人生苦短我学Java-15-递归、文件IO/字节/字符/转换/打印流
一、递归
什么是递归?方法内调用自己
注意事项:
- 递归方法内需要有个return 出口,非继续递归
- 递归次数不宜过多,否则堆栈溢出程序报错
1.递归:5的阶乘
// 递归:5的阶乘 public static int factorial(int n) { if (n == 1) { return 1; } return n * factorial(n - 1); }
2.递归:斐波那契数列:1 1 2 3 5 8
// 斐波那契数列:1 1 2 3 5 8 public static int fibonacci(int n) { if (n == 1 || n == 2) { return 1; } return fibonacci(n - 2) + fibonacci(n - 1); }
3.递归删除文件夹与文件
// 递归删除文件夹与文件 public static boolean del(File file) { if (!file.isDirectory() || !file.exists()) { return false; } File[] files = file.listFiles(); for (File f : files) { if (f.isDirectory()) { del(f); } else f.delete(); } return file.delete(); }
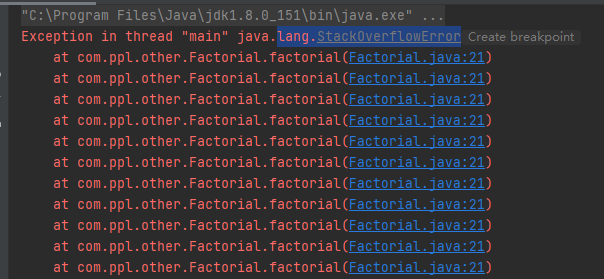
递归深度过大报错如下:

package com.ppl.other; /* com.ppl.other:学习项目 @user:广深-小龙 @date:2022/3/19 10:00 --递归 */ import java.io.File; public class Factorial { public static void main(String[] args) { // 注意递归次数不可以过多,否则递归深度太深导致堆栈溢出报错:StackOverflowError System.out.println("阶乘:" + factorial(5)); System.out.println("斐波那契:" + fibonacci(10)); File file = new File("aaa"); System.out.println(del(file)); Java(new File("src")); } // 递归:5的阶乘 public static int factorial(int n) { if (n == 1) { return 1; } return n * factorial(n - 1); } // 斐波那契数列:1 1 2 3 5 8 public static int fibonacci(int n) { if (n == 1 || n == 2) { return 1; } return fibonacci(n - 2) + fibonacci(n - 1); } // 递归删除文件夹与文件 public static boolean del(File file) { if (!file.isDirectory() || !file.exists()) { return false; } File[] files = file.listFiles(); for (File f : files) { if (f.isDirectory()) { del(f); } else f.delete(); } return file.delete(); } // 递归查询.java文件 public static void Java(File file) { File[] files = file.listFiles(); for (File f : files) { if (f.isDirectory()) { Java(f); } else { if (f.getName().endsWith("java")) { System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath()); } } } } }
二、file文件流
JAVA操作文件对象,使用File类主要用于文件和文件夹的创建、查询、删除等
样例:

package com.ppl.other; /* com.ppl.other:学习项目 @user:广深-小龙 @date:2022/3/19 10:22 --文件对象 */ import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Arrays; public class MyFile { String path = "C:\\Users\\PPL\\Desktop"; String fileName = "api.txt"; public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { new MyFile().structure(); new MyFile().member(); } // 常用成员方法 public void member() throws IOException { File file = new File(fileName); File file1 = new File("test"); // 创建单个文件夹 boolean isMkdir = file1.mkdir(); // 创建多级文件夹 boolean isMkdirs = new File("tests/ppl").mkdirs(); // 创建文件 createNewFile() boolean isCreate = file.createNewFile(); // 判断文件是否存在 exists() boolean exists = file.exists(); // 删除文件或文件夹 // 注意:如果要删除的文件夹里还有子文件或者子文件夹的话,是没法删除成功,必须先把子文件和文件夹都删除掉,才能删除自身 boolean isDel = file.delete(); boolean isDel1 = file1.delete(); boolean isDel2 = new File("tests/ppl").delete(); boolean isDel3 = new File("tests").delete(); // 判断是不是 文件对象 isFile() boolean isFile = new File("src").isFile(); // 判断是不是 文件夹对象 isDirectory() boolean isDirectory = new File("src").isDirectory(); // 获取字节长度 File file2 = new File("README.md"); System.out.println(file2.length()); // 获取文件或文件夹的名字 String fileName = file.getName(); // 获取文件或文件夹的相对路径 String filePath = file.getPath(); // 获取文件或文件夹的绝对路径 String absFilePath = file.getAbsolutePath(); System.out.println(absFilePath); // 获取文件夹下的所有文件或文件夹 File file3 = new File("project"); File[] files = file3.listFiles(); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(files)); } // 常见构造方法 public void structure() { // 常见构造方法1 public File(String pathname) File file1 = new File(fileName);// 相对路径 System.out.println(file1 + " " + file1.exists()); // 常见构造方法2 public File(String parent, String child) // 父+子path拼接 File file2 = new File(path, fileName);// 绝对路径 System.out.println(file2 + " " + file2.exists()); // 常见构造方法3 public File(File parent, String child) // 父file+子path拼接 File file3 = new File(path);// 绝对路径 File file4 = new File(file3, fileName);// 绝对路径 System.out.println(file4 + " " + file4.exists()); } }
什么是IO流?
- I:input,是指输入,读取文件。
- O:output,是指输出,写入文件。
- 流:数据传输传递过程。
1、FileInputStream
class MyOutput { // 创建字节输入或输出流对象,如果文件不存在会创建;注意:需要文件路径,不能是文件夹 public void member() throws IOException { // 1.FileOutputStream(String name) name:文件名 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("README.md"); // 2.FileOutputStream(File file) 文件输出流对象 File file = new File("README.md"); FileOutputStream fos1 = new FileOutputStream(file); // 3.write(int b) 向文件输出一个字节数据 (单字节字符) FileOutputStream fos2 = new FileOutputStream("test.txt"); fos2.write(97); // ---换行符: \r\n fos2.write("\r\n".getBytes()); // 4.write(byte[] b) 向文件输出一个字节数组数据 byte[] bytes = {97, 98, 99}; fos2.write(bytes); // 5.write(byte b[], int off, int len) 向文件输出自定义字节数组范围数据,如0-2个 fos2.write(bytes, 0, 2); } public void structure() throws IOException { // 追加输出到文件:FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append) FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("test.txt", true); fos.write("\n这是一个换行的追加开始呀".getBytes()); fos.write("\nend".getBytes()); } }
2、FileOutputStream
class MyOutput { // 创建字节输入或输出流对象,如果文件不存在会创建;注意:需要文件路径,不能是文件夹 public void member() throws IOException { // 1.FileOutputStream(String name) name:文件名 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("README.md"); // 2.FileOutputStream(File file) 文件输出流对象 File file = new File("README.md"); FileOutputStream fos1 = new FileOutputStream(file); // 3.write(int b) 向文件输出一个字节数据 (单字节字符) FileOutputStream fos2 = new FileOutputStream("test.txt"); fos2.write(97); // ---换行符: \r\n fos2.write("\r\n".getBytes()); // 4.write(byte[] b) 向文件输出一个字节数组数据 byte[] bytes = {97, 98, 99}; fos2.write(bytes); // 5.write(byte b[], int off, int len) 向文件输出自定义字节数组范围数据,如0-2个 fos2.write(bytes, 0, 2); } public void structure() throws IOException { // 追加输出到文件:FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append) FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("test.txt", true); fos.write("\n这是一个换行的追加开始呀".getBytes()); fos.write("\nend".getBytes()); } }
复制文件例子:
class CopyDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { demo1(); demo2(); } public static void demo1() throws IOException { // 第一种 // 输入流:读取文件 FileInputStream fii = new FileInputStream("README.md"); // 输出流:写文件 FileOutputStream fio = new FileOutputStream("test.txt"); // 读取文件内容重写如另一个文件:一次读一个字节 int by = 0; while ((by = fii.read()) != -1) { fio.write(by); } // 关闭流 fii.close(); fio.close(); } public static void demo2() { // 第二种 + 自定义抛异常 FileInputStream fis1 = null; FileOutputStream fio1 = null; try { // 输入流:读取文件 fis1 = new FileInputStream("README.md"); // 输出流:写文件 fio1 = new FileOutputStream("test.txt"); byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int len = 0; while ((len = fis1.read(bytes)) != -1) { fio1.write(bytes, 0, len); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // finally 是否抛异常都会执行的代码块 if (fis1 != null) { try { fis1.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (fio1 != null) { try { // 关闭流 fio1.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream
高效缓冲流:
package com.ppl.other; /* com.ppl.other:学习项目 @user:广深-小龙 @date:2022/4/4 10:55 */ import java.io.*; public class MyBufferStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 缓冲字节输入流:传入new对象为装饰设计模式 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("README.md")); byte[] bytes = new byte[5]; int len = bis.read(bytes); while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) { String str = new String(bytes, 0, len); System.out.println(len + ":" + str); } // 缓冲字节输出流 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("a.txt")); bos.write(97); bos.write(98); // 写完后需要刷新缓冲区 bos.flush(); // copy copy(); } public static void copy() throws IOException { // 复制文件 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("a.txt")); BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("b.txt")); byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; int len = 0; while ((len = bis.read(bys)) != -1) { bos.write(bys, 0, len); } bis.close(); bos.close(); } }
三、字符流
为什么有字符流:中文一个文字占3个字节,所以我们使用字节流读取文件可能会出现中文乱码。因为字符流一个中文或者一个符合就是一个字符。
推荐我们使用高效流
- FileReader:普通输入流
- FileWriter:普通输出流
- BufferedReader:高效输入流,读取推荐使用 readLine 方法 或数组字节读取。
- BufferedWriter:高效输出流,换行推荐使用 newLine 方法。
package com.ppl.other; /* com.ppl.other:学习项目 @user:广深-小龙 @date:2022/4/17 23:14 */ import java.io.*; public class MyStrFlow { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { myRead(); myWrit(); myBuffRead(); myBuffWrit(); // BufferedReader一行一行读,特有方法:readLine() BufferedReader fr = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("README.md")); String str = null; while ((str = fr.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println(str); } // BufferedWriter换行写入数据,特有方法:newLine() BufferedWriter bfw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("a.txt", true)); bfw.newLine(); } public static void myBuffRead() throws IOException { // 输入流 BufferedReader fr = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("README.md")); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 单个读 int ch = 0; while ((ch = fr.read()) != -1) { System.out.print((char) ch); } // 多个读 char[] chs = new char[1024]; int len = 0; while ((len = fr.read(chs)) != -1) { System.out.print(new String(chs)); } long end = System.currentTimeMillis() - start; System.out.println("耗时:" + end); } public static void myBuffWrit() throws IOException { BufferedWriter bfw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("a.txt", true)); bfw.write("高效:测试写入字符串\n"); bfw.write("高效:123456asdasd\n"); bfw.write("高效:@%#$$%#$%\n"); bfw.close(); } public static void myRead() throws IOException { // 输入流 FileReader fr = new FileReader("README.md"); // 单个读 int ch = 0; while ((ch = fr.read()) != -1) { System.out.print((char) ch); } // 多个读 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); char[] chs = new char[1024]; int len = 0; while ((len = fr.read(chs)) != -1) { System.out.print(new String(chs)); } long end = System.currentTimeMillis() - start; System.out.println("耗时:" + end); } public static void myWrit() throws IOException { FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("a.txt", true); fw.write("测试写入字符串\n"); fw.write("123456asdasd\n"); fw.write("@%#$$%#$%\n"); fw.close(); } }
四、转换流
package com.ppl.other; /* com.ppl.other:学习项目 @user:广深-小龙 @date:2022/4/20 20:32 */ import java.io.*; public class MyOtherFlow { /* 其它流,方法和前面的是一样的。 什么是转换率? 可以将字节流转换成字符流 */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { myFlowReader(); myFlowWriter(); buffFlowReader(); buffFlowWriter(); } // 普通转换输入流 public static void myFlowReader() throws IOException { InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("README.md")); char[] chs = new char[1024]; int len = 0; while ((len = isr.read(chs)) != -1) { System.out.print(new String(chs)); } } // 普通转换输出流 public static void myFlowWriter() throws IOException { OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("README.md", true)); osw.write("高效:测试写入字符串\n"); } // 高效转换输入流 public static void buffFlowReader() throws IOException { BufferedReader isr = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("README.md"))); char[] chs = new char[1024]; int len = 0; while ((len = isr.read(chs)) != -1) { System.out.print(new String(chs)); } } // 高效转换输出流 public static void buffFlowWriter() throws IOException { BufferedWriter osw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("README.md"))); osw.write("高效:测试写入字符串\n"); } }
五、打印流
只有输出流
package com.ppl.other.Flow; /* com.ppl.other.Flow:学习项目 @user:广深-小龙 @date:2022/4/20 21:14 */ import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.PrintWriter; public class MyPrint { // 打印流 public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter("t.md"); pw.write("不不不哈哈"); pw.println("123213131"); pw.flush(); } }
总结:
IO流的选择 在以后对文件进行复制的时候,到底该选择哪个流进行复制?
- 1.如果文件打开之后,你看不懂,就使用高效字节流
- 2.如果文件打开之后,你看得懂,就使用高效字符流,也可以使用高效字节流
- 3.如果有需求需要将字节流转换成字符流,那就使用高效转换流,也还可以指定编码
一般mp4,mp3,jpg,png...这些文件我们是看不懂的 一般.txt,.java这些文件我们是看得懂的






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!