolean matchingScore(String s) { return s.matches(scoreInput1) || s.matches(scoreInput2); } private static boolean matchingExp(String s) { return s.matches(expInput); } } class Course implements Comparable<Course> { String name;//课程名字 String mode;//课程性质 String type;//考查方式 int choose; int totalmark;//这门课的分数 int psmark;//总的平时成绩 int finalmark;//最后的成绩 int expTimes;//实验次数 ArrayList<Integer> expMarks;//每次实验成绩 Course(String name, String mode, String type) { this.name = name; this.mode = mode; this.type = type; this.totalmark = 0; this.psmark = 0; this.finalmark = 0; this.choose = 0; this.expTimes = 0; this.expMarks = new ArrayList<>(); } void setMark(int psmMark, int finalmark) { this.psmark += psmark; this.finalmark += finalmark; this.choose++; } void setMark(int finalmark) { this.finalmark += finalmark; this.choose++; } void setExpMark(ArrayList<Integer> expMarks) { int expTotal = 0; int finalmark; for (int i = 0; i < this.expTimes; i++) { expTotal += this.expMarks.get(i); } finalmark = expTotal / this.expTimes; this.finalmark += finalmark; this.choose++; } @Override public int compareTo(Course o) { Collator collator = Collator.getInstance(Locale.CHINA); return collator.compare(this.name, o.name); } void courseShow() { setGrade(); if (this.choose == 0) { System.out.println(this.name + " has no grades yet"); } else { if (this.mode.equals("实验")) { int expTotal = 0; for (int i = 0; i < this.expTimes; i++) { expTotal += this.expMarks.get(i); } System.out.println(this.name + " " + expTotal / this.expTimes); } else { if (this.psmark == 0) { System.out.println(this.name + " " + this.finalmark + " " + this.finalmark); } else { System.out.println(this.name + " " + this.psmark + " " + this.finalmark + " " + this.totalmark); } } } } void setGrade() { if (this.choose == 0) { } else { if (this.mode.equals("实验")) { int expTotal = 0; for (int i = 0; i < this.expTimes; i++) { expTotal += this.expMarks.get(i); } this.totalmark = expTotal / this.expTimes; } else { this.psmark = this.psmark / this.choose; this.finalmark = this.finalmark / this.choose; this.totalmark = (int) (this.psmark * 0.3 + this.finalmark * 0.7); } } } } class Coursechoose { ArrayList<Course> classmenu = new ArrayList<>(); void addCourse(Course newCourse) { classmenu.add(newCourse); } Course searchCourse(String name) { for (Course c : classmenu) { if (c.name.equals(name)) return c; } return null; } } class Class implements Comparable<Class> { String num; int totalMark; int studentNum; int expTimes;//实验次数 ArrayList<Integer> expMarks;//每次实验成绩 Class(String num) { this.num = num; this.studentNum = 0; this.totalMark = 0; this.expTimes = 0; this.expMarks = new ArrayList<>(); } ArrayList<Student> studentmenu = new ArrayList<>(); Student searchStudent(String studentNum) { for (Student student : this.studentmenu) { if (student.num.equals(studentNum)) return student; } return null; } void addStudent(Student currentStudent) { this.studentmenu.add(currentStudent); this.studentNum++; } void setMark(int mark1, int mark2) { this.totalMark += mark1 * 0.3 + mark2 * 0.7; } void setMark(int mark1) { this.totalMark += mark1; } void setExpMark(ArrayList<Integer> expMarks) { int expTotal = 0; for (int i = 0; i < this.expTimes; i++) { expTotal += this.expMarks.get(i); } this.totalMark = expTotal / this.expTimes; } @Override public int compareTo(Class o) { return this.num.compareTo(o.num); } void classShow() { setGrade(); if (this.studentNum == 0 || this.totalMark == 0) { System.out.println(this.num + " has no grades yet"); } else { System.out.println(this.num + " " + this.totalMark); } } void setGrade() { if (this.studentNum == 0) { } else { for (int i = 0; i < this.studentmenu.size(); i++) { if (this.studentmenu.get(i).countCourse > 1) { this.studentNum += this.studentmenu.get(i).countCourse - 1; } } this.totalMark = this.totalMark / this.studentNum; } } } class Student implements Comparable<Student> { String num; String name; int mark; int countCourse; int expTimes;//实验次数 ArrayList<Integer> expMarks;//每次实验成绩 int texpmarks; ArrayList<Course> courses = new ArrayList<>(); Student(String num, String name) { this.num = num; this.name = name; this.mark = 0; this.countCourse = 0; this.expTimes = 0; this.texpmarks = 0; this.expMarks = new ArrayList<>(); } void addCourse(Course course) { this.courses.add(course); this.countCourse++; } void setMark(int mark1, int mark2) { this.mark += (int) (mark1 * 0.3 + mark2 * 0.7); } void setMark(int mark1) { this.mark += mark1; } void setExpMark(ArrayList<Integer> expMarks) { int expTotal = 0; for (int i = 0; i < this.expTimes; i++) { expTotal += this.expMarks.get(i); } texpmarks = expTotal / this.expTimes; this.mark += texpmarks; } @Override public int compareTo(Student o) { return this.num.compareTo(o.num); } void stuShow() { setGrade(); if (this.mark == -1) { System.out.println(this.num + " " + this.name + " did not take any exams"); } else { System.out.println(this.num + " " + this.name + " " + this.mark); } } void setGrade() { if (this.countCourse == 0) { this.mark = -1; } else { this.mark = this.mark / this.countCourse; } } } class Class1 { Class currentClass; Student currentStudent; Course currentCourse; ArrayList<Class> classes = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<>(); Coursechoose coursechoose = new Coursechoose(); ArrayList<Integer> expMarks = new ArrayList<>(); void parseInput(String a) { switch (InputMatching.matchingInput(a)) { case 1: addCourse(a); break; case 2: addScore(a); break; } } void addCourse(String a) { String[] b = a.split(" "); currentCourse = coursechoose.searchCourse(b[0]); if (currentCourse == null) { if (a.matches("\\S* 必修* 考察") || a.matches("\\S* 必修* 实验")) { System.out.println(b[0] + " : course type & access mode mismatch"); } if (a.matches("\\S* 选修* 实验")) { System.out.println(b[0] + " : course type & access mode mismatch"); } else { if (a.matches("\\S* 必修* 考试")) { currentCourse = new Course(b[0], b[1], b[2]); } else if (a.matches("\\S* 选修* 考试")) { currentCourse = new Course(b[0], b[1], b[2]); } else if (a.matches("\\S* 选修* 考察")) { currentCourse = new Course(b[0], b[1], b[2]); } else if (a.matches("\\S* 实验* 实验")) { currentCourse = new Course(b[0], b[1], b[2]); } coursechoose.addCourse(currentCourse); } } } void addScore(String a) { String[] s = a.split(" "); String classNum = s[0].substring(0, 6); String studentNum = s[0]; String studentName = s[1]; if (searchClass(classNum) == null) { currentClass = new Class(classNum); addClass(currentClass); currentStudent = new Student(studentNum, studentName); currentClass.addStudent(currentStudent); students.add(currentStudent); solveGrade(a); } else { currentClass = searchClass(classNum); if (currentClass.searchStudent(studentNum) == null) { currentStudent = new Student(studentNum, studentName); currentClass.addStudent(currentStudent); if (students.contains(currentStudent)) { } else { students.add(currentStudent); } } else { currentStudent = currentClass.searchStudent(studentNum); if (students.contains(currentStudent)) { } else { students.add(currentStudent); } } solveGrade(a); } } Class searchClass(String classNum) { for (Class aClass : classes) { if (aClass.num.equals(classNum)) return aClass; } return null; } void addClass(Class currentClass) { classes.add(currentClass); } void solveGrade(String a) { String[] b = a.split(" "); if (b.length == 5) { int pscore = Integer.parseInt(b[3]); int examScore = Integer.parseInt(b[4]); if (coursechoose.searchCourse(b[2]) != null) { currentCourse = coursechoose.searchCourse(b[2]); if (currentCourse.type.equals("考试")) { if (currentStudent.courses.contains(currentCourse)) { } else { currentStudent.addCourse(currentCourse); currentStudent.setMark(pscore, examScore); currentClass.setMark(pscore, examScore); currentCourse.setMark(pscore, examScore); } } expMarks.add(Integer.parseInt(b[3])); if (coursechoose.searchCourse(b[2]) != null) { currentCourse = coursechoose.searchCourse(b[2]); if (currentCourse.type.equals("实验")) { if (currentStudent.courses.contains(currentCourse)) { } else { currentStudent.addCourse(currentCourse); currentStudent.setExpMark(expMarks); currentClass.setExpMark(expMarks); currentCourse.setExpMark(expMarks); } } else { System.out.println(b[0] + " " + b[1] + " : access mode mismatch"); } } else { System.out.println(b[2] + " does not exist"); } } else { int normalScore = Integer.parseInt(b[3]); if (coursechoose.searchCourse(b[2]) != null) { currentCourse = coursechoose.searchCourse(b[2]); if (currentCourse.type.equals("考察")) { if (currentStudent.courses.contains(currentCourse)) { } else { currentStudent.addCourse(currentCourse); currentStudent.setMark(normalScore); currentClass.setMark(normalScore); currentCourse.setMark(normalScore); } } else { System.out.println(b[0] + " " + b[1] + " : access mode mismatch"); } } else { System.out.println(b[2] + "dose not exist"); } } } } void showStudents () { Collections.sort(students); for (Student s : students) { s.stuShow(); } } void showClasses () { Collections.sort(classes); for (Class s : classes) { s.classShow(); } } void showCourses () { Collections.sort(coursechoose.classmenu); for (Course s : coursechoose.classmenu) { s.courseShow(); } } }
第八次题目集

题目描述
编辑
输入多个学生的成绩信息,包括:学号、姓名、数学成绩、物理成绩。
学号是每个学生的唯一识别号,互不相同。
姓名可能会存在重复。
要求:使用ArrayList存储学生信息。
输入格式:
输入多个学生的成绩信息,每个学生的成绩信息格式:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+数学成绩+英文空格+物理成绩
以“end”为输入结束标志
输出格式:
按数学/物理成绩之和从高到低的顺序输出所有学生信息,每个学生信息的输出格式:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+数学/物理成绩之和
成绩相同的情况,按输入的先后顺序输出。
源代码
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.Scanner; class Student { String id; String name; int mathScore; int physicsScore; public Student(String id, String name, int mathScore, int physicsScore) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.mathScore = mathScore; this.physicsScore = physicsScore; } public int getScoreSum() { return mathScore + physicsScore; } public String toString() { return id + " " + name + " " + getScoreSum(); } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<>(); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); while (true) { String input = scanner.nextLine(); if (input.equals("end")) { break; } String[] inputs = input.split(" "); String id = inputs[0]; String name = inputs[1]; int mathScore = Integer.parseInt(inputs[2]); int physicsScore = Integer.parseInt(inputs[3]); students.add(new Student(id, name, mathScore, physicsScore)); } Collections.sort(students, new Comparator<Student>() { public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) { int scoreSum1 = s1.getScoreSum(); int scoreSum2 = s2.getScoreSum(); if (scoreSum1 > scoreSum2) { return -1; } else if (scoreSum1 < scoreSum2) { return 1; } else { return 0; } } }); for (Student student : students) { System.out.println(student); } } }
- 输入n,然后连续输入n个身份证号。
- 然后根据输入的是sort1还是sort2,执行不同的功能。输入的不是sort1或sort2,则输出
exit并退出。
输入sort1,将每个身份证的年月日抽取出来,按年-月-日格式组装,然后对组装后的年-月-日升序输出。
输入sort2,将所有身份证按照里面的年月日升序输出。
注意:处理输入的时候,全部使用Scanner的nextLine()方法,以免出错。
源代码
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); int n = scan.nextInt(); scan.nextLine(); String A[] = new String[n], C[] = new String[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { A[i] = scan.nextLine(); } String B = scan.nextLine(); for (; B.equals("sort1") || B.equals("sort2");) { if (B.equals("sort1")) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { C[j] = A[j].substring(6, 10) + "-" + A[j].substring(10, 12) + "-" + A[j].substring(12, 14); } Arrays.sort(C); for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { System.out.println(C[j].toString()); } } else if (B.equals("sort2")) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { C[j] = A[j].substring(6, 14); } Arrays.sort(C); for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) if (A[k].contains(C[j])) System.out.println(A[k].toString()); } System.out.println("exit"); B = scan.nextLine(); } scan.close(); } }
定义IntegerStack接口,用于声明一个存放Integer元素的栈的常见方法:
public Integer push(Integer item);
//如果item为null,则不入栈直接返回null。如果栈满,也返回null。如果插入成功,返回item。
public Integer pop(); //出栈,如果为空,则返回null。出栈时只移动栈顶指针,相应位置不置为null
public Integer peek(); //获得栈顶元素,如果为空,则返回null.
public boolean empty(); //如果为空返回true
public int size(); //返回栈中元素个数
定义IntegerStack的实现类ArrayIntegerStack,内部使用数组实现。创建时,可指定内部数组大小。
main方法说明
- 输入n,建立可包含n个元素的ArrayIntegerStack对象
- 输入m个值,均入栈。每次入栈均打印入栈返回结果。
- 输出栈顶元素,输出是否为空,输出size
- 使用Arrays.toString()输出内部数组中的值。
- 输入x,然后出栈x次,每次出栈均打印。
- 输出栈顶元素,输出是否为空,输出size
- 使用Arrays.toString()输出内部数组中的值。
源代码
import java.util.*; interface IntegerStack{ public Integer push(Integer item); //如果item为null,则不入栈直接返回null。如果栈满,也返回null。如果插入成功,返回item。 public Integer pop(); //出栈,如果为空,则返回null。出栈时只移动栈顶指针,相应位置不置为null public Integer peek(); //获得栈顶元素,如果为空,则返回null. public boolean empty(); //如果为空返回true public int size(); //返回栈中元素个数 } class ArrayIntegerStack{ public Integer [] array; private int len; public ArrayIntegerStack(int n) { this.array = new Integer[n]; len=0; } public Integer push(Integer item) { if(item==null) { return null; } if(len==this.array.length) { return null; } array[len++]=item; return item; } public Integer pop() { if(len==0) { return null; } len--; return array[len]; } public Integer peek() { if(len==0) { return null; } return array[len-1]; } public boolean empty() { if(len==0) { return true; } else { return false; } } public int size() { return len; } } public class Main{ public static void main(String [] args){ Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); int n = in.nextInt(); ArrayIntegerStack stack = new ArrayIntegerStack(n); int m = in.nextInt(); for(int i=0;i<m;i++) { int temp = in.nextInt(); System.out.println(stack.push(temp)); } System.out.println(stack.peek()+","+stack.empty()+","+stack.size()); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(stack.array)); int x = in.nextInt(); for(int j = 0;j<x;j++) { System.out.println(stack.pop()); } System.out.println(stack.peek()+","+stack.empty()+","+stack.size()); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(stack.array)); } }
Java每个对象都继承自Object,都有equals、toString等方法。
现在需要定义PersonOverride类并覆盖其toString与equals方法。
1. 新建PersonOverride类
a. 属性:String name、int age、boolean gender,所有的变量必须为私有(private)。
b. 有参构造方法,参数为name, age, gender
c. 无参构造方法,使用this(name, age,gender)调用有参构造方法。参数值分别为"default",1,true
d.toString()方法返回格式为:name-age-gender
e. equals方法需比较name、age、gender,这三者内容都相同,才返回true.
2. main方法
2.1 输入n1,使用无参构造方法创建n1个对象,放入数组persons1。
2.2 输入n2,然后指定name age gender。每创建一个对象都使用equals方法比较该对象是否已经在数组中存在,如果不存在,才将该对象放入数组persons2。
2.3 输出persons1数组中的所有对象
2.4 输出persons2数组中的所有对象
2.5 输出persons2中实际包含的对象的数量
2.5 使用System.out.println(Arrays.toString(PersonOverride.class.getConstructors()));输出PersonOverride的所有构造方法。
提示:使用ArrayList代替数组大幅复简化代码,请尝试重构你的代码。
源代码
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Scanner; class PersonOverride { private String name; private int age; private boolean gender; public PersonOverride() { this("default", 1, true); } public PersonOverride(String name, int age, boolean gender) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.gender = gender; } @Override public String toString() { return name + "-" + age + "-" + gender; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) { return true; } if (obj == null || getClass() != obj.getClass()) { return false; } PersonOverride person = (PersonOverride) obj; return age == person.age && gender == person.gender && name.equals(person.name); } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); int n1 = scanner.nextInt(); ArrayList<PersonOverride> persons1 = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < n1; i++) { persons1.add(new PersonOverride()); } int n2 = scanner.nextInt(); ArrayList<PersonOverride> persons2 = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < n2; i++) { String name = scanner.next(); int age = scanner.nextInt(); boolean gender = scanner.nextBoolean(); PersonOverride person = new PersonOverride(name, age, gender); if (!persons2.contains(person)) { persons2.add(person); } } for (PersonOverride person : persons1) { System.out.println(person); } for (PersonOverride person : persons2) { System.out.println(person); } System.out.println(persons2.size()); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(PersonOverride.class.getConstructors())); } }
课程成绩统计程序-3在第二次的基础上修改了计算总成绩的方式,
要求:修改类结构,将成绩类的继承关系改为组合关系,成绩信息由课程成绩类和分项成绩类组成,课程成绩类组合分项成绩类,分项成绩类由成绩分值和权重两个属性构成。
完成课程成绩统计程序-2、3两次程序后,比较继承和组合关系的区别。思考一下哪一种关系运用上更灵活,更能够适应变更。
题目最后的参考类图未做修改,大家根据要求自行调整,以下内容加粗字体显示的内容为本次新增的内容。
某高校课程从性质上分为:必修课、选修课、实验课,从考核方式上分为:考试、考察、实验。
考试的总成绩由平时成绩、期末成绩分别乘以权重值得出,比如平时成绩权重0.3,期末成绩权重0.7,总成绩=平时成绩*0.3+期末成绩*0.7。
考察的总成绩直接等于期末成绩
实验的总成绩等于课程每次实验成绩乘以权重后累加而得。
课程权重值在录入课程信息时输入。(注意:所有分项成绩的权重之和应当等于1)
必修课的考核方式必须为考试,选修课可以选择考试、考察任一考核方式。实验课的成绩必须为实验。
1、输入:
包括课程、课程成绩两类信息。
课程信息包括:课程名称、课程性质、考核方式、分项成绩数量、每个分项成绩的权重。
考试课信息格式:课程名称+英文空格+课程性质+英文空格+考核方式+英文空格+平时成绩的权重+英文空格+期末成绩的权重
考察课信息格式:课程名称+英文空格+课程性质+英文空格+考核方式
实验课程信息格式:课程名称+英文空格+课程性质+英文空格+考核方式+英文空格+分项成绩数量n+英文空格+分项成绩1的权重+英文空格+。。。+英文空格+分项成绩n的权重
实验次数至少4次,不超过9次
课程性质输入项:必修、选修、实验
考核方式输入选项:考试、考察、实验
考试/考查课程成绩信息包括:学号、姓名、课程名称、平时成绩(可选)、期末成绩
考试/考查课程成绩信息格式:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+课程名称+英文空格+平时成绩+英文空格+期末成绩
实验课程成绩信息包括:学号、姓名、课程名称、每次成绩{在系列-2的基础上去掉了(实验次数),实验次数要和实验课程信息中输入的分项成绩数量保持一致}
实验课程信息格式:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+课程名称+英文空格+第一次实验成绩+...+英文空格+最后一次实验成绩
以上信息的相关约束:
1)成绩是整数,不包含小数部分,成绩的取值范围是【0,100】
2)学号由8位数字组成
3)姓名不超过10个字符
4)课程名称不超过10个字符
5)不特别输入班级信息,班级号是学号的前6位。
2、输出:
输出包含三个部分,包括学生所有课程总成绩的平均分、单门课程总成绩平均分、班级所有课程总成绩平均分。
为避免四舍五入误差,
计算单个成绩时,分项成绩乘以权重后要保留小数位,计算总成绩时,累加所有分项成绩的权重分以后,再去掉小数位。
学生总成绩/整个班/课程平均分的计算方法为累加所有符合条件的单个成绩,最后除以总数。
1)学生课程总成绩平均分按学号由低到高排序输出
格式:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+总成绩平均分
如果某个学生没有任何成绩信息,输出:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+"did not take any exams"
2)单门课程成绩按课程名称的字符顺序输出
课程成绩输出格式:课程名称+英文空格+总成绩平均分
如果某门课程没有任何成绩信息,输出:课程名称+英文空格+"has no grades yet"
3)班级所有课程总成绩平均分按班级由低到高排序输出
格式:班级号+英文空格+总成绩平均分
如果某个班级没有任何成绩信息,输出:班级名称+英文空格+ "has no grades yet"
异常情况:
1)如果解析某个成绩信息时,课程名称不在已输入的课程列表中,输出:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+":"+课程名称+英文空格+"does not exist"
2)如果解析某个成绩信息时,输入的成绩数量和课程的考核方式不匹配,输出:学号+英文空格+姓名+英文空格+": access mode mismatch"
以上两种情况如果同时出现,按第一种情况输出结果。
3)如果解析某个课程信息时,输入的课程性质和课程的考核方式不匹配,输出:课程名称+" : course type & access mode mismatch"
4)格式错误以及其他信息异常如成绩超出范围等,均按格式错误处理,输出"wrong format"
5)若出现重复的课程/成绩信息,只保留第一个课程信息,忽略后面输入的。
6)如果解析实验课程信息时,输入的分项成绩数量值和分项成绩权重的个数不匹配,输出:课程名称+" : number of scores does not match"
7)如果解析考试课、实验课时,分项成绩权重值的总和不等于1,输出:课程名称+" : weight value error"
信息约束:
1)成绩平均分只取整数部分,小数部分丢弃
参考类图(与第一次相同,其余内容自行补充):
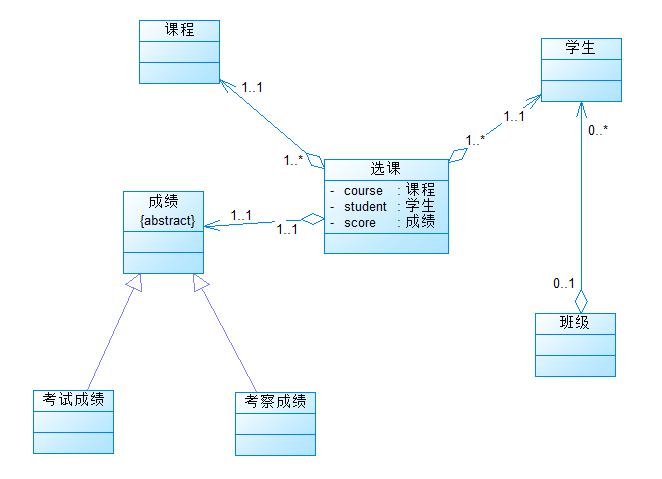
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
java 实验 实验 4 0.2 0.3 0.2 0.3
end
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
java has no grades yet
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
java 实验 实验 4 0.2 0.3 0.2
end
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
java : number of scores does not match
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
java 实验 实验 4 0.2 0.3 0.2 0.1
end
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
java : weight value error
输入样例4:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
java 实验 实验 4 0.2 0.3 0.2 0.3
20201116 张三 java 70 80 90 100
end
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
20201116 张三 86
java 86
202011 86
输入样例5:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
java 实验 实验 4 0.2 0.3 0.2 0.3
20201116 张三 java 70 80 90 100 80
end
输出样例5:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
20201116 张三 : access mode mismatch
20201116 张三 did not take any exams
java has no grades yet
202011 has no grades yet
2.类图


3.题目分析
根据题目得
根据用户输入的内容,使用正则表达式进行匹配,判断输入的类型是课程信息还是成绩信息。
如果是课程信息,根据输入的内容创建Course对象,并将其添加到课程菜单中。
如果是成绩信息,根据输入的内容创建Student对象和Class对象,并将其添加到学生列表和班级列表中。
根据输入的成绩信息,将成绩添加到对应的课程、学生和班级中,并计算平均分。
最后,按照要求显示学生的成绩、课程的平均分和班级的平均分。
所以类要包含以下几个类:
-
Main类:包含主函数,用于接收用户输入并调用School类的方法进行处理。
-
InputMatching类:包含用于匹配输入格式的正则表达式,并提供了匹配输入类型的方法。
-
Course类:表示课程,包含课程的名称、类型、考察方式以及成绩信息。
-
Coursemenu类:表示课程菜单,包含所有课程的列表,并提供了添加课程和搜索课程的方法。
-
Class类:表示班级,包含班级号、学生列表以及班级的总分。
-
Student类:表示学生,包含学号、姓名、成绩列表以及学生的平均成绩。
-
School类:表示学校,包含班级列表、学生列表和课程菜单,并提供了解析输入、添加课程和成绩、显示学生、课程和班级信息的方法。
4.源代码
import java.text.Collator; import java.util.*; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); School school = new School(); String a; while(!(a=in.nextLine()).equals("end")) { school.parseInput(a); } school.showStudent(); school.showCourse(); school.showClass(); } } class InputMatching { static String stuNumMatching = "[0-9]{8}";//8个0-9的数字 static String stuNameMatching = "\\S{1,10}";//1到10个非空格(TAB)字符 static String scoreMatching = "([1-9]?[0-9]|100)"; static String courseNameMatching = "\\S{1,10}";//1到10个非空格(TAB)字符 static String courseTypeMatching = "(选修|必修|实验)"; static String checkCourseTypeMatching = "(考试|考察|实验)"; //courseInput用于定义课程信息模式(正则表达式) static String courseInput = courseNameMatching + " " + courseTypeMatching + " " + checkCourseTypeMatching; static String courseInput1 = courseNameMatching + " " + courseTypeMatching + " " + checkCourseTypeMatching+" "+"[0-9]+(\\.[0-9]+)*(\\s[0-9]+(\\.[0-9]+)*\\s?)*"; //scoreInput用于定义成绩信息模式(正则表达式) static String scoreInput1 = stuNumMatching + " " + stuNameMatching + " " + courseNameMatching + " " + scoreMatching + " "+scoreMatching; static String scoreInput2 = stuNumMatching + " " + stuNameMatching + " " + courseNameMatching + " " + scoreMatching ; public static int matchingInput(String s) { if (matchingCourse(s)) { return 1; } if (matchingScore(s)) { return 2; } String [] s1 = s.split(" "); if(s1.length>5) { return 2; } return 0; } private static boolean matchingCourse(String s) { return s.matches(courseInput)||s.matches(courseInput1);//判断课程信息 } private static boolean matchingScore(String s) { return s.matches(scoreInput1)||s.matches(scoreInput2);//判断学生成绩信息 } } class Course implements Comparable<Course> { String allXingxi; String name; String mode; String type; int chooseCount; float totalMark; float normalMark; float finalMark; Course(String name, String mode, String type,String allow) { this.name = name; this.mode = mode; this.type = type; this.allXingxi = allow; this.totalMark = 0; this.normalMark = 0; this.finalMark = 0; this.chooseCount = 0; } void setMark(float normalMark,float finalMark) { this.normalMark += normalMark; this.finalMark += finalMark; this.chooseCount++; } void setMark(float finalMark) { this.finalMark+=finalMark; this.chooseCount++; } @Override public int compareTo(Course o) { Collator collator= Collator.getInstance(Locale.CHINA); return collator.compare(this.name,o.name); } void courseShow() { setGrade(); if(this.chooseCount==0) { System.out.println(this.name+" has no grades yet"); } else { if(this.type.equals("实验")) { System.out.println(this.name+" "+(int)this.finalMark); return ; } if(this.normalMark == 0) { System.out.println(this.name+" "+(int)this.finalMark+" "+(int)this.finalMark); } else { System.out.println(this.name+" "+(int)this.normalMark+" "+(int)this.finalMark+" "+(int)this.totalMark); } } } void setGrade() { if(this.chooseCount==0){} else { this.normalMark = this.normalMark/this.chooseCount; this.finalMark = this.finalMark / this.chooseCount; this.totalMark = this.normalMark+this.finalMark; } } } class Coursemenu { ArrayList<Course> classmenu= new ArrayList<>(); void addCourse(Course newCourse) { classmenu.add(newCourse); } Course searchCourse(String name) { for (Course c : classmenu) { if (c.name.equals(name)) return c; } return null; } } class Class implements Comparable<Class> { boolean hasChooseErrorStudents; String num; double totalMark; int studentNum; Class(String num) { this.num = num; this.studentNum=0; this.totalMark=0; this.hasChooseErrorStudents = false; } ArrayList <Student> studentmenu = new ArrayList<>(); Student searchStudent(String studentNum) { for (Student student : this.studentmenu) { if (student.num.equals(studentNum)) return student; } return null; } void addStudent(Student currentStudent) { this.studentmenu.add(currentStudent); this.studentNum++; } void setMark(float mark1,float mark2) { this.totalMark += (mark1 +mark2); } void setMark(float mark1) { this.totalMark += mark1; } @Override public int compareTo(Class o) { return this.num.compareTo(o.num); } void classShow() { setGrade(); if(this.hasChooseErrorStudents) { return ; } if(this.studentNum==0||this.totalMark==0) { System.out.println(this.num + " has no grades yet"); } else { System.out.println(this.num+" "+(int)this.totalMark); } } void setGrade() { if(this.studentNum == 0){} else { for(int i=0 ;i<this.studentmenu.size() ;i++) { if(this.studentmenu.get(i).hasChooseError) { this.hasChooseErrorStudents = true; return ; } if(this.studentmenu.get(i).countCourse>1) { this.studentNum += this.studentmenu.get(i).countCourse-1; } } this.totalMark = this.totalMark/this.studentNum; } } } class Student implements Comparable<Student> { boolean hasChooseError; String num; String name; float mark;//记录分数的代码 int countCourse;//记录课程数量 ArrayList<Course> courses = new ArrayList<>(); Student(String num,String name) { this.num = num; this.name = name; this.mark = 0; this.countCourse = 0; this.hasChooseError = false; } void addCourse(Course course) { this.courses.add(course); this.countCourse++; } void setMark(float mark1,float mark2) { this.mark += (mark1 + mark2); } void setMark(float mark1) { this.mark += mark1;//考察成绩就是最后成绩 } @Override public int compareTo(Student o) { return this.num.compareTo(o.num); } void stuShow() { setGrade(); if(this.hasChooseError == true) { return ; } if(this.mark==-1) { System.out.println(this.num+" "+this.name+" did not take any exams"); } else { System.out.println(this.num+" "+this.name+" "+(int)(this.mark)); } } void setGrade() { if(this.countCourse==0) { this.mark=-1; } else { this.mark=this.mark/this.countCourse; } } } class School { Class currentClass; Student currentStudent; Course currentCourse; ArrayList<Class> classes = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<>(); Coursemenu coursemenu = new Coursemenu(); void parseInput(String a) { switch (InputMatching.matchingInput(a)) { case 0: System.out.println("wrong format"); break; case 1: addCourse(a); break; case 2: addScore(a); break; } } boolean isOne(String a) { String[] c = a.split(" "); String regex = "\\d+(\\.\\d+)?"; // 编译正则表达式 Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex); // 匹配字符串并计算总和 Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(a); float sum = 0; while (matcher.find()) { float num = Float.parseFloat(matcher.group()); sum += num; } sum -= (float) Integer.parseInt(c[3]); if (sum == 1.0f) return true; else return false; } boolean isTwo(String a) { String regex = "\\d+(\\.\\d+)?"; // 编译正则表达式 Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex); // 匹配字符串并计算总和 Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(a); float sum = 0; while (matcher.find()) { float num = Float.parseFloat(matcher.group()); sum += num; } if (sum == 1.0f) return true; else return false; } void addCourse(String a) { String[] b = a.split(" "); currentCourse = coursemenu.searchCourse(b[0]); if (currentCourse == null) { //" "+"[0-9]+(\\.[0-9]+)*(\s[0-9]+(\\.[0-9]+)*\s?)*" if (a.matches("\\S* 实验* 实验 [0-9]+(\\.[0-9]+)*(\\s[0-9]+(\\.[0-9]+)*\\s?)*")) { String[] oop = a.split(" "); if (Integer.parseInt(oop[3]) == oop.length - 4) { if (Integer.parseInt(oop[3]) >= 4 && Integer.parseInt(oop[3]) <= 9) { if (isOne(a)) { currentCourse = new Course(b[0], b[1], b[2], a); coursemenu.addCourse(currentCourse); } else { System.out.println(b[0] + " : weight value error"); } } else { System.out.println("wrong format"); } } else { System.out.println(b[0] + " : number of scores does not match"); } return;//结束当前的函数 } else if (a.matches("\\S* 实验* 考试 [0-9]+(\\.[0-9]+)*(\\s[0-9]+(\\.[0-9]+)*\\s?)*") || a.matches("\\S* 实验* 考察 [0-9]+(\\.[0-9]+)*(\\s[0-9]+(\\.[0-9]+)*\\s?)*")) { System.out.println(b[0] + " : course type & access mode mismatch"); return; } if (a.matches("\\S* 必修* 考察 [0-9]+(\\.[0-9]+)*(\\s[0-9]+(\\.[0-9]+)*\\s?)*"))//不符合的情况 { System.out.println(b[0] + " : course type & access mode mismatch"); } else { if (a.matches("\\S* 必修* 考试 [0-9]+(\\.[0-9]+)*(\\s[0-9]+(\\.[0-9]+)*\\s?)*"))//"^java\\s+必修\\s+考试\\s+(\\d+(\\.\\d+)?\\s+){2}$"; { if (isTwo(a)) { currentCourse = new Course(b[0], b[1], b[2], a); } else { System.out.println("wrong format"); return; } } else if (a.matches("\\S* 选修* 考试 [0-9]+(\\.[0-9]+)*(\\s[0-9]+(\\.[0-9]+)*\\s?)*")) { if (isTwo(a)) { currentCourse = new Course(b[0], b[1], b[2], a); } else { System.out.println("wrong format"); return; } } else if (a.matches("\\S* 选修* 考察")) { currentCourse = new Course(b[0], b[1], b[2], a); } coursemenu.addCourse(currentCourse); } } } void addScore(String a) { String[] s = a.split(" "); String classNum = s[0].substring(0, 6); String studentNum = s[0]; String studentName = s[1]; String courseName = s[2]; if (searchClass(classNum) == null) { currentClass = new Class(classNum); addClass(currentClass); currentStudent = new Student(studentNum, studentName); currentClass.addStudent(currentStudent); students.add(currentStudent); solveGrade(a); } else { currentClass = searchClass(classNum); if (currentClass.searchStudent(studentNum) == null) { currentStudent = new Student(studentNum, studentName); currentClass.addStudent(currentStudent); if (students.contains(currentStudent)) { } else { students.add(currentStudent); } } else { currentStudent = currentClass.searchStudent(studentNum); if (students.contains(currentStudent)) { } else { students.add(currentStudent); } } solveGrade(a); } } Class searchClass(String classNum) { for (Class aClass : classes) { if (aClass.num.equals(classNum)) return aClass; } return null; } void addClass(Class currentClass) { classes.add(currentClass); } void solveGrade(String a) { String[] b = a.split(" "); if (b.length > 5) { if (coursemenu.searchCourse(b[2]) != null) { currentCourse = coursemenu.searchCourse(b[2]); if (currentCourse.type.equals("实验")) { String[] temp = currentCourse.allXingxi.split(" "); if (b.length - 3 == Integer.parseInt(temp[3])) { if (currentStudent.courses.contains(currentCourse)) { } else { float sum = 0; float ccup; for (int i = 0; i < b.length - 3; i++) { ccup = Float.parseFloat(temp[4 + i]); sum += ccup * Integer.parseInt(b[i + 3]); } currentStudent.addCourse(currentCourse); currentStudent.setMark((int) sum); currentClass.setMark(sum); currentCourse.setMark(sum); } } else { System.out.println(b[0] + " " + b[1] + " : access mode mismatch"); } } else { System.out.println(b[0] + " " + b[1] + " : access mode mismatch"); } } else//在课表上面不存在该课 { System.out.println(b[2] + " does not exist"); } } else if (b.length == 5) { int normalScore = Integer.parseInt(b[3]); int examScore = Integer.parseInt(b[4]); if (coursemenu.searchCourse(b[2]) != null) { currentCourse = coursemenu.searchCourse(b[2]); if (currentCourse.type.equals("考试")) { String[] temp = currentCourse.allXingxi.split(" "); if (currentStudent.courses.contains(currentCourse)) { } else { float ccup1; float ccup2; ccup1 = Float.parseFloat(temp[3]); ccup2 = Float.parseFloat(temp[4]); currentStudent.addCourse(currentCourse); currentStudent.setMark(normalScore * ccup1, examScore * ccup2); currentClass.setMark(normalScore * ccup1, examScore * ccup2); currentCourse.setMark(normalScore * ccup1, examScore * ccup2); } } else { System.out.println(b[0] + " " + b[1] + " : access mode mismatch"); } } else//在课表上面不存在该课 { System.out.println(b[2] + " does not exist"); } } else //存在而且该考察方式是考察 { int normalScore = Integer.parseInt(b[3]); if (coursemenu.searchCourse(b[2]) != null) { currentCourse = coursemenu.searchCourse(b[2]); if (currentCourse.type.equals("考察")) { if (currentStudent.courses.contains(currentCourse)) { } else { currentStudent.addCourse(currentCourse); currentStudent.setMark(normalScore); currentClass.setMark(normalScore); currentCourse.setMark(normalScore); } } else { System.out.println(b[0] + " " + b[1] + " : access mode mismatch"); } } else//在课表上面不存在该课 { System.out.println(b[2] + " does not exist"); } } } void showStudent() { Collections.sort(students); for (int i = 0; i < students.size(); i++) { students.get(i).stuShow(); } } void showCourse() { ArrayList<Course> temp = new ArrayList<>(); for (Course c : coursemenu.classmenu) { temp.add(c); } Collections.sort(temp); for (Course c : temp) { c.courseShow(); } } void showClass() { Collections.sort(classes); for (int i = 0; i < classes.size(); i++) { classes.get(i).classShow(); } } }
(3)采坑心得:
第一,题目不要看错。
第二,对与数据精度度处理,比如题目限制float,但使用double会超出范围。
(4)改进建议:
主要就是测试点的问题,有些测试点可以不用,或者说把测试点要求给的详细一点。
(5)总结
经过这几次pta练习,我更理解了java HashMap的使用,接口的定义和使用,以及接口方法的重写,而题目的难度也是层层递进的,大大提高了我编写java程序的能力,我的代码更加模块化和可复用。



