【Java学习】pom.xml配置

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> 5 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> 6 7 <groupId>com.dycs</groupId> 8 <artifactId>dycs</artifactId> 9 <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> 10 11 <!-- maven 参数配置,这里引用不同的testng.xml --> 12 <properties> 13 <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> 14 <xmlFileName>testng.xml</xmlFileName> 15 </properties> 16 17 18 <!-- maven 引用依赖不同的jar --> 19 <dependencies> 20 21 <!-- 依赖testNg --> 22 <dependency> 23 <groupId>org.testng</groupId> 24 <artifactId>testng</artifactId> 25 <version>6.9.10</version> 26 <scope>test</scope> 27 </dependency> 28 29 <!-- 依赖reportNg 关联testNg --> 30 <dependency> 31 <groupId>org.uncommons</groupId> 32 <artifactId>reportng</artifactId> 33 <version>1.1.4</version> 34 <scope>test</scope> 35 <exclusions> 36 <exclusion> 37 <groupId>org.testng</groupId> 38 <artifactId>testng</artifactId> 39 </exclusion> 40 </exclusions> 41 </dependency> 42 43 <!-- 依赖Guice --> 44 <dependency> 45 <groupId>com.google.inject</groupId> 46 <artifactId>guice</artifactId> 47 <version>3.0</version> 48 <scope>test</scope> 49 </dependency> 50 51 <!-- 依赖Selenium驱动包 --> 52 <dependency> 53 <groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId> 54 <artifactId>selenium-java</artifactId> 55 <version>2.52.0</version> 56 <scope>compile</scope> 57 <!-- 58 scope标签中对应值的解释: 59 * compile,缺省值,适用于所有阶段,会随着项目一起发布。 60 * provided,类似 compile,期望 JDK、容器或使用者会提供这个依赖。如 servlet.jar。 61 * runtime,只在运行时使用,如 JDBC 驱动,适用运行和测试阶段。 62 * test,只在测试时使用,用于编译和运行测试代码。不会随项目发布。 63 * system,类似 provided,需要显式提供包含依赖的 jar, Maven 不会在 Repository 中查找它。 64 --> 65 </dependency> 66 67 </dependencies> 68 69 70 71 72 <build> 73 <plugins> 74 <!-- 添加插件 关联testNg.xml --> 75 <plugin> 76 <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> 77 <artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId> 78 <version>2.17</version> 79 <configuration> 80 <suiteXmlFiles> 81 <suiteXmlFile>res/${xmlFileName}</suiteXmlFile> 82 </suiteXmlFiles> 83 </configuration> 84 </plugin> 85 86 <!-- 添加插件,添加ReportNg的监听器,修改最后的TestNg的报告 --> 87 <plugin> 88 <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> 89 <artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId> 90 <version>2.5</version> 91 <configuration> 92 <properties> 93 <property> 94 <name>usedefaultlisteners</name> 95 <value>false</value> 96 </property> 97 <property> 98 <name>listener</name> 99 <value>org.uncommons.reportng.HTMLReporter</value> 100 </property> 101 </properties> 102 <workingDirectory>target/</workingDirectory> 103 <!-- <forkMode>always</forkMode> --> 104 </configuration> 105 </plugin> 106 </plugins> 107 </build> 108 </project> 109 110 111 112 113 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 114 <!DOCTYPE suite SYSTEM "http://testng.org/testng-1.0.dtd"> 115 <suite name="Default suite"> 116 <test verbose="2" name="Default test"> 117 <classes> 118 <class name="TestHelloWorld" /> 119 </classes> 120 </test> <!-- Default test --> 121 </suite> <!-- Default suite -->

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> 5 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> 6 7 <groupId>org.example</groupId> 8 <artifactId>AppiumAndroid</artifactId> 9 <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> 10 11 <!-- maven 参数配置,这里引用不同的testng.xml --> 12 <properties> 13 <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> 14 <xmlFileName>testng.xml</xmlFileName> 15 </properties> 16 17 18 <!-- maven 引用依赖不同的jar --> 19 <dependencies> 20 21 <!-- 依赖testNg --> 22 <dependency> 23 <groupId>org.testng</groupId> 24 <artifactId>testng</artifactId> 25 <version>6.9.10</version> 26 <scope>test</scope> 27 </dependency> 28 29 <!-- 依赖fastjson --> 30 <dependency> 31 <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> 32 <artifactId>fastjson</artifactId> 33 <version>1.2.74</version> 34 </dependency> 35 36 <!-- 依赖reportNg 关联testNg --> 37 <dependency> 38 <groupId>org.uncommons</groupId> 39 <artifactId>reportng</artifactId> 40 <version>1.1.4</version> 41 <scope>test</scope> 42 <exclusions> 43 <exclusion> 44 <groupId>org.testng</groupId> 45 <artifactId>testng</artifactId> 46 </exclusion> 47 </exclusions> 48 </dependency> 49 50 <!-- 依赖Guice --> 51 <dependency> 52 <groupId>com.google.inject</groupId> 53 <artifactId>guice</artifactId> 54 <version>3.0</version> 55 <scope>test</scope> 56 </dependency> 57 58 <!-- 依赖Selenium驱动包 --> 59 <dependency> 60 <groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId> 61 <artifactId>selenium-java</artifactId> 62 <version>2.52.0</version> 63 <scope>test</scope> 64 <!-- 65 scope标签中对应值的解释: 66 * compile,缺省值,适用于所有阶段,会随着项目一起发布。 67 * provided,类似 compile,期望 JDK、容器或使用者会提供这个依赖。如 servlet.jar。 68 * runtime,只在运行时使用,如 JDBC 驱动,适用运行和测试阶段。 69 * test,只在测试时使用,用于编译和运行测试代码。不会随项目发布。 70 * system,类似 provided,需要显式提供包含依赖的 jar, Maven 不会在 Repository 中查找它。 71 --> 72 </dependency> 73 74 <!-- 依赖Appium java-client驱动包 --> 75 <dependency> 76 <groupId>io.appium</groupId> 77 <artifactId>java-client</artifactId> 78 <version>5.0.0-BETA9</version> 79 </dependency> 80 81 <!-- 依赖Appium java-client驱动包 --> 82 <dependency> 83 <groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId> 84 <artifactId>selenium-server-standalone</artifactId> 85 <version>LATEST</version> 86 </dependency> 87 88 </dependencies> 89 90 <build> 91 <plugins> 92 <!-- 添加插件 关联testNg.xml --> 93 <!-- 添加插件,添加ReportNg的监听器,修改最后的TestNg的报告 --> 94 <plugin> 95 <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> 96 <artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId> 97 <version>2.5</version> 98 <configuration> 99 <suiteXmlFiles> 100 <suiteXmlFile>res/${xmlFileName}</suiteXmlFile> 101 </suiteXmlFiles> 102 <properties> 103 <property> 104 <name>usedefaultlisteners</name> 105 <value>false</value> 106 </property> 107 <property> 108 <name>listener</name> 109 <value>org.uncommons.reportng.HTMLReporter</value> 110 </property> 111 </properties> 112 <workingDirectory>target/</workingDirectory> 113 <!-- <forkMode>always</forkMode> --> 114 </configuration> 115 </plugin> 116 </plugins> 117 </build> 118 </project>
https://recomm.cnblogs.com/blogpost/7190868
https://www.cnblogs.com/zhoudaxing/p/11338183.html
setting.xml主要用于配置maven的运行环境等一系列通用的属性,是全局级别的配置文件;而pom.xml主要描述了项目的maven坐标,依赖关系,开发者需要遵循的规则,缺陷管理系统,组织和licenses,以及其他所有的项目相关因素,是项目级别的配置文件。
基础配置
一个典型的pom.xml文件配置如下:
1 <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
2 xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
3
4 <!-- 模型版本。maven2.0必须是这样写,现在是maven2唯一支持的版本 -->
5 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
6
7 <!-- 公司或者组织的唯一标志,并且配置时生成的路径也是由此生成, 如com.winner.trade,maven会将该项目打成的jar包放本地路径:/com/winner/trade -->
8 <groupId>com.winner.trade</groupId>
9
10 <!-- 本项目的唯一ID,一个groupId下面可能多个项目,就是靠artifactId来区分的 -->
11 <artifactId>trade-core</artifactId>
12
13 <!-- 本项目目前所处的版本号 -->
14 <version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
15
16 <!-- 打包的机制,如pom,jar, maven-plugin, ejb, war, ear, rar, par,默认为jar -->
17 <packaging>jar</packaging>
18
19 <!-- 帮助定义构件输出的一些附属构件,附属构件与主构件对应,有时候需要加上classifier才能唯一的确定该构件 不能直接定义项目的classifer,因为附属构件不是项目直接默认生成的,而是由附加的插件帮助生成的 -->
20 <classifier>...</classifier>
21
22 <!-- 定义本项目的依赖关系 -->
23 <dependencies>
24
25 <!-- 每个dependency都对应这一个jar包 -->
26 <dependency>
27
28 <!--一般情况下,maven是通过groupId、artifactId、version这三个元素值(俗称坐标)来检索该构件, 然后引入你的工程。如果别人想引用你现在开发的这个项目(前提是已开发完毕并发布到了远程仓库),-->
29 <!--就需要在他的pom文件中新建一个dependency节点,将本项目的groupId、artifactId、version写入, maven就会把你上传的jar包下载到他的本地 -->
30 <groupId>com.winner.trade</groupId>
31 <artifactId>trade-test</artifactId>
32 <version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
33
34 <!-- maven认为,程序对外部的依赖会随着程序的所处阶段和应用场景而变化,所以maven中的依赖关系有作用域(scope)的限制。 -->
35 <!--scope包含如下的取值:compile(编译范围)、provided(已提供范围)、runtime(运行时范围)、test(测试范围)、system(系统范围) -->
36 <scope>test</scope>
37
38 <!-- 设置指依赖是否可选,默认为false,即子项目默认都继承:为true,则子项目必需显示的引入,与dependencyManagement里定义的依赖类似 -->
39 <optional>false</optional>
40
41 <!-- 屏蔽依赖关系。 比如项目中使用的libA依赖某个库的1.0版,libB依赖某个库的2.0版,现在想统一使用2.0版,就应该屏蔽掉对1.0版的依赖 -->
42 <exclusions>
43 <exclusion>
44 <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
45 <artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
46 </exclusion>
47 </exclusions>
48
49 </dependency>
50
51 </dependencies>
52
53 <!-- 为pom定义一些常量,在pom中的其它地方可以直接引用 使用方式 如下 :${file.encoding} -->
54 <properties>
55 <file.encoding>UTF-8</file.encoding>
56 <java.source.version>1.5</java.source.version>
57 <java.target.version>1.5</java.target.version>
58 </properties>
59
60 ...
61 </project>
classifier元素用来帮助定义构件输出的一些附属构件。附属构件与主构件对应,比如主构件是 kimi-app-2.0.0.jar,该项目可能还会通过使用一些插件生成 如kimi-app-2.0.0-javadoc.jar (Java文档)、 kimi-app-2.0.0-sources.jar(Java源代码) 这样两个附属构件。这时候,javadoc、sources就是这两个附属构件的classifier,这样附属构件也就拥有了自己唯一的坐标。
classifier的用途在于:
1. maven download javadoc / sources jar包的时候,需要借助classifier指明要下载那个附属构件
2. 引入依赖的时候,有时候仅凭groupId、artifactId、version无法唯一的确定某个构件,需要借助classifier来进一步明确目标。比如JSON-lib,有时候会同一个版本会提供多个jar包,在JDK1.5环境下是一套,在JDK1.3环境下是一套:
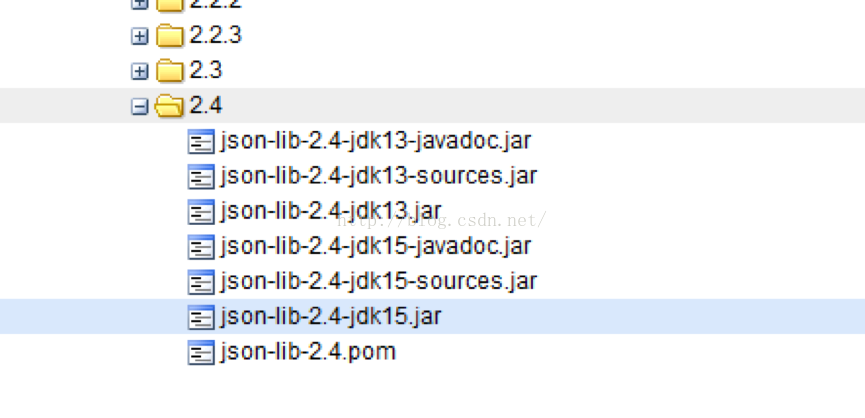
引用它的时候就要注明JDK版本,否则maven不知道你到底需要哪一套jar包:
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.json-lib</groupId>
<artifactId>json-lib</artifactId>
<version>2.4</version>
<classifier>jdk15</classifier>
</dependency>
构建配置
<build>
<!-- 产生的构件的文件名,默认值是${artifactId}-${version}。 -->
<finalName>myPorjectName</finalName>
<!-- 构建产生的所有文件存放的目录,默认为${basedir}/target,即项目根目录下的target -->
<directory>${basedir}/target</directory>
<!--当项目没有规定目标(Maven2叫做阶段(phase))时的默认值, -->
<!--必须跟命令行上的参数相同例如jar:jar,或者与某个阶段(phase)相同例如install、compile等 -->
<defaultGoal>install</defaultGoal>
<!--当filtering开关打开时,使用到的过滤器属性文件列表。 -->
<!--项目配置信息中诸如${spring.version}之类的占位符会被属性文件中的实际值替换掉 -->
<filters>
<filter>../filter.properties</filter>
</filters>
<!--项目相关的所有资源路径列表,例如和项目相关的配置文件、属性文件,这些资源被包含在最终的打包文件里。 -->
<resources>
<resource>
<!--描述了资源的目标路径。该路径相对target/classes目录(例如${project.build.outputDirectory})。 -->
<!--举个例子,如果你想资源在特定的包里(org.apache.maven.messages),你就必须该元素设置为org/apache/maven/messages。 -->
<!--然而,如果你只是想把资源放到源码目录结构里,就不需要该配置。 -->
<targetPath>resources</targetPath>
<!--是否使用参数值代替参数名。参数值取自properties元素或者文件里配置的属性,文件在filters元素里列出。 -->
<filtering>true</filtering>
<!--描述存放资源的目录,该路径相对POM路径 -->
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<!--包含的模式列表 -->
<includes>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<!--排除的模式列表 如果<include>与<exclude>划定的范围存在冲突,以<exclude>为准 -->
<excludes>
<exclude>jdbc.properties</exclude>
</excludes>
</resource>
</resources>
<!--单元测试相关的所有资源路径,配制方法与resources类似 -->
<testResources>
<testResource>
<targetPath />
<filtering />
<directory />
<includes />
<excludes />
</testResource>
</testResources>
<!--项目源码目录,当构建项目的时候,构建系统会编译目录里的源码。该路径是相对于pom.xml的相对路径。 -->
<sourceDirectory>${basedir}\src\main\java</sourceDirectory>
<!--项目脚本源码目录,该目录和源码目录不同, <!-- 绝大多数情况下,该目录下的内容会被拷贝到输出目录(因为脚本是被解释的,而不是被编译的)。 -->
<scriptSourceDirectory>${basedir}\src\main\scripts
</scriptSourceDirectory>
<!--项目单元测试使用的源码目录,当测试项目的时候,构建系统会编译目录里的源码。该路径是相对于pom.xml的相对路径。 -->
<testSourceDirectory>${basedir}\src\test\java</testSourceDirectory>
<!--被编译过的应用程序class文件存放的目录。 -->
<outputDirectory>${basedir}\target\classes</outputDirectory>
<!--被编译过的测试class文件存放的目录。 -->
<testOutputDirectory>${basedir}\target\test-classes
</testOutputDirectory>
<!--项目的一系列构建扩展,它们是一系列build过程中要使用的产品,会包含在running bulid‘s classpath里面。 -->
<!--他们可以开启extensions,也可以通过提供条件来激活plugins。 -->
<!--简单来讲,extensions是在build过程被激活的产品 -->
<extensions>
<!--例如,通常情况下,程序开发完成后部署到线上Linux服务器,可能需要经历打包、 -->
<!--将包文件传到服务器、SSH连上服务器、敲命令启动程序等一系列繁琐的步骤。 -->
<!--实际上这些步骤都可以通过Maven的一个插件 wagon-maven-plugin 来自动完成 -->
<!--下面的扩展插件wagon-ssh用于通过SSH的方式连接远程服务器, -->
<!--类似的还有支持ftp方式的wagon-ftp插件 -->
<extension>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.wagon</groupId>
<artifactId>wagon-ssh</artifactId>
<version>2.8</version>
</extension>
</extensions>
<!--使用的插件列表 。 -->
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId></groupId>
<artifactId>maven-assembly-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.5.5</version>
<!--在构建生命周期中执行一组目标的配置。每个目标可能有不同的配置。 -->
<executions>
<execution>
<!--执行目标的标识符,用于标识构建过程中的目标,或者匹配继承过程中需要合并的执行目标 -->
<id>assembly</id>
<!--绑定了目标的构建生命周期阶段,如果省略,目标会被绑定到源数据里配置的默认阶段 -->
<phase>package</phase>
<!--配置的执行目标 -->
<goals>
<goal>single</goal>
</goals>
<!--配置是否被传播到子POM -->
<inherited>false</inherited>
</execution>
</executions>
<!--作为DOM对象的配置,配置项因插件而异 -->
<configuration>
<finalName>${finalName}</finalName>
<appendAssemblyId>false</appendAssemblyId>
<descriptor>assembly.xml</descriptor>
</configuration>
<!--是否从该插件下载Maven扩展(例如打包和类型处理器), -->
<!--由于性能原因,只有在真需要下载时,该元素才被设置成true。 -->
<extensions>false</extensions>
<!--项目引入插件所需要的额外依赖 -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>...</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!--任何配置是否被传播到子项目 -->
<inherited>true</inherited>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<!--主要定义插件的共同元素、扩展元素集合,类似于dependencyManagement, -->
<!--所有继承于此项目的子项目都能使用。该插件配置项直到被引用时才会被解析或绑定到生命周期。 -->
<!--给定插件的任何本地配置都会覆盖这里的配置 -->
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>...</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
pom里面的仓库与setting.xml里的仓库功能是一样的。主要的区别在于,pom里的仓库是个性化的。比如一家大公司里的setting文件是公用的,所有项目都用一个setting文件,但各个子项目却会引用不同的第三方库,所以就需要在pom里设置自己需要的仓库地址。
分发配置:
<!--项目分发信息,在执行mvn deploy后表示要发布的位置。 -->
<!--有了这些信息就可以把网站部署到远程服务器或者把构件部署到远程仓库。 -->
<distributionManagement>
<!--部署项目产生的构件到远程仓库需要的信息 -->
<repository>
<!--是分配给快照一个唯一的版本号(由时间戳和构建流水号),还是每次都使用相同的版本号 -->
<!--参见repositories/repository元素 -->
<uniqueVersion>true</uniqueVersion>
<id> repo-id </id>
<name> repo-name</name>
<url>file://${basedir}/target/deploy </url>
<layout />
</repository>
<!--构件的快照部署到哪里,如果没有配置该元素,默认部署到repository元素配置的仓库 -->
<snapshotRepository>
<uniqueVersion />
<id />
<name />
<url />
<layout />
</snapshotRepository>
<!--部署项目的网站需要的信息 -->
<site>
<!--部署位置的唯一标识符,用来匹配站点和settings.xml文件里的配置 -->
<id> site-id </id>
<!--部署位置的名称 -->
<name> site-name</name>
<!--部署位置的URL,按protocol://hostname/path形式 -->
<url>scp://svn.baidu.com/banseon:/var/www/localhost/banseon-web </url>
</site>
<!--项目下载页面的URL。如果没有该元素,用户应该参考主页。 -->
<!--使用该元素的原因是:帮助定位那些不在仓库里的构件(由于license限制)。 -->
<downloadUrl />
<!--如果构件有了新的groupID和artifact ID(构件移到了新的位置),这里列出构件的重定位信息。 -->
<relocation>
<!--构件新的group ID -->
<groupId />
<!--构件新的artifact ID -->
<artifactId />
<!--构件新的版本号 -->
<version />
<!--显示给用户的,关于移动的额外信息,例如原因。 -->
<message />
</relocation>
<!--给出该构件在远程仓库的状态。不得在本地项目中设置该元素,因为这是工具自动更新的。 -->
<!--有效的值有:none(默认),converted(仓库管理员从Maven 1 POM转换过来), -->
<!--partner(直接从伙伴Maven 2仓库同步过来),deployed(从Maven 2实例部署),verified(被核实时正确的和最终的)。 -->
<status />
</distributionManagement>
仓库配置:
<!--发现依赖和扩展的远程仓库列表。 -->
<repositories>
<!--包含需要连接到远程仓库的信息 -->
<repository>
<!--如何处理远程仓库里发布版本的下载 -->
<releases>
<!--true或者false表示该仓库是否为下载某种类型构件(发布版,快照版)开启。 -->
<enabled />
<!--该元素指定更新发生的频率。Maven会比较本地POM和远程POM的时间戳。 -->
<!--这里的选项是:always(一直),daily(默认,每日), -->
<!--interval:X(这里X是以分钟为单位的时间间隔),或者never(从不)。 -->
<updatePolicy />
<!--当Maven验证构件校验文件失败时该怎么做: -->
<!--ignore(忽略),fail(失败),或者warn(警告)。 -->
<checksumPolicy />
</releases>
<!--如何处理远程仓库里快照版本的下载。有了releases和snapshots这两组配置, -->
<!--POM就可以在每个单独的仓库中,为每种类型的构件采取不同的策略。 -->
<!--例如,可能有人会决定只为开发目的开启对快照版本下载的支持 -->
<snapshots>
<enabled />
<updatePolicy />
<checksumPolicy />
</snapshots>
<!--远程仓库唯一标识符。可以用来匹配在settings.xml文件里配置的远程仓库 -->
<id> repo-id </id>
<!--远程仓库名称 -->
<name> repo-name</name>
<!--远程仓库URL,按protocol://hostname/path形式 -->
<url>http://192.168.1.169:9999/repository/ </url>
<!--用于定位和排序构件的仓库布局类型-可以是default(默认)或者legacy(遗留)。 -->
<!--Maven 2为其仓库提供了一个默认的布局; -->
<!--然而,Maven1.x有一种不同的布局。 -->
<!--我们可以使用该元素指定布局是default(默认)还是legacy(遗留)。 -->
<layout> default</layout>
</repository>
</repositories>
<!--发现插件的远程仓库列表,这些插件用于构建和报表 -->
<pluginRepositories>
<!--包含需要连接到远程插件仓库的信息.参见repositories/repository元素 -->
<pluginRepository />
</pluginRepositories>
profile配置:
<!--在列的项目构建profile,如果被激活,会修改构建处理 -->
<profiles>
<!--根据环境参数或命令行参数激活某个构建处理 -->
<profile>
<!--自动触发profile的条件逻辑。Activation是profile的开启钥匙。 -->
<activation>
<!--profile默认是否激活的标识 -->
<activeByDefault>false</activeByDefault>
<!--activation有一个内建的java版本检测,如果检测到jdk版本与期待的一样,profile被激活。 -->
<jdk>1.7</jdk>
<!--当匹配的操作系统属性被检测到,profile被激活。os元素可以定义一些操作系统相关的属性。 -->
<os>
<!--激活profile的操作系统的名字 -->
<name>Windows XP</name>
<!--激活profile的操作系统所属家族(如 'windows') -->
<family>Windows</family>
<!--激活profile的操作系统体系结构 -->
<arch>x86</arch>
<!--激活profile的操作系统版本 -->
<version>5.1.2600</version>
</os>
<!--如果Maven检测到某一个属性(其值可以在POM中通过${名称}引用),其拥有对应的名称和值,Profile就会被激活。 -->
<!-- 如果值字段是空的,那么存在属性名称字段就会激活profile,否则按区分大小写方式匹配属性值字段 -->
<property>
<!--激活profile的属性的名称 -->
<name>mavenVersion</name>
<!--激活profile的属性的值 -->
<value>2.0.3</value>
</property>
<!--提供一个文件名,通过检测该文件的存在或不存在来激活profile。missing检查文件是否存在,如果不存在则激活profile。 -->
<!--另一方面,exists则会检查文件是否存在,如果存在则激活profile。 -->
<file>
<!--如果指定的文件存在,则激活profile。 -->
<exists>/usr/local/hudson/hudson-home/jobs/maven-guide-zh-to-production/workspace/</exists>
<!--如果指定的文件不存在,则激活profile。 -->
<missing>/usr/local/hudson/hudson-home/jobs/maven-guide-zh-to-production/workspace/</missing>
</file>
</activation>
<id />
<build />
<modules />
<repositories />
<pluginRepositories />
<dependencies />
<reporting />
<dependencyManagement />
<distributionManagement />
<properties />
</profile>
profile配置项在setting.xml中也有,是pom.xml中profile元素的裁剪版本,包含了id,activation, repositories, pluginRepositories和 properties元素。这里的profile元素只包含这五个子元素是因为setting.xml只关心构建系统这个整体(这正是settings.xml文件的角色定位),而非单独的项目对象模型设置。如果一个settings中的profile被激活,它的值会覆盖任何其它定义在POM中或者profile.xml中的带有相同id的profile。
pom.xml中的profile可以看做pom.xml的副本,拥有与pom.xml相同的子元素与配置方法。它包含可选的activation(profile的触发器)和一系列的changes。例如test过程可能会指向不同的数据库(相对最终的deployment)或者不同的dependencies或者不同的repositories,并且是根据不同的JDK来改变的。只需要其中一个成立就可以激活profile,如果第一个条件满足了,那么后面就不会在进行匹配。
报表配置:
<!--描述使用报表插件产生报表的规范,特定的maven 插件能输出相应的定制和配置报表. -->
<!--当用户执行“mvn site”,这些报表就会运行,在页面导航栏能看到所有报表的链接。 -->
<reporting>
<!--true,则网站不包括默认的报表。这包括“项目信息”菜单中的报表。 -->
<excludeDefaults />
<!--所有产生的报表存放到哪里。默认值是${project.build.directory}/site。 -->
<outputDirectory />
<!--使用的报表插件和他们的配置。 -->
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId />
<artifactId />
<version />
<inherited />
<configuration>
<links>
<link>http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.5.0/docs/api/</link>
</links>
</configuration>
<!--一组报表的多重规范,每个规范可能有不同的配置。 -->
<!--一个规范(报表集)对应一个执行目标 。例如,有1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9个报表。 -->
<!--1,2,5构成A报表集,对应一个执行目标。2,5,8构成B报表集,对应另一个执行目标 -->
<reportSets>
<!--表示报表的一个集合,以及产生该集合的配置 -->
<reportSet>
<!--报表集合的唯一标识符,POM继承时用到 -->
<id>sunlink</id>
<!--产生报表集合时,被使用的报表的配置 -->
<configuration />
<!--配置是否被继承到子POMs -->
<inherited />
<!--这个集合里使用到哪些报表 -->
<reports>
<report>javadoc</report>
</reports>
</reportSet>
</reportSets>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</reporting>
环境配置:
<!--项目的问题管理系统(Bugzilla, Jira, Scarab,或任何你喜欢的问题管理系统)的名称和URL,本例为 jira -->
<issueManagement>
<!--问题管理系统(例如jira)的名字, -->
<system> jira </system>
<!--该项目使用的问题管理系统的URL -->
<url> http://jira.clf.com/</url>
</issueManagement>
<!--项目持续集成信息 -->
<ciManagement>
<!--持续集成系统的名字,例如continuum -->
<system />
<!--该项目使用的持续集成系统的URL(如果持续集成系统有web接口的话)。 -->
<url />
<!--构建完成时,需要通知的开发者/用户的配置项。包括被通知者信息和通知条件(错误,失败,成功,警告) -->
<notifiers>
<!--配置一种方式,当构建中断时,以该方式通知用户/开发者 -->
<notifier>
<!--传送通知的途径 -->
<type />
<!--发生错误时是否通知 -->
<sendOnError />
<!--构建失败时是否通知 -->
<sendOnFailure />
<!--构建成功时是否通知 -->
<sendOnSuccess />
<!--发生警告时是否通知 -->
<sendOnWarning />
<!--不赞成使用。通知发送到哪里 -->
<address />
<!--扩展配置项 -->
<configuration />
</notifier>
</notifiers>
</ciManagement>
项目信息配置:
<!--项目的名称, Maven产生的文档用 -->
<name>banseon-maven </name>
<!--项目主页的URL, Maven产生的文档用 -->
<url>http://www.clf.com/ </url>
<!--项目的详细描述, Maven 产生的文档用。 当这个元素能够用HTML格式描述时 -->
<!--(例如,CDATA中的文本会被解析器忽略,就可以包含HTML标签),不鼓励使用纯文本描述。 -->
<!-- 如果你需要修改产生的web站点的索引页面,你应该修改你自己的索引页文件,而不是调整这里的文档。 -->
<description>A maven project to study maven. </description>
<!--描述了这个项目构建环境中的前提条件。 -->
<prerequisites>
<!--构建该项目或使用该插件所需要的Maven的最低版本 -->
<maven />
</prerequisites>
<!--项目创建年份,4位数字。当产生版权信息时需要使用这个值。 -->
<inceptionYear />
<!--项目相关邮件列表信息 -->
<mailingLists>
<!--该元素描述了项目相关的所有邮件列表。自动产生的网站引用这些信息。 -->
<mailingList>
<!--邮件的名称 -->
<name> Demo </name>
<!--发送邮件的地址或链接,如果是邮件地址,创建文档时,mailto: 链接会被自动创建 -->
<post> clf@126.com</post>
<!--订阅邮件的地址或链接,如果是邮件地址,创建文档时,mailto: 链接会被自动创建 -->
<subscribe> clf@126.com</subscribe>
<!--取消订阅邮件的地址或链接,如果是邮件地址,创建文档时,mailto: 链接会被自动创建 -->
<unsubscribe> clf@126.com</unsubscribe>
<!--你可以浏览邮件信息的URL -->
<archive> http:/hi.clf.com/</archive>
</mailingList>
</mailingLists>
<!--项目开发者列表 -->
<developers>
<!--某个项目开发者的信息 -->
<developer>
<!--SCM里项目开发者的唯一标识符 -->
<id> HELLO WORLD </id>
<!--项目开发者的全名 -->
<name> banseon </name>
<!--项目开发者的email -->
<email> banseon@126.com</email>
<!--项目开发者的主页的URL -->
<url />
<!--项目开发者在项目中扮演的角色,角色元素描述了各种角色 -->
<roles>
<role> Project Manager</role>
<role>Architect </role>
</roles>
<!--项目开发者所属组织 -->
<organization> demo</organization>
<!--项目开发者所属组织的URL -->
<organizationUrl>http://hi.clf.com/ </organizationUrl>
<!--项目开发者属性,如即时消息如何处理等 -->
<properties>
<dept> No </dept>
</properties>
<!--项目开发者所在时区, -11到12范围内的整数。 -->
<timezone> -5</timezone>
</developer>
</developers>
<!--项目的其他贡献者列表 -->
<contributors>
<!--项目的其他贡献者。参见developers/developer元素 -->
<contributor>
<name />
<email />
<url />
<organization />
<organizationUrl />
<roles />
<timezone />
<properties />
</contributor>
</contributors>
<!--该元素描述了项目所有License列表。应该只列出该项目的license列表,不要列出依赖项目的license列表。 -->
<!--如果列出多个license,用户可以选择它们中的一个而不是接受所有license。 -->
<licenses>
<!--描述了项目的license,用于生成项目的web站点的license页面,其他一些报表和validation也会用到该元素。 -->
<license>
<!--license用于法律上的名称 -->
<name> Apache 2 </name>
<!--官方的license正文页面的URL -->
<url>http://www.clf.com/LICENSE-2.0.txt </url>
<!--项目分发的主要方式: repo,可以从Maven库下载 manual, 用户必须手动下载和安装依赖 -->
<distribution> repo</distribution>
<!--关于license的补充信息 -->
<comments> Abusiness-friendly OSS license </comments>
</license>
</licenses>
<!--SCM(Source Control Management)标签允许你配置你的代码库,供Maven web站点和其它插件使用。 -->
<scm>
<!--SCM的URL,该URL描述了版本库和如何连接到版本库。欲知详情,请看SCMs提供的URL格式和列表。该连接只读。 -->
<connection>scm:svn:http://svn.baidu.com/banseon/maven/</connection>
<!--给开发者使用的,类似connection元素。即该连接不仅仅只读 -->
<developerConnection>scm:svn:http://svn.baidu.com/banseon/maven/
</developerConnection>
<!--当前代码的标签,在开发阶段默认为HEAD -->
<tag />
<!--指向项目的可浏览SCM库(例如ViewVC或者Fisheye)的URL。 -->
<url> http://svn.baidu.com/banseon</url>
</scm>
<!--描述项目所属组织的各种属性。Maven产生的文档用 -->
<organization>
<!--组织的全名 -->
<name> demo </name>
<!--组织主页的URL -->
<url> http://www.clf.com/</url>
</organization>




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号