Java
Java笔记
UML
统一建模语言
面向对象三大特征
封装性
类的内部信息不能被外部程序直接访问
但是可以用该类提供的方法(Method)对隐藏信息进行操作和访问
(注意,private成员只是不能被直接访问)
封装步骤
1.修改属性的可见性:
改为private
2.创建公有方法:
getter方法/setter方法
(分别用于属性的读/写)
Mydate d = new MyDate();
d.setDay(31);
d.setDay(d.getDay()+1);
3.在getter/setter方法中加入属性控制语句:
对属性值的合法性进行判断
(不懂,判断什么合法性?这条看着像硬凑上去的)
继承性(Inheritance)
表示关系常用:is-a
父类更通用(一般特性),子类更具体(自身特性)
想象一棵树
多态性
不同对象对于同一个方法实现不同的行为
class X{...}
class Y extends X{...}
public class TestExtend {
public static void main(String[] args) {
X x = new X();//x的静态类型为X,动态类型为X
Y y = new Y();
x = y;//x的静态类型为X,动态类型为Y
...
}
}
在概念上X包含Y。
在所有期望X为实例的场合,都允许用Y的实例来代替。
编译时完成的绑定为静态绑定,反之为动态绑定。
x为一多态引用变量,调用时使用的时Y中重定义的代码。
实际操作
创建项目\(\rightarrow\)新建类 guagua.java\(\rightarrow\)编译\(\rightarrow\)得到guagua.class
一个类对应一个文件
package shipping.reports;
import shipping.domain.*;
import java.util.List;
import java.io.*;
pubilc class Guagua {
private String salutation;
Guagua(String S){
salutation = S;
}
public void guagua(String C) {
System.out.println(salutation + " " + C);
}
//out 是 System 类的一个static属性,它的类型是PrintStream
//PrintStream 是 java.io 包里定义的一个类
}
public class TestGuagua {
public static void main(String[] args){
Guagua hello = new Guagua("Hello");
hello.guagua("World");
}
}
//提供输入参数,该参数就存入字符串中args[]中
//
标记(token)
return 0 三个标记
return0 一个标记
词法分析器的"贪婪性"
j = i+++++i;
j = i++ + ++i;
类型
默写一下基本类型?
boolean
char
byte(8),short(16),int(32),long(64) (bits)
注意一下,8 bits 代表 \(-2^7 to 2^7-1\)
整数型默认为int
float(32),double(64) (bits)
浮点数默认是double
String 是一个类
引用类型
Primitive Variable
byte x =7;
Referenve Variable
Dog myDog = new Dog();
"Java中唯一的对象引用字面值(literals)是null"
这句话的意思就是,如果现在我们要写一个引用类型,然后现在其实并没有什么要引用的东西,我们就直接写个null,但是不能写别的东西,比如123,321这种东西(C++貌似就可以)
String s = null;也可以
现在又讲到堆(Heap)和栈(Stack)
栈用来存指令,堆用来存实例;
对象实例在heap中进行分配,然后呢在stack中保存一个4字节的heap的内存地址(这一部分好好玩,和我想象的一样);
然后再来说一下,栈里到底存什么:
1.基本数据类型,也就是刚才默写的那些东西啦~;
2.指令代码:函数方法属于指令;
3.对象的引用地址;
4.常量.也就是final 量?
变量生命周期
1.成员变量
类被实例化的时候创建
没有赋值的话是会有默认值的
2.局部变量
静态成员变量的初始化要先于非静态成员变量
class F{
int x = 20;//被F的构造函数调用前,x被设置为20;
static int y = 30;//在F被加载时设置为30;
}
局部变量不会被自动赋值
等一下,赋值这个东西...
public class LocalVariable{
public static void main(String[] args){
String[] s = new String[2];//可以,初值为null
String[] s;//不可以
System.out.println(s[0]);
}
}
方法参数(Method parameter)
1.定义传入方法的参数
2.当调用该方法时,新变量被创建,生命周期持续到方法结束
这一块不太懂,不知道这个方法参数应该怎么放
在那里写这个所谓的方法参数?方法参数指的具体是什么
3.类变量
即静态变量
一看就是,和类同生同灭
"无论有多少对象,类变量始终只有一个拷贝,被多个对象共享"
初始化方法和成员变量相同,对
final变量
这个东西跟const没设么区别
如果一个final变量是对一个对象的引用,其引用必须相同,但对象本身可以不同
什么意思,这句话?
引用一个对象,引用必须相同,什么意思
是指我本来指向了一个地址,然后现在那个地址里的对象都换了,但是地址必须还指向那里的意思嘛??
class Walrus{
int weight;
Walrus(int w){
weight = w;
}
}
class Tester{
final Walrus w1 = new Walrus(1500);
void test() {
w1 = new Walrus(1400); //不合法的
w1.weight = 1800;//合法的
}
}
public void getValue(final int a){
a = 10;//wrong!
}
public void getValue(final Contract c){
c.hourSpanName = "aa";//right
}
所以意思就是说,某类(并且是final)的里面的局部变量是可以被改变的
...对吧?
数组
通俗易懂的一段话:
在java中数组是对象,比如int是基本型,但是int[]是对象
数组的声明没有创建数组对象,只创建了对数组对象的引用
数组元素所占用的内存是通过new或者初始化有系统动态分配的
数组具体怎么用我们就...先不说啦,感觉很简单
String[] a = new String[]{"x","y","z"};
int[] ages;
ages = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5};
关于heap和stack
int a = 3;//stack memory
int[] b = {1,2,3,4,5};//stack里面有int[]b的地址
//heap里面有1,2,3,4,5的内存
数组长度
int len = i.length;
用new创建的变量都是引用型变量
Shirt myShirt = new Shirt();
Shirt [] shirts = {new Shirt(),new Shirt(),new Shirt()};
其中stack中存shirts和myShirt的地址
heap里面存shirts里面三个新的Shirt的地址,然后继续存它们的具体值,还有myShirt的具体值。(看图)
二维数组
一旦数组被创建,就不能修改长度(和C++一样)
但是可以写:
int Array[] = new int[6];
Array = new int[10];
运算符
instanceof 判断已给的对象是否是某个类或者是接口
等一下 接口到底是啥啊??
右移运算符
算术右移,有符号,>>
逻辑右移,无符号,>>>,最高位补0,只允许对int和long型,byte型会被扩展成int型
表达式类型
表达式中,char被扩展成int
隐式转换
基本类型转换
变宽转换是合法的,变窄转换是不合法的
引用转换
Oldtype x = new Oldtype();
Newtype y = x;
//Oldtype 貌似是 Newtype的 子类
显示转换
强制转换导致信息损失,需要显示转换
long BigValue = 99L;
int squashed = bigValue;
int squashed = (int)bigValue;
//所以显式转换就是...加“(类型)”??
public void doSomething(Employee e){
if(e instanceof Manager){
Manager m = (Manager) e;
System.out.println("This is the magager of"+m.getDepartment());
}
}
//if you do not make the cast,an attempt to execute e.getDepartment() would fail,because the compiler cannot locate a method called getDepartment in the Employee class
$,abcd$可以作为java标识符
char[] a = {'1','2','3'};
char a[] = {'1','2','3'};
都是合法的
(?)
基本
int random = (int)(Math.random()*10);
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = input.nextInt();
"switch(表达式)支持字串、枚举的语法糖"
“JDK1.5之前switch只支持byte,short,char,int”
“JDK1.5之后的自动拆箱,对应的这四种基础类型的封装类型类也同样支持Byte,Short,Character,Integer“
对不起看不懂,还反编译
算了...
switch支持String,其实是支持String的hash值
本质上是switch-int结构
并且利用equals方法来放置hash冲突的问题
最后利用switch-byte精确匹配
特殊循环控制
带标号的continue语句 和 带标号的break语句
这两个语句用来代替goto语句
outer:
do{
statement;
do{
statement;
if(boolean expression){
break outer;
}
else if(boolean expression){
continue outer;
}
statement;
} while(boolean expression);
statement;
} while(boolean expression);
使用增强的for循环
public void printElement(int[] list){
for(int element : list){
System.out.println(element);
}
}
privete Map<String,Integer>stockMap = new HashMap();
for(Object i:stockMap.keySet()){
System.out.println("代号:"+i+",数量:"+stockMap.get(i));
}
类和对象
类
类包括:
字段field:对象包含的数据
方法
构造器(也就是构造函数)
初始化程序块
嵌套类(inner class)
类的修饰符
public:如果没写public 就只能在自己所属的包里访问
abstract:不能实例化
final:没有子类
类不可以是private和protected
包(package) 是用于区别类
java中的一个包相当于系统中的一个文件夹
protected 可以被子类的实例、同一个包内的所有类访问
构造器
其实就是构造函数
public class A{
private int x;
public Thing(){
x = 233;
}
public Thing(int new_x){
x = new_x;
}
public int getX(){
return x;
}
public void setX(int new_x){
x = new_x;
}
}
如果不写构造器的话,系统自动创建
但如果写了带参数的构造器,系统不会帮忙创造一个不带参数的构造器
构造器之间的相互调用(使用this)
public class Hello{
String title;
int value;
public Hello(){
title+="Hello";
}
public Hello(int value){
this();//必须在第一行调用,不能使用Hello();
this.value = value;
}
public Hello(String title,int value){
this(value);
this.title += title;
}
}
初始化块
不知道在说什么,不想看
public class InitializationBlock{
private int x;
static double d = 3.14;
//非静态初始化块:在创建对象时执行(先于构造器);
{
x = 5;
System.out.println("字段x = "+x);
}
//静态初始化块:仅在类被加载时执行一次;
static{
int x = 10;//静态初始化块中的局部变量
System.out.println("局部变量x = "+ x);
//静态初始化块中,this.x不可用
System.out.println("静态字段d = "+ d);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
new InitializationBlock();
}
}
起名可以用字母,'_','$'开头
类的方法
静态方法
public class Count {
private int serialNumber;
private static int counter = 0;
public static int getTotalCount() {
return counter;
}
public Count() {
counter++;
serialNumber = counter;
}
}
public class TestCounter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Number of counter is " + Count.getTotalCount());//输出了0
Count count1 = new Count();
System.out.println("Number of counter is "+ Count.getTotalCount());//输出了1
}
//应该直接用类名来调用静态方法
}
class SomeClass {
static int i = 48;
int j = 1;
public static void main(String args[]) {
i += 100;
// j *= 5;
}
}
import java.awt.*;
public class MyFrame extends Frame {
MyFrame() {
setSize(300,300);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
MyFrame theFrame = new MyFrame();
theFrame.setVisible(true);
}
}
// 不知道写这一段东西是干嘛的
public class refValExample {
static void Change(int[] pArray) {
pArray[0] = 888;
pArray = new int[] {-3,-1,-2,-3,-4};
System.out.println("方法内,第一个元素是:"+pArray[0]);//-3
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,4,5};
System.out.println("调用方法之前,第一个元素是:"+arr[0]);//1
Change(arr);
System.out.println("调用方法之后,第一个元素是:"+arr[0]);//888
}
}
包装类
Java collection类中的元素必须为objects
List<Integer> a = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int i = 5;
Integer itg = new Integer(i);
Integer jtg = new Integer(6);
int j = jtg.intValue();
//long转为Long
long l = 8;
Long lng = new Long(l);
//Long转long
Long gng = new Long(9);
long g = gng.longValue();
Integer i1 = Integer.valueOf(42);
Integer i2 = Integer.valueOf("42");
Boolean b1 = Boolean.valueOf(true);
Boolean b2 = Boolean.valueOf("true");
Long n1 = Long.valueOf(42000000L);
Long n2 = Long.valueOf("42000000L");
int i = Integer.parseInt("42");
boolean b = Boolean.parseBoolean("true");
double d = Double.parseDouble("3.14");
自动装箱的例子
List<Integer> li = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i = 1;i<50;i++)li.add(i);
//等价于li.add(Integer.valueOf(i));
public static int sumEven(List<Integer>li) {
int sum = 0;
for(Integer i:li){
if(i%2==0){ //等价:if(i.intValue()%2==0)
sum += i;//等价:sum += i.intValue();
}
}
return sum;
}
static
1.在类被加载的时候,就会加载被static修饰的部分
2.静态对象与实例对象相对
静态变量
是由static修饰的成员变量,又叫做类变量。说明这个变量属于类而不是属于对象
内存:则它在内存中只存在一份。JVM为静态变量分配一次内存空间。
实例变量
指这个变量是属于某个具体的对象的。
内存:创建几次对象,就有几次成员变量。
不要通过对象的方式去访问静态变量或者静态方法
静态不能访问非静态,非静态可以访问静态。(很常见的例子)
静态方法
不存在this关键字
静态是由类的加载而加载,this是由对象的创建而存在的。所以静态比对象优先存在。
class Test {
/*
public static class Fruit{
Fruit() {
System.out.println("Yeah!Fruit!");
}
}
public static class Watermelon extends Fruit {
Watermelon() {
super();
System.out.println("Haha!Watermelon!");
}
}
*/
{
System.out.println("Maybe...you?");
}
static {
System.out.println("Haha!Who first?");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Test();
}
}
多线程
分时利用CPU,也叫并发
每一次调用start()相当于:放入等待队列,等待CPU调度,处于就绪状态
方法run()称为线程体,它包含了执行线程的内容
只有用start()方法来启动线程,才能实现真正的多线程运行,
将run()方法当作普通方法的方式调用,程序仍然按照顺序进行.
实现多线程的两种方法
1.继承Thread类
Thread类在java.lang包中定义
一个类继承Thread类同时覆写了本类中的run()方法 \(\rightarrow\) 用start()启动线程 \(\rightarrow\)实现多线程操作
此方法的局限:一个类只能继承一个父类
$\rightarrow $Runnable 接口为非Thread子类的类提供了一种激活方式
2.实现Runnable接口
属于java.lang包
package org.runnable.demo;
class MyThread implements Runnable {
private String name;
public MyThread(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<100;i++) {
System.out.println("gua gua stand up!!");
}
}
}
实现run()方法,用new Thread(Runnable target).start()方法来启动
在使用Runnable定义的子类中没有start()方法,只有Thread类才有
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runner1 runner1 = new Runner1();
Runner2 runner2 = new Runner2();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(runner1);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(runner2);
//thread1.start();
//thread2.start();
thread1.run();
thread2.run();
}
}
class Runner1 implements Runnable {
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<100;i++) {
System.out.printlen("Runner1 : i");
}
}
}
class Runner2 implements Runnable {
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<100;i++) {
System.out.printlen("Runner2 : i");
}
}
}
Class
异常处理
java中异常被封装成了一个类
出现问题时,会创建异常类对象并且抛出异常相关信息
自定义的异常类
https://www.cnblogs.com/heliusKing/p/10858832.html
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Statements/try...catch
https://www.runoob.com/jsref/jsref-statements.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/0328dongbin/p/9186676.html
创建自定义的异常类需要继承自Exception类
并提供含有一个String类型形参的构造方法,该形参就是一场的描述信息,
可以通过getMessage()方法获得。例如:
public class NewException extends Exception{ public NewException(String s){//这个s就是自定义的精髓所在,想传啥传啥 super(s); } }
什么叫“自定义异常类”?
它具有哪几部分?try-catch,throw,throws,finally
throw用来抛出一个指定的异常
throw new 异常类名(参数);
throws用来声明异常
捕获异常:try...catch...finally
Throwable类是所有异常类的超类
Exception类继承自Throwable类
RuntimeException类是运行异常类,继承自Exception类,它以及它的子类只能在运行过程中存在,无需throws声明,也无需处理,一旦发生,需要修改源代码
Error类与Exception类平级,表示java中的严重错误,只能通过修改代码来解决
异常:编译或运行时出现的异常问题
错误:运行时,无法处理,系统级别,只能通过修改源代码解决
过程:
1.运行或者编译时产生异常
2.创建异常类的对象
3.声明异常类
4.将异常类对象传给调用者(main()方法)处理
5.调用者无法处理,再将异常类对象传给jvm虚拟机
6.jvm虚拟机将异常类的信息(名称、详细信息、异常所处的位置)打印在屏幕上,并且停止程序的运行
API:
先跳过异常处理...
finally是无论有没有异常都会执行
JAVA虚拟机
Java Virtual Machine
https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1615674728647851945&wfr=spider&for=pc
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41701956/article/details/81664921
https://baike.baidu.com/item/java%E8%99%9A%E6%8B%9F%E6%9C%BA/6810577?fr=aladdin
包括
一套字节码(Bytecode)(目标代码)指令集:
操作码(8位二进制,高位bits在低字节)+操作数
一组寄存器
若JVM定义较多的寄存器,则减少对栈和内存进行访问,提高运行速度
但如果JVM的寄存器比CPU的寄存器多,则JVM运行速度实际降低
JVM设置了4个常用的寄存器
pc 程序计数器:记录程序的执行
optop 操作数栈顶指针
frame 当前执行环境指针
vars 指向当前第一个局部变量的指针
optop,frame,vars用于记录指向Java栈区的指针
寄存器均为32位
一个栈
JVM模拟真实计算机,作为基于栈结构的计算机,Java栈是储存JVM存储信息的主要方法
栈框架
一个垃圾回收堆
一个存储方法域
Java数组被当作Object处理
try-catch
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34427165/article/details/83929470
try {
//可能出现异常的代码
} catch(异常类名A e){
//如果出现了异常类A类型的异常,那么执行该代码
} ...(catch可以有多个)
finally {
//最终肯定必须要执行的代码(例如释放资源的代码)
}
代码执行的顺序:
1.try内的代码从出现异常的那一行开始,中断执行
2.执行对应的catch块内的代码
3.继续执行try catch结构之后的代码
1.儿子不能比父亲的本事大
2.儿子要比父亲开放
3.儿子不能比父亲惹更大的麻烦(子类的异常的类型不能是父类的异常的父类型)
接口
接口存在的重要原因:Java不支持多继承,所以要用接口实现多个类的功能
抽象方法的集合
一个类继承接口,从而继承接口的抽象方法
接口不是类
类描述对象的属性和方法, 接口包含类要实现的方法
除非实现接口的类是抽象类,否则该类要定义接口中的所有方法。
接口无法被实例化,但是可以被实现。
一个实现接口的类,必须实现接口内所描述的所有方法,否则就必须声明为抽象类。
接口类型可用来声明一个变量,他们可以成为一个空指针,或是被绑定在一个以此接口实现的对象。
接口和接口中的方法隐式抽象,声明时不必使用abstract
接口中的方法均为公有
接口与类相似点:
- 一个接口可以有多个方法。
- 接口文件保存在 .java 结尾的文件中,文件名使用接口名。
- 接口的字节码文件保存在 .class 结尾的文件中。
- 接口相应的字节码文件必须在与包名称相匹配的目录结构中。
接口与类的区别:
接口不能用于实例化对象。
接口没有构造方法。
接口中所有的方法必须是抽象方法。
接口不能包含成员变量,除了 static 和 final 变量。
接口中的变量都是public static final (会被隐式的指定)
接口不是被类继承了,而是要被类实现。
接口支持多继承。
抽象类和接口的区别
抽象类中的方法可以有方法体,就是能实现方法的具体功能,但是接口中的方法不行。
抽象类中的成员变量可以是各种类型的,而接口中的成员变量只能是 public static final 类型的。
接口中不能含有静态代码块以及静态方法(用 static 修饰的方法),而抽象类是可以有静态代码块和静态方法。
一个类只能继承一个抽象类,而一个类却可以实现多个接口。
多对多
//Animal.java
package animals;
interface Animal extends Nature,Universe {
public void eat();
public void travel();
}
package animals;
public class MammalInt implements Animal{
public void eat(){
System.out.println("Mammal eats");
}
public void travel(){
System.out.println("Mammal travels");
}
public int noOfLegs(){
return 0;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
MammalInt m = new MammalInt();
m.eat();
m.travel();
}
}
命令行操作如下:
$ mkdir animals
$ cp Animal.class MammalInt.class animals
$ java animals/MammalInt
Mammal eats
Mammal travel
import 声明必须在包声明之后,类声明之前。
例子:
package haha;
public class Hello {
public void Bye(Guagua a) {
a.standup();
}
}
import guaguastandup.Guagua;
//improt guaguastandup.*;
public class Hello {
public void Bye(Guagua a) {
a.standup();
}
}
类名:guaguastandup.Guagua.Hello
路径名:guaguastandup\Guagua\Hello.java
标记接口
没有任何方法
目的:
建立一个公共的父接口
" 正如EventListener接口,这是由几十个其他接口扩展的Java API,你可以使用一个标记接口来建立一组接口的父接口。例如:当一个接口继承了EventListener接口,Java虚拟机(JVM)就知道该接口将要被用于一个事件的代理方案。 "
向一个类添加数据类型
让该类通过多态性变成一个接口类型
instanceof
boolean result = obj instanceof Class
/*
author by runoob.com
Main.java
*/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Vector;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object testObject = new ArrayList();
displayObjectClass(testObject);
}
public static void displayObjectClass(Object o) {
if (o instanceof Vector)
System.out.println("对象是 java.util.Vector 类的实例");
else if (o instanceof ArrayList)
System.out.println("对象是 java.util.ArrayList 类的实例");
else
System.out.println("对象是 " + o.getClass() + " 类的实例");
}
}
package
java.awt 图形,用户界面。
java.lang 打包基础的类
java.io 通过数据流、序列化和文件系统提供系统输入输出。
java.util 包含集合框架,旧集合类,事件模型,日期和时间设施。
super
指向自己超类或父类的指针
超类指离自己最近的父类
class Country {
String name;
void value() {
name = "China";
}
}
class City extends Country {
String name;
void value() {
name = "Shanghai";
super.value();
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(super.name);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
City c = new City();
c.value();
}
}
引用构造函数
class Person {
public static void prt(String s) {
System.out.println(s);
}
Person() {
prt("父类无参数构造方法: " + "A person.");
}
Person(String name) {
prt("父类含参数构造方法: "+"A person's name is" + name);
}
}
public class Chinese extends Person {
Chinese() {
super();
prt("子类·调用父类"无参数构造方法": "+"A chinese coder.);
}
Chinese(String name) {
super(name);//调用基类的某一个构造函数
prt("子类·调用父类"含一个参数的构造方法": "+"his name is " + name);
}
Chinese(String name, int age) {
this(name);//调用本类的构造函数
prt("子类:调用子类具有相同形参的构造方法:his age is " + age);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Chinese cn = new Chinese();
cn = new Chinese("codersai");
cn = new Chinese("codersai",18);
}
}
class Test {
public static class Fruit{
Fruit() {
System.out.println("Yeah!Fruit!");
}
}
public static class Watermelon extends Fruit {
Watermelon() {
super();
System.out.println("Haha!Watermelon!");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Watermelon guagua = new Watermelon();
}
}
//Yeah!Fruit!
//Haha!Watermelon!
this是指向本身对象的指针,super是Java关键字
this和super不能同时出现在一个构造函数里面
this可以调用一个构造器,但不能调用两个
如果调用super(),必须写在子类构造方法的第一行
事实上,构造器的第一句都会隐式调用super(),因为要初始父类
Object类
属于java.lang包
常用方法:
equals()
相当于==,比较内存
如果需要比较对象内容,需要重写equal方法
**hashCode() **
返回对象的哈希值
toString()
返回值是String类型,描述当前对象的有关信息,当对象与String型数据的连接时,自动调用其toString()方法。
改写的时候:
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
....
return true;
...
return false;
}
重写
重写Object中的equals时应该遵循的
1.自反性
x.equals(x) == true
2.对称性
x.equals(y) == y.equals(x)
3.传递性
x.equals(y) == y.equals(z) == x.equals(z)
4.一致性
5.非空性
System类
位于java.lang包内
用于获取系统的属性数据,没有构造方法
试题
class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double sum = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++) {
sum = sum + i;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
//输出:15.0
class Test2 {
{
System.out.println("1");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Test2();
}
static {
System.out.println("2");
}
}
//输出:
2
1
//报错
class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double x;
System.out.println(x+2);
}
}
//报错
class Test2 {
double x;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(x+2);
}
}
class Test2 {
static double x;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(x+2);
}
}
//输出:2.0
class Test {
public String toString() {
return "Yayo~";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test t = new Test();
System.out.println(t);
}
}
//输出:Yayo~
class Test {
//public String toString() {
// return "Yayo~";
//}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test t = new Test();
System.out.println(t);
}
}
//输出:Test@5d22bbb7
class Test {
//public String toString() {
// return "Yayo~";
//}
public static void main(String[] args) {
{
String x = "";
for(int i=1;i<=3;i++) {
x = x+i;
}
System.out.println(x);
}
}
}
//输出:123
class Point {
public double x,y;
public Point(double x,double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public double distance(Point that) {
double xdiff,ydiff;
xdiff = x - that.x;
ydiff = y - that.y;
return Math.sqrt(xdiff*xdiff+ydiff*ydiff);
}
public String toString() {
return "x=" + x + "," + "y=" + y;
}
public void clear() {
x = 0;
y = 0;
}
}
class Polygon {
private Point[] vertices;
public Polygon(Point... vers) {
vertices = new Point[vers.length];
for(int i = 0; i < vertices.length; i++) {
vertices[i] = vers[i];
}
}
public void print() {
for(Point p : vertices) {
System.out.println(p);
}
}
public int getEdgeNum() {
return vertices.length;
}
}
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point p = new Point(1,2);
System.out.println(p);
p.clear();
Polygon triangle = new Polygon(new Point(0,1),new Point(1,1),new Point(1,0),new Point(0,0));
System.out.println(triangle.getEdgeNum());
triangle.print();
}
}
class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "guaguaStandup";
s[4] = 'a';
System.out.println(s);
}
}
//报错:A.java:4: 错误: 需要数组, 但找到String
// s[4] = 'a';
字符串对象是只读的
class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "guaguaStandup";
String t = "guaguaStandup";
String u = s;
if(s.equals(t)) {
System.out.println("Yes");
}
else {
System.out.println("No");
}
}
}
//Yes
class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean f = "guagua" instanceof String;
System.out.println(f);
//true
//f = 'a' instanceof String;
f = null instanceof String;
System.out.println(f);
//false
}
}
class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer s = new StringBuffer();
s.append("guagua").append("standup");
System.out.println(s);
}
}
//guaguastandup
class A{
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
System.out.println(a);
new A();
//表示申请了一个没有名字的A()类,调用了A类的构造函数
//匿名对象
A a;
//代表一个名为a的引用变量
//保存对象地址
A a = new A();
//此时a是A的实例化对象
}
}
class A{
public int x;
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
System.out.println(a.x);
}
}
//输出:0
每个数组都有一个length域
数组越界,系统会引发:IndexOutOfBoundsException异常
Java标准版:J2SE,企业版J2EE,微缩版J2ME
静态域
用static说明的一个域是一个类域或类变量,通常称为静态域
复用
println是一种名复用的方法
名复用
名字相同,基调不同
基调:signature,方法名字及形参数目和类型
基调不包括返回类型和引发异常,不能依据这些因素来得到名复用
路径
JAVA_HOME:也就是jdk的安装路径
path:PATH = JAVA_HOME\bin
PATH=%JAVA_HOME%\bin;%PATH%
class_path:绝对路径,定位到.class文件处
classpath = .; JAVA_HOME \lib
CLASSPATH=.;%JAVA_HOME%\lib;%JAVA_HOME%\lib\tools.jar
构造器
自动提供的无参构造器与相对应的类具有相同的访问控制
Java不自动提供一个缺省的拷贝构造器
Body(Body other){
idNum = other.idNum;
name = other.name;
}
UML
https://www.jianshu.com/p/2828874af134
https://blog.csdn.net/shenshenzhiwen/article/details/80299747
字符串
String类是只读类型
如果要修改一个字符串:使用一个与String独立的类:StringBuffer类
public static void replace(StringBuffer str,char oldChar,char newChar) {
for(int i=0;i<str.length;i++) {
if(str.charAt(i)==oldChar) {
str.setCharAt(i,newChar);
}
}
}
class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "abc";
String t = "abc";
System.out.println(s==t);
t = new String("abc");
System.out.println(s==t);
System.out.println(s.equals(t));
}
}
//输出:true
// false
// true
试卷
选择题
第一张试卷(2015年12月)
1.java中定义常量需要的修饰符:final
2.为了使自定义异常类受检测,必须使它为哪个类的子类:Exception
A.Exception B.Object C.RuntimeException D.Error
3.哪个类创建的对象是线程:Thread类
4.("hello" instanceof Object)取值:True
5.对应于float的包装类是:Float
6.若要在自定义的类中改写Object类中的toString方法,则访问控制可以是:
public
class A {
public String toString() {
return "haha";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
System.out.println(a);
}
}
//输出:haha
7.java中隐藏信息体现了面向对象的哪一特性:封装性
class A {
{
System.out.println("init");
}
static {
System.out.println("static init");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new A();
}
}
//static init
//init
class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int w = 0;
for(int x = 0; x<5; x++) {
inner:
for(int y = 0;y<100; y++) {
if(y==3)
break inner;
w++;
}
}
System.out.println(w);
}
}
//15
10.Unicode码的长度是:
2字节==16比特
11.为了使一个名为MyClass的自定义类在mypack命名包,则在源程序的第一行应该是:
package mypack;
class A {
public void f(int... x) {
String sum = "";
for(int i = 0; i<x.length; i++) {
sum = sum + x[i];
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
a.f(1,2,3,4,5);
}
}
//12345
class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final double x = 0;
System.out.println(x+2);
}
}
//2.0
第二张试卷(2016)
1.Java程序的安装路径为c:\java,则环境变量设置正确的是:
PATH = C:\java\bin
2."下列属于合法标识符的为":......
合法标识符满足:首字母: $ 或者 _ 或者 字母
后面的字符:$ 或者 __ 或者 字母 或者 数字
3.用64位储存的数据类型是:...
4.下列表达式正确的是:
float f = 0.9;
byte b = -128;
int i = 0L;
boolean B = null;
byte b = -128;正确
从大精度往小精度转化,必须强制转化
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(args[0]+args[1]);
//命令行javac Test.java&&java Test 1 2
//输出:12
}
}
6.错误的是:A
A.数组下标不能为表达式
B.数组成份的数目是由使用new创建时确定的,不是在说明时确定的
C.Java数组是同类型元素的有序集合
D.对数组的越界访问会引发IndexOutOfBoundsException异常
7.关于静态域的描述,错误的是: C
A.Java中用static来说明的域 ->对
B.不论是否创建对象,静态域都存在-> 对
C.抽象类中不能有静态域 错
abstract class Test {
abstract void f();
static {
int x = 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int length = 4;
String[] a = new String[length*5+10];
//命令行javac Test.java&&java Test 1 2
//输出:12
}
}
D.静态域的调用方法时:类名.域名
8.接口中的所有方法的默认为:
public abstract
9.java中定义实例方法和类方法区别:
前者没有static修饰,后者有static修饰
10.启动线程执行的方法:start();
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean b = true;
System.out.println(b+"hello");
}
//输出:truehello
}
12.关于下列接口和抽象类的说法,错误的是:B
A.含有抽象方法的类必须是抽象类
B.抽象类可以用final修饰,接口不可以
错,抽象类不能被final修饰
C.接口与抽象类一样,不能用new实例化一个对象
D.接口类可以被继承,再派生类中实现接口的方法
13.处理异常使用的关键字:
A.catch B.switch C.throws D.throw
14.关于继承正确的是:B
A.抽象方法不能继承
错
B.静态方法可以被继承
对
class y {
public static void f() {
System.out.println(123);
}
}
class Test extends y{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test y = new y();
y.f();
}
}
C.final修饰的类可以有子类
错
D.继承的方法的权限只能缩小不能扩大
错
第三张试卷(2013)
1.哪种访问控制修饰符的方法不能被改写:final
2.“任何非检测异常被引发后,都不能对其进行捕获处理”是正确的吗?
不正确
3.“利用Runnbale接口实现类所创建的对象使线程“,是正确的吗
不正确
4."Java语言中,接口只支持单一继承机制",正确吗?
错
class T {
{
System.out.println("haha");
}
}
public class A extends T{
{
System.out.println("gaga");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new A();
}
}
//输出:haha
// gaga
6.”一个类中有两个基调相同的方法,但返回类型不同,这两个方法是否为名复用?“ B
A.正确 B.不正确 C.不能肯定是否正确
7.若要在自定义的类中改写Object类中的toString()方法,形参的数目可以是: B
A.1个 B.不能有形参 C.可变数目 D.任意多个
8.方法改写属于:多态性
9.安装好JDK,在命令行方式下,为了运行解释器,一般要正确设置哪个环境变量?
classpath
class Test {
double x;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(x+1);
}
}
//b编译失败
第四张试卷
1.不能用于顶层类的定义的修饰符:private
class A {
public static int counter = 0;
public static int getInstanceCount() {
return counter;
}
public A(){
counter++;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a1 = new A();
A a2 = new A();
A a3 = new A();
System.out.println(A.getInstanceCount());
}
}
//输出:3
class A {
private int counter = 0;
public static int getInstanceCount() {
return counter;
}
public A(){
counter++;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a1 = new A();
A a2 = new A();
A a3 = new A();
System.out.println(A.getInstanceCount());
}
}
//编译错误,静态无法引用非静态
class A {
static {
int x = 5;
}
static int x,y;//x=0,y=0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
myMethod();
System.out.println(x+" "+y);//0 0
System.out.println(x++ + y + ++x);//2
}
public static void myMethod() {
y = x-- + ++x;
}
}
//输出:0 0
// 2
public class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] c = {'南','大'};
String[] s = {"南邮","南航","东南"};
A ex = new A();
ex.modify(c,s);
for(char c1 : c) {
System.out.print(c1);
}
System.out.print("不比" + s[2] + "差!");
}
public void modify(char[] c,String[] s) {
c = new char[] {'南','理','工'};//这种新申请的不行
s[s.length-1] = "南大";//引用可以改变,因为现在指针正指在原地址进行修改
}
}
//输出:南大不比南大差!
public class A {
static String s;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("s=" + s);
}
}
//输出:s = null
public class B {
public String show() {
return "hello";
}
}
public class A extends B{
public boolean show() {
return super.show().length() < 10;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
B b = new B();
B c = new A();
System.out.println(b.show()+" "+c.show());
}
}
//编译报错:
/*
A.java:1: 错误: 类 B 是公共的, 应在名为 B.java 的文件中声明
public class B {
^
A.java:7: 错误: A中的show()无法覆盖B中的show()
public boolean show() {
^
返回类型boolean与String不兼容
2 个错误
*/
class A{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("NJUST");
String s2 = "NJUST";
System.out.print((s1==s2)+",");
StringBuffer b1 = new StringBuffer("ABC");
StringBuffer b2 = b1;
b1.append("D");
System.out.print(b1==b2);
}
//输出:false,true
}
class A{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("NJUST");
String s2 = "NJUST";
System.out.print((s1==s2)+",");
StringBuffer b1 = new StringBuffer("ABC");
StringBuffer b2 = b1;
b1.append("D");
System.out.println(b1==b2);
System.out.println(b1);
}
/*
输出:
false,true
ABCD
*/
}
interface Jumpable{}
class Animal{}
class lion extends Animal implements Jumpable{}
下列哪个代码是正确的:D
A.Jumpable var1 = new Jumpable();
B.Lion var3 = new Animal();
C.Jumpable var4 = new Animal();
D.Jumpable var5 = new Lion();
class B{}
class A extends B{
String name;
A(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
B b = new A("haha");
A a = new A(RED);//WRONG
}
}
11.
//package njust;
class Book {
int pages = 2;
protected int interviews = 5;
}
public class Magazine extends Book {
private int totalPages(){
interviews = 8;
//System.out.println(super.interviews);//8
return this.interviews*super.interviews*pages;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new Magazine().totalPages());
}
}
//输出:128
class A {
public A() {
System.out.print("x");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new C("z");
}
}
class B extends A {
public B(String y) {
System.out.print(y);
}
}
class C extends B {
public C(String c) {
super(c);
A b = new B("y");
}
}
//输出:xzxy
第五张试卷(2013年)
1.定义局部变量可以用的修饰符:
final(唯一可用的)
2.异常类必是__的子类
Object\Exception\Throwable都对!!!
3.在自定义的类中该写Object类中的toString()类型,返回类型可以是
String
class A{
static{
System.out.println("init");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new A();
}
static{
System.out.println("static init");
}
}
class SuperClass {
int x;
void method0(){
method1();
}
void method1() {
x=11;
}
}
class SubClass extends SuperClass {
int x;
void method1() {
x = 2;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SubClass rSub = new SubClass();
SuperClass rSuper = rSub;
rSub.method0();
System.out.println(rSuper.x + "," +rSub.x);
}
}
//输出:0,2
第六张试卷(2014)
class B {
}
class A extends B {
public static void main(String[] args) {
B a = new B();
B b = a;
System.out.println(b instanceof A);
}
}
class A {
static {
System.out.println("haha");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new A();
}
{
System.out.println("hh");
}
}
/*
输出:
haha
hh
*/
class A {
{
System.out.println("haha");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new A();
}
static {
System.out.println("hh");
}
}
/*
输出:
hh
haha
*/
3.在类中定义一个toString方法,形参限定为:无形参
改写保证基调相同
class SuperClass {
int x;
void method0() {
method1();
}
private void method1() {
x = 11;
}
}
public class SubClass extends SuperClass {
int x;
private void method1() {
x = 2;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SubClass rSub = new SubClass();
SuperClass rSuper = rSub;//
rSub.method0();//
System.out.println(rSuper.x+","+rSub.x);
}
}
/*
输出:11,0
*/
去掉private后!
class SuperClass {
int x;
void method0() {
method1();
}
void method1() {
x = 11;
}
}
public class SubClass extends SuperClass {
int x;
void method1() {
x = 2;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SubClass rSub = new SubClass();
SuperClass rSuper = rSub;
rSub.method0();
System.out.println(rSuper.x+","+rSub.x);
}
}
/*
输出:0,2
*/
判断题
第一张试卷
1.抽象方法必须定义在抽象类中,所以抽象类中的方法都是抽象方法
错
抽象类中不一定要包含抽象方法,且不一定都是抽象方法
只要一个类里面有抽象方法,则该类一定是抽象类
abstract class B {
public void print() {
System.out.println("GUAGUA");
}
}
class A extends B {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
a.print();
}
}
2.接口中只能定义常量和抽象方法
对
3.一个类中如果没有定义构造器,那么这个类就没有构造器
错,
缺省构造器
4.static关键字可以修饰成员变量,也可以修饰局部变量
错,不可以修饰局部变量
成员变量:类变量、实例变量和常量统称成员变量
5.Java配置环境变量path的目的是为了可以查找到.class文件
错
查找或创建?
6.一个实例对象只能被一个变量引用
错
7.子类中改写父类的方法需要和父类被改写的方法具有相同的方法名、参数列表以及返回值类型
答案写的是错
因为返回值类型可以是原返回类型的子类
class A_father{
public void print() {
System.out.println("guagua");
}
}
class A extends A_father{
public String print() {
System.out.println("standup");
return "guagua";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
a.print();
}
}
//编译错误
/*
A.java:7: 错误: A中的print()无法覆盖A_father中的print()
public String print() {
^
返回类型String与void不兼容
*/
//需要改成:
class A_father{
public void print() {
System.out.println("guagua");
}
}
class A extends A_father{
public void print() {
System.out.println("standup");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
a.print();
}
}
//standup
sclass A_father{
public void print() {
System.out.println("guagua");
}
}
class A extends A_father{
public void print() {
System.out.println("standup");
}
public void superprint() {
super.print();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
a.print();
a.superprint();
}
}
/*
输出:
standup
guagua
*/
//看起来要在子类里写一个调用父亲print函数的函数
//如果要避免改写造成的后果,可以在改写的时候调用super.print();
8.构造器不是方法,不能名复用
错,构造器可以名复用
9.Android技术由Google公司创立
对
10.I为接口,由于不能用I创建对象,因此也不能利用“new I[10]"创建数组对象
错
interface H { }
class A implements H{
public static void main(String[] args) {
H[] h = new H[20];
}
}
//正常运行
11.基本数据的局部变量没有缺省值,但引用数据类型的局部类型有缺省值
错,引用数据类型的局部类型也没有缺省值
12.接口中的方法都是final的
错
接口中的变量都是final的
但是方法都不是 默认public abstract
13.在java中,子类可以改写父类的任意方法
错
父类的不能被继承的不能改写 比如private方法
父类中final的也不能
//package njust;
class Book {
int pages = 2;
protected int interviews = 5;
static void f() {
System.out.println(234);
}
}
public class Magazine extends Book {
private int totalPages(){
interviews = 8;
//System.out.println(super.interviews);//8
return this.interviews*super.interviews*pages;
}
static void f() {
System.out.println(123);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new Magazine().totalPages());//128
Book.f();//234
new Magazine().f();//123
}
}
//输出:128
14.抽象类不能定义引用
错
15.Java中没有缺省的访问控制修饰符
错
貌似是对的
java中的缺省访问控制就是friendly,也可以认为访问限制为包(包权限)
错?
错!!
缺省值为default
貌似是对的.....???
错!
就是package
class B{
int i;
void f() {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
B x = new B();
x.f();
System.out.println(x.i);
}
}
第二张试卷
1.java的int类型所占字节有具体软硬件环境决定
错
2.Java的形参唯一可用的修饰符为final
对
形参指的是调用时传递的值
3.在局部变量中,如果没有给定初始值,Java会按照默认值赋值
错
4.Java程序中,可以将一个数组赋给一个类型为Object的变量
对
5.在类型转换中有些类型转换是不允许的,如boolean不能够转换为int
对,boolean与int不兼容
6.null instanceof Object 总是返回false
对
7.Java源文件中最多只能有一个public类,所以编译后只能产生一个.class文件
错
8.子类中如果使用super()调用超类构造器,必须子类构造器的第一条语句
对
9.如果超类没有无参构造器,则子类必须至少提供一个构造器
对
10.子类重写超类的方法抛出的异常只可以列出比其超类更少更具体地类型(子类型)
错
只需要保证是原来的类型或者是原来类型的子类
11.如果一个方法会抛出异常,必须用try catch语句进行处理
错
12.在Java中十六进制整型常量是以数字字符0x开头进行表示
对
13.java语言中,利用对象引用作为实参调用System.out.println方法可以得到该对象的字符串表示
对
14.一个源文件中最多只有一个main方法
错
class B{
void main() {
System.out.println("guagua");
}
}
class A{
public static void main(String[] args) {
new B().main();
}
}
15.实现接口的类可以有非静态域,也可以用静态方法
对
第三章试卷
1.JVM只能由软件实现
错
2.Java中String是基本类型
错
3.任何类中都有缺省的构造器
错
自己写过就没有了
4.final类可以是抽象的
错!!!
抽象类用于被改写
final类不能被改写
QuQ
5.Java中的私有方法不能被改写
对
public 和 protected可以
6.类B是A的子类,C是B的子类,则A是C的超类型
对
7.整型实例变量的缺省值为0
对
8.作为程序执行入口的main方法中可以出现this引用
错,不可以用静态引用非静态
9.Java中没有缺省的拷贝构造器
对
10.通过对象引用也可以访问静态成员
对
11.受保护的成员在包外无法被访问
对
12.Java中提供了带标号的break语句
对
13.java中的构造器可以名复用
对
14.java中的构造器可以被继承
错
15.java中字符数组不是字符串对象
对
第四章试卷
1..因为抽象的类不能实例化,故抽象的类中不能有构造器
错
abstract class abstractClass{
abstract void print();
public abstractClass() {
//抽象类中可以定义构造器,虽然不能初始化,但仍然可以被调用
System.out.println("abstract class");
}
public static void aFunc() {
System.out.println("i am static func");
}
}
public class AbstractClassTest extends abstractClass{
public AbstractClassTest() {
System.out.println("子类构造器");
}
@Override
void print() {
System.out.println("test");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbstractClassTest.aFunc();
new AbstractClassTest().print();
}
}
//output:
//i am static func
//abstract class
//子类构造器
//test
2.父类中的final方法不能被子类改写
对
3.如果一个类声明可以实现某个接口,就必须给出该接口的所有方法的具体实现
对
要给出主体
否则报错显示"未覆盖"
4.表达式3.0+2类型为double
对
5.接口中可以声明非静态的属性(域)
错
6.X是一个接口,Y是一个类,"X extends Y"是正确的
错
7.异常处理时,应先捕获父类异常,再捕获子类异常
先捕获子类,再捕获父类
否则会直接抛出父类的异常不再往上捕获
8.既然调用线程对象start()方法会执行run()方法,我们也可以直接调用线程对象的run()方法来实现多线程功能
错
9.Java内部符号编码为Unicode码
对
10.protected修饰的成员变量只能被自身或同一个包中的类访问
错
11.Java方法重载(方法名复用)不受方法返回值的限制
对
基调不同即可
class B{
boolean f(int t) {
return true;
}
void f() {
System.out.println(1);
}
}
public class A extends B{
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
12.异常处理时必须要有finally程序块
错
13.创建二维数组时,第二个维度的大小可以不固定
对
14.Exception类是Error的子类
错
它俩都是Throwable的子类
15.只要某个对象不是null,都可以调用该对象的同String()方法
对
class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = null;
s.toString();//报错
System.out.println(s);//输出null
}
}
第五张试卷
1.接口中不能有数据成员
错
2.Java抽象类不能创建对象
对
3.java中类和接口都只支持单一继承机制
错
4.final类可以派生子类
错
5.4的类型是long
错
默认int
6.私有方法不能被改写
对
7.0.5的类型为double
对
默认double
8........
9.Java构造器可以被继承
错
10.通过对象引用无法访问静态成员
错
11.一个类只能实现一个接口
错
接口支持多继承
12.数组对象的length域不允许被程序修改
对
13.Java中任何类都有缺省的构造器
错
自己定义之后就没有缺省的构造器了
14.局部变量无缺省值
对
第六张试卷
1.改变数组的length域....
错
2.无参构造器只能缺省提供,不能自己定义
错错错!
3.Java的类只支持单一继承机制
对
4.final类不能创建对象
错
final class B{
B() {
System.out.println(1);
}
}
class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
B b = new B();
}
}
5.字符串对象的长度可以通过调用其length()方法得到
对
6.Java中任意方法都能被改写
错
7.Java中没有缺省的访问控制修饰符
缺省为:package
8.final方法不能被改写
对
9.Java中提供了带标号的continue语句
对
10.抽象类可以创建对象
...错
abstract class B{
B() {
System.out.println(1);
}
}
class A extends B{
public static void main(String[] args) {
B x = new A(); //引用,没有实例化B
B[] y = new B[20]; //创建数组对象,没有实例化B
}
}
11.接口中的方法都是抽象的
yes
12.java中缺省的访问控制修饰符是package
yes
13.Java中任何类都有缺省的拷贝构造器
错
大题
第一张试卷
第一大题


interface I{
void setXY(float x,float y);
float getX();
float getY();
float distance();
float distance(float x,float y);
}
class City implements I{
private float x = 0;
private float y = 0;
public void setXY(float x,float y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public float getX() {
return this.x;
}
public float getY() {
return this.y;
}
public float distance() {
return (float)Math.sqrt((double)(this.x*this.x+this.y*this.y));
}
public float distance(float x,float y) {
x -= this.x;
y -= this.y;
return (float)Math.sqrt((double)(x*x+y*y));
}
}
class TestCity{
public static void main(String[] args) {
City[] c = new City[1000];
for(int i=0;i<c.length;i++) {
c[i] = new City();
c[i].setXY(i,i+1);
}
I[] p = c;
float ans1 = 0;
float ans2 = 0;
for(int i=0; i<p.length; i++) {
ans1 += p[i].distance();
}
for(int i=1; i<p.length; i++) {
ans2 += (p[i].distance(p[i-1].getX(),p[i-1].getY()));
}
System.out.println(ans1);
System.out.println(ans2);
}
}
第二题
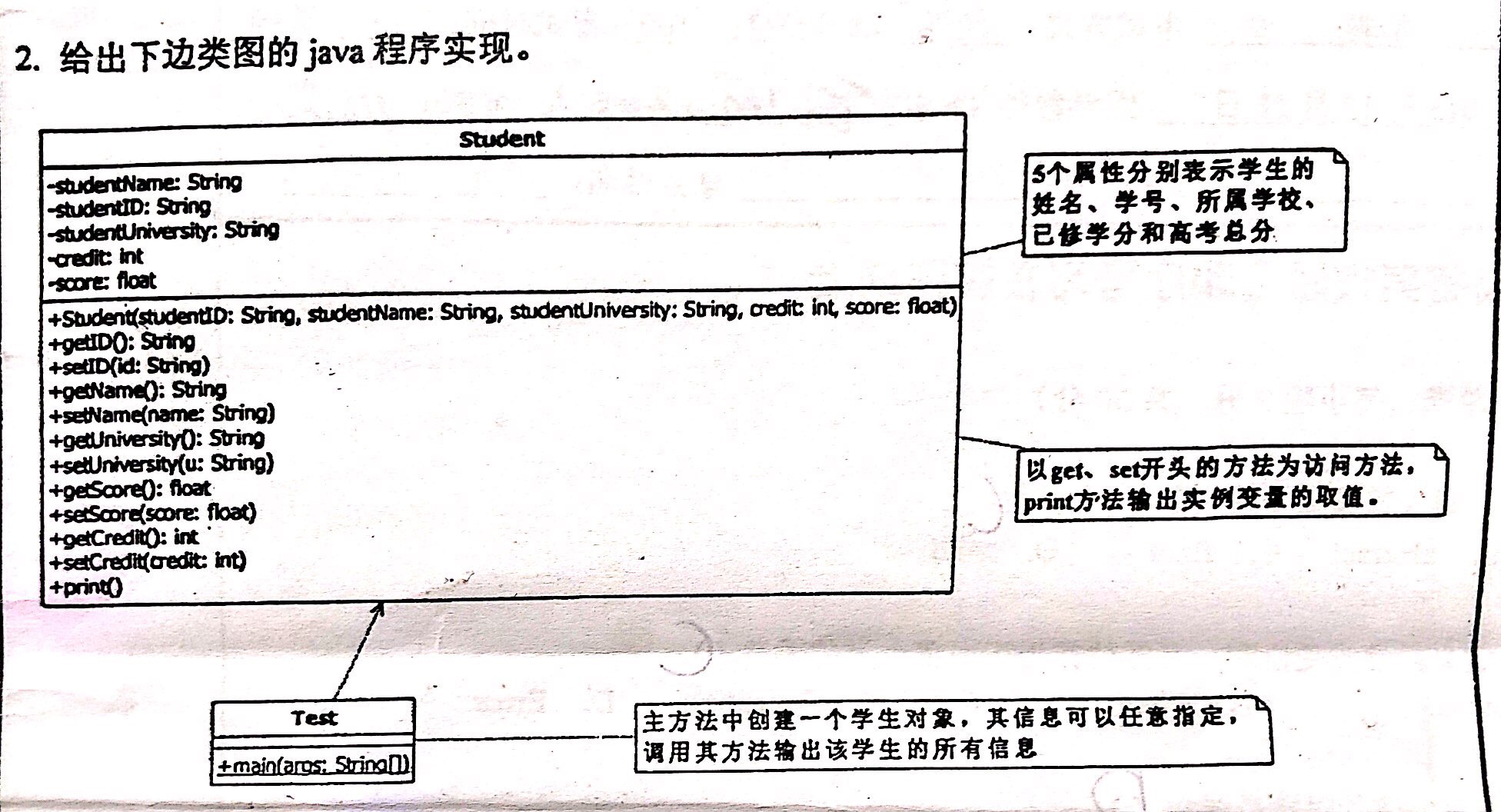
class Student {
private String studentName;
private String studentID;
private String studentUniversity;
private int credit;
private float score;
public Student(String studentID,String studentName,String studentUniversity,int credit,float score){
this.studentID = studentID;
this.studentName = studentName;
this.studentUniversity = studentUniversity;
this.credit = credit;
this.score = score;
}
public String getID() {
return studentID;
}
public void setID(String studentID) {
this.studentID = studentID;
}
public String getName() {
return studentName;
}
public void setName(String studentName) {
this.studentName = studentName;
}
public String getUniversity() {
return studentUniversity;
}
public void setUniversity(String studentUniversity) {
this.studentUniversity = studentUniversity;
}
public int getCredit() {
return credit;
}
public void setCredit(int credit) {
this.credit = credit;
}
public float getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(float score) {
this.score = score;
}
public void print() {
System.out.println("Student ID = "+studentID);
System.out.println("Student Name = "+studentName);
System.out.println("Student University = "+score);
System.out.println("Credit = "+credit);
System.out.println("score = "+score);
}
}
class TestStudent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student("123","guagua","NJUST",100,100);
s.print();
}
}
第三题

import java.util.Random;
class Number {
public int value;
public boolean isEven;
}
class Triangle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int depth = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
Random random = new Random();
int fib[] = {1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,34,55};
Number[][] x = new Number[depth][];
//System.out.println(x.length);
for(int i=0;i<x.length;i++) {
int length = random.nextInt(10);
x[i] = new Number[length];
for(int j=0;j<length;j++) {
x[i][j] = new Number();
x[i][j].value = fib[j];
if(fib[j]%2==0) {
x[i][j].isEven = true;
}
else x[i][j].isEven = false;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<x.length;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<x[i].length;j++) {
System.out.print(x[i][j].value);
if(j==x[i].length-1) {
System.out.println();
}
else{
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
}
}
}
第二张试卷
1.输入一系列整数,输入0时结束。输出最大值和最大值的个数
import java.util.Scanner;
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int max = 0;
int id = 0;
int cnt = 0;
int[] a = new int[1000];
while(true) {
int num = sc.nextInt();
if(num==0) {
break;
}
//a[id] = new int();
a[id] = num;
id++;
if(num>max) {
max = num;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<id;i++) {
if(a[i] == max) {
cnt++;
}
}
System.out.println("The maximum number is "+max+",The number of the max number is "+cnt);
}
}
2.
class Rectangle2D {
private double x,y;
private double width,height;
Rectangle2D() {
this.x = 0;
this.y = 0;
this.width = 0;
this.height = 0;
}
Rectangle2D(double x,double y,double width,double height) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
void setwidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
void setheight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
double getX() {
return this.x;
}
double getY() {
return this.y;
}
double getWidth() {
return this.width;
}
double getHeight() {
return this.height;
}
double getPerimter() {
return (this.width+this.height)*2;
}
double getArea() {
return (this.width)*(this.height);
}
}
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle2D t1 = new Rectangle2D();
Rectangle2D t2 = new Rectangle2D(0,0,6,4);
System.out.println(t1.getPerimter()+" "+t1.getArea());
System.out.println(t2.getPerimter()+" "+t2.getArea());
}
}
3。
class Rectangle2D {
private double x,y;
private double width,height;
Rectangle2D() {
this.x = 0;
this.y = 0;
this.width = 0;
this.height = 0;
}
Rectangle2D(double width,double height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
Rectangle2D(double x,double y,double width,double height) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
void setwidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
void setheight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
double getX() {
return this.x;
}
double getY() {
return this.y;
}
double getWidth() {
return this.width;
}
double getHeight() {
return this.height;
}
double getPerimter() {
return (this.width+this.height)*2;
}
double getArea() {
return (this.width)*(this.height);
}
}
interface Comparable {
public int compareTo(Object obj);
}
class ComparableRectangle2D extends Rectangle2D implements Comparable {
ComparableRectangle2D(double a,double b) {
super(a,b);
}
ComparableRectangle2D(double a,double b,double c,double d) {
super(a,b,c,d);
}
ComparableRectangle2D() {
super();
}
public int compareTo(Object obj) {
double a = this.getArea();
double b = ((Rectangle2D)obj).getArea();
if(a>b)
return 1;
else return 0;
}
}
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ComparableRectangle2D t1 = new ComparableRectangle2D();
ComparableRectangle2D t2 = new ComparableRectangle2D(6,4);
System.out.println(t1.compareTo(t2));
System.out.println(t1.getPerimter()+" "+t1.getArea());
System.out.println(t2.getPerimter()+" "+t2.getArea());
}
}
第三张试卷
1.easy
class Course {
private String CourseId;
private String CourseName;
private String CourseClass;
private int time;
private float score;
Course(String CourseId,String CourseName,String CourseClass,int time,float score) {
this.CourseId = CourseId;
this.CourseName = CourseName;
this.CourseClass = CourseClass;
this.time = time;
this.score;
}
/*
getXXX();
setXXX();
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Course c = new Course(..........);
}
}
interface I {
public float calCircum();
public float claArea();
}
class MyGraphic {
public String lineColor;
public String fillColor;
MyGraphic(String lineColor,String fillColor) {
this.lineColor = lineColor;
this.fillColor = fillColor;
}
void print() {
System.out.println("Linecolor is "+lineColor);
System.out.println("Fillcolor is "+fillColor);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyCircle c = new MyCircle("black","white",4);
MyRectangle r = new MyRectangle("red","blue",1,2);
c.print();
System.out.println(c.claArea()+" "+c.calCircum());
r.print();
System.out.println(r.claArea()+" "+r.calCircum());
}
}
class MyRectangle extends MyGraphic implements I{
public float rLong,rWidth;
MyRectangle(String lineColor,String fillColor,float rLong,float rWidth) {
//this.lineColor = lineColor;
//this.fillColor = fillColor;
super(lineColor,fillColor);
this.rLong = rLong;
this.rWidth = rWidth;
}
public float calCircum() {
return 2*(rLong+rWidth);
}
public float claArea() {
return rLong*rWidth;
}
}
class MyCircle extends MyGraphic implements I{
public float radius;
MyCircle(String lineColor,String fillColor,float radius) {
//this.lineColor = lineColor;
//this.fillColor = fillColor;
super(lineColor,fillColor);
this.radius = radius;
}
public float calCircum() {
return 2*3.1415926535f*radius;
}
public float claArea() {
return 3.1415926535f*radius*radius;
}
}
class Number {
public int value;
public boolean isEven;
}
class Pascal {
public static int cal(int i,int j) {
int ans = 1;
for(int k = j+1;k<=i;k++) {
ans*=k;
}
for(int k = 1;k<=i-j;k++) {
ans/=k;
}
if(i==j)return 1;
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int depth = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);//将字符串转化为整数
Number[][] x = new Number[depth][];
for(int i=0;i<x.length;i++) {
int length = i+1;
x[i] = new Number[length];
for(int j=0;j<length;j++) {
x[i][j] = new Number();
x[i][j].value = cal(i,j);
if(x[i][j].value%2==0) {
x[i][j].isEven = true;
}
else x[i][j].isEven = false;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<x.length;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<x[i].length;j++) {
System.out.print(x[i][j].value);
if(j==x[i].length-1) {
System.out.println();
}
else{
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
}
}
}
第四张试卷
import java.util.Scanner;
class cosx {
public float f(float x,int n) {
float ans = 1;
for(float i=1;i<=n;i++){
ans*=(-1)*(x*x);
}
for(float i=1;i<=n*2;i++) {
ans/=i;
}
/*
String s = Float.toString(ans);
System.out.println(s);
if(s.length()>=7){
return ans;
}
*/
//System.out.println(ans);
if(ans<=0.00001&&ans>=0){
return ans;
}
else if(ans<=0&&ans>=-0.00001){
return ans;
}
else{
return ans+ f(x,n+1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("please input the value:");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
float x = sc.nextFloat();
cosx c = new cosx();
float ans = c.f(x,0);
System.out.println("cos("+x+") = "+ans);
}
}
2.简单
class Teacher {
private String name;
private int age;
private String education;
private String position;
Teacher(String name,int age,String education,String position) {
/*......*/
}
/*
setXX(XX ..){}
getXX() {}
*/
public void introduction() {
System.out.println(".......................");
}
}
class TeacherTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Teacher t = new Teacher("123",213,"132","321");
t.introduction();
}
}
假题???
interface Pet {
public String play();
}
class Animal{
protected int legs;
protected Animal(int legs) {
this.legs = legs;
}
protected String walk() {
String l = Integer.toString(legs);
return "This animal use " + l + "legs to walk.";
}
public int getLegs(){
return this.legs;
}
}
class Cat extends Animal implements Pet{
private String name;
Cat(int legs,String name) {
super(legs);
this.name = name;
}
public String play() {
return name + " likes to catch the mouse.";
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
}
class Fish extends Animal implements Pet{
private String name;
Fish(int legs,String name) {
super(legs);
this.name = name;
}
public String play() {
return name + " likes to swim.";
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
}
class TestAnimal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal[] animal= new Animal[2];
animal[0] = new Cat(4,"doudou");
animal[1] = new Fish(0,"blue gem");
for(int i=0;i<=1;i++) {
System.out.println(animal[i].play());
System.out.println(animal[i].walk());
}
}
}
第五张试卷
1.简单不写了
2.写过了不写了
3.写过了不写了
第六张试卷
简单不写了
第七张试卷(2007)
class A{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 50,b = 30,c=20;
System.out.println((a==(b-10)&&(b<=c)));
//输出:false
}
}
一个char是_____ 个字节,一个汉字需要______char存放
两个字节,一个char
class A{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10,b = 20;
System.out.println(a<b?b-20:a+12);
//输出:0
}
}
_____方法,可以直接通过类名来调用.
静态方法
_____方法,其名字和类名相同,并且没有返回类型
构造器
定义一个包用package关键字,包由一组____和_____组成.
class A{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("\\");
//输出:\
}
}
class A {}
class B extends A {}
class TestA {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
B b = (B)a;
//B类型不可以强制转化为A
}
}
class TestA {
private int count;
public void print() {
System.out.println(count);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new TestA().print();
}
}
byte的范围为-128~127



